Content
- When to remove a nerve
- What to do before visiting the doctor
- How to remove a dental nerve
- How long does it take to remove a nerve?
- Is it painful to remove a nerve?
- Recommendations for care after removal
- Prevention of dental diseases
Each tooth has a pulp in which blood, lymphatic vessels and nerve endings are intertwined. This system is designed to protect the tooth, provide it with nutrition, blood and minerals. After removing the nerve (pulp), the nutrition of the tooth stops, as a result of which it loses some of its properties and will deteriorate faster. If caries is in its initial stage and does not affect the pulp, dental treatment does not involve its removal.
Removal of the tooth nerve: methods, indications and contraindications
Inside the tooth there is a neurovascular bundle (pulp). It is located under the hard tissues of the tooth: enamel and dentin. When the infection completely affects hard tissues, inflammation occurs, which spreads to the nerve. Then discomfort or acute toothache occurs: depulpation (nerve removal) is required.
Nerve removal is indicated when there is:
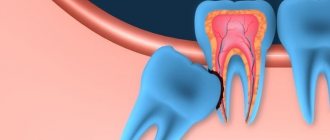
- deep carious cavity: caries initially affects the hard tissues of the tooth: enamel, dentin. Then, spreading deeper and deeper, caries reaches the neurovascular bundle. The inflammatory process begins. Because of this, acute pain appears: throbbing, paroxysmal. Pain can occur on its own or due to various irritants. To eliminate the pain, the nerve must be removed.
- trauma: strong mechanical impact leads to fractures, chips, bruises. All this affects the pulp, and infection in the pulp chamber also causes inflammation, which leads to acute pain. In this case, removal of the nerve is required.
- an infectious process near the root of a tooth: it occurs due to infection through the blood and lymph nodes. The infection reaches the pulp and the nerve must be removed.
- planned prosthetics: if the walls of the tooth are not enough, then doctors resort to depulpation to prevent the occurrence of an infectious process. Sometimes it is not necessary to remove the nerve before prosthetics: all this is individual, depending on the initial clinical situation after a series of diagnostic procedures.
- retreatment: if the tooth was initially treated incorrectly (for example, caries was left under the filling), then the infection reaches the nerve, the tooth begins to hurt, and retreatment is required: removal of the nerve, filling of the canals.
- chronic pulpitis: inflammation of the nerve can sometimes be asymptomatic or have minor manifestations (rare pain, sensitivity). In this case, it is also necessary to remove the pulp to prevent complications.
Activities before visiting the doctor
If the tooth hurts and it is obvious that nerve removal cannot be avoided, you should immediately make an appointment with the dentist. To relieve pain in the period before your visit to the office, you can perform a number of manipulations. Pain can be reduced or relieved by:
- Carefully remove food debris from the cavity in the tooth.
- Rinse with warm soda solution.
- Avoid chewing food on the affected side.
- Minimize exposure to high and low temperatures (including cold air).
- Mouth slightly open. If the bite is incorrect, closing the jaws may increase the pain.
- Painkillers.
PROMOTION
Inexpensive dentistry
Prices are 1.5-2 times lower
General recommendations after treatment
- You can eat and drink immediately after treatment;
- Until the anesthesia wears off, you should not eat rough food;
- in the days following treatment on the side of the diseased tooth, do not chew rough, hard food;
- in some cases, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and oral baths are prescribed;
- If a temporary filling falls out, consult a doctor immediately;
- If pain occurs after placing a temporary filling, also consult a doctor immediately.
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel discomfort in the area of the treated tooth. If pain, throbbing, or swelling occurs, you should consult a dentist.
How to remove a dental nerve
The times when nerves were removed using arsenic are in the past. Today, the dentist has powerful anesthesia, a modern drill and a comfortable chair in his arsenal.
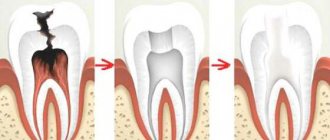
- Before starting manipulation of the diseased tooth, local anesthesia is administered (a combination with a topical anesthetic is also used to preliminarily numb the injection site).
- Afterwards, the doctor provides access to the pulp, removing the affected tissue.
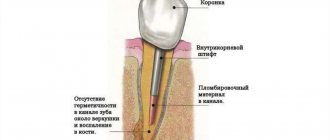
- The nerve is removed and the canal is sealed.
- A temporary or permanent filling is installed depending on the situation.
- To control the quality of the canal filling, an x-ray is taken.
Functions of the tooth nerve, consequences of removal
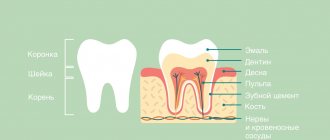
Any healthy tooth consists of the following elements:
- Enamel.
This is the shell of the tooth that protects it from external irritants, acid-base and mechanical influence.
- Dentine.
This is the “body” of the entire tooth, in which nutrients and microelements are concentrated.
- Pulp.
The “heart” of a healthy tooth, which contains all the nerve endings and blood vessels.
The pulp performs a number of important functions:
- Nutrition of dentin and enamel.
The nerve ensures correct circulation of microelements.
- Immune protection.
In case of infection, the pulp strongly protects the tooth itself and also blocks its further spread.
- “Delivery” of minerals from blood plasma to dentin.
The most important minerals for teeth are calcium and fluoride.
- Blood supply to dental tissues
from root to crown.
- Functioning of receptors.
Thanks to the nerve fibers in the pulp, the patient experiences pain when a tooth is damaged or diseased, which makes it possible to realize the need for treatment.
Is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth?
Modern dentistry has the widest possibilities and powerful universal anesthesia. Thanks to this, removal of the flock nerve is a painless procedure that is carried out during the visit. The only discomfort that the patient may feel concerns the injection into the gum. This can also be easily avoided by applying anesthesia, after which inserting a needle will not cause any discomfort.
Pain may occur in rare cases for one of the following reasons:
- Individual characteristics of the path of nerves, which is why standard techniques provide insufficient pain relief.
- Taking painkillers the day before by the patient, in particular from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia.
- The patient took alcohol before visiting the doctor.
- The patient belongs to the 2% of all people with immunity to anesthetics.
The solution to the problem in each case is the same - repeated anesthesia.
Why does a tooth from which the nerve has been removed hurt?
Patients often complain that the tooth from which the nerve was removed continues to hurt. This is a completely natural pain, the result of intervention in the body. In a couple of days the pain will go away. It can be observed when clenching teeth, when reacting to hot and cold. To reduce discomfort, take analgesic medications.
But if, due to improper treatment, the nerve was not completely removed, the pain and inflammation will return. It is possible that the canals were poorly treated, and there may also be an allergy to the filling material. It is necessary to go to the doctor immediately, since advanced inflammation can lead to tooth loss.
The tooth from which the nerve has been removed becomes dead, but it still remains and is not lost, so if you have a toothache, immediately go to the dentist. There is nothing to be afraid of - modern treatment is painless, and after it your diseased tooth will serve you for many years to come.
Conservative treatment
The conservative method of treating inflammation is otherwise called biological and involves the preservation of nerve endings. Unfortunately, this option is only suitable for restoring a tooth at an early stage of pathology; in case of extensive tissue damage, more drastic methods will have to be used.
Conservative treatment is indicated for acute pulpitis, in cases where the chamber was opened due to negligence, as well as for the chronic course of a fibrotic disease.
This method also has a number of contraindications. The main ones are considered to be old age and the presence of serious inflammatory processes of the periodontium.
Also, this method of treatment will have to be abandoned if caries is detected in the neck or roots of the tooth, if prosthetics are needed in the future, if you are allergic to the materials used, as well as if existing diseases worsen at the time of treatment.
Surgery
The surgical method of treating pulpitis involves removing the nerve and comes in several types: vital and non-vital. In the first case, the indications are the following: the presence of focal inflammation, acute diffuse pulpitis and pulpitis in the chronic stage (fibrous or hypertrophic).
Pulp removal is performed by an experienced specialist and only under local anesthesia. First of all, the pulp chamber is opened and treated with powerful antiseptic drugs. To extract the top of the chamber, a special tool called a pulp extractor is used, only after this can you begin to remove the root section.
The method, which involves preliminary destruction of the pulp, is based on the use of a special composition - depulpin. This option is considered optimal for patients who are panicky about anesthesia injections and pain. It is also suitable for people who have allergic reactions to the painkillers used.
Why does deep caries develop?
The process of tooth decay under the influence of microorganisms and other factors is caries. Its onset and development is caused by the activity of pathogenic microflora of the oral cavity, in particular the bacteria Streptococcus mutans. They feed on sugars from food, cause fermentation and produce acid. It corrodes tooth tissue, which leads first to demineralization of the enamel, then to deformation of its structure and the formation of carious cavities. Gradually, the process spreads deeper and affects dentin - the bone tissue under the tooth enamel.
Caries most often does not develop at lightning speed and goes through several stages. First, a barely noticeable chalky spot forms on the enamel - an area that is different in color from the rest of the tooth. This is the area of demineralization where the carious process began. Enamel loses the mineral compounds that make up its structure, becomes more fragile and less resistant to harmful influences. This is the initial stage of caries - the spot stage. People often miss it due to the lack of obvious symptoms. Then tooth decay continues, and the disease progresses to the stage of superficial caries. The tooth begins to react to hot/cold, sour/sweet, and a clear defect is noticeable in the enamel.
Without treatment, superficial caries progresses to intermediate caries when dentin begins to deteriorate. Symptoms become more pronounced, pain occurs not only as a reaction to an irritant, but also on its own. According to statistics, most patients seek help from a dentist at the stage of average caries.
But there are also people whom even acute toothache will not force them to go to the dentist. And then the most complex and advanced form can develop - deep caries. At this stage, the carious cavity is in close proximity to the dental pulp; at any moment, inflammation can spread to the dental nerve and lead to pulpitis, and then to periodontitis.
Painfulness of the procedure
Since pulpitis is an inflammatory process of nerve endings, any manipulation of the affected tooth can cause severe discomfort to the patient. Fortunately, modern dentistry offers a huge selection of anesthetics, so pain is reduced to a minimum. Conservative and devital methods of treatment are considered to be the most unpleasant.
Some dental patients experience pain after surgery. In this case, the dentist can prescribe appropriate medications. If the pain does not go away a week after treatment, but, on the contrary, becomes stronger, this may indicate a medical error. In this case, it is recommended to seek advice from your doctor as soon as possible.
To avoid the need for pulpitis treatment and nerve removal, it is very important to follow the rules of daily oral hygiene. For prevention, you can use professional toothpastes with a high content of beneficial additives, such as fluoride. Strong enamel is able to resist the effects of dangerous bacteria, so it becomes less vulnerable.
previous post
How painful is it to get an injection?
next entry
Change in tooth color (darkening of the tooth) - when a nerve is removed
When the nerve is removed from the tooth, after a while (from six months to several years) due to the fact that the nervous, circulatory and lymphatic supply to the tooth has ceased, the color of the tooth changes - discoloration and darkening are noted in the future. If chewing teeth have been depulped, the color change is not noticeable in most patients, unlike the front teeth. Anterior teeth after root canal treatment often require color correction to achieve smile aesthetics. This is achieved through endodontic whitening, veneers, or crowning such teeth. In most cases, when the crown of a tooth is filled or a permanent crown-shaped prosthesis is installed after root canal treatment, this discoloration is not noticeable. In cases where a tooth crown is not required, and the tooth itself is located in the frontal area of the smile, whitening or veneering helps eliminate discoloration of the teeth.
Treatment and prevention
The doctor determines the method of treating a pulpless tooth based on the results of x-ray diagnostics. The standard procedure includes:
- opening the tooth and unfilling the canals,
- complete depulpation in case of detection of pulp residues,
- thorough disinfection, treatment, grinding and filling of channels,
- restoration work to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth.
To prevent complications, follow simple rules after treatment:
- Avoid eating and drinking for 2 hours after the procedure to reduce the risk of infection,
- take anti-inflammatory drugs in the recommended dosage as prescribed by your doctor,
- Perform regular oral hygiene,
- Have it professionally cleaned every 6 months.