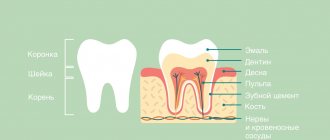
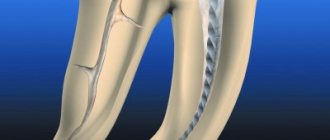
The dental nerve is one of the components of the soft tissues of the tooth, its central part (pulp). The pulp is located under the enamel and dentin layer and makes up the dental cavity. The pulp consists of three main elements - artery, vein and nerve. They penetrate into the dental cavity through the apical canals, which open at the tips of the roots. The number of canals is equal to the number of roots in the tooth. If a tooth has one root, then the number of canals is correspondingly equal to one, if there are two roots, then two, etc.
Functions of nerves in teeth
The main function of the nerve is sensory. When bacterial damage (caries) spreads to the deep tissues of the tooth, a painful reaction occurs. Pain is the body’s signal that something is wrong and help is needed. The nerve is not located in the tooth cavity in isolation. It is part of the neurovascular bundle, a component of the dental pulp. The functions of the pulp are varied:
- tooth nutrition;
- growth and development;
- mineralization of enamel and dentin;
- immune protection.
The tooth pulp is treated and tried to be preserved in all cases where possible. It is especially important to do this in children and adolescents, since their teeth have not yet fully formed.
Signs of tooth pulpitis
It is divided into acute and chronic phases.
The acute stage of pulpitis is characterized by:
- throbbing, sharp pain;
- External irritants can cause pain: temperature changes, cold or hot food, poor quality dental procedures, touching a sore tooth;
The chronic stage is characterized by:
moderate pain that occurs only with temperature changes, cold, or biting on a sore tooth. Increased tooth sensitivity occurs. Often a fistula also forms, with purulent contents that will periodically come out of the formed hole in the gum.
Other symptoms of the disease: headache, sleep disturbances, fever, loss of appetite.
It happens that the cause of tooth pain can be inflammation of the trigeminal nerve or facial nerve.
In what cases is it necessary to remove the dental nerve?
The dental nerve should always be removed when pulpitis develops - inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Pulpitis occurs when bacteria enter the tooth cavity during deep caries, with blood flow from distant foci of infection or through intraosseous sinuses (for example, in chronic sinusitis). In this case, the pulp becomes inflamed, due to the small space of the dental cavity, the outflow of blood is hampered, compression of the nerve occurs, and, as a result, severe pain.
Pulpitis can be recognized by the following signs:
- pain occurs spontaneously, and not just under the influence of temperature or sweet, sour foods;
- the pain is throbbing, paroxysmal in nature - it weakens, then intensifies again;
- at night the pain is felt more acutely - this is due to vasodilation at night;
- often a person cannot tell which tooth hurts, since the entire nerve of the dentition is involved in the inflammatory process; If pulpitis is not treated for a long time, the pain subsides - this indicates the death of the nerve.
Is it possible to remove a nerve painlessly?
Modern dentistry involves painless removal of the nerve in one visit. In this case, conduction anesthesia is most often used, when the entire branch of the nerve that provides sensitivity to the corresponding half of the jaw is blocked. With a large volume of intervention, a temporary filling is required for several days. This way, the dentist will be able to understand how the tooth reacts to the filling material, and whether it was possible to achieve complete cleaning of the inflamed pulp. At the follow-up appointment, a permanent filling is installed. Arsenic is rarely used today due to its high toxicity and the inability to completely kill living nerve tissue in a certain percentage of cases.
What is pulp?
The pulp, or dental nerve, is a bundle of nerve endings and capillaries in the internal cavity of the tooth. It is protected from external irritants and infection by the tissue that is located in the root and crown.
After removal of the nerve, the blood supply and mineralization of the tooth deteriorate significantly. In addition, its sensitivity decreases, the enamel becomes dull and weakens. In other words, pulp removal negatively affects the structure and strength of the tooth, but makes it possible to preserve it.
Indications for the procedure:
- exposure of the nerve as a result of tooth trauma and damage to the crown;
- consequences of improper dental treatment;
- the presence of caries-affected tissues;
- preparation for prosthetics;
- chronic inflammation of the pulp (pulpitis);
- inflammation of the root membrane of the tooth (periodontitis);
- low placement of crowns;
- extensive pulp area;
- bactericidal infection of the apex of the tooth root.
How long can a tooth survive without a nerve?
A tooth without a nerve can darken and decay faster, since metabolic processes in it are not maintained at the same level. However, with proper treatment and subsequent care, such a tooth can live indefinitely. The dentist fills the canals (often under a microscope) and isolates the tooth tissue as much as possible from the influences of the external environment. This is called a sealed restoration. With modern crowns or inlays, the tooth lasts a lifetime.
Nerve removal at Russian-American Dental provides services for painless removal of the dental nerve, followed by canal filling and sealed tooth restoration. The tooth acquires an aesthetic appearance and a lifelong service life. You can make an appointment by calling Moscow +7 (499) 269-13-92 or. The clinic is located at st. Rusakovskaya, 28 (Sokolniki metro station).
Why is it not necessary to remove the nerve to install crowns?
The need to remove the nerve arises primarily when the tooth is completely destroyed. It can also be dictated by the qualifications of the doctor: when heating or deeply removing the top layer, there is a risk of damage to the nerve endings, and this is very painful. That is why many dentists prefer a safer route, that is, preliminary removal of the nerve. Especially in the presence of the initial stage of caries.
