Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry aimed at correcting defects in the development of teeth and the maxillofacial skeleton. The result of orthodontic treatment largely depends on the correct diagnosis. Modern diagnostics in orthodontics
performed using special devices and equipment.
In this article we will consider popular methods of orthodontic diagnostics and answer frequently asked questions about orthodontics
.
Diagnostic methods in orthodontics
The treatment of defects of the masticatory-speech apparatus is carried out by a specialized orthodontist. After a visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity, the specialist decides on the need to conduct additional research procedures using modern diagnostic methods. Based on the analysis obtained, it is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and select the correct treatment to achieve a successful result.
Diagnostic methods in orthodontics:
1. Radiography.
2. Tomography of the temporomandibular joint.
3. Orthopantomography.
4. Examination using diagnostic models (taking impressions of the patient’s jaw with subsequent production of working models).
5. Electromyography.
6. Mask model (determining facial asymmetry taking into account three planes).
7. Simon's photostat.
8. Teleradiography.
The most popular diagnostic methods in orthodontics are dental radiography and orthopantogram, which allow identifying various deviations of the dentofacial apparatus. In difficult cases, additional research methods are used to clarify the identified pathologies.
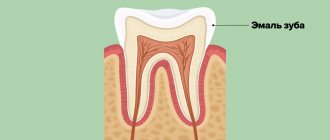
X-ray
The most common type of diagnosis. With its help, the dentist sees the condition of bone tissue and their structure. Using an x-ray, the doctor will accurately determine the extent of damage to the tooth tissue and prescribe effective treatment.
The following types of radiography are used in dental diagnostics:
- Dental. If the doctor needs to see how abnormally located the roots are in the jaw bone, changes in periodontal tissues, evaluate the condition of the root after a previous injury, or establish the stage of formation of the rudiments, dental radiography is used. In this case, the dentist must prescribe x-rays before and after treatment.
- Transillumination of the palatal suture. The close-focus shooting method is used. During the study, the dentist sees ossification and determines the degree of need for surgical manipulations for plastic surgery of the upper lip frenulum.
- CT scan. The procedure takes little time (2-3 minutes) and allows you to create a three-dimensional image. This type of diagnosis helps determine the state of the bone tissue structure and choose the most effective way to eliminate orthodontic pathology.
Important! CT scanning is not harmful to humans, but sometimes patients complain about the body’s reaction to the effects of the injected contrast fluid (slight dizziness, nausea, iron taste in the mouth).
- Orthopantomogram. Characterized by high rates of effectiveness in studying jaws. It is often used before prosthetics and implantation, as it allows you to determine the condition of the roots of the teeth, jaw joints and nasal sinuses.
Note: this type of diagnosis is inferior to computed tomography, since an orthopantomogram gives the dentist a two-dimensional image of the dentition, which does not allow a full assessment of the condition of the tissues in the oral cavity.
Questions about orthodontics
Many patients have different questions about orthodontics. Let's look at the most popular ones.
Is it possible to correct dental defects without braces?
The vestibular brace system is by far the most effective way to correct bite defects. But as an alternative, the patient may be offered aligners. A set of mouth guards is made from impressions taken from the patient’s jaw. While wearing them, you must maintain careful oral hygiene. The orthodontic structure is changed once a month. The patient needs to regularly visit an orthodontist to monitor the treatment process.
Cons of aligners:
- Not suitable for everyone;
- not used in complex cases;
- are more expensive than braces.
How quickly do teeth straighten with braces?
On average, teeth move into an even arch after 3-4 months. These periods can be shortened or increased, depending on the type of braces chosen and the complexity of the particular case.
What is the function of orthodontic screws?
Screws in orthodontics
are used to stabilize the brace system in the absence of some teeth in a row, as well as in case of bone tissue atrophy. They eliminate the movement of supporting teeth and speed up the process of dental correction.
How do teeth move?
In some cases, it becomes necessary to move one or more teeth. For this purpose, orthodontists use removable or non-removable structures. Fixed bracket systems include bracket systems that ensure the movement of teeth in the desired direction, under the supervision of a specialist.
Types of tooth movement in orthodontics
:
1. Corpus technique, which involves moving the tooth crown and root in one direction.
2. Oblique-rotational – involves moving the crown and tooth root to different distances.
In orthodontic treatment, it is possible to move not only one tooth, but also a whole series. This technique is successfully used in the treatment of occlusion with a distal position of the lower jaw.
When are orthodontic implants installed?
When treating complex defects of the dental system, there is often a need to install orthodontic implants aimed at providing the necessary support for fixed structures that correct bite defects.
Indications for installation of orthodontic implants:
- crowded dentition;
- strong protrusion of molars or front incisors;
- distal bite;
- severe curvature of teeth;
- if it is necessary to change the size or position of the jaw;
- to ensure the required degree of impact on the dentition (if braces do not cope with this task);
- lack of positive results after wearing braces for a long time.
Implants in orthodontics
differ from standard designs used to restore lost teeth. They are smaller in size and thickness, are installed temporarily, and the implantation method itself is minimally invasive and does not require cutting the gums or suturing.
What is diagnostics through the eyes of the doctors at our clinic?
More than one (!) hour of work in the clinic to create a presentation after the diagnosis, which will contain conclusions on a large number of evaluation criteria. Why is this happening?
You need to understand that all doctors have completely different approaches to analyzing diagnostic data.
Some people don’t do it at all and are ready to lay out a treatment plan immediately during the consultation without the slightest doubt. And this, in general, does not indicate high qualifications, rather the opposite.
For some doctors, one panoramic (overview) image and casts are enough. Which is also unacceptable for a modern orthodontist.
Orthodontic treatment of bite defects in
Experienced orthodontists who see patients at the specialized dental clinic “Aesthetics” are ready to answer all your questions about orthodontics. The center is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment that gives highly accurate results, which guarantees a quick correct diagnosis and the correct choice of treatment protocol.
Orthodontic treatment uses high-quality lingual braces, mouth guards, plates and other structures that can effectively eliminate various malocclusion defects, even in the most difficult cases. You can make an appointment with an orthodontist by phone. The first consultation appointment is free.
All patients who leave reviews on our website are guaranteed to receive an additional 3% discount on everything dental (the discount is added to the client’s main discount). Share your opinion and experience of orthodontic treatment in our clinic, do not miss the opportunity to save your own money on the services of an experienced orthodontist!
Orthodontist appointment
The orthodontist’s task is to identify the main problems of bite and abnormalities in the structure of the jaw within an hour. After this, the doctor finds out the patient’s expectations and wishes, suggests possible treatment, and determines the approximate time and cost. Also, the orthodontist can talk about the experience of correcting the bite in similar situations and show the final result. And, of course, our specialists are sure to answer all questions that patients have.
An important part of dental treatment is maintaining a personal medical record. The following data is entered into it:
- The problem the patient addressed and the desired result
- History of the formation of malocclusion. This includes the time when teeth began to change, their characteristics and recent changes in their condition.
- Results of the initial examination
- Presumable diagnosis
- Results of additional examinations, consultations and diagnostics.
At this stage, if the patient agrees to further treatment, an action plan is drawn up. Although after the first consultation we can draw a conclusion about which equipment and which treatment method is best suited, we in no case neglect diagnostics. The use of scans and x-rays increases the accuracy of the forecast for the final result. Consultations with an osteopath, ENT specialist, neurologist and other specialists allow you to get the most complete picture of what is happening with the bite, jaws and skull, sensibly assess all the possible pros and cons and choose a treatment plan.
Over the years of practice, we have been convinced more than once that no two cases are identical, so this approach helps to remember the uniqueness of the patient and create an individual project for occlusion correction.
Taking dental impressions
Nowadays, few people do calculations using models; they are created more formally. In general, all this can be done using computed tomography, provided the orthodontist has sufficient knowledge and skills. Using plaster models, the orthodontist calculates the size of the teeth, the amount of space required to move them, looks at the proportionality of the teeth, whether restoration will be required, and how they will fit together after treatment.
Why do we continue to make impressions at the Confidential Clinic?
At the Confidence clinic, we do not treat the patient so that he has straight teeth and everything is fine only according to calculations. We treat so that your smile is beautiful in real life.
The first and most important reason is the need for models for indirect fixation. The second reason is that they provide an opportunity to once again see some real object live, because CT and TRG are virtual things, and models make it possible to visually see the patient’s bite.
It happens that an orthodontist, during the treatment process, encounters some unexpected effect for him and is lost. At the Confidence clinic, we calculate everything “on the shore” in order to continue strictly according to the treatment plan, which we drew up even before fixing the braces.
Photo protocol, assessment of smile and facial harmony
Plays an important role in monitoring changes and quality of treatment. At the consultation stage, photographs are necessary to visualize the patient's problem. During the diagnosis, intraoral photographs are taken, photographs of teeth in a closed, open state, from different angles of the face and smile - including the so-called “Emma test”, which shows the patient how his teeth are usually visible during speech. The younger the person, the more the upper incisors are visible when speaking and the lower ones are not visible. With age, soft tissues sink, lose tone, and the upper teeth become less and less visible and the lower teeth become increasingly visible. If a patient comes for orthodontic treatment, we pay attention to this because we can change this and “rejuvenate” him in terms of perception during speech.
The patient takes up to 20 photographs of teeth and face from different angles
What is being assessed?
- Facial aesthetics
- Profile
- Bite and condition of teeth in their positions
- Incisor centerline relationship
- Width and arc of the smile (visibility and parallelism of the lip line)
- Condition of tooth enamel
The movement of the dentition can affect the position of the lips, so the orthodontist can reduce the worsening of wrinkles by increasing the height of the bite. A decrease in bite height leads to a greater likelihood of wrinkles and folds, which the doctor must take into account in the treatment plan.
More details about the photo protocol
Indications for wearing removable appliances
It is better, of course, to take your child to the orthodontist on a preventive basis once every six months, at least to understand whether he needs treatment or not. The classic indicator is a small jaw. Let's say a patient was at the dentist and was told that his jaw was small and his teeth would erupt crookedly. Or an incorrect bite - the upper jaw overlaps the lower jaw too much. Or the child has a bad habit - mouth breathing, which stems from problems with the ENT organs. The ENT doctor also refers you to an orthodontist with this problem.
Tasks
The list of tasks that are solved during the examination using diagnostic devices depends on the specific case. As a rule, the doctor prescribes functional diagnostics in order to identify:
- Presence of problems associated with chewing mechanics;
- The presence of hidden pathologies and underlying causes of the disease;
- Possible congenital and acquired deviations in the development of the jaws;
- Concomitant pathologies of other organs.
In addition, a set of studies is necessary to assess the complexity of treatment, stages and duration of treatment. Functional diagnostics and the latest technologies make it possible to identify problems, establish their root causes and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What does functional orthodontics include?
- joint treatment by an osteopath and a dentist;
- equalizing the pressure between the muscles of the tongue and the muscles of the cheeks and lips through special exercises - uneven muscle tension during the period of jaw growth can cause significant deformations of the jaws;
- wearing jaw growth activators;
- installation of removable pads;
- installation of non-removable expansion pads;
- jaw expansion using the Planas apparatus;
- expansion with ALF and Crozat devices;
- finishing linings to stabilize the bite and occlusal planes in the presence of tooth wear.