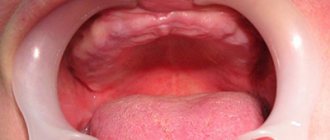
In dentistry, complete or partial absence of teeth is called adentia. This pathology can be congenital (anomaly of the development of the dental system) or acquired. The disease is characterized by a violation of the continuity of the dentition. A person cannot chew, speak normally and experiences discomfort from a cosmetic defect in his smile. His diction and articulation are deteriorating, and his gastrointestinal tract is functioning worse.
Both complete and partial adentia are dangerous because, due to tooth loss, deformation of the facial skeleton and diseases of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) are possible.
Types of pathology
In dentistry, adentia is considered as a primary or secondary defect of the dentition.
- Complete congenital adentia is extremely rare, occurring in approximately 1% of cases.
- Partial secondary adentia is diagnosed in 45–75% of cases.
- Also, complete adentia occurs in 25% of people over 60 years of age.
Depending on the causes and time of occurrence of the pathology, dentists, as mentioned above, distinguish between congenital and secondary tooth loss, as well as edentia of temporary and permanent rows. True adentia is the absence of a tooth germ, and when adjacent crowns merge and there is a delay in their eruption, dentists speak of false adentia.
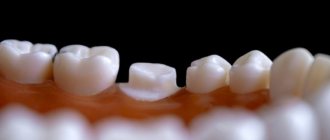
Taking into account the number of missing teeth, partial and complete edentia are distinguished. The first involves a deficiency of up to 10 units of dentition, usually the upper lateral incisors, second premolars and third molars. If more than 10 teeth are missing, doctors diagnose multiple adentia.
Ask a Question
Using a facebow and articulator for correct bite
The only possibility in case of complete edentia is to determine the relationship of the jaws. We use SAM3, Protar or Amann Girrbach systems
- Manufacturing a precise prosthesis taking into account the individual characteristics of the jaw system
- Prevention of temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Causes
The main and only cause of adentia is the absence or death of tooth buds. Primary pathology can be caused by heredity or provoked by various harmful factors acting during the formation of the fetal dental plate.
Complete congenital edentia is an extremely rare phenomenon. Formed due to ectodermal dysplasia. In this case, along with the absence of teeth, patients experience underdevelopment of hair, skin, nails, as well as sebaceous and sweat glands, eye lenses, and nerves.
Other common causes of pathology include the following:
- disturbance of mineral metabolism during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus against the background of diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- illnesses in early childhood;
- heredity;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- disruptions in the development of ectoderm - the outer germ layer of the embryo;
- treatment of concomitant diseases, including malignant neoplasms;
- chemotherapy, treatment with ionizing radiation;
- osteomyelitis and other purulent inflammations of the jaws.
The causes of secondary tooth loss in the process of life can be untreated caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, dental trauma, phlegmon, abscesses, illiterate provision of dental or orthopedic care, as well as other pathologies of the teeth and gums.
Why do you need to restore your teeth?
Edentia is not only discomfort, but also early aging. The absence of teeth leads to changes in facial features, sunken cheeks, and the appearance of deep wrinkles. The person looks older, his appearance becomes sickly. In addition to visible imbalances in proportions and a deterioration in the quality of life, when there are no teeth at all, health problems
:
- The diet is reduced, the body does not receive the required amount of vitamins and minerals. The immune system suffers, metabolic processes are disrupted, and cells do not receive enough nutrients.
- Gastrointestinal diseases are provoked. Food is chopped poorly, making digestion difficult. Sometimes patients switch to eating pureed food or pureed food - this method also contributes to the appearance of dysfunction of the stomach and intestines.
- The absence of teeth in the jaws leads to improper distribution of the load on the gums and bone. Tissues atrophy and become thinner.
The bite also changes, diction is impaired - speech is slurred, most sounds are distorted. The absence of teeth affects the emotional state, lowers self-esteem, and the circle of friends narrows. Researchers have also established a direct connection with the presence of teeth and the state of intelligence and activity of older people.
Complications
Adentia leads to a variety of physical and aesthetic complications:
- in the area where a tooth is missing, the unloaded bone gradually atrophies;
- the face may become asymmetrical, lip closure is disrupted, and the chin and nasolabial folds deepen. Often the position of the corners of the mouth changes, they begin to sink;
- underdevelopment of the jaws occurs. It is expressed more strongly the more teeth are missing, various dentofacial deformations appear;
- with multiple edentia of the lower jaw, its strong protrusion and deep bite are observed;
- with anomalies of the upper jaw, the lower dentition begins to overlap the upper one;
Underdevelopment of the jaws is not observed in all cases, and not all children and adults express it in the same way. However, in all cases, edentia leads to negative changes in appearance.
With complete or multiple edentia, the bite is formed incorrectly and the function of oral digestion is disrupted. The food is poorly crushed, and the patient is forced to give up many tasty dishes. We should not forget that with this pathology a person’s self-esteem decreases, he begins to worry about the fact that he looks unattractive, withdraws into himself and is less likely to make contact with people.
Lack of teeth in humans: what is it and what does it mean?
What is jaw edentia? If in some species of animals the dentition is renewed continuously or at least repeatedly (for example, in Indian elephants), then people have only two sets of teeth - milk and molars. Unfortunately, they can be lost during life, and with some types of anomalies and diseases, a person initially lacks one, several or even all tooth germs. Adentia is a situation where there is a lack of teeth on one or both jaws. In this case, the absence of eights is not taken into account, since they are a rudiment and may not appear in principle. Experts highlight the absence of primary and molar teeth. In the latter case, the loss is irreparable. Therefore, most often they talk about edentulous molars, taking into account the fact that all the most negative consequences of this disease are especially pronounced in adulthood.
What does missing teeth affect?
- Chewing dysfunction.
- Problems with the digestive system.
- Deterioration of aesthetics. The most noticeable consequence of edentia. A diagnosis of “missing teeth” is often a death sentence for a beautiful smile.
- Bone tissue atrophy. Without the load that the teeth bear, the bone tissue begins to dissolve. When there is a lack of teeth, over time the face seems to shrink in the lower part and those same senile sunken cheeks appear. This is a consequence of bone atrophy.
- Curvature of teeth. In the absence of teeth, the bite is disrupted and the dentition shifts. It also distorts a person's facial features.
- Problems with diction.
Unlike many dental diseases, signs of missing molars (as well as milk teeth) are very obvious. Diagnosis of edentia is usually carried out visually. However, to assess the condition of the bone tissue and the entire dentofacial apparatus as a whole, an x-ray examination is necessary. Now that it has become clear what jaw edentia is, it is necessary to talk about the causes and types of the disease.
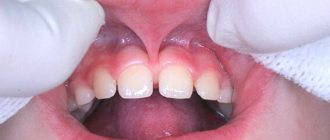
Edentia of the upper jaw
The upper jaw is more often than the lower jaw and is subject to various types of anomalies. As a rule, patients have symmetrical hypodentia of two teeth. And since the front teeth are involved in sound production and form the purity of pronunciation, this type of deformation is the most noticeable. The patient's speech becomes lisping and slurred, the smile “creeps away”, and saliva splashes.
Edentia of the lower jaw
The lower jaw has a small prosthetic bed, so when edentulous, the tongue begins to take the place of the lower teeth. As a result, the patient’s diction changes significantly and his well-being worsens.
Bone grafting for jaw implantation
The more implants are installed, the greater the likelihood that the existing bone tissue will not be enough to install implants and it will be necessary to build it up. Bone deficiency can be in thickness (very thin bone) or in height (close to the maxillary sinuses in the upper jaw, nerve in the lower jaw).
If there is a slight lack of bone tissue in thickness, one-step bone grafting with the installation of implants is possible. It is also possible to carry out a sinus lift (a type of bone tissue augmentation when the distance to the maxillary sinus is insufficient) with the one-step installation of implants.
If there is a large deficiency of bone tissue, operations are first performed to build it up (open sinus lift, harvesting and replanting of a bone block), and after 3-6 months, implantation is performed. In this case, the total duration of treatment can be from one to one and a half years.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose the disease, the dentist needs a detailed examination of the patient’s oral cavity. The doctor asks the patient a number of things:
- causes and timing of tooth loss;
- information about previous diseases;
- data on dental prostheses previously used by the patient.
During the examination, the dentist notes the asymmetry of the face, the severity of the chin and nasolabial folds, the degree of reduction in the height of the lower part of the face, the presence of a jam, the nature of the closure of the lips, the topography of the transitional fold, the degree of mouth opening, the nature of the jaw relationship. The specialist also determines the presence of crunching in the joints, pain when moving the lower jaw and diagnoses the degree of atrophy of the alveolar processes.
The examination necessarily includes palpation of the oral cavity and radiography of the TMJ. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines further treatment tactics (prosthetics), selects the appropriate type of prosthesis and impression material for the patient.
Stages of prosthetics
Creating a comfortable prosthesis with a minimal adaptation period will require several visits to the clinic. To eliminate inaccuracies in manufacturing, several pairs of impressions, fittings and bite testing are necessary.
- Taking impressions Taking preliminary impressions of the jaws to make a plaster model and final impressions to make a prosthesis template with the exact boundaries of the base.
- Bite study Determination and fixation of central occlusion based on facial characteristics using a facebow for transfer to the articulator in order to recreate the bite.
- Creating a template In the laboratory, the artificial teeth are first placed in the articulator on a wax template, taking into account the occlusion and the data obtained during the diagnosis.
- Try-ons The patient can visually evaluate the result and determine the degree of comfort. The doctor determines the relationship of the jaws in the oral cavity and their correspondence to facial features.
- Making a prosthesis When the template of the prosthesis is perfected, in the laboratory the model goes through a technological stage, the wax is replaced with a permanent plastic base through polymerization.
- Check in the articulator The bite is fixed with the finished prosthesis, the closure of the jaws is checked in the articulator in the clinic. If the smallest deviations are detected, adjustments are made.
The finished prosthesis is fixed to the jaw by applying slight pressure. Next comes the most important stage - getting used to or adapting to a removable denture. Sometimes there may be some discomfort in the first 1-2 weeks. It may be necessary to make a few more adjustments - we bring the prosthesis to an ideal state so that the person is extremely comfortable and convenient, so that he stops feeling it .
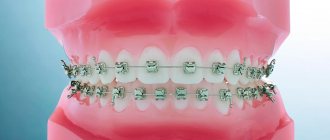
Treatment of adentia in children
It is important for parents to understand that treatment of children who experience pathological tooth loss must be carried out without fail. For example, if a child lacks primary teeth in the anterior and lateral segments, the row may not form correctly during adolescence.
Children's adentia is characterized by:
- delay in changing permanent teeth;
- asymmetrical teething;
- unilateral preservation of primary teeth;
- non-loss of a baby tooth and its fusion with a depression in the jaw bone.
If at least one of these signs is detected, the child should definitely be shown to an orthodontist.
The choice of orthopedic design depends on the type of pathology and the condition of the small patient’s oral cavity. Children most often have fixed bridges installed - cantilever or sliding. To fix the structure, crowns are installed. Children respond well to prosthetics and adapt well to new designs.
Bridges can also be installed in young patients, but such designs are more suitable during the period of late mixed and permanent dentition. The most successful designs are considered to be sliding bridges. The only drawback of such a system is the formation of a gap when the structure moves apart and food gets into it.
Bridges are sometimes installed for preventive purposes to preserve space in the dentition.
During the period of early mixed and temporary dentition, removable plate dentures are used, which do not retard the growth of the jaw bones.
Removable dentures - an affordable alternative to implantation
When a person has lost all his teeth and needs them quickly restored, a complete removable denture can be the ideal solution to the problem. However, the vast majority of patients associate it with an uncomfortable denture that constantly falls out of the mouth, which must be placed in a cup at night. Such speculations are relics of the past.
The removable denture of the upper jaw is aesthetically indistinguishable from its teeth
A modern removable denture (if it is properly manufactured) is aesthetic, comfortable and functional . It is a structure in the form of a plastic gum and crowns attached to it. Fixation in the mouth is ensured by the effect of suction to the gums. Artificial elements look extremely natural, no one will guess about your problem.
Undoubtedly, prostheses without any support have worse fixation, and at this point completely removable structures are inferior to prostheses with implant fixation. But if there are contraindications or certain fears of surgery, this is the only way out.
Treatment of adentia in adults
Adult patients are offered various types of removable and fixed dentures. Prosthetics on implants, installation of bridges on four implants and other prosthetic options at the patient’s choice are possible. Depending on the condition of his dental system, financial capabilities and wishes, dentists, as a rule, offer several treatment options to choose from.