In addition, depulpation can be performed in a number of cases before prosthetics: with increased sensitivity, with small sizes and in the presence of more than 15-degree inclination of the teeth. The pulp may also be removed for aesthetic reasons.
It is not necessary to perform depulpation before installing crowns, since the nerve can always be removed through the top of the crown.
After depulpation, the hole is filled. The main disadvantage of this procedure is the exposed tooth root, which can cause complications in the future.
Causes of pain
Inflammatory diseases in the pulp chamber do not appear without reason. The pathological process develops as a result of certain factors:
- Caries or inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues of the mouth.
- Mechanical damage to the tooth or jaw bones, which exposes the nerve.
- Poorly performed dental treatment.
- Internal problems in the body of an infectious nature.
Signs of nerve inflammation always present with the same clinical picture, regardless of the cause of the problem. At the initial stages of the disease, a person notices an acute reaction of the teeth to temperature, chemical and taste stimuli.
As pulpitis progresses, other symptoms arise:
- bad breath associated with decay of tooth tissue;
- spasms of a pulsating nature, which are difficult to eliminate even with the help of powerful painkillers.
If not treated in a timely manner, pulpitis can develop into gumboil. In this case, there can be no question of saving the dental nerve. The main goal of flux treatment is to prevent further spread of infection in the body.
Why else can a nerve become inflamed? Factors that increase the risk of pulp damage include:
- poor quality or untimely oral care;
- unbalanced diet and predominance of soft foods in the diet;
- lack of preventive visits to the dentist.
What does tooth color change mean after pulp removal?
Nowadays, almost all private dental clinics adhere to international depulpation protocols, but outdated practices are still in use in budgetary medical institutions. The main reasons for tooth discoloration are improper preparation of the cavity for installation of a filling, poor quality of instrumentation of the canal and poor materials for filling. For example, when using endomethasone, the enamel turns yellow (a similar outcome is even prescribed in the instructions). If resorcinol-formalin paste was used for filling, the teeth may turn pink. Most often, this material is used in the treatment of baby teeth.
The nerves from wisdom teeth, which dentists call “problem eights,” are extremely rarely removed. Given their location and short service life, as well as the difficulty of cleaning from stone and plaque, they are easier to remove. As a rule, the figure eight is removed in case of incorrect eruption (if there is a slope towards the tongue or towards the cheek), tooth retention, carious lesions, pulpitis, changes in bite, displacement of the dentition.
After depulpation, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid physical activity for the first 2 hours after the procedure.
- To avoid infection and injury to the tooth, do not eat food for 3 hours after pulp removal (you can drink warm water through a straw).
- For 5 days, exclude rough, solid foods from the diet.
- To avoid irritation of the oral mucosa, it is advisable not to smoke, drink alcoholic beverages, or eat spicy, cold or hot foods for at least 5 days.
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptics prescribed by your dentist for at least 1 day.
It is impossible to remove the dental nerve using folk remedies. Even if it can be destroyed, the pulp will need to be removed, and this can only be done with a special medical instrument.
When planning a visit to the dentist, remember that the longer you delay, the more difficult and expensive depulp removal will be. And do not forget that such intervention is recommended only if there are good reasons for it. Any dentist will try his best to keep the tooth “alive” if possible.
Possible complications after depulpation
After the procedure, you may experience:
- Canal bleeding. The main reason for this phenomenon is the separation of the pulp by the pulp extractor. To avoid this problem, dentists practice gradual cutting of soft tissue using files and copious rinsing with an antiseptic. Only a doctor can stop canal bleeding.
- Short-term pain. Their duration may vary, but if they do not go away for a long time, it is necessary to re-open the canals and disinfect them.
- The appearance of a cyst, granuloma, gumboil or fistula.
- Facial paralysis. May occur due to improper application of material. If it protrudes beyond the upper part of the root, it will not only affect the tooth, but also compress the nerve of the jaw. That is why if you have pain in the chin area, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If disinfection is of poor quality during pulp removal, there is a risk of suppuration and the development of periodontal abscess. In this case, tooth extraction cannot be avoided.
Question about pain when removing a nerve.
Usually, when it is necessary to remove a nerve, patients succumb to the fear that this is a very painful procedure. But there is no point in worrying! Each qualified specialist in his arsenal has a large number of anesthetics that desensitize the diseased tooth and surrounding tissues. Just one injection, and the person does not feel anything in the area of the diseased tooth.
Local anesthesia is most often used. If the drug is chosen correctly, the entire operation from injection to nerve extraction will be completely painless.
Practical recommendations after visiting the dentist
If depulpation is performed correctly, pain may be observed. The pain may persist for several days. In this case, you can use painkillers prescribed by your dentist. However, if the pain does not stop for a week or more, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In this article, we learned why there are nerve endings in teeth, what important function they perform, and how to act in case of severe pain. In addition, you can learn more about why nerves are needed in teeth on specialized medical web resources, where dentists describe and explain everything in detail.
Alpha Dent specialists provide high-quality dental services. The clinic uses advanced equipment and innovative drugs, which ensures impeccable quality of therapy. Dentists will be happy to tell you how the nerves are located in a person’s teeth and what treatment is needed to achieve the desired result.
Pain Management Options
The duration of action of a standard anesthetic injection is 45 minutes. Patients who are afraid of injections are offered treatment of the depulpation site with a special paste-like composition of a similar effect. Tablet analgesics may reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia, so dentists do not recommend their use.
The dentist chooses the painkiller, as well as the dosage. Since everyone's pain threshold is different, the dose of anesthetic is often doubled or tripled. If the doctor has administered anesthesia according to the protocol, the patient will not feel any pain or discomfort.