- Published by: Laima Jansons
Loss of taste is a disease that is accompanied by disruption of the taste buds . It can be short-term - after eating too hot or cold food, or long-term, and this already signals problems with internal organs:
- ageusia is a pathological process accompanied by a complete loss of taste perception ;
- hypogeusia is a disease in which there is a partial loss of taste ;
- Dysgeusia is a pathology that is characterized by distortion of taste sensations and changes in perception.
Causes of complete loss of taste
The main factor in the complete loss of taste for sweetness or salt is long-term depressive and stressful conditions . Other ageusia factors include:
- infectious lesions of the nervous system pathways;
- inflammation of the lingual nerve or chorda tympani, accompanied by neuritis of the facial nerve;
- damage to the back of the tongue, which leads to neuritis of the glossopharyngeal nerve;
- pathologies of the medulla oblongata;
- inflammation of the vagus nerve.
This is interesting! In the human body there are significantly more bitter receptors than others. This is due to the fact that most toxic substances have a bitter and pungent taste.
Diseases in which there is a complete or partial loss of taste
- Neuritis of the facial nerve or inflammatory damage to the nerve that is responsible for facial muscles. In addition to loss of taste, the patient experiences weakening of the facial muscles and asymmetry . The patient cannot smile or frown, and the process of chewing food is difficult.
- Facial nerve paresis or paralysis is a pathology of the nervous system that occurs due to an infection of the upper respiratory tract. The pathology is accompanied by impaired taste perception and facial asymmetry .
- Acute viral hepatitis is an infectious lesion of the liver, as a result of which taste perception is impaired . The main symptoms of the disease are jaundice, diarrhea, vomiting and loss of appetite .
- Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that is accompanied by a decrease in secretion production from the salivary and lacrimal glands. Dryness in the nasopharynx, burning in the eyes and loss of taste are symptoms of this disease.
- ARVI - viral damage to the taste buds, damage to the nerve endings of the receptors responsible for taste, nasal congestion contribute to partial loss of taste . Normalization of taste perception is achieved after suppression of the virus in the body.
Taste qualities with dysgeusia are distorted
Based on the above, taste qualities in dysgeusia are not completely absent, but are distorted. Some experts call dysgeusia (taste distortion) any taste disorder, while others use this term to mean a certain type of taste disorder. That is, dysgeusia is any change in taste, including a strange taste. No one is immune from the occurrence of taste deviations. They can occur at any age. People with dysgeusia constantly experience an unpleasant, salty, rancid or metallic taste in their mouth.
Even ice cream can have a salty or metallic taste. There are cases when people also experience changes in smell. Taste buds and receptors responsible for smell are interconnected, so this phenomenon is quite common.
One of the most common symptoms of dysgeusia is the presence of a metallic taste in the mouth.
Causes of partial loss of taste
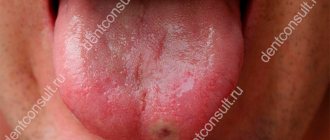
Conventionally, the tongue can be divided into four parts, each of which is responsible for the perception of a certain taste.
Photo 1: The tip of the tongue is responsible for the sensation of sweet taste, the middle - for salty, the back of the tongue perceives bitter, and the edges of the tongue are responsible for sour sensations. Impaired perception is associated with various pathological processes in different parts of the tongue. Source: flickr (“R☼Wεnα”).
Sweet taste is lost
Loss of sweet taste can occur due to an inflammatory process at the tip of the tongue, a burn, or injury to this area. Disturbances in the papillae of the tongue, pathologies of nerve impulses to the brain are also factors in reducing the sensation of sweetness.
If you don't feel the salty taste
A weakening of the sensation of salty taste or its complete loss indicates injury to the middle part of the tongue. Bacterial and fungal infections (candidiasis) affect the tissues where taste buds are located .
Loss of salty taste perception is often caused by heavy smoking , which causes the taste buds to atrophy. Malignant neoplasms in the brain provoke ageusia or hypogeusia of salty taste, since the brain cannot recognize the incoming impulse.
Loss of sweet and salty taste
There are also several reasons that provoke the loss of sweet and salty taste at the same time:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants;
- hypovitaminosis (especially vitamin B12);
- lack of zinc in the body.
Partial loss of taste (sweet or salty) is often noted in patients suffering from epileptic seizures . Also common factors of hypogeusia are:
- changes in the deep parts of the temporal lobe of the brain, which is accompanied by mental disorders and schizophrenia;
- neuritis of the fifth or seventh pair of cranial nerves;
- damage to the brain stem.
Loss of smell
A person smells through receptors. Molecules of substances carrying aroma enter the receptors, these waves are transmitted along the nerve endings to the brain, where this impulse is processed. Most often, loss of smell occurs in men, much less often in women. With age, the risk increases, and you need to be more careful about your body.
There are different types of loss of smell:
- Hyposmia is an extremely poor perception of smells. Also, with hyposmia, there is an incomplete loss of smell, i.e. only for certain smells.
- Hyperosmia is, on the contrary, excessive sensitivity to odors.
- Cacosmia - perception in this case is turned upside down. Attractive smells seem disgusting.
- Anosmia is the complete loss of olfactory processes. It is formed due to colds, and in some cases even after a stroke.
Loss of smell can occur from birth, due to the fact that the respiratory organs have not had time to form properly. You can also acquire anosmia during your life.
Causes of loss of smell
During the loss of smell, the receptors will not respond to stimuli. The brain does not receive signals and does not distinguish smells. If the problem is in the central nervous system, then the receptors, on the contrary, send impulses to the brain, but the brain does not perceive them. And sometimes it may be that the receptors in the nose recognize and send odors to the brain, but along the way they are blocked.
ARVI and COVID-19
Loss of smell can be a consequence of a common cold, flu or acute respiratory viral infection. In this case, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which disrupts not only the breathing process, but also deprives the receptors of their functions - transmitting impulses to the brain.
Not long ago, doctors found out that loss of smell is, in most cases, also a symptom of coronavirus. It appears in 80% of cases on about 3–5 days. Moreover, during this period the person may not experience any other symptoms. It is known that the nasal mucosa is the first to encounter viruses and bacteria, and the immune system begins to work from the nose to destroy as many viral agents as possible. Perhaps damage to the receptors and cells of the mucous membrane occurs precisely because of the “smart” attack of the virus in order to break the defense at the attack stage and easily penetrate the body.
Another opinion is that the sense of smell disappears due to the body’s protective reaction to the virus; the receptors sacrifice themselves to prevent the infection from spreading. The sense of smell returns approximately 2 weeks after complete healing. But there are rare cases when the return is delayed and the sense of smell is fully restored within several months.
According to statistics, in most cases this symptom indicates that the disease will not develop into a particularly acute form with serious consequences. Most often, anosmia develops immediately after the incubation period, 3-4 days after the viral agents have entered the body, but before the appearance of other symptoms - sore throat, cough, fever, rash and chest congestion, weakness and fever.
According to another version, with covid, olfactory receptors are damaged at the level of the nervous system, when the transmission of impulses from the receptors to the brain and back is blocked by viral agents. But why this happens and how the virus acts in the body of a particular person is an area that has not been sufficiently studied.
That is why sleeping pills and sedatives are often prescribed in doctors’ protocols. To support the nervous system that is being attacked.
Also, we can assume that in mild, moderate and severe forms of the disease without critical complications, the return of the sense of smell with proper treatment of coronavirus indicates that the virus is receding, even if other symptoms are partially preserved.
Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease
Loss of smell in such diseases is the most striking symptom. Sometimes it can become the very first and earliest sign of impending irreversible disorders in the brain. Thus, scientists can determine the risk of disease for a person by how he is able to recognize, remember and remember smells.
In this case, we have to say that the loss of smell is exclusively neurological in nature. Atrophic changes in the cerebral cortex, characteristic of these diseases, affect the central part of the olfactory analyzer. According to MRI, degeneration processes affect the primary olfactory cortex, hippocampus, thalamus and hypothalamus. Which inevitably leads not only to disturbances in coordination activity, but also to memory loss and impaired sense of smell.
Other causes of loss of smell
- Allergy. If a person is susceptible to allergic reactions to the smells of flowers or something else, his nasal cavity may become inflamed.
- Injuries. If the nose or brain is injured, the sense of smell may disappear immediately.
- Age. The older a person gets, the processes in his body slow down. This happens with the membranes of the nose. Older people are more likely to experience dryness and atrophy of the nasal mucosa.
- Tumor. If a benign tumor is found, it is removed and the sense of smell gradually returns.
- Polyps. New growths in the nose can interfere with olfactory processes.
- Smoking. Nicotine destroys the nerve endings in the nose, this happens gradually, but can lead to a complete loss of smell.
- Neurosis. Loss of smell can be caused by long-term emotional problems or a lot of stress.
- Burns. Toxic vapors, when inhaled, can burn the nasal mucosa or lubrication with alcohol-containing liquids.
- Incorrect structure of the nasal cavity.
- Lack of vitamins (vitamin A) or other substances in the body.
Consequences of loss of smell
Problems in the perception of smells are a big problem that has a great impact on the entire body. Bright and juicy aromas of food trigger the digestive system and stimulate the secretion of gastric juice. If a person cannot smell the food he eats, the gastrointestinal tract will also suffer.
If viruses or harmful substances enter the body through the nose, a defensive reaction is provoked, for example, sneezing. If the receptors do not awaken a defensive reaction when the sense of smell is lost, then harmful substances will continue to freely penetrate deep into the body, causing even more damage.
How to treat loss of taste
To quickly restore your sense of taste, you should consult a specialist to diagnose the cause of the disease. Depending on the factor contributing to the loss of taste, appropriate treatment is prescribed:
- Dryness in the mouth, accompanied by insufficient secretion of saliva, will be eliminated by drugs that help moisturize the oral mucosa. For this purpose, artificial saliva preparations are prescribed - Salivart, Mouth Kote.
- In addition to medications, you can use mouth rinses . They not only moisturize the mucous membrane, but also have an antibacterial effect.
- If the loss of taste is associated with fungal infections of the mouth , drugs for candidiasis are prescribed - Clotrimazole solution, Decamine ointment.
- When diagnosing a lack of Zinc and vitamin B12 in the body, Zincteral, Berocca, and intramuscular injections of cyanocobalamin are prescribed. Additionally, multivitamin complexes may be prescribed.
- restore taste perception . The leaves of peppermint, lemon balm and motherwort have a sedative effect and eliminate the main cause of pathology - neurosis. When the oral cavity is infected with a bacterial or fungal nature, rinses made from chamomile flowers, calendula and oak bark are used.
- To increase the spiciness, you need to add spices to your food such as cloves, cinnamon, mustard and lemon.
Photo 2: Regular cleaning of the surface of the tongue reduces the risk of loss of taste. Source: flickr (Gabriella Yazickr).
Lost sense of smell and taste: what to do
Ways to restore sensitivity:
- Surgical. Surgical intervention is required when malignant and benign neoplasms are detected in patients (polyps, oncological processes), as well as when changes in the structure of the nasal cavity (deviated septum).
- Medication. Drug treatment is prescribed to patients with allergic and infectious processes. Antiviral, antibacterial and antihistamine drugs are used for therapy.
- Physiotherapeutic. To restore the sense of smell and taste, patients are prescribed inhalations, heating and laser exposure.
Restoration of sensory functions can occur in some cases without treatment, that is, on its own. However, if a symptom occurs, you should not rely on chance and it is recommended to consult a specialist to determine the cause of the phenomenon and prescribe adequate therapy.
Various traditional methods are also used for treatment. However, they should not be used in isolation, but only in combination with medical prescriptions and after consultation with the doctor. Most often, nasal rinsing is used with a decoction of oak bark, chamomile flowers, as well as nasal drops based on aloe juice.
Homeopathic treatment for loss of taste
Homeopathic treatment differs from traditional treatment by increased efficiency and minimal negative impact on the human body . The homeopathic doctor individually selects the name of the drug, dosage and method of use.
| Drugs | Purpose | Additional symptoms |
| Hepar sulfur | Returns taste sensations. | Nasal discharge (including putrefactive discharge), sneezing. |
| Hyoscyamus | Lack of taste due to paralysis. | Accompanied by nervous exhaustion, increased weakness, and thirst. |
| Sepia | With a complete absence of taste and smell. | The patient is not comfortable in a warm room, there is increased dryness of the mucous membranes, and a herpes rash around the nose. |
| Silicea | In the absence of smell and taste. | Abscess, itching on the tip of the nose, weakened immunity, pale skin tone. |
Eating disorder
Malnutrition is one of the reasons that can lead to a number of serious diseases that affect the functioning of the entire body. Symptoms can be extremely varied, and the appearance of a taste in the mouth is no exception. One study showed that nutritional deficiency is one of the causes of gum disease and multiple forms of caries.
Patients who adhere to certain dietary principles, such as veganism, vegetarianism, or following strict diets, may suffer from such symptoms. Using laboratory blood tests, the doctor will help determine what substances and vitamins are missing and give appropriate recommendations.
Proper nutrition can be considered as a factor in preventing various problems and maintaining normal functioning of the body. The doctor can give appropriate recommendations, for example, prescribe nutritional supplements and multivitamins.
Symptoms of dehydration
Dehydration can cause a number of symptoms, one of which is dry mouth. Due to a lack of fluid, saliva becomes more viscous and rich in minerals, which is what causes a taste in the mouth.
It is worth remembering that this is not the only sign. The following symptoms are typical for dehydration:
- fatigue, decreased performance;
- dizziness;
- change in urine: color, quantity;
- decreased number of urinations;
- strong thirst.
Dehydration can be caused by food poisoning, accompanied by prolonged diarrhea and repeated vomiting, alcohol abuse, excessive exercise and a number of other diseases and conditions.
Reason: ENT diseases
The salty taste sometimes has rather trivial causes: for example, bacterial sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis or a cold. During inflammation, mucus appears in the sinuses, which consists of mucin protein, salt, nucleic acids and water. In the acute course of the disease, snot flows down the walls of the nasopharynx into the throat, and accordingly, a feeling of salt occurs. With sluggish inflammation of the ENT organs, mucus is also constantly disturbing by its appearance in the mouth.
ENT diseases also contribute to the appearance of a salty taste
Dehydration
When the body loses too much fluid, such as after severe diarrhea or vomiting, saliva thickens and becomes salty due to the increased concentration of mineral salts in it.
What to do?
To prevent dehydration, doctors recommend drinking 1.5 to 2 liters of fluid per day. In case of severe dehydration, special solutions are prescribed to restore the water-salt balance.
Reason: dehydration
If you have a salty taste in your mouth, then it’s time to calculate how much clean water you drink per day. Because it is the imbalance of fluid in the body that often becomes the answer to the question of why the salty taste bothers us. Our saliva contains sodium chloride, in other words, it is ordinary salt. When fluid is lost in the body, blood and saliva thicken, causing dry mouth. Saliva undergoes a process of dehydration, causing it to contain more salt and less liquid and other useful minerals. The more severe the dehydration, the more clearly the unpleasant symptom appears.
The cause of dehydration could be a low-carbohydrate diet, taking diuretics, poisoning and indigestion, drinking alcoholic beverages, drinking too much strong coffee or soda, or smoking a large number of cigarettes. Dehydration can develop during intense physical activity, after spending a long time in the scorching sun or in hot, stuffy rooms.
An imbalance of fluid in the body often causes a bothersome salty taste.
When dehydrated, the taste of salt may be accompanied by other alarming symptoms: weakness, dizziness, thirst, rare urination, diarrhea. The first thing to do in such a condition is to drink as much liquid as possible, in particular clean water. It’s better to generally make it a rule to drink at least one and a half or two liters of water a day every day. This is approximately 8 glasses. However, in cases where the body suffers from dehydration, this figure can be safely increased. For example, lovers of strong coffee drinks who drink up to 5 mugs of coffee a day should regulate the balance of healthy fluids in the body by taking 2-3 glasses of clean water more than those who are not fond of coffee.
Complications of ignoring taste
Ignoring the problem leads to the development of various complications:
- There is a loss of appetite. It seems to a person that his favorite dishes have a strange, unusual taste, so he stops enjoying eating.
- Against the background of sluggish infections, a decrease in immunity occurs.
- If you delay visiting a doctor, the disease enters the chronic phase.
- Transfer of infection from the oral cavity to vital organs.
- Insomnia, aggression, developing against a background of discomfort, irritation from the constant salty taste.
- Atherosclerosis resulting from dehydration, a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels.