Carrying out any surgical interventions in the area of the facial part of the skull, including dental procedures, is extremely dangerous due to the close location of important anatomical structures. When performing seemingly simple tasks during surgery, damage to atypically located nerves, vessels, and ducts of the salivary glands is possible, which leads to significant complications. Numbness after sinus lift and bone grafting may appear at different stages of the operation and postoperative period; its causes can be very diverse and closely intertwined with each other.
A little about the anatomy and course of the branches of the trigeminal nerve
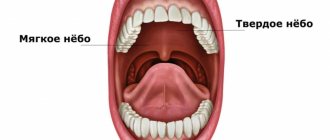
The teeth of the upper and lower jaw are innervated by the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which provide all types of sensitivity directly to the teeth, skin and mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks. The lower jaw - by the mandibular nerve, the upper - by the alveolar branches of the maxillary nerve, forming the dental plexus.
The alveolar branches of the maxillary nerve pass along the wall of the maxillary sinus to the apexes of the roots of the upper teeth, where they form a nerve plexus responsible for the sensitivity of the upper teeth and gums. The mandibular nerve passes through the bone canal of the same name, innervating the lower teeth and gums, lower lip, and part of the cheek.
What to do if your lips go numb?
The treatment regimen depends on the cause that provoked paresthesia.
Recovery requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- taking medications;
- quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages;
- physiotherapy.
It is important to balance the diet, introduce foods rich in vitamins and minerals, and maintain a drinking regime, drinking at least 1.5 liters of water per day. Traditional methods are allowed as an auxiliary treatment.
Treatment with drugs
For diseases leading to numbness of the face and lips, different groups of drugs are prescribed.
| Group of drugs | Name | Action |
| Diuretics. | Lasix, Spironolactone, Bumetanide. | They relieve swelling, help regulate blood pressure, and help remove salt from the body. |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets. | Nurofen, Ibuprofen. | Reduce the inflammatory process, reduce the intensity of headaches. |
| Glucocorticosteroids. | Dexamethasone, Prednisolone. | They improve the conduction of nerve impulses and have antiallergic and immunosuppressive effects. |
| Antispasmodics. | Trental, Diprofen, Spasmalgon. | Relaxes vascular walls, improves blood circulation. |
| Nootropic drugs. | Piracetam, Nootropil. | They enhance metabolic processes in nerve cells and restore cerebral circulation. |
| Vitamin preparations. | Cyanocobalamin, Pyridoxine hydrochloride, Thiamine bromide. | Stimulate metabolism, prevent a lack of B vitamins, and normalize the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. |
| Vasodilator tablets | Vazonite. | Reduces viscosity, improves blood circulation, and ensures oxygen supply to tissues. |
Folk remedies for loss of sensitivity
- Take 1 tbsp. l. medicinal clover. Pour 500 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 20 minutes. Pass through a filter, divide into 3 doses and drink before meals. To prepare an infusion according to the same recipe, you can use geranium leaves, stinging nettle, and St. John's wort. Repeat treatment for 7 days.
- Dissolve 1 tsp in 200 ml of warm water. baking soda and add 4 drops of iodine. Stir, soak gauze in the product, fold it 3 times and apply to your lips for 30 minutes. Apply the lotions daily in the evening until the symptoms go away.
- Measure out 1 tsp. oak bark and chamomile. Brew the raw material in 200 ml of boiling water. After 15 minutes, strain and use for lotions 2 times a day.
- Peel the garlic cloves, chop and fill a 250 ml jar. Fill with vodka, seal with a plastic lid and place in a closet for a week. Shake contents regularly. Filter and take 5 drops 3 times a day, dissolving the tincture in 50 ml of water.
- Peel the pumpkin, cut into pieces, cover with water and simmer until tender. Drain the liquid, cool the vegetable slightly and blend with a blender. Apply warm to numb lips in the evenings for 20 minutes.
Physiotherapy for paresthesia
Physiotherapy is recommended to improve the passage of nerve impulses and blood circulation. The procedures activate metabolic processes, eliminate swelling and inflammation.
In the rehabilitation therapy of stroke, neuritis of the facial nerve, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the following are used:
- UHF to reduce swelling;
- electrophoresis with nicotinic acid, which dilates blood vessels;
- acupuncture to stimulate nerve endings;
- magnetic therapy to restore blood circulation;
- ultraphonophoresis with Proserin and Hydrocortisone.
Paraffin therapy helps a lot. Heated paraffin transfers heat deep into the tissues, dilates blood vessels and normalizes blood circulation. During the procedure, lips are lubricated with Vaseline. Heat the paraffin in a water bath to 60 degrees. Apply the product to the lips with a brush, cover with a napkin and apply several more layers. Insulate with polyethylene, cloth and leave for 30 minutes. Carefully remove the cooled paraffin and moisturize your lips with cream. For the procedure to provide a noticeable result, you need to undergo at least 10 sessions, which are done every other day.
Characteristics of sinus lifting and bone grafting
Bone grafting in dentistry is designed to increase the volume of bone tissue to create suitable conditions for placing a dental implant. An increase in the volume of hard tissues can be carried out both through the use of one’s own bone material and with the use of synthetic substitutes. Bone grafting is performed on both the lower jaw and the upper jaw.
Sinus lifting is an operation performed exclusively on the upper jaw and, in essence, is a type of bone grafting. Its task is to raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus in order to increase the volume of bone mass. Additional bone material can be either your own or artificial. There are two ways to perform a sinus lift: open and closed. They differ in the complexity of execution and the ability to add different amounts of bone tissue.
Dental implant placement should not be confused with bone grafting or sinus lifting. These are two different operations, although they can be performed simultaneously. If there is initially a small amount of bone tissue, it may not be possible to place a dental implant immediately. Then, first, bone tissue is built up, and only a few months later, an artificial tooth is implanted.
Psychogenic causes of facial neurosis
Undoubtedly, disturbances in facial sensations quite often become a consequence of pathology of internal organs and blood vessels.
But often they are caused by psychological disorders and pathological thoughts that arise in our heads.
Facial paresthesias can be situational in nature and develop during episodic nervous excitement: as a result of quarrels, prolonged and intense screams. Such phenomena cause overstrain of the muscles, especially the cheeks and those located around the mouth. As a result, we experience facial numbness and even mild soreness.
The feeling of fear causes us to breathe quickly and shallowly, or to hold our breath. Disturbances in the respiratory rhythm can also provoke impressions that are atypical for us. A feeling arises that is characterized as a “chill running through.” Moreover, it is more concentrated at the roots of the hair. In this case they say: “chills to the marrow of the bones.” The face also becomes cold, a slight tingling appears in its area.
Such phenomena are disturbing when we are overwhelmed by strong emotions. But they accompany people suffering from mental disorders systematically.
A special type of neurotic facial manifestations is a nervous tic. It is characterized as an uncontrolled and systematic contraction of the facial muscles.
The disorder more often accompanies men. And it manifests itself with the following symptoms:
1.Motor:
- frequent blinking, winking;
- setting the lips with a tube;
- nodding head;
- constant spitting or sniffing;
- opening or upturning of the corner of the mouth;
- wrinkling of the nose.
2. Vocal:
- screaming;
- grunt;
- coughing;
- repetition of words.
There are also signs – precursors – that signal the appearance of a tic.
These include itching, facial heat and other paresthesias. Naturally, these signs are considered pathological if they occur in an inappropriate situation. It happens that only the patient himself feels them, but they are not visible to others.
But often twitching and other nervous symptoms become noticeable by other people, and they cause a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Tics can be simple, when there is only one symptom, or complex, which combines several manifestations.
The most common, main cause of tics is mental stress. It can be caused by a strong stress factor of one-stage action. Perhaps you were very scared of something, or broke up with your loved one. That is, the shock was so strong for you that your nervous system lost control.
Or, on the contrary, disorders develop as a result of prolonged monotonous exposure. Symptoms often appear due to lack of sleep and overwork.
Their duration varies. A situational nervous tic disappears a few hours or days after the cause is eliminated. In another case, it persists for years or haunts the patient throughout his life. In such a situation, in addition to eliminating the provoking factor, subsequent psychological work with the patient is required. This type of disorder is called chronic.
A nervous tic can be one of the signs of mental disorders such as neurosis, obsessive thoughts and phobias, depression.
Another group of provoking factors include:
- diseases - stroke, brain injury, infections or poisons;
- neurodegenerative diseases - Huntington's chorea. Characterized by destruction of brain tissue. Accompanied by uncoordinated, sudden movements, as well as neurological disorders of the face. Of these, the first sign is slow eye movements. Then a muscle spasm of the face occurs, which manifests itself in grotesque facial expressions - grimacing. Speech, chewing and swallowing are impaired;
- burdened heredity;
- parasitic infestations;
- eye fatigue due to prolonged eye strain;
- unbalanced diet, when the body receives little magnesium, calcium, glycine. These elements participate in the normal conduction of nerve impulses and are responsible for the coordinated functioning of the nervous system.
Causes of numbness after surgery
It should be immediately mentioned that numbness associated with anesthesia will not be considered, since it is a normal reaction to the administration of the drug. Anesthesia can be maintained to one degree or another from several hours to a day, after which sensitivity returns in full and sometimes painful sensations of varying severity are observed. Also, a slight decrease in sensitivity may persist due to existing edema, which is a variant of the normal condition.
Severe loss of sensation occurs when the branches of the trigeminal nerve are damaged or compressed.
Which doctor should I contact?
To undergo the examination, make an appointment with a therapist, who will issue a referral to a neurologist - a doctor who treats neurological disorders.
To establish a diagnosis, consultation may be required:
- cardiologist;
- endocrinologist;
- dentist;
- immunologist;
- toxicologist.
Problems in the lower jaw
Loss of sensitivity after bone grafting, like any other surgical interventions, is much more common in the lower jaw. This is due to the fact that during surgery, with an atypically high location of the mandibular canal or a small amount of bone tissue, nerve damage or compression may occur.
Nerve damage during surgery
Thanks to the widespread use of radiography and computed tomography, such a complication is now extremely rare. It may be associated with an atypical location of the mandibular canal, fragility of bone tissue, or medical error.
During the process of access, removal of tooth root debris, and formation of new bone tissue, the nerve may be damaged by the instrument or compressed by excessive amounts of new bone mass. In this case, after the end of anesthesia, numbness of the teeth anterior to the site of bone grafting, the lower lip, chin, and part of the cheek may persist.
Nerve compression due to implant displacement
If a dental implant changes its location due to injury, inflammation, or violation of medical instructions, compression of the mandibular nerve may occur. A similar situation can develop both in the first days and weeks after surgery, and after a long time.
With such a nerve trunk injury, extremely severe pain may initially be felt, and only then numbness may appear.
Nerve compression due to abnormal healing
After bone grafting, the slow process of new bone formation begins. Sometimes regenerative processes follow a pathological path, when newly formed tissues compress surrounding structures, blood vessels, and nerves.
This condition develops gradually, over 1-3 months after surgery. Numbness also does not appear immediately. Initially, it may be almost invisible or appear occasionally, passing after some time. Over time, numbness may increase or may remain at the same level.
Causes of glossalgia and stomalgia
The development of the condition is influenced by local and general factors. Local ones include:
- Damage to the mucous membrane due to low-quality dentures, abundant deposits of tartar, and sharp chips on the teeth.
- Burning of the tongue and palate with the development of galvanosis caused by the presence of dentures made of different metals in the dentition.
- Development of allergies to plastic prostheses.
- Trauma to the oral cavity during orthopedic procedures.
These factors do not always cause glossalgia, so they cannot be unambiguously called the causes of the disease, and in the treatment of burning tongue, their elimination is only part of a set of procedures.
Common factors include:
- Diseases of the nervous system of any nature.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Menopause.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system and vascular disorders.
- Advanced syphilis or neurosyphilis.
- Encephalitis.
The development of common diseases almost always leads to disruption of the nervous system, which, in turn, provokes the occurrence of glossalgia. The “trigger” can be severe stress, serious nervous overload, or physical fatigue.
Problems in the upper jaw
Numbness after sinus lifting and bone grafting in the area of the upper teeth and gums is less common than in the lower jaw. This is due to the fact that the innervation of these structures is carried out by three groups of branches of the maxillary nerve, intertwined with each other and forming the dental nerve plexus. Such a structure is quite difficult to damage or completely disable.
The loss of sensitivity in the area of the upper lip and upper half of the cheek cannot in any way be associated with dental interventions due to the fact that completely different branches of the maxillary nerve go to them.
Damage to the alveolar branches or dental plexus
This complication can only develop in conjunction with penetration into the maxillary sinus during surgery, which should not occur if the operation is performed correctly.
Local, mild numbness develops. One or two teeth may be involved with incomplete loss of sensitivity.
Improper placement of the implant or complications in the postoperative period
Dislocation of the skeleton of a prosthetic tooth can occur due to injury, inflammatory processes, or neglect of the dentist’s recommendations. Diagnosis of this condition is not particularly difficult due to the obvious pathological state of the implant.
There may be loss of sensitivity due to chronic odontogenic sinusitis. The condition develops over a long period of time, occurs with severe symptoms of sinusitis, and numbness develops in extremely severe and advanced cases.
Various localizations
More than 50% of patients suffer from head tremors. Often, it is from this localization that the disease begins, and later trembling of the limbs occurs. The head most often moves left and right, less often - down and up, in a circle or diagonally.
Quite often, patients suffer from facial muscles - trembling of the lower lip develops in adults when smiling or talking. Tremor can also manifest itself as isolated, rapid, small twitches of the facial muscles. This type of tremor can occur at an early stage of the disease.
In addition, patients may experience mild tremor of the tongue or eyelids.
Elderly and middle-aged patients who have had the disease for more than 10 years may experience a trembling voice. Sometimes this symptom also occurs in younger people (up to 20 years old) with a disease duration not exceeding 5 years.
Almost a quarter of patients experience trembling of the lower extremities.
Trembling of the entire body is observed in rare cases, most often after physical exertion or emotional outbursts. This symptom may indicate the spread of the disease.
In a small number of patients, diaphragmatic trembling is observed, which can be confirmed by x-ray. When a combination of tremor of the tongue, lips, diaphragm and vocal cords occurs, speech and breathing rhythm may be disrupted.
Regardless of location, trembling intensifies with excitement, significant physical exertion, and hypothermia. When drinking alcohol, there is a decrease in tremor, but it intensifies the next day.
There is a childhood and youthful form of tremor, as well as a form of mature and senile age.
The disease is often diagnosed in patients of childhood and adolescence.
Essential tremor is benign: it does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, but it is constantly progressing, so this disease cannot be ignored.
Doctors at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital provide assistance to patients with essential tremor, aimed at eliminating symptoms that significantly worsen the quality of life of patients. The clinic provides high-quality drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures that significantly improve the patient’s condition.
Diagnostics
If partial or complete numbness occurs after sinus lifting and bone grafting, you should undergo a number of diagnostic procedures:
- Examination of the oral cavity by a dentist. Allows you to assess the general situation and in some cases even make a diagnosis immediately. Must go through first. If there is displacement of the implant or nerve injury during surgery, then further examination methods can be of a purely clarifying nature.
- Assessment of neurological status based on damaged branches of the trigeminal nerve. This task is more likely for a neurologist, rather than for a dentist. By testing reflexes and using special methods to determine sensitivity, it is possible to assess the presence/absence of nerve damage.
- X-ray or computed tomography. These examination methods make it possible to establish in detail and accurately the cause of loss of sensitivity. With the use of modern technologies, it becomes possible to calculate down to the millimeter the direction and degree of displacement of the installed structure, existing pathological foci of regeneration, and determine the presence of an inflammatory process both at the site of bone grafting and directly in the maxillary sinus.
What to do - how to eliminate numbness?
At the first signs of loss of sensation in the lips or other parts of the body, it is better to seek advice from a specialist. He will conduct a thorough examination and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Most often, for various types of paresthesia, the following is prescribed:
- Agaricus (to eliminate muscle tension and pain relief);
- Cedron (to eliminate numbness);
- Kalmium (in order to normalize sensitivity and restore blood flow);
- Magnesium phosphoricum (for the sake of resumption of nervous activity);
- Mesereum (for general strengthening action);
- Spigelia (for sedation and pain relief);
- Verbascum (locally and internally);
- Viola odorata (as an antispasmodic, antipsychotic and tonic),
In addition to these medications, the doctor will also prescribe other medications. Depending on the provoking factor, these may be:
- antifungal medications;
- vitamin complexes;
- means for normalizing metabolic processes;
- medications to maintain proper blood sugar levels, etc.
In especially severe cases, the specialist will recommend surgical intervention.
A good addition to medication is physical therapy (for example, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, mud therapy or diadynamic currents).
Regardless of the prescribed treatment, a mandatory requirement to alleviate the condition of loss of sensitivity is compliance with the following regimen:
- eating healthy foods;
- walks in clean air;
- charger;
- control of blood pressure and sugar levels;
- moderate physical activity.
Treatment options
If the nerve trunk, plexus or branches of the nerve are damaged or compressed, there are two ways to solve the problem.
The first is to leave everything as is, without performing surgery. Such a solution to the problem is acceptable in case of incomplete loss of sensitivity or a small area of focus, with the exception of cases with displacement of the denture. Compression of the nerve due to regenerative processes will stop progressing after a certain point, “frozen” in one place. Odontogenic sinusitis can be treated with medication using antibiotics.
The second method is to perform surgery. The operation is indicated for injuries during sinus lifting and bone grafting, displacement of dentures or bone mass, extensive or complete loss of sensation. During the operation, the cause of the numbness is eliminated and, if necessary, the damaged nerve is sutured. Restoration of sensitivity takes a long time, sometimes never returning to its original state.
Symptoms
Most often, essential tremor manifests itself as medium-amplitude and small tremors of the hands, alternating contractions of the flexor and extensor muscles, while muscle tone remains the same. Trembling becomes noticeable during purposeful movements; when approaching the target, its persistence or even a slight increase is observed. Rest tremor is much less common.
As the disease progresses, patients become unable to work. They become unable to serve themselves: due to difficulties in holding cutlery, they cannot eat food or drink water from a mug. Patients are unable to perform many activities that are necessary in everyday life; they need help even with buttoning up buttons and other trivial matters.
Due to the layering of emotional disturbances on the manifestations of tremor, patients develop social maladjustment. Hand tremors with essential tremor occur earlier than, for example, trembling of the lip (in adults) and other parts of the body. For a long time, hand tremors remain the only manifestation of the disease. As a rule, simultaneous trembling of both hands is observed, in rare cases - first only one, then the other.
Physiological reasons
Tissue sensitivity may decrease upon contact with very hot or cold food or drinks. This happens when a person eats ice cream, drinks tea or coffee that is too hot, or eats too spicy food. A similar phenomenon is observed outside in cold weather. The skin of the lips becomes chapped, cracks appear, and sensitivity decreases. Physiological numbness in most cases does not cause harm to health. As soon as contact with the irritant ceases, tissue sensitivity is restored.
To avoid the negative consequences of low-temperature exposure, you should use lipsticks and balms that will protect the skin from chapping and painful cracks.
Another possible cause of tissue numbness is cosmetic and cosmetic procedures. For example, lip products with red pepper extract may cause a slight burning sensation or numbness of the tissues. Some women experience a decrease in lip sensitivity after tattooing if the procedure was performed incorrectly or the wrong lip care was chosen after it.