Dental implantation is a complex procedure that requires intervention in the soft tissues of the oral cavity. To avoid all sorts of complications, it is very important to follow the dentist’s recommendations. Swelling and redness may be observed for several days after surgery, which is considered normal. If other unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist to prevent rejection of the prosthesis and other pathological conditions.
What happens to gum tissue during the implantation process?
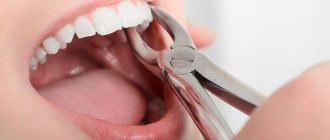
There are different types of implants: subosseous implants are inserted into the jaw bone, periosteal implants are inserted into the soft tissues of the jaw. Sometimes the socket of an extracted tooth is used for implantation, but in some cases it is necessary to artificially deepen the socket or completely dissect the gum from the outside - this is done either with a scalpel or a laser.
After the incision, surgical sutures are made on the gums to hold the tissue until it heals completely.
In some cases, after installation of the implant, gum grafting is performed separately - then healing takes several weeks longer.
The main advantages of implantation:
- No interference with the structures of neighboring teeth.
- Long service life of the denture structure (15 years or more).
- Lightweight and physiological denture structure (root - implant, tooth - crown).
Dental implantation as a method of replacing lost teeth was most suitable for the patient. The patient chose treatment at the Dial-Dent clinic for several reasons:
- The presence in the clinic of an experienced implant surgeon with extensive experience Alaverdova V.P.
- The Dial-Dent clinic demonstrated the features of various tooth replacement options using real clinical cases as examples. The use of animation and computer modeling during consultation helped the patient to fully understand the essence of the proposed manipulations.
- The use of the “Implant Assistant” computer program in the clinic, which allows for a virtual operation to install implants.
- The patient could undergo all the necessary consultations and studies at the clinic.
How does healing occur, what consequences of the operation are considered normal?
It is worth mentioning right away that the process of implant integration does not end with the regeneration of soft tissues - osteogenesis must occur, that is, fusion of the bone with the implant. It takes about six months for complete restoration of both bone and soft tissue, starting from the day the pin was installed - even with a step-by-step procedure, this is usually enough. But at the VivaDent clinic, patients are warned that the speed of healing varies from person to person - there are lucky ones who, after three months, do not notice any consequences of the intervention, but there are those patients who really need six months or a little more for full recovery .
In the first hours after surgery, the patient feels numbness - these are residual effects of pain relief. Then a slight pain appears - since the cut tissue cannot help but hurt after the anesthetic wears off, and this is normal. Patients describe the nature of the pain as “pulsating” or “twitching”, and these sensations spread to the jaw area around the socket of the implanted tooth. But you don’t have to endure them at all - the dentist will recommend what painkillers you can use to cope with the pain. As a rule, the pain goes away within four to five days after the intervention.
During the first week, itching in the gums is also possible - and this is considered a normal phenomenon during tissue regeneration.
A month after implantation, the patient stops experiencing any painful or uncomfortable sensations completely - as the surface of the gum and the place where it connects to the abutment heals.
Bleeding from the gums should stop within the first 24 hours (and even then, we are not talking about continuous streams of blood, but drops); then, over the course of several days, the appearance of a small amount of blood or exudate cannot be ruled out.
Also, in the first five days, a slight increase in temperature and the presence of slight swelling of the gums in the area of intervention are considered acceptable. Sometimes the gums of neighboring teeth also swell - this is also normal if it does not last longer than a few days.
If sutures were placed on the gums, the patient should come for examination weekly or more often (as the doctor says), and the sutures will be removed 3-4 weeks after the gums have been sutured.
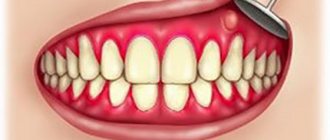
Normal gum condition after implantation
Because the gums are exposed during surgery, your gums may appear inflamed in the first few days after surgery. The patient may experience the following symptoms:
- bleeding;
- pain;
- hematoma.
If symptoms do not subside after a week, you should consult an implantologist.
The implant adaptation period can take from 2 to 6 months, depending on the complexity of the manipulation and the individual characteristics of the body. For example, artificial roots take root faster on the lower jaw than on the upper jaw.
Caring for gums and taking medications after surgery
To ensure that nothing interferes with healing and that this process occurs as quickly as possible, dentists recommend following some rules for postoperative oral care. Basically, these rules apply to meals.
- For the first few hours after surgery, you should not take any food at all, even soft or liquid. Drinking is allowed through a straw. But, as a rule, patients themselves do not want to lean too heavily on food - since anesthesia may still be felt, and immediately after the anesthesia stops working, quite natural painful sensations may appear that interfere with eating.
- In the first weeks after installation of the implant, it is recommended to refrain from hard, crumbly, and sticky foods - crackers, nuts (including those contained in sweets and chocolates), toffees, kozinaki, tough meat, etc.
- You should also refrain from foods and dishes with a high content of both salt and sugar - salt irritates the unhealed surfaces of the mucous membrane, and sugar promotes the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity and on the teeth.
- Hot spices, garlic, hot pepper, etc. are undesirable.
- Hot and very cold drinks are also temporarily prohibited.
- It is advisable to bite off and chew pieces of food with the healthy half of the jaw - on the side opposite to the operated one.
- The diet should contain calcium-containing foods and mineral salts - this is important, since the body literally grows a section of the jaw bone, and “building materials” are needed for this.
- In addition, it is highly not recommended to smoke (and not only tobacco products, but also hookahs, bongs and even vapes), since the unhealed mucous membrane is highly irritated due to hot smoke or steam.
- You should not be in hot rooms, sunbathe on the beach, or visit a bathhouse or sauna.
Typically, the dentist should recommend an antibiotic to the patient, as there is an increased risk of infection during the postoperative period. You should not select and take an antibiotic drug on your own, without consulting a doctor, since the dentist must take into account all the characteristics of a particular patient and recommend a medication for a specific case. But you shouldn’t refuse to take the prescribed antibiotic - after all, this is not only an “emergency” remedy in case of any complications, inflammation, etc.: antibiotics allow you to avoid complications in principle. This is a preventive measure necessary after oral surgery. But for daily rinsing, antiseptic solutions and wound-healing preparations are prescribed.
If the patient follows all the prescribed rules and regularly visits the VivaDent clinic for routine examinations, then the implantation will take place without unnecessary problems and complications!
Possible complications
In most cases, swelling, discomfort, and pain disappear 5-7 days after implantation. If after this time the symptoms do not disappear or increase, you should consult a specialist to rule out the following pathologies:
- hyperplasia. Rapid proliferation of mucous membranes at the implantation site. Elimination will require partial removal of mucous tissue;
- fistulas, purulent foci. A characteristic sign of such consequences may be white dotted plaque on the gums. Inflammation can result from infection during surgery, medical negligence, injury to the nasal sinuses, incorrect choice of implant, poor oral hygiene, and bad habits;
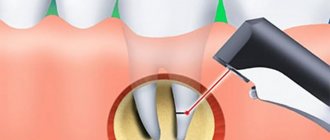
- peri-implantitis. Beginning of prosthesis rejection. Bleeding, severe swelling, redness, pain, and numbness may indicate pathology. In this case, immediate treatment and curettage are required;
- implant rejection. It is rarely recorded in dental practice. Characterized by the mobility of the installed rod. The cause of the violation may be physiological characteristics, doctor errors, chronic diseases in the acute phase, poor hygiene, and bad habits.
To minimize the risk of such conditions, you should follow your doctor's postoperative recommendations.
How to care for implants and your mouth after installation
After implantation, you need to follow a number of rules that will speed up the engraftment of the artificial root. The implantation site should be subject to as little trauma as possible. To do this you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Brush your teeth regularly with a soft toothbrush;
- Intensive mouth rinsing is prohibited before removing sutures;
- oral baths with antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions are allowed;
- you can use dental floss;
- You should visit the doctor at least 2 times a week before the stitches are removed.
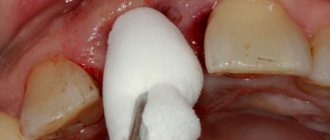
Photos of the surgical stage of dental implantation
X-rays are used to check the correct installation of the dental implant.
- After the implants have healed, 2 months later, final prosthetics are performed. 6 visits to the clinic.
The x-ray shows complete healing of the implants.
After the implants have healed, the gums are opened and a gum former is screwed into the implant to expand the gums around the neck of the future tooth, since it will be wider than the implant. After the gums have formed, you can begin prosthetics on implants.
Temporary plastic crowns were made for the patient during prosthetics.
Metal-ceramic crowns were manufactured in our own dental laboratory.
View of installed crowns from different angles.
When should you see a doctor outside of your plan?
Postoperative symptoms are most often an explainable physiological reaction. However, under certain circumstances they can turn into signs of dangerous complications. The patient must be able to distinguish pathology from normality.
Among the complications that arise during the rehabilitation period, the first place always remains infection of the wound site and internal structures, for example, the maxillary sinus after sinus lifting. In this situation, the patient notes:
- severe pain;
- worsening swelling;
- redness of the gums;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- temperature increase.
Contact a doctor should be immediate . The surgeon treats the oral cavity, sometimes it is necessary to remove sutures and clean the area with bone material. A course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs will be prescribed.
There is another unpleasant complication - suture dehiscence. In such a situation, you should immediately go to the clinic, where the dentist will apply new surgical sutures. As a rule, no additional action is required, but in rare cases the graft may become dislodged, which requires almost a second surgical intervention.
Complications associated with rejection of the osteoplastic material or poor fixation of the implants require another bone grafting. Such adverse outcomes may be associated with improper implementation of the dentist's recommendations, so it is important to strictly follow them.
Read more here - Complications after sinus lift and bone grafting
Dental implantation: healing time, features of care for the operated area.
The operation is not complicated, and the process itself, thanks to high-quality painkillers and modern techniques, is quick and painless. An implant is a titanium rod that is screwed directly into the bone. To do this, soft tissues are dissected, and upon completion of the procedure, to quickly heal them and engraft the artificial root, sutures are placed on the gums. It is during this period, which lasts no more than a couple of weeks, that the patient most acutely feels pain and discomfort. It can take from three to six months for the implant to completely fuse with the bone - everything is individual. It is also important to consider that the rate of tissue regeneration will be different for each person.
Healing after dental implantation depends on the patient’s compliance with all the dentist’s recommendations. To prevent the development of inflammation and complications, it is necessary to carefully monitor the wound. This is due to the fact that the operated area is vulnerable for 2-4 weeks due to bacteria.
In the first two weeks after surgery you must:
- Quit smoking, alcoholic beverages, and solid foods. Eat crushed and semi-liquid food.
- Minimize physical activity.
- Avoid hot, cold foods and drinks,
- Do not chew on the side where the implant is installed.
- Do not touch the operated area with your hands, tongue or various objects.
Oral hygiene should be especially carefully observed, then wound healing will occur quickly and with minimal discomfort. Use a toothbrush to walk around the implanted area; it can be carefully treated with a cotton swab dipped in saline solution. To reduce pain, the doctor may recommend taking painkillers, which are prescribed on an individual basis.