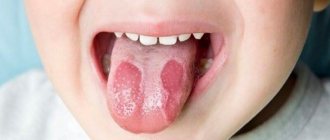
Syphilitic chancre is an ulcerative or erosive formation that appears in the primary stage of syphilis infection and is its main symptom. There are 13 types of chancre due to syphilis: ordinary and atypical. Syphilis is treated with medications and a special regimen.
Causes and course of the disease
The development of syphilis of the pharynx is possible at all 3 stages of the disease.
Primary lesions are more often in the nasopharynx than in the oropharynx. Moreover, infection can also occur through the use of infected medical instruments (iatrogenic factor of infection).
When the nasopharynx is affected, the most common manifestations of the disease are:
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes of the neck, which in some cases are very pronounced;
- Severe pain when swallowing, which radiates to the ear and is accompanied by congestion.
Basics of pathology
Oral syphilis is a type of sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease. The pathology is caused by a pale spirochete localized on the oral mucosa. The first signs are visualized in this part of the body.
According to the International Classification of Diseases according to etiology, syphilis is classified into:
- Congenital
- Acquired
Important! Syphilis in the mouth can be treated only at the initial stage of pathology development. If left untreated, the infection quickly spreads through the flow of blood and lymph to all organs and tissues.
Diagnosis of primary syphilis
Hard chancre should be distinguished from cancer of the palatine tonsil and remember that the cancerous ulcer is located deep and has dense, uneven, corroded edges, and its bottom bleeds easily.
To make a correct diagnosis, in addition to the Wasserman reaction, a biopsy of pharyngeal tissue is necessary. A sore throat-like chancre is not difficult to distinguish from a sore throat by the following symptoms: unilateral lesions, absence of pain and such general phenomena as fever and malaise.
For the secondary period of development of syphilis on the mucous membranes of the pharynx and pharynx
characterized by the simultaneous occurrence of similar manifestations on the skin - roseola and papules. Secondary syphilides of the mucous membranes contain a lot of treponemes (the causative agents of syphilis), and therefore patients who have lesions of the mucous membranes of the pharynx, mouth and pharynx pose a serious danger to others.
The disease can have erythematous, erosive and papular forms. Syphilitic erythema is a continuous spot that has sharp boundaries and a bluish-red color. In some cases, slight swelling is observed. Such erythemas are most often localized on the anterior and posterior palatine arches, tongue, tonsils and soft palate.
If the erythema is located on the anterior palatine arches, then it occurs under the guise of a sore throat. This sore throat is one of the early secondary manifestations of syphilis.
Varieties of chancre
Syphilitic hard chancres are dark red, evenly shaped ulcers with clear boundaries and slightly raised edges that appear after infection with syphilis. You can see what this formation looks like in the photo:
There are 10 main forms of chancre:
- unit;
- multiple;
- giant;
- dwarf;
- diphtheritic;
- cortical;
- slit-like;
- erosive;
- burn;
- herpetiform.
Important!
All varieties appear a month after infection and disappear after 20-50 days. Their occurrence is often accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes and blood vessels. Unlike trypanosomal chancroid, hard syphilitic chancre is usually not accompanied by severe symptoms. It does not itch, is not accompanied by a burning sensation, and only hurts when localized near the urethra or anus.
Single (regular, simple)
A single chancre, also known as a “common” or “simple” chancre, is the classic manifestation of syphilis and is found in most cases of infection. Their diameter is 2-3 cm, the edges are clear, slightly raised.
Simple chancre can be localized in different areas:
- Genital
: on the penis in men, on the labia majora and minora, as well as in the vagina in women, in some cases on the cervix. - Extragenital
: on the face, on the legs and pubic area, in the armpits, near the anus, on the chest in women, in the mouth - on the tongue, on the gums, in the throat, on the lips.
The genital location of syphilomas is more common: about 90% of all cases of the disease are accompanied by hard chancre in the genital area.
Multiple
Multiple ulcers form very rarely: in 8-12% of cases. There are 2 subtypes of profuse syphilomas: twin chancres, which appear during simultaneous infection, and sequential hard chancre, which occur during infection at different times.
Factors that provoke the formation of a large number of syphilomas include:
- skin injuries;
- ulcerative formations on the skin;
- skin infections: scabies, eczema;
- acne disease.
Unlike single syphilomas, multiple chancre can be localized bipolarly: in both the genital and extragenital areas simultaneously. The number of ulcers depends on the specifics of the patient’s body, and ranges from 2 to 10 pieces.
Giant
Large and very large syphilomas occur in 10-15% of cases of syphilis infection. In diameter they can reach 4-5 cm or more, matching the size of a child's palm.
Giant chancre occurs in areas rich in subcutaneous fat:
- on the pubis;
- on the stomach;
- on the hips;
- on the scrotum;
- on the forearms.
Apart from size, a giant syphilitic ulcer is no different from a regular one.
Dwarf
Dwarf syphilomas are called poppy seed sized syphilomas, with a diameter not exceeding 1-5 mm. Such ulcerative formations can only be seen with the help of a magnifying glass.
Dwarf chancres are often located:
- In the oral cavity: on the tongue and gums, on the roof of the mouth, in the throat.
- On the external genitalia: on the labia majora and minora, on the penis.
- In the area of the armpits and anus.
- Inside the vagina and on the cervix in women.
In medical practice, small primary syphilomas are rare. In women, dwarf ulcers form 3-4 times more often than in men.
Diphtheritic
Hard chancres with an unusual appearance are called diphtheritic: unlike simple ulcers that have a smooth and shiny surface, they are covered with a necrotic film of an ashy-grayish hue.
Syphilomas of this type are common and can be localized in any area.
Cortical
Chancre with crusting on the surface occurs in areas where the ulcer can easily dry out:
- on the face (nose, chin, lip skin);
- on the shaft of the penis;
- on the stomach, especially in the lower part.
Visually, the cortical type of syphiloma may resemble ecthyma or impetigo.
Slit-shaped
Slit-shaped chancre visually resembles a crack or book leaves.
They are located in small skin folds:
- in the corners of the mouth;
- in the folds between the fingers;
- in the pubic folds;
- in the anal area.
They are very rare: only 5-7% of cases of syphilis. Slit-like chancres are more common in men.
Erosive (Folman's balanitis)
Erosive chancre, also known as Folman's balanitis, is a primary syphiloma that does not have a clear compaction at the base and combines many sharply limited erosions, partially merging with each other.
It occurs exclusively in the genital area:
- on the head of the penis in men;
- on the labia of women.
In 87% of cases of Folman's erosive chancre, it appears in men.
Burn
Burn, or combustioform chancre is an erosion on a leaf-shaped base, which has a weak, unexpressed compaction at the base. This type of erosion is prone to strong peripheral growth.
As it grows, burn syphiloma loses its smooth contours and regular shape, and its bottom becomes granular, with a pronounced red tint.
Herpetiformis
Chancroid herpetiformis has a strong resemblance to genital herpes. This erosive formation resembles Folman's balanitis: it contains many grouped erosions with sharp edges located nearby in a small area.
Small erosions that make up chancre herpetiformis have a vague compaction at the base. This type of syphiloma differs from burn and erosive ones in its regular shape, as well as the absence of fusion between its component parts.
Diagnosis of secondary syphilis
Secondary syphilitic lesions of the pharynx must be distinguished from diseases such as leukoplakia, aphthous stomatitis, diphtheria, ulcerative membranous tonsillitis, and pharyngeal tuberculosis.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
In the tertiary period of development of syphilis of the mucous membranes
The most common and important manifestations are lesions of the oral cavity, pharynx and pharynx.
Tertiary lesions of the tongue can manifest themselves in the form of isolated gummas (soft tumor), which develop in its thickness, or as diffuse infiltration, which covers most of the tongue, and then turns into diffuse sclerosis (pronounced coarsening) of the mucous membrane and muscle tissue.
But most often the location of the tertiary form of syphilides is the soft and hard palate. Most often in this case there is a diffuse form, but in some cases limited gummous tumors are observed. The pathological process begins with virtually no pain and is a diffuse swelling, and then thickening and compaction of the soft palate, which gradually loses its mobility. Infiltrates usually have a bluish-red color. Then the gummas disintegrate and deep ulcers are formed, which have sharply defined edges.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Tertiary lesions in the pharynx can take the form of tubercular syphilis or gummous lesions, which are mainly localized on the vault of the pharynx and its posterior wall. Such lesions are very rarely detected before ulceration, because they practically do not bother the patient.
After the healing process of gummous-ulcerative lesions, dense scars appear, as well as adhesions between the arches, walls of the pharynx and the soft palate, which often causes atresia (fusion) of the pharynx and disruption of the swallowing process.
Atypical forms of syphilitic chancre
Atypical chancres are types of syphilomas that differ from the usual types in one or more characteristics.
These include:
- Chancroid felon:
an ulcer with jagged edges that appears on the fingers. Most often it occurs on the index finger and thumb, accompanied by shooting pain, swelling, blue discoloration and suppuration. This is an “occupational disease” of surgeons and gynecologists who violate safety regulations. - Indurative edema:
chancre in the genital area, causing severe swelling, bluish skin and swelling of the genitals. Occurs on the labia and foreskin. Not accompanied by pain or inflammation. - Amygdalitis:
unilateral, less often bilateral chancre, located on the tonsils. Enlarges and deforms the tonsil on which it is located, which can cause pain. The color of the tonsil tissue does not change, so the disease can be confused with a sore throat.
With the exception of these features, atypical forms of chancroid do not differ in any way from the usual varieties. The development of atypical syphilomas, the time of their appearance and disappearance are similar to the classical forms.
Diagnosis of tertiary syphilis
Tertiary syphilis of the pharynx must be differentiated from tuberculosis, scleroma and malignant neoplasms of the pharynx. Gummous ulcerations are painless and have sharply defined edges and a bluish-red color. They do not cause the disorders that occur with pharyngeal tuberculosis. The bottom of a syphilitic ulcer is shiny, smooth and shaped like a crater. For a final diagnosis, histological examination is necessary.
Preventive measures
Prevention of sexually transmitted syphilis is based on the following measures:
- Systematic screening for syphilis, especially if you are sexually active.
- Avoid casual sexual relationships with little-known partners.
- Mandatory use of barrier contraceptives, especially during oral sex.
Household syphilis can be prevented by observing the following preventive measures:
- Strict adherence to personal hygiene rules.
- Avoiding physical contact with an infected person.
- When living together with a sick person, there must be strictly individual dishes, personal hygiene items, clothing and bedding.
- Systematic disinfection of bathroom items.
Reference! Preventive therapy is prescribed to family members who have a sick person.
Prevention of congenital syphilis consists of:
- Preliminary examination for syphilis at the preparatory stage for pregnancy.
- Throughout pregnancy, undergo routine examinations for syphilis RPHA.
- If the results are positive, the woman undergoes mandatory treatment.
- Undergoing preventive treatment provided that the woman has previously had syphilis.
Within 2 days after sexual contact with a possibly infected person, you can get emergency prevention of syphilis from a venereologist.
Throat lesion
The pharynx is involved in the formation of the voice; it is part of the digestive tract and respiratory system.
Primary syphilis provokes the appearance of a formation, usually on one side.
The defeat leads to constant coughing and hoarseness.
Secondary syphilis leads to infection of the larynx.
Accompanied by a skin rash, it usually covers all areas of the skin.
Elements can be located on the palms and soles.
Tertiary syphilis entails gummous lesions.
Decay is the destruction of the bones of the spinal column and skull.
Bleeding may occur and breathing may be disrupted.
With such disorders, the patient is able to breathe through the mouth, and a change in voice occurs.
Note! When the first signs of syphilis appear, you should immediately visit a specialist and begin treatment.
An infection detected in a timely manner can be easily treated.
If the course of the disease has been started, complications develop.
One of these complications is the death of soft tissues.
The function of the vascular system is impaired, and constant bleeding may occur.
The third period of syphilis is always organ damage.
If treatment is not started in time, death is possible.
How to distinguish syphilis on the tongue from lichen planus
Ringworm appears accompanied by headaches and malaise.
The first symptom is the formation of small red spots.
There can be from one to three.
The spots are round or oval in shape.
Such elements grow rapidly and can increase in size up to 3 centimeters.
In the center the spot has a slightly yellowish tint.
Hairy areas of the body, as a rule, are not subject to changes.
Itching is quite common.
The condition lasts 4 weeks, sometimes it lasts up to 6 weeks.
Relapses of the disease are not observed.
The rash with syphilis is polymorphic, it has a recurrent course.
More about symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the current stage. So, at first, signs of infection appear only by the appearance of papules on the skin (or mucous membranes, in the case of a photo of syphilis in the throat), in place of which an ulcer later forms. By the end of the first stage, the ulcers disappear on their own and appear with renewed vigor in the second. With the beginning of the second stage, internal organs begin to suffer. At the third stage, total intoxication of the body occurs. The rash on the body becomes massively lumpy.