Publication date: 01/25/2021
Every person's teeth are designed to last for many years. They have several levels of protection:
- Enamel is a highly durable mineralized tissue that protects the surface of the tooth.
- Dentin is a less hard tissue, but also strong. The main task of dentin is to protect the pulp - the inner tissue. It is the nerve endings in the pulp that signal us about the problem. If the surface layers are broken, we experience pain.
- Cement - covers the roots, protecting them from adverse influences
Overcoming these layers of defense is not easy, but it is possible. And then the teeth rot.
Causes of rotting
In the first place is fear. It is the irrational fear of the dentist, which is difficult to control, that makes us put off visiting the doctor. Often to the point where it is no longer possible to save the tooth. No matter what facts they give us, no matter how much we persuade ourselves, phobias do not lend themselves to rational arguments.
But this is far from the only reason.
General diseases
Our body is a single system. Discord in one place leads to problems in another. Thus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract cause dental problems.
Infections, fungal diseases, even hormonal imbalances often lead to inflammatory processes in the mouth.
Ecological problems
In regions where drinking water is of poor quality, dental problems are 3-4 times more common. The same picture is observed where there are large industrial enterprises. Increased amounts of toxic microelements in the environment harm overall health and negatively affect teeth.
Diet
There are foods that provoke the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity, which means they contribute to tooth decay. Yes, that same sugar, but not only that. Acids formed during the fermentation of carbohydrates are the main enemies of enamel.
Lifestyle
Addictions of any kind are not good for dental health. Cigarettes, drugs, alcohol are a direct path to problems.
This also includes restrictive diets. Vegetarians, vegans, and Keto fans need to carefully ensure that the body receives all trace elements and vitamins.
Oral diseases
Inflammatory processes in the mouth are a paradise for bacteria. Therefore, it is important to regularly sanitize and do ultrasonic cleaning of teeth. Periodontal disease, periodontitis, stomatitis, gingevitis, cheilitis require special treatment, which is better not to delay.
Oral hygiene
This is perhaps the easiest way to destroy teeth. All that’s left to do is brush and floss twice a day. 90% of the population does this, but not as carefully as we would like. There are special teeth cleaning schemes. They involve treating surfaces from all sides and for a certain time. Unfortunately, now
90% are those who brush their teeth for less than 1 minute.
Genetic predisposition
Alas, often all preventive measures are not able to help keep teeth safe and sound. Healthy, strong teeth, just like bad ones, are inherited.
Is it possible to cure pulpitis and how are nerves removed: types of anesthesia
As mentioned earlier, pulp inflammation is an extremely painful pathology, which primarily affects the nerve endings inside the oral cavity. The process of its treatment necessarily includes an operation to select a high-quality antiseptic that is suitable for a particular person. Moreover, the drug is applied to the desired places using various methods:
- application;
- infiltration;
- conductive;
- stem
The anesthetics used are traditional pairs of lidocaine and novocaine, as well as more advanced and modern formulations: Ultracaine, Ubistezin, Septanest, and so on.
Stages of decay development
There is no acute form of caries, so small changes are difficult to notice, they accumulate - and now a person cannot smile, only stumps of teeth remain. Therefore, it is important to undergo preventive examinations regularly. The dentist can identify the problem at the initial stage and can easily fix it.
- Rotting begins at the spot stage. The color of part of the surface changes. Enamel demineralization begins. At this stage, treatment is quick and easy.
- The superficial process of demineralization is increasing, but the pain syndrome has not yet manifested itself. The tooth can react to sweet, sour, cold, hot.
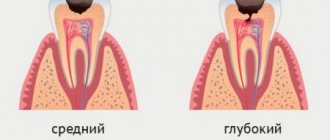
- Middle stage The lesion reaches the enamel-dentin junction. Painful sensations occur periodically. Large areas are affected.
- Deep damage The decay process affects the dentin surrounding the pulp. If this process is left unattended, pulpitis will develop. And this is far from the only problem.
TMJ dysfunction
Caries and subsequent pulpitis lead to tooth loss, occlusal disorders, problems with chewing, etc. This changes the load on the temporomandibular joint, causing dysfunction. When the TMJ “does not work” correctly, headaches, neck pain, bruxism, ringing and noise in the ears, and disturbances in the movements of the lower jaw may appear. If the dysfunction persists for a long time and worsens, eating disorders may develop against its background (the patient is afraid to eat solid, chewing foods because of pain), sleep disorders, depression, and other disorders.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Complications
Bad teeth are a direct path to a heart attack
. When the tooth's protection is destroyed, bacteria enter directly into the bloodstream. There they can provoke the development of blood clots, inflammation of blood vessels, and this leads to the development of coronary artery disease, which is not far from a heart attack.
Gastrointestinal problems
Rotten teeth make it difficult to chew food well. Not only do poorly chewed pieces irritate the mucous membrane, pathogenic flora from damaged teeth enters the stomach and intestines, where they can multiply uncontrollably, causing diseases such as gastritis, pancreatitis, stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers. Competent gastroenterologists always advise visiting a dentist.
Diseases of the throat and nose
A constant source of infection in the mouth means that any malfunction in the body will cause a relapse of diseases such as sore throat and sinusitis. Purulent infections are dangerous because they can lead to blood poisoning. And such diseases are difficult, often causing complications. Inflammation of the tonsils often causes rheumatism and heart problems. Those who struggle with chronic sinusitis need to especially carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Chronic manifestations will not go away if there are rotten teeth in the mouth.
And the head too
An advanced inflammatory process can spread to the trigeminal nerve. It is closely connected with the brain, and this is a serious matter. Chronic migraines, memory problems, even Alzheimer's disease are associated with oral health. Although there is no direct evidence that Alzheimer's is caused by the same bacteria that cause inflammation in the mouth, it is better to be on the safe side.
Abscesses and cellulitis are also the result of bacterial inflammation.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Inflammation of the pulp is a disease characterized by pronounced, extremely acute symptoms, mainly in terms of pain. Almost any manipulation with a damaged element of the oral cavity causes severe discomfort to patients in medical clinics. However, such a problem can be resolved quite simply - a good dentist will easily select a high-quality, suitable anesthetic agent. That is why the process of surgical intervention itself, as a rule, takes place without third-party excesses. Much more unpleasant sensations await people who refuse to visit a doctor in a timely manner.
What to do when the process of tooth decay begins
Modern dentistry is not about pain at all. This is about caring for the patient and the desire to preserve his teeth.
Dentists' advice is simple, but how many people follow it?
How to prevent teeth from rotting:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle
- Takes good care of your teeth
- Carry out hygiene procedures regularly
- Monitor your general health
Plaque on teeth is the beginning of the decay process. Regular cleaning of tartar is one way to keep your teeth healthy.
What can cause caries
There are several suggestions, for example, that tooth decay is transmitted genetically or that lack of hygiene contributes to the development of the disease. All this is true, but does not give the complete picture.
Where a person lives can also influence the occurrence of caries, namely the quality of water in that area.
Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of caries. There are scientific studies confirming that eating fresh vegetables, greens and foods rich in proteins helps prevent tooth decay. That is, those people who like to chew raw carrots are less susceptible to dental diseases. That's why you should eat meat and a lot of raw vegetables - this is not only smart advice from nutritionists, but sound prevention in the fight against the development of dental caries.
Treatment
Sick teeth need to be treated, the sooner the better. The dentist’s task is to save the tooth, but if measures are not taken in time, it will have to be removed to avoid serious consequences.
Methods:
- Remineralization Applications of calcium and fluoride preparations and electrophoresis help restore enamel at the initial stage.
- Filling the cavity The affected tissues are removed, their place is filled with filling material.
- Partial prosthetics A crown is placed on the tooth, which protects it from mechanical and biological influences. The crown is placed on a previously depulped, dead tooth.
- Removal If the pulp is affected and the inflammatory process threatens to develop into an abscess, the tooth is pulled out. You should not resist the removal of rotten teeth - they do nothing but harm.
It is easier to prevent any process than to take a long time to eliminate the consequences. By following simple preventive measures and regularly visiting the doctor, you can avoid tooth decay and maintain your smile and self-confidence for many years.
Classification of caries by location
The Black classification system includes five types of caries:
Caries on the chewing surface of the tooth
Caries on the lateral surface of the tooth
Caries on the lateral surface of the central tooth with destruction of the cutting edge
Cervical dental caries
Now this system is to some extent outdated, since modern filling materials have a wide range of applications. And the dentist makes a choice between filling methods, because a filling, to some extent, is also a prosthesis. The doctor chooses how best to place a filling and what type of construction to make.
What about the treatment of caries? We’ll tell you about the treatment of caries, the types of fillings, inlays and other benefits for teeth in another article.
What to do if your child is afraid of the dentist
When children say they're afraid of the dentist, this is a common reaction. The reason for fear usually lies in the fact that the child has not previously visited the dentist, but may have heard negative reviews from surrounding children or adults. Also, children are scared by the unknown.
Playing doctor will help you cope with fear, where parents will cheerfully talk about the bacteria living in the mouth, how they destroy teeth, methods of protection and dental examination. You can watch a children's program together about the work of a dentist, go on a tour of a children's dentistry, or allow your child to communicate with the doctor on their own.
Periodontitis - forms, classification, photos
It is a consequence of pulp necrosis, which allows microorganisms to enter the hard and soft tissues of the jaw through the dental canal. The inflammatory process includes the peridontal ligament, cementum, root dentin together with the alveolar bone. Signs of periodontitis:
- the occurrence and intensification of pain when pressing on the tooth during the chewing process. There is a constant painful pulsation affecting half of the face;
- increased body temperature, feeling of weakness;
- swelling and tenderness of the gums in the affected area, as well as lymph nodes (mental and submandibular);
- discharge of pus from the root canal;
- facial asymmetry due to edema.
Consequences : lack of medical care leads to independent release of pus through the bones under the periosteum, as a result of which periodontitis becomes chronic.
Chronic periodontitis
A person may not be aware of the presence of the disease for a long time, since it occurs without the slightest symptoms. The reason to suspect the disease is the presence of a history of pain that was in the past, but gradually disappeared and does not remind of itself. A feature of chronic periodontitis is the melting of bone tissue around the affected tooth . Further development of the disease leads to loosening of the damaged tooth, as well as neighboring ones. Consequences: a common result is the loss of several teeth or granuloma .
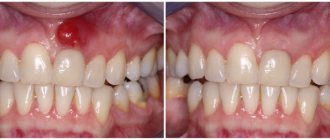
Granuloma
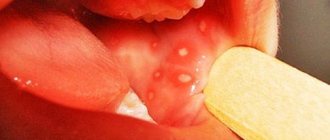
It is a natural consequence of advanced periodontitis. The disease is marked by the spread of the inflammatory process, which is presented in the form of a small purulent nodule or sac in the area of the tooth root. Consequences: the infectious focus poses a serious danger to the body, as it acts as a catalyst for inflammation. At the initial stage, granulomas are characterized by practically asymptomatic progression. Severe pain gradually arises, which becomes more noticeable when pressing on the tooth or chewing solid food. Redness and swelling of the gums are noted, and tooth enamel becomes darker.
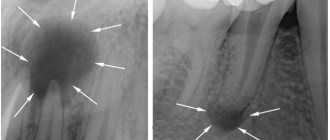
Root cyst
Lack of measures to treat granuloma leads to complications in the form of a root cyst. It forms at the top of the tooth root and is firmly attached to it. It looks like a round cavity located in the bone tissue, inside of which there is purulent contents. The root cyst grows slowly and imperceptibly, and therefore poses a significant danger. It can be visually determined only if it grows strongly, when protrusion of the bone is observed. Consequences: there is a possibility of the cyst growing into the maxillary sinus and nasal cavity. Displacement of teeth to the sides, as well as pathological fracture of the lower jaw.
Periostitis of the jaw bone, tooth
If treatment of root cysts and periodontitis was not carried out or was carried out in bad faith, then the likelihood of periostitis or inflammation of the periosteum sharply increases. The inflammatory process begins to emerge from the periodontal fissure and enters under the periosteum. Surgery is required, which involves making an incision in the mouth under anesthesia to release the pus. Consequences : failure to see a doctor in a timely manner carries the risk of an abscess.
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of purulent tissue in a confined space. The pus begins to put pressure on the root apex area, which leads to the tooth being pushed upward and possible destruction of the bone tissue in the affected area. If the abscess does not open for a long time, then the spread of pus to the periosteum, skin and mucous membrane begins. Consequences : severe and painful swelling occurs.
Phlegmon
It is considered one of the most dangerous forms of abscess. Cellulitis carries with it the risk of serious infection of the body, since infection and purulent accumulations from the swollen area enter the body. In fact, pus begins to spread throughout the surrounding tissues and can reach the neck and even the heart. The following symptoms are characteristic of phlegmon:
- swelling and tenderness of the soft tissue of the gums around the affected area;
- difficulty swallowing and opening the mouth;
- painful sensations behind the eyeball;
- deterioration of appetite and sleep;
- fever and weakness.
Consequences: the disease carries with it a significant risk of death! (we do not publish photos of phlegmon, copy and paste the word into a search engine to see the pictures).
Sinusitis
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (pulpitis, deep caries stage, cysts, periodontitis and others) aggravate the risk of single-gene sinusitis (sinusitis). It is caused by the penetration of infection from the affected tooth into the maxillary sinuses (we are mainly talking about infection in the upper molars and premolars, which are practically in contact with the maxillary sinuses). Initially, the infection enters only one maxillary sinus, then it spreads to the other. There is a possibility of getting into the sphenoid, frontal and other sinuses. Sinusitis manifests itself:
- severe headaches;
- swelling of the cheek;
- elevated temperature;
- thick mucous discharge of a purulent nature;
- pathological reaction to light.
If adequate treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, sinusitis can lead to the following consequences :
- transition to a chronic form;
- meningitis;
- sepsis, which is localized near the brain;
- purulent otitis;
- inflammation and swelling of nerve endings.
Tooth loss
Due to improper oral care and delays in seeking medical help, teeth decay and fall out. What are the consequences of losing teeth? Consequences :
- irreversible imbalance in the activity of the oral system. The absence of even one tooth disrupts the position of neighboring teeth; they do not hold so firmly in the gums, which can lead to their loss;
- a decrease in the efficiency of eating, as the degree of chewing and, accordingly, digestion of food deteriorates. A natural consequence is gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic disorders;
- curvature of the dentition, malocclusion, increased risk of diseases of the periodontal tissues;
- loss of aesthetic appeal (change in facial oval, sunken cheeks, visual unattractiveness due to missing teeth).
Bone atrophy
Atrophic processes in the maxillofacial region are a natural consequence of the absence of even one tooth. Its loss means the displacement of an entire row of teeth, a significant decrease in the volume of bone tissue. If atrophy is not stopped by building up bone tissue, then the lips and cheeks begin to “sink” into the oral cavity, and healthy teeth begin to move along the dentition due to loss of support. Consequences:
- the appearance of cosmetic facial defects (wrinkles, sunken lips, cheeks, etc.);
- deterioration of chewing function and the occurrence of gastrointestinal disorders;
- pathological changes in speech;
- displacement of the dentition, loss of healthy teeth.
Avoiding such unpleasant consequences is both easy and difficult. The main thing is to carefully observe oral hygiene and consult a dentist as soon as possible!
Caries on baby teeth
As a result of long-term research, scientists were able to identify the main cause of caries in baby teeth. It becomes: microorganisms transmitted to the child from the mother. Streptococcus gets to the baby through a kiss, through a pacifier licked by the mother, or shared cutlery. Microbes come from other people through these same routes. When teething, babies are especially vulnerable to streptococcus. In addition, lack of oral hygiene, poor diet, and the composition of saliva have a negative impact.
Dentists point out that regular use of baby formulas from a bottle with a high carbohydrate content creates ideal conditions for the development of bacteria. Getting your baby used to a cup and rinsing his mouth after eating helps reduce their negative effects.
previous post
Pin in a tooth: types and advantages of design
next post
Installing a seal
The task of the doctor who has discovered a tooth damaged by caries is:
- drilling out dead tooth tissue and darkened parts of enamel;
- expansion of the carious cavity;
- checking the condition of the pulp;
- preparing the tooth for filling.
The filling process consists of:
- in disinfecting the drilled cavity and drying it;
- installing a medicinal inlay into the tooth canals;
- installation of a temporary filling;
- A permanent filling is installed when a tooth is cured and the lost parts need to be restored.
Types of permanent fillings
- Metal seal. Advantages: long service life, inexpensive cost. Disadvantages: long hardening time, contrasting color with the color of the enamel.
- The cement filling can be phosphate or glass ionomer. Advantages: release of fluoride ions, which prevent the formation of caries. Disadvantages: fragility and short service life.
- Composite fillings are made from an epoxy mixture. Advantages: long service life. Disadvantages: long time to install the filling.
- Plastic fillings are made on the basis of acrylic acid. Advantages: high strength. Disadvantages: the formation of micropores in the filling, through which caries can penetrate.
- Ceramic inlays are used to restore a damaged tooth. Advantages: strength and reliability. Disadvantages: high cost and long installation time.
Bacteria
Next, bacteria are introduced into the already weakened cells, which are able to completely destroy the cell, feeding on its insides. According to the nature of their development, they are divided into those that are able to divide and grow only inside the cell (chlamydia, etc.) and those that multiply both inside and outside the cell (mycoplasma, legionella, listeria, rickettsia, etc.). The variety of lesions they cause is explained by their sensitivity to different types of host cells (human, animal).
Intracellular bacteria:
Chlamydia:
- chlamydia trichomatis (trachoma, urogenital chlamydia and pneumonia of newborns, lymphogranuloma venereum, arthritis, arthrosis, heart damage)
- chlamydia from birds (ornithosis - pneumonia, fever)
- chlamydia pneumoniae (pneumonia, acute respiratory infections, atherosclerosis, bronchial asthma)
Rickettsia:
- rickettsia (rickettsiosis, typhus)
- rohalimia (trench fever, cat scratch disease)
- Klebsiella (Congo red fever)
Escherechia:
- Escherechia (maculopapular rash)
- bartonella (bartonellosis)
By multiplying in cells, intracellular bacteria are protected not only from various influences from the human body, but also from the effects of most antibacterial drugs that are not able to penetrate inside cells. Extracellular bacteria feed on already decomposed cells, “melting” them and turning them into pus. They are a kind of orderlies (cleaners) of the body, cleaning out diseased organs and systems.
Extracellular bacteria:
- Staphylococcus (skin pustular infections, endocarditis, pneumonia, arthritis, osteomyelitis, peritonitis, eye infections, toxic shock syndrome, food toxic infections)
- Oral sticks (gingivitis, stomatitis, endocarditis, sepsis)
- Streptococci (pharyngitis, postpartum infections, neonatal sepsis, bacteremia, meningitis, arthritis, genitourinary tract infections, pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis of the middle ear, rheumatic attack, abscesses of the lungs, liver, brain)
- Bacilli (Anthrax, bacteremia, septicemia, meningitis, eye infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, food poisoning
- Corynebacteria (diphtheria, erythrasma, skin lesions in the axillary and groin area, cellulitis, septicemia, brain abscesses and osteomyelitis)
- Clostridia (gas gangrene, foodborne illnesses, necrotic enteritis, tetanus, botulism)
- Gonorrheal bacillus (infections of the lower parts of the genitourinary tract (cervicