Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
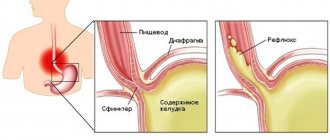
is a disease caused by repeated spontaneous reflux of stomach contents (and in some cases, duodenum) into the esophagus.
Our body is designed in such a way that movement must occur in only one direction: food from the esophagus must enter the stomach.
The reverse movement is prevented by a ring of muscle, the lower esophageal sphincter, which provides a barrier that prevents stomach contents from naturally flowing into the esophagus. The digestive process begins in the stomach. Gastric juice secreted to digest food contains aggressive hydrochloric acid. Once in the esophagus, where it is not intended to be located, the acid causes irritation of the mucous membrane, manifested as a burning sensation along the esophagus, which we call heartburn. Heartburn can occur even in a healthy person, but if reflux occurs quite often, irritation of the esophageal mucosa can cause inflammation.
Thus, isolated cases of heartburn are not a disease, but if irritation of the esophageal mucosa occurs often enough, GERD is diagnosed. In this case, endoscopic examination may not reveal mucosal erosion. This form of the disease is called endoscopically negative reflux disease.
.
It accounts for approximately 70% of cases. In 30% of cases, endoscopy reveals mucosal lesions. This form of the disease is called reflux esophagitis
.
Causes of GERD
Reflux (reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus) can occur for the following reasons:
decreased tone of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Sphincter weakness may result from:- consumption of caffeinated drinks, chocolate;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy;
taking certain medications;
- flatulence (which, in turn, can be a consequence of poor nutrition, gastrointestinal diseases, digestive disorders - dyspepsia);
pregnancy;
- hiatal hernia.
For the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease, not only the reflux itself is important, but also some other factors that contribute to the aggravation of the situation, for example:
- depressed state of the esophageal mucosa, in which it is unable to resist damage;
- impaired ability of the esophagus to cleanse itself. Normally, the esophagus should quickly be cleared of the stomach contents that have entered it - due to gravity and peristalsis, and the acidity of the environment should be eliminated by sodium bicarbonate, which is part of the saliva.
Factors that provoke reflux are:
- stress;
- eating too much food (overeating);
- eating foods that cause increased gas formation and other digestive disorders;
- physical activity after meals.
Diagnosis and which doctor to contact?
It is worth noting! If a person experiences the taste of fish in his mouth and those around him smell it, then this becomes a big psychological problem.
To avoid it and understand the causes of this condition, you should seek help from a doctor.
Initially, you can contact your dentist to rule out problems with the oral cavity.
If everything is fine with this, then plan your next visit to a therapist .
The doctor will conduct a general examination and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
Diagnostic procedures may include the following research techniques:
- Abdominal ultrasound to identify gastrointestinal diseases and sinus ultrasound to rule out problems in this area;
- taking scrapings from the mouth ;
- donating blood for analysis;
- checking sputum for the presence of fungal infection;
- X-ray of lung tissue, nasal septum;
- in extreme cases, a biopsy is performed;
- immunogram;
- CT and MRI.
After receiving all the test results, the general practitioner will be able to decide which specialist to refer the patient to.
Depending on in which organ the problem of fishy taste in the oral cavity lies, the attending physician is determined who can eliminate the disease.
Keep in mind! This could be an endocrinologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, otolaryngologist and other specialized specialists.
Symptoms of GERD
Acid from the stomach can enter the respiratory tract (this usually happens when lying down) and cause a sore throat, hoarseness, dry mouth, and cough. GERD can stimulate the development of bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis, and aspiration pneumonia.
The constant presence of acidic contents in the esophagus leads to scarring of the mucous membrane of the lower part of the esophagus, as a result of which the lumen of the esophagus narrows (this complication of GERD is called peptic stricture of the esophagus). In this case, pain when swallowing and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) may occur.
But first of all, GERD is characterized by symptoms that usually appear an hour and a half after eating. This:
Heartburn
Heartburn is the main symptom of GERD. The presence of heartburn that regularly occurs after eating is the basis for diagnosing the disease.
More about the symptom
Belching
With GERD, belching after eating is typical.
More about the symptom
Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
A sour taste in the mouth means that acid from the stomach has traveled up the esophagus and irritated the taste buds. The taste in the mouth may be bitter if bile enters the esophagus, which normally should not rise above the duodenum.
Chest pain
A burning sensation may be felt behind the sternum (along the esophagus). Often the complaint is formulated as chest pain, so it is important to make sure that the pain is caused by irritation of the esophageal mucosa, and not by heart problems. In the case of GERD, the pain is usually associated with food intake, begins in the epigastric region and only then rises higher. Pain can radiate to the neck, shoulders, interscapular area, and lower jaw.
Diagnosis of hepatosis and its signs
Hepatosis in pregnant women is a disease that is sometimes very difficult to diagnose. By this time, the uterus already occupies the entire abdominal cavity, which makes palpation of the liver impossible. This disease is often confused with gallstone disease, because their symptoms are very similar. The most common signs of hepatosis include:
- skin itching;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, the appearance of vascular networks on the face and hands, redness of the palms (they seem to be covered with red spots from the inside);
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, bitterness in the mouth, stool disorders, loss of appetite;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- lightening of stool and darkening of urine (from orange to dark brown);
When the bile duct is disrupted, a large amount of bile accumulates in the liver. Unable to escape, bile begins to break through into the lymphatic system, and from there into the general bloodstream. If you conduct a blood test, it will show an increase in the level of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin and cholesterol, a decrease in hemoglobin, as well as red blood cells and platelets. A urine test will reveal the presence of bile acids and increased secretion of urobilin.
When bile enters the bloodstream, it causes itching, which intensifies in the evening and at night. Most often, pregnant women with this disease consult a doctor with complaints of an acute and irresistible desire to scratch. It drives you crazy, disrupts sleep, leads to fatigue and irritation. As a rule, the arms, legs and stomach itch the most. Filling the liver with bile causes overstretching of its capsule, the surface of which has a large number of pain receptors. This causes constant dull pain in the right side.
If hepatosis is suspected, the doctor at the antenatal clinic should carefully examine the patient, try to palpate the liver area, prescribe extensive blood and urine tests, as well as an ultrasound examination of the liver, gall bladder and neighboring organs.
GERD Treatment Methods
Treatment of GERD is carried out by a gastroenterologist. Treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation of the esophageal mucosa, reducing the frequency of reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, reducing the damaging properties of refluxate (the substance that enters the esophagus from the stomach), and increasing the protective properties of the esophageal mucosa.
Of great importance is:
Drug treatment
Treatment with medications is prescribed by a doctor and must take into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Lifestyle change
Normalization of lifestyle is of great importance. It is necessary to quit smoking, limit, or better yet eliminate, alcohol consumption. You should not eat fatty, spicy, sour foods, as well as coffee, tea, chocolate, legumes, cabbage, peas, and brown bread. It is better to take food more often (4-6 times a day), but in small portions. You should not eat before bed (the last meal should be 2-2.5 hours before bedtime). You should sleep with your upper body elevated to reduce the likelihood of reflux during sleep.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Many patients feel relief after rinsing their mouth with water and a small amount of lemon juice or a weak solution of soda. It is important to maintain oral hygiene: brush your teeth thoroughly 2 times a day, rinse your mouth with water after each meal, and use dental floss if necessary. In order not to suffer from bitterness in the morning, you should refrain from fatty foods and smoked foods at dinner.
Pregnant women are advised to eat often, in small portions, so as not to overload the gastrointestinal tract. After eating, you should not take a horizontal position or engage in physical labor. If an unpleasant taste in the mouth is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders, pain or a progressive deterioration of the general condition, it is important to consult a doctor in time to determine why the taste occurs in the mouth.
Conservative therapy
A specific taste occurs in many diseases, so only the main directions of therapy can be identified, and the selection of an individual set of therapeutic measures is carried out by a specialist. When caries is detected, treatment by a dentist is indicated: usually, after the elimination of chronic foci of infection, the unpleasant taste disappears. Most often used in therapeutic regimens:
- Antiseptics
. Regular rinsing of the oral cavity with a solution of chlorhexidine and its analogues ensures moisturizing and cleansing of the mucous membrane, and prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. For stomatitis with pain, solutions of local anesthetics are used. - Antacids
. If the symptom is due to hyperacid conditions, modern non-absorbable drugs that quickly reduce acidity are recommended. A course of treatment with antisecretory agents is often required to achieve a lasting effect and healing of mucosal defects. - Choleretic drugs
. In case of biliary pathology, the composition of bile is improved and its release into the duodenum is stimulated, due to which the bitterness disappears. The drugs can be combined with hepatoprotectors to protect the liver from the effects of bile acids. - Antidotes
. Heavy metal poisoning is an indication for the prescription of specific complexones that bind and remove toxic substances from the blood. To speed up detoxification, large volumes of crystalloid solutions are administered intravenously.
Prevention of hepatosis in pregnant women
Although hepatosis is considered the result of certain genetic characteristics, there are a number of recommendations to avoid it or delay its appearance for a longer period:
- Dieting. If you have a tendency to overload the liver, then you must completely avoid everything fried, fatty, smoked, salty, spicy and sour. The diet should consist of fruits, vegetables (except potatoes, legumes, onions and garlic), low-fat dairy products, chicken breast meat, and low-fat fish. You should not eat chocolate and other cocoa-containing products, egg yolks, cheese, pastries (1-2 pieces of black bread per day are allowed).
- Physical activity. Movement is life, so you need to move more. This speeds up metabolic processes in the body, eliminates congestion, and facilitates the functioning of the liver.
- Refusal of oral hormonal contraceptives and antibacterial agents. They can cause great harm to the liver.
- Take vitamins carefully or avoid them. If possible, you should try to get all the substances the body needs from food, and not from vitamin complexes.
- Treatment of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- The use of hepatoprotectors and choleretic drugs. If pregnancy is not planned yet, then it is enough to carry out preventive courses with these drugs, and if pregnancy has already occurred, then they must be taken according to a special schedule agreed with the attending physician.
Hepatosis in pregnant women is a very insidious disease. If you suspect you have signs of it, be sure to tell your doctor so that he can order a blood test and make or rule out a diagnosis.