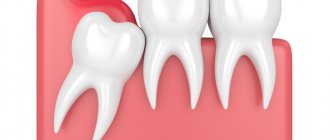
A wisdom tooth is the third molar, which appears later than the others, and sometimes does not erupt at all. A person cannot have more than 4 wisdom teeth. The approximate time when teething begins is 18 - 27 years.
Modern experts classify wisdom teeth as rudiments - elements that, in the course of evolution, have lost their role for humans. The specific location of third molars causes a number of difficulties in terms of caring for them.
“Eights” are not loaded like other teeth. In addition, they almost always tend to erupt painfully. It is not surprising that they are called the most problematic, and most dentists recommend removing wisdom teeth at the first opportunity.
Where does the figure eight grow?
It is called so because of its late eruption. If a child’s first milk teeth appear at the age of one, and molars appear before the age of twelve, then at what age do wisdom teeth grow? They will appear when the jaw bone tissue is fully formed. This period occurs between 16 and 27 years of a person’s life. In 3% of people they may appear after many years, and in 8% they do not appear at all. These are four chewing eights on the jaw - third molars, which normally are no different from the rest. Every person has rudiments, but not everyone has them.
The process is not associated with pathology; rather, the problem is that the eighth painters are considered a rudiment that does not carry a functional load.
Causes of pain
Pain after wisdom tooth removal is the body’s protective reaction to external intervention. This is absolutely normal, since an open, fresh wound remains in place of the figure eight. Gradually, a blood clot forms in the socket, acting as a “protective cushion” that prevents pathogenic microflora from entering and multiplying. That is, the pain syndrome appears due to damage that occurred during the operation:
- injuries to bone tissue or gums;
- damage to nerve fibers or blood vessels;
- inflammation of the gums.
In addition to pain after removing the figure eight, there are a number of other symptoms that should be taken into account:
- in the first few hours it hurts to open your mouth;
- soft tissue swelling;
- pain radiating to the temple;
- increase in temperature (37-37.5°C);
- feeling of ear fullness;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the cheeks or lips.
The listed symptoms are considered normal if they begin to subside after 1-2 days.
Function of the eighth molars
Dentists call them spares. Where does the wisdom tooth grow? It stands on par with the others, is classified as molars, but is practically not used for chewing food. The main purpose is to hold teeth so that they do not become loose and move apart. If a nearby molar is lost, it will take its place and perform the necessary functions. During dental prosthetics, the figure eight can become a support. During development, the human skull has changed, the jaw has become smaller and there is no room for a molar. Young people do not have such a tooth even in its rudiments.
Wisdom tooth hurts. What to do?
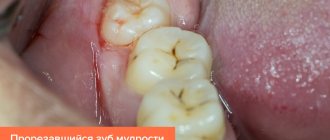
According to statistics, it is wisdom teeth that most often cause problems. Erupted “eights” are quickly affected by caries, and sometimes even remain in the bone tissue and in most cases cause discomfort. So what to do with a wisdom tooth when it hurts, haunting you day and night? Is it worth keeping the “eight”, or is it better to delete it?
What is known about wisdom teeth?
They got their name because they begin to erupt between the ages of 18 and 30. Scientists consider them to be a vestigial organ that does not bear any functional load when chewing food.
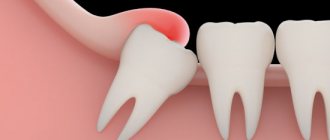
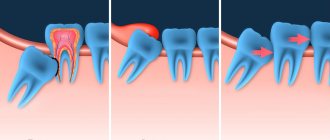
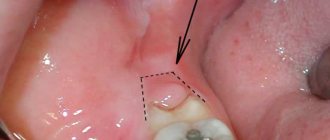
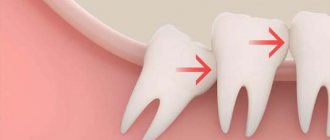
Typically, discomfort is caused by recumbent “eights”, which grow horizontally in the jaw. They don't have enough space to erupt and put pressure on neighboring teeth. As a result, the entire dentition shifts. Moreover, recumbent “eights” severely injure the gums, which leads to chronic inflammation.
Signs of wisdom teeth erupting
- Pain in the jaw, radiating to the ears and temples
- Inflammation, swelling and itching of the gums behind the last tooth
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Temperature increase
- Painful swallowing
- Persistent runny nose
- Difficulty opening your mouth
What are wisdom teeth?
For “eights” that have difficulties with eruption, there are special terms in dentistry - “dystopic” and “retained”.
Dystopic teeth are those that grow incorrectly due to lack of space in the jaw. Usually they are shifted towards the tongue, cheeks or located at an angle. Impacted teeth are unerupted teeth that remain completely in the bone.
Why do wisdom teeth hurt and gums become inflamed?
- Dystopia . Due to the incorrect position during teething, the soft tissues of the cheek are injured, and bite deformities appear.
- Retention . Late eruption affects the general well-being of the patient.
- Pericoronitis . Inflammation of the gums occurs when the “eight” erupts. Soreness, swelling and redness appear.
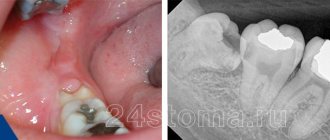
- Caries . It is quite difficult to qualitatively remove plaque from the surface of a wisdom tooth, since the “figure eight” is located far away. As a result, caries occurs.
What to do if an erupted wisdom tooth hurts?
Most often, a wisdom tooth hurts due to the fact that it has to erupt in cramped conditions - its “neighbors” have already taken their place, leaving it a minimum of space. One should also take into account the fact that in an adult, the volume of jaw bone tissue decreases over the years, which complicates the eruption of the last molars. Sometimes they can be affected by caries, which is complicated by pulpitis and periodontitis.
As can be seen from the above, a wisdom tooth can hurt for various reasons - from physiological to pathological. If it begins to bother you, you should immediately consult a dentist - the doctor will find out what caused the pain and give recommendations. Even if treatment is required, it will be carried out early, which will eliminate further complications.
What to do: treat or remove wisdom teeth
When the “eight” causes severe discomfort, you need to consult a specialist. After the examination, he will conduct a diagnosis. Dental treatment is possible only if there are no caries complications. Pulpitis and periodontitis will definitely require removal. Our doctors will take care of your comfort and perform the operation painlessly.
Stages of wisdom tooth removal
- Diagnostics . A panoramic photo of your jaw reveals comprehensive information about the location of the figure eight.
- Pain relief . Local anesthesia is performed, after which you will not feel the surgeon’s manipulations.
- Removal . The doctor carefully extracts the tooth and treats the hole with an antiseptic.
Recommendations after wisdom tooth removal
Recovery will be faster if you listen to the recommendations of a specialist. You should not eat during the first 2–3 hours. Try to refrain from smoking, alcohol, spicy and hot foods, physical activity and hot water procedures, such as baths or saunas. Brush your teeth carefully without touching the socket. If necessary, take medications prescribed by your doctor.
If you have problems with your wisdom tooth, you should not self-medicate. It’s better to immediately contact ActiveDent dentistry, where you will receive qualified assistance.
Duration of figure eight eruption
The process is long and painful. Since they erupt in adulthood, the bone tissue is formed, it is harder for the tooth to pass through the bone. If there is a place on the jaw, it appears painlessly. If it is not enough, the person faces difficulties. Let's look at the signs that indicate problems with wisdom teeth. When a wisdom tooth breaks through the bone, the symptoms are as follows:
- Painful sensations and swelling. During chewing, unpleasant sensations arise.
- When the tooth does not cut through the gum, it lifts it and forms a hood. When food and bacteria enter, inflammation develops.
- Sore throat often occurs as a result of inflammation spreading to nearby tissues.
- Unpleasant sensations in the ear, including otitis media or otalgia.
- Along with eruption, the lymph nodes become inflamed and lymphadenitis occurs.
- It happens that the figure eight, the eruption of which is just beginning on the gum, is partially located in the mandibular canal.
- There is a feeling of stiffness that extends over half of the head.
- If the dentition becomes crooked, there is no room left for the eighth molar. It will not fall out, but will move the formed row and make room for itself.
Symptoms of physiological and pathological eruption of wisdom teeth
Tooth eruption can occur physiologically or pathologically. Discomfort occurs in any case, but if the “eight” grows without complications and other teeth do not interfere with it, inflammation usually does not occur. The complex of symptoms may vary, but most note the appearance of such phenomena as:
- engorgement and hardening of the gums;
- distension in the area of eruption;
- aching pain of varying intensity.
Important! Symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. Even one patient can experience completely different sensations when wisdom teeth erupt on the lower and upper jaws.
Severe pain, tumors, and inflammatory processes accompany pathological eruption. In this case, saving the tooth is not always advisable. If your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums hurt, you need to see a dentist.
Signs of pathological eruption are:
- constant, intense, aching pain;
- swelling of the gums or cheeks;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- pain when swallowing;
- temperature increase.
Are you experiencing one or more symptoms? Don't delay your visit to the doctor. Such phenomena may be a sign of pericoronitis, purulent inflammation, abscess and other pathologies. Without adequate treatment, the inflammatory process will spread to adjacent tissues, and phlegmon will form in the oral cavity. In advanced cases, the problem can only be dealt with surgically in a hospital setting. Purulent inflammation is opened through external incisions, the treatment process is accompanied by the use of antibiotics.
Even if the symptoms of wisdom tooth eruption do not cause concern, it is recommended to visit a dentist. This is necessary to exclude a pathological process.
The doctor will refer you for an x-ray or computer examination. It helps determine the position of the new tooth relative to the existing ones and assess whether there is enough space for it. The photographs clearly show any deviations in the figure eight position. Based on the examination, the doctor will decide whether the wisdom tooth needs to be removed.
What to do if a tooth hurts during pregnancy?
Against the background of toxicosis and a general decrease in immunity, the mother’s body becomes especially vulnerable to the effects of pathogenic bacteria. Unfortunately, wisdom teeth do not warn in advance about their appearance. If it begins to erupt during pregnancy, standard treatment methods are often not suitable. This is especially true when taking most antibiotics and painkillers. If the patient does not have serious complications during teething, it is recommended to use gentle means (Cholisal, Kalgel, etc.) to eliminate inflammation. Many experts allow the use of paracetamol. In the most severe cases, surgical intervention and tooth extraction are performed: this is recommended to be done in the second trimester.
When to see a doctor
Wound healing after removal of the figure eight is always a painful process, but sometimes it is accompanied by complications. To avoid causing a serious deterioration in your health, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- the pain intensifies every day, analgesics help little;
- the pain does not go away a week after tooth extraction;
- the pain is not aching, but pulsating, it radiates to the neck, eye, temple, and interferes with sleep. Such sensations are a sign of an inflammatory process; you should consult a doctor immediately;
- swelling does not disappear completely on the 2nd–3rd day after surgery, but, on the contrary, increases;
- temperature rises above 37.5 °C;
- the temperature does not drop to normal on the 2nd–3rd day after surgery;
- an allergic reaction to a hemostatic sponge or analgesics occurs;
- alveolitis (inflammatory disease) occurs in the socket. This happens if a part of the root remains in the hole, a blood clot did not form or was washed out during hygiene procedures, the patient violated the rules of oral care, which is why an infection got into the wound;
- your health worsens on the 2nd–3rd day after the procedure.
Rules for oral care after wisdom tooth removal
In order for healing to proceed normally, without any additional problems, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- remove the tampon 20 minutes after surgery;
- for 3 hours after removing the figure eight, do not eat or drink;
- Do not rinse your mouth on the day of surgery;
- In the first few days after surgery, avoid hard foods and eat warm, soft foods. Chew food on the other side of the jaw, protecting the wound from foreign particles getting into it. Do not drink anything hot;
- in the first 7–10 days, avoid alcohol (it slows down healing and cannot be combined with analgesics);
- in the first week, do not visit training rooms and swimming pools, do not work in the garden, do not do cleaning, avoid physical activity, especially those associated with bending;
- in the first week do not visit baths, saunas, solariums, or sunbathe in the open air;
- do not heat the socket area (do not use warming compresses), do not use a UHF device;
- Do not brush your teeth for the first 24 hours after surgery, then for 10 days when brushing your teeth, try not to catch the socket with the brush;
- on the 2-3rd day after the operation, make passive baths with chlorhexidine or another antiseptic (spiking the solution into your mouth and tilting your head towards the hole, just hold for a while, then spit), starting from the 4th day - use chamomile or sage decoctions ;
- take only those analgesics prescribed by the doctor, apply cold compresses.
If the pain intensifies or other alarming symptoms appear, you should never touch the socket with your fingers to check its condition. You need to see a doctor: if there really is a problem, he can prescribe an x-ray, and then select a treatment regimen.