Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
What it is
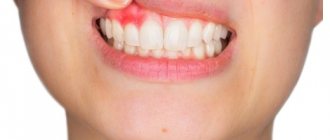
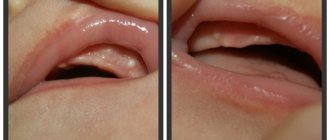
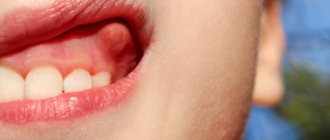
Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm that develops on the alveolar process of the jaw. It also has other names - epulid, supragingival, giant cell granuloma. More often it is localized in the area of incisors, canines and small molars of the upper jaw, less often the tumor is detected in the lower jaw. The growth has a round or irregular shape and a wide stalk; the size of the formation varies from 3 mm to 5 cm.
Despite the fact that such a tumor looks frightening, it practically does not cause concern to the patient, unlike, for example, a burn, with the exception of a violation of aesthetics and the sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity. Large tumors may cause difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
If epulis is accompanied by bleeding, infection may occur, which will lead to complications.
The disease mainly affects adults, but the neoplasm can also appear in children; in the latter, it occurs during teething. Studies have shown that women are more susceptible to developing epulis than men.
Periodontitis by location
There are two main divisions in the classification of periodontitis based on the location of the disease: apical and marginal. The first option (apical) is also apical, based near the apex of the tooth root. This type is the most common, since periodontal infection in most cases occurs through a descending channel: from caries to inflammation of the pulp, and then through the root canal the infection descends into the periodontal tissue. This process most often becomes chronic, since the protective mechanisms of the periodontium are much more powerful than those of the pulp. Therefore, the infection can enter the deep tissues of the tooth for years without causing signs of disease.
Marginal chronic periodontitis is located on the lateral walls of the tooth root and has the etiology of microtraumas.
Periodontitis, the treatment stages of which are a complex, complex process, requires immediate attention to a dental clinic. It is safe to say that such a diagnosis requires highly qualified specialists with extensive experience in solving such problems. Dentists of the LeaderStom network of clinics are rightfully considered the best in this area of dental therapy. The latest technologies, progressive techniques and extensive practice allow them to cope with the most complex, advanced cases.
Varieties of epulis
Conventionally, there are 3 types of epulis:
- Fibrous. The neoplasm is dense, the basis is coarse fibrous tissue. Characterized by slow growth. There is no pain or bleeding.
- Angiomatous. The tumor contains a large number of blood vessels and is localized mainly in the lateral parts of the jaw. With this form of the disease, bleeding is observed even with slight pressure, for example, with a toothbrush or food. When pressed, the tumor is painless and has a soft consistency.
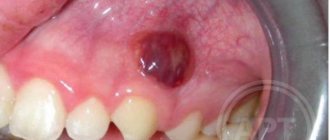
- Giant cell. The tumor can reach large sizes, displacing teeth that are located in the epulis growth zone. The mucous membrane of the epulis is bluish-red in color. On palpation, the neoplasm is painless, but may bleed moderately if injured.
Depending on the nature of the process, epulis can be benign or malignant. In the first case, the neoplasm is characterized by slow development and, as mentioned above, in most cases does not cause pain. The tumor size in this case rarely exceeds 10–20 mm. When the process becomes malignant, rapid tissue growth is observed. In this case, the process is often accompanied by pain, bleeding gums and affects the root canals of neighboring teeth.
Dangerous symptoms
If a lump appears after tooth extraction, you should inform your doctor about it. Particularly dangerous symptoms are:
- discharge of pus;
- severe swelling;
- acquisition of bluish tint by fabrics;
- pain on palpation;
- absence of a protective blood clot.
Trying to cure a disorder without medical help is not only unwise, but also dangerous. By engaging in amateur activities and experimenting with folk recipes, a person risks creating conditions for the further spread of the inflammatory process. Then it is possible that the extraction will be followed by a second operation. This time it will be aimed at removing tissues affected by the purulent process.
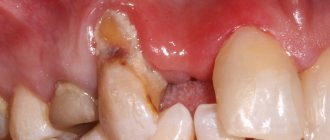
Diagnosis and treatment of epulis
Diagnosis of epulis comes down to collecting complaints, clinical examination, radiography and histological examination of the material.
The primary task in making such a diagnosis is to eliminate the provoking factor: professional cleaning of dental plaque, treatment of caries and its complications, replacement or correction of orthopedic structures according to indications. In fibromatous and angiomatous forms, dynamic observation is indicated, since after sanitation of the oral cavity and elimination of the causes of the disease, the tumor may decrease in size until it disappears completely.
Treatment of epulis is carried out surgically. The growth on the gum under local anesthesia or general anesthesia is excised with a scalpel or laser within the healthy tissue along with the periosteum. The second method is preferable, since the laser simultaneously coagulates the vessels and stops bleeding. With giant cell epulis, the area of bone tissue involved in the process is also removed. To do this, use a bur or cutter. The wound is closed with gauze with an iodoform mixture or a formed mucoperiosteal flap. If necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
Intact teeth in the area of tumor localization must be removed with a high degree of mobility and severe exposure of the roots. If the bone lesion is extensive or epulis recurs, partial resection of the alveolar part along with the teeth is performed.
To speed up the healing of a fresh wound, the doctor prescribes compresses with medicinal ointments and rinses to the patient.
Tartar: removal
When you brush your teeth, you can only remove soft plaque from the surface of your teeth. Partially mineralized plaque, as well as hard dental deposits, can no longer be removed by regular teeth cleaning at home. And in this case, only a dentist can clean the tartar.
1) Cleaning the stone at the dentist’s appointment –
The traditional way to remove hard plaque is ultrasonic teeth cleaning. In this case, stone removal is carried out using an ultrasonic scaler. Removing supragingival calculus is a very simple procedure, and 1 hour is enough to remove calculus from all teeth. But to effectively remove subgingival stones, you need several visits and a highly qualified doctor. Therefore, it is best to remove stones not from ordinary dental therapists, but from periodontists (these are dentists who specialize in the treatment of gum inflammation).
Ultrasonic tartar removal –
There is also the “AirFlow” procedure, with which you can remove small dental deposits, pigment plaque, and polish your teeth. In this case, cleaning and polishing of teeth occurs due to a water-air mixture containing granules of an abrasive substance, sprayed under high pressure from a special tip. But AirFlow will not be effective against massive hard dental plaque, which in any case will first have to be removed with ultrasound.
Tartars: photos before and after their removal
On average, the price for tartar removal is about 100-150 rubles per 1 tooth, including polishing.
2) How to remove tartar at home –
Some patients use recipes for removing plaque, which are replete with many unprofessional websites, promising complete relief from tartar. We'll disappoint you, but these methods not only don't work, but also cause harm to tooth enamel and gums. Just for fun, you can check them out at the link above.
It is impossible to remove well-mineralized tartar and dense pigment plaque with any home remedies. However, not too pronounced pigment plaque and only partially mineralized plaque can still be removed with the help of the following modern dental care products. First of all, we are talking about Oral-B electric toothbrushes - in combination with special highly abrasive toothpastes.
Important: Oral-b electric brushes have a round head with bristles that performs 8,800 reciprocating movements per minute, as well as a minimum of 20,000 pulsating movements. Pulsations help loosen dense plaque (even that which may already be partially mineralized), and rotational movements sweep it away and polish the teeth. This brush is a miniature dentist’s tool and is probably familiar to everyone who has gone to the dentist for professional oral hygiene.
The second component is highly abrasive toothpastes, which can help remove pigmented and partially mineralized plaque. They can only be used once a week. If you are using them in combination with an Oral-b electric brush, it is advisable to use the electric brush only at low speed (in the “whitening/polishing” mode). You can find out how this is done correctly and what toothpastes are used at the link below.
You can also purchase professional teeth polishing products, which the dentist uses to finish polishing teeth after ultrasonic cleaning (they are sold in stores that sell consumables for dental clinics). For example, pastes such as “Detartrine” or “Detartrine – Z” (this one is more effective). They are able to remove even small tartar and not too pronounced smoker’s plaque. Used in combination with an Oral-B electric toothbrush (rotation of the nozzle should be at low speed).
→ Scheme for removing dental plaque at home
Preventive actions
Monitoring the condition of the teeth and oral cavity will reduce the likelihood of tumors.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity. Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene twice a year will prevent the growth of caries, the appearance of defects in fillings and the formation of tartar, leading to gum injury and the appearance of epulis.
- Prevention of gum injury. If systematic injury to soft tissue occurs as a result of poorly fitted orthopedic or orthodontic structures, consult your doctor about this problem. He will adjust the crowns or dentures.
If these preventive measures are followed, the prognosis is favorable and epulis does not recur.
We hope that our article about epulis will be for informational purposes only. And if you want to soothe your gums, make them strong and strong, try the unique two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE.
This is the only rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzydamine for the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases. The product has a combined effect: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. Instant anesthetic effect allows you to quickly reduce pain.
Dentists' recommendations
Epulis is a gum tumor that poses a great danger to the health of teeth and the entire body. Treatment of the pathology is complex and lengthy, but even with high-quality treatment, the risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
It is not always possible to prevent the occurrence of epulis on the gums of a child or an adult, but with timely consultation with a specialist, complications, complex treatment, long recovery and aesthetic defects that remain after surgery can be avoided.
The best prevention is to visit the dentist every 6 months. If you are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of rubbing of the mucous membranes or gums, you should immediately consult a dentist, without waiting for a tumor or other pathologies to occur.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova