What is dysgeusia and what causes its occurrence?
Dysgeusia (distortion of taste) is a disease in which the sense of taste is partially or completely absent. There are many reasons for this disease. Using the sense of taste, we can determine the taste of food and other elements entering the body. The sense organs that are responsible for this function are called taste buds.
They are located on the surface of the tongue. Under some conditions, a person may lose the ability to taste foods. Experts distinguish four main types of such disorders, namely pargeusia, dysgeusia, ageusia or hypogeusia. The complete absence of all taste sensations is called ageusia, partial weakening is called hypogeusia . Sometimes, a person constantly feels an unpleasant taste, regardless of the product he consumes. Distorted taste, which has a metallic taste, is a sign of dysgeusia.
Causes
The main reason for the appearance of a sour taste in the mouth is a violation of the acid-forming function of the stomach. This condition develops with hyperacid gastritis. A similar phenomenon is typical for gastritis with high acidity, as well as for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. Also, a sour taste in the mouth can be observed with gastroesophageal reflux, when gastric contents reflux into the esophagus due to weakness of the gastroesophageal sphincter. The occurrence of a bitter taste in the mouth may be associated with the following factors:
- Violation of the process of bile discharge and cholelithiasis.
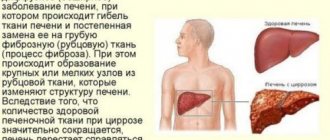
- All types of hepatitis, including viral and alcoholic type.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Oncology of the liver or gallbladder.
The most common cause of a sweetish taste in the mouth is poor nutrition, when a person is prone to chronic overeating, and also when his diet is dominated by simple carbohydrates and fatty foods. Other potential causes of a sweet taste in the mouth include:
- Diabetes. If a characteristic sweetish taste in the mouth occurs spontaneously, regardless of food intake, then this may indicate developing diabetes mellitus. In addition to this symptom, additional concerns include dry mouth, intense thirst, increased appetite, and an increase in the daily volume of urine excreted.
- Ketoacidosis. With previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus, a complication such as ketoacidosis may develop. In addition to a sweetish taste in the mouth, this condition is accompanied by severe malaise, confusion, even entering a coma. After a sweet taste appears in the mouth, with ketoacidosis a characteristic smell of acetone appears from the mouth.
- Pregnancy. If a woman of reproductive age who is regularly sexually active has a sweet taste in her mouth, this may indicate pregnancy, since this condition is characterized by atypical taste sensations, as well as atypical taste preferences.
- Oral diseases. With pathologies such as deep caries, stomatitis, gingivitis, chronic bleeding of the gums develops, which leads to the appearance of a sweetish taste in the mouth.
A less common cause of this symptom is traumatic brain injury, when the nuclei of the cranial nerves, whose role in the formation of taste sensations is key, were involved in the traumatic process. With this type of injury, a person ceases to feel the entire taste palette.
The appearance of a sour taste in the mouth after eating or other atypical tastes does not differ significantly between men and women. In addition, an atypical taste in the mouth may be accompanied by an unpleasant odor, which creates not only physical, but primarily psychological discomfort, and negatively affects interaction in society and interpersonal relationships.
Taste qualities with dysgeusia are distorted
Based on the above, taste qualities in dysgeusia are not completely absent, but are distorted. Some experts call dysgeusia (taste distortion) any taste disorder, while others use this term to mean a certain type of taste disorder. That is, dysgeusia is any change in taste, including a strange taste. No one is immune from the occurrence of taste deviations. They can occur at any age. People with dysgeusia constantly experience an unpleasant, salty, rancid or metallic taste in their mouth.
Even ice cream can have a salty or metallic taste. There are cases when people also experience changes in smell. Taste buds and receptors responsible for smell are interconnected, so this phenomenon is quite common.
One of the most common symptoms of dysgeusia is the presence of a metallic taste in the mouth.
Diagnosis of taste disorders in children
If you suspect a taste disorder, you should contact a specialist. Parents should be alerted by the refusal of familiar and favorite foods, and at a more conscious age, by the child’s complaints. Also, the baby may begin to eat things that are not intended for this (it should be noted that at a certain age children “put everything in their mouths” in order to explore the world around them, and this is absolutely normal).
Diagnosing taste disorders in preschool children is quite difficult, since children cannot always clearly describe their sensations. During the examination, the corresponding side of the tongue is moistened alternately with a sweet, sour and bitter solution using pipettes. After each session, rinse your mouth thoroughly. In infants, the doctor pays attention to the general motor and facial reaction. Children over two years old can most often consciously talk about their feelings. Source: E.V. Pavlovskaya Selective appetite in children // Issues of modern pediatrics / 2013/ Volume 12/ No. 6
Is taste distortion always associated with dysgeusia?
Distortion of taste can signal not only dysgeusia, but also other diseases. Often, after the disease is completely cured, the disturbance in taste disappears and everything returns to normal. If the symptom remains, the possibility of a chronic taste disorder should be considered.
Distortion of taste sensations occurs as a result of disruptions in the functioning of the receptors responsible for taste. Research has shown that dysgeusia may be caused by a decrease in the number of microvilli in taste receptor cells. It should be noted that with a decrease in the nucleus and cytoplasm of receptor cells, similar deviations occur.
Another important reason for the development of dysgeusia is the use of certain medications. These include certain diuretics, tetracycline, metronidazole, penicillamine, as well as anigestamines of the H1 series. Each drug has a different effect on taste receptors. However, the result is the same - a change and disturbance in taste.
When the body is not friendly with milk: what is lactose intolerance?
Are you suffering from cramps and bloating? Do you hear rumbling in your stomach? Do you occasionally worry about loose stools? If these signs appear some time after drinking milk and milk-containing products, lactose intolerance (hypolactasia) can be assumed.
Why does such a pathology occur and can it be avoided? Let's figure it out.
Lactose (milk sugar) is a substance found in the milk of mammals and humans. The role of lactose in the body is great: it helps the absorption of certain minerals, including calcium, in the intestines, and also promotes the proliferation of lactobacilli necessary for the body.
Normally, in all babies, lactose is broken down in the small intestine by a special enzyme - lactase. As people age, the amount of lactase in some people's bodies decreases.
It is difficult to imagine the diet of a modern person without dairy products, and the presence of this enzyme in the body is extremely important for the normal digestion process.
The mechanism of development of hypolactasia
Lactose intolerance occurs when there is a complete absence or insufficient amount of lactase. The task of this enzyme is to participate in the conversion of lactose in the small intestine into glucose and galactose. These carbohydrates are able to penetrate the intestinal wall into the bloodstream.
With a deficiency or absence of lactase, milk sugar in an undigested form enters the large intestine, where it becomes “food” for the bacteria living here. The result of the processing of lactose by bacteria is carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen and water. Gases formed in the lumen of the large intestine stretch its walls, causing bloating (flatulence) and pain in it, and water causes the development of diarrhea (loose stools).
Lactose intolerance is much less common in children than in adults. It can be congenital or acquired. Alactasia, or the complete absence of the enzyme, is associated with a structural disorder of the lactase gene. In this case, the baby should receive lactose-free nutrition from birth. Fortunately, this disease is quite rare. More often one can observe the functional immaturity of the enzyme system of infants, causing insufficient milk tolerance; some time after birth, the amount of enzyme increases and the breakdown of lactose improves.
Acute and chronic intestinal infections, immune, inflammatory, and atrophic processes in the intestines can lead to secondary (acquired) intolerance to milk sugar.
Factors such as age, ethnicity (in the countries of North America, Africa, and Southeast Asia the percentage of people suffering from hypolactasia are higher), and premature birth increase the risk of developing this pathology.
How does lactose intolerance manifest?
Rumbling in the stomach and distension, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headaches - these symptoms of lactose intolerance occur in some people an hour after taking whole milk or dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese, kefir, ice cream).
The higher the degree of hypolactasia, the more intense the clinical manifestations. However, it should be remembered that such a reaction of the body can also be caused by the consumption of stale products that have expired or are incompatible. In both cases, if you have the symptoms mentioned above, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of lactose intolerance
A biopsy of the small intestinal mucosa is a direct way to measure the activity of the lactase enzyme it contains. Due to the traumatic nature and complexity of this study, it is used during operations or other life-saving interventions.
Genetic tests can identify genes that block lactase production.
One of the common indirect tests for lactose intolerance, among others, is the lactose load test. It is based on a comparison of blood glucose levels in an adult before the study and after ingesting 50 grams of lactose dissolved in 0.5 liters of water. If lactose is broken down and the resulting glucose is absorbed into the blood, the glucometer will show an increase in blood glucose. Otherwise, we can conclude that lactase does not work.
How to treat lactose intolerance?
Primary hypolactasia is a type of normal, not a disease, so there is no specific treatment for this form of lactose intolerance, but it is necessary to follow a lactose-free diet. Secondary hypolactasia is corrected by treating the underlying disease that led to its development. Taking the missing enzyme in the form of tablets and drops must be combined with a balanced diet developed by a nutritionist.
Do not forget that with a mild degree of lactose intolerance, you can avoid the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms if you reduce the amount of whole milk you drink and include lactose-free cheese, cottage cheese, kefir, and yogurt in your diet. Eating milk porridge will cause much less consequences than a glass of milk, since lactose will enter the intestines in portions, and its processing will be more efficient.