When choosing a treatment method, it is important to understand the features of each design. The doctor, based on the condition of the patient’s oral cavity, offers him a choice of several prosthetic options.
Removable dentures
Partial or complete dentures should be replaced every 1.5 to 2 years. Therefore, even with complete loss of teeth, dentists offer an alternative type of prosthetics based on implants.
Clasp dentures
Dentures on a metal frame, on which an acrylic base is installed, and artificial teeth are installed on it. This solution makes it possible to significantly lighten the design of the prosthesis, making it thinner and more comfortable.
Bridges
In case of partial edentia, it is possible to install bridges. The non-removable structure is fixed on adjacent non-grindable teeth.
Implant-supported prosthetics
Implant-supported prosthetics are considered the most reliable and aesthetic way to restore dentition. The main advantages of this type of bone implantation include:
- long service life of the structure;
- aesthetic appearance;
- no need to grind adjacent teeth.
A denture installed on implants completely replaces missing teeth and performs a functional and aesthetic task.
Which implants to choose?
Today there are more than 3,000 implant systems in the world. However, not all of them can boast a long history of observations and clinical trials around the world. There are also some implant systems that, despite their reliability, are not very common in Russia. This may lead to difficulties in terms of delivery of original components of implant systems.
It is worth choosing only generally recognized implant systems, which are used by different doctors independent of each other. Otherwise, the patient risks finding himself in a situation where no one can help him.
An important point when choosing an implant system is the type of implant-abutment connection. It determines how long the implant will last. The most reliable today is the conical implant-abutment connection with the effect of switching platforms. It is able to withstand greater loads compared to a flat connection, is leak-tight and does not cause resorption of bone tissue around the implant.
The healing of implants is affected by the purity of the titanium from which they are made. The most common is Grade 4 - commercially pure titanium. Grade 1,2,3 alloys are even purer. Grade 5 – less pure, contains impurities of vanadium and aluminum.
The surface of each implant is a unique patented technology, because... It is on the surface of the implant that osseointegration occurs—the fusion of the implant with the bone tissue. Serious implant manufacturing companies conduct a lot of research, proving that their implants are integrated not only in standard situations, but also, for example, in people suffering from diabetes or bleeding disorders. The following systems meet all these requirements: Straumann (Switzerland), Ankylos (Germany), Astra tech (Sweden), Nobel biocare (USA/Sweden). Among the inexpensive systems, we can highlight Osstem implants (South Korea). They have proven themselves throughout the world as a reliable and economical implant system.
Prevention of edentia
The best prevention is competent, timely oral care. Regular brushing of teeth and gums, preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year, giving up bad habits, switching to a balanced diet - all this will help keep your teeth healthy and strong for as long as possible.
If you or your child is experiencing this disease, do not delay visiting the dentist. Experienced therapists, orthopedists and implantologists at STOMA clinics will help solve the problem of partial or complete absence of teeth: they will select a comfortable and aesthetic prosthesis that will significantly improve the quality of life, make you more confident and beautiful.
Call and make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 416-94-37. Our clinics are located in different areas of St. Petersburg and are open from Monday to Saturday, from 9 to 21 hours.
Which prosthetics for the lower jaw is better?
Patients are often interested in which prosthetics are best for restoring lower jaw teeth. Progressive experts believe that implantation and installation of structures today is the optimal and gentle option to maintain quality of life at any age. Root-shaped implants for the lower units are selected taking into account the upcoming high chewing load.
We use the basal method of prosthetics on implants extremely rarely and only at the stage of temporary prosthetics in the distal part as part of the “All on 6 implants” protocol in the absence of teeth, severe tissue atrophy and the inability to install 2 classical artificial roots. Then the elongated implants are introduced into the deep layers of the jawbone during the formation of bone in the distal section after bone grafting. After the bone tissue has formed, the basal implants are removed and normal classical implants take their place. And after this, the patient undergoes permanent prosthetics on 6 implants.
Modern implant designs are characterized by directional threading; some models have a porous surface with a coating that accelerates the integration of the artificial root into the bone. Fixed dentures in the absence of teeth are installed on a larger number of supports, minimum 6-8. One- or two-stage protocols are warranted. In the first option, until complete engraftment, the patient wears a traditional removable denture; in the second, a temporary option with artificial gums attached to pins is installed.
The fixed structure consists of metal-free crowns (usually zirconium dioxide), there is no artificial gum, and there is no need to remove the denture for cleaning. It is enough to follow standard hygiene procedures.
The “All on 4” protocol is ideal for restoring missing teeth in the lower jaw, if it is small, and allows, in most cases, to avoid bone augmentation. This is usually a one-stage implantation with immediate loading. Primary stabilization is high, there is an orthopedic stage. Within a week after the implants are inserted, a temporary prosthesis is put on.
If the bone has atrophied and for some reason it is decided to give preference to classical implantation, then bone grafting will be required. Special membrane materials are used that are embedded in the bone and stimulate its development. After osteoplasty there is a rehabilitation period of 4 months. up to six months.
New generation dentures without palate –
The Sandwich denture, developed by one of the Moscow dentists, is positioned in advertising as a new generation of removable dentures without a palate. It was quite interesting for us to study this type of prosthesis, which is a combination of different elements of different types of removable dentures and, in its own way, is truly unique in some way.
Sandwich dentures are used only in cases of partial absence of teeth. It got its name due to the combination in the body of the prosthesis of 2 different layers of materials (having practically opposite properties) - hard acrylic plastic and elastic polyurethane.
The body (base) of the prosthesis itself consists of hard pink acrylic plastic into which artificial teeth are inserted. However, in those areas where the patient still has his own teeth, the prosthesis has something like “telescopic” crowns made of soft elastic material (in the picture they are located on both sides at the end of the prosthesis). These crowns are, as it were, stretched over the remaining teeth and provide fixation of the prosthesis.
There is a patent for the invention for new generation dentures without a palate. Essentially, this is a removable denture made of acrylic plastic, in which the base is greatly reduced, and instead of metal wire clasps, telescopic crowns made of polyurethane are used (similar to the telescopic crowns of a clasp denture).
New generation removable dentures: cost
For new generation dentures without a palate, the price will be from 40,000 rubles. The cost may be higher if more expensive sets of artificial teeth are used or the number of supporting teeth is increased, which complicates the production of the prosthesis.
New generation dentures: who are they suitable for?
Let's start with the fact that these dentures are not the only dentures without a palate. Removable clasp-type dentures also do not have a massive base, and therefore practically do not cover either the palate on the upper jaw or the sublingual space on the lower jaw. Moreover, the fixation of clasp dentures, as well as their chewing efficiency, is three orders of magnitude better.
In fact, this prosthesis can only be suitable for those who have only a few chewing teeth left on both sides of the upper or lower jaw. Considering that polyurethane crowns (about 1-1.5 mm thick) are also stretched over the natural crowns of the teeth, the teeth in these sections will look very bulky and unsightly, which is critical if the remaining teeth fall into the smile line.
Important: what you should be prepared for is
- Even with the best types of removable dentures (clasp with micro-locks), the chewing load is distributed approximately 50/50 on the gums and on the supporting teeth. Considering that a sandwich prosthesis has “telescopic” crowns made of elastic material, which, due to elasticity, are simply not capable of transmitting chewing pressure to the remaining teeth - all the chewing pressure will go to the hard plastic base of the prosthesis.
- The manufacturer claims an extremely small base for the prosthesis. But the smaller the base area, the greater the chewing load falls on the remaining tissues of the prosthetic bed. This means that with the prosthesis shown in the figure above it will simply be impossible to chew anything. Chewing will be painful, of course, if you are not going to eat only semolina porridge from now on.
- Fixation of such a prosthesis in the anterior section will be practically absent, because fixation can be provided either by a clasp or a prosthesis base. And these so-called removable dentures of the new generation have neither clasps nor a volumetric base on both sides of the alveolar process of the jaw (like dentures made of plastic and nylon).
Conclusions: the cost of removable dentures of the new generation is quite high, and in our opinion, for that kind of money, it is better to give preference to a clasp denture (the cost of which is equivalent). In addition, if you have an increased gag reflex, then clasp dentures are no less compact in the oral cavity than a Sandwich denture, and their chewing efficiency is much higher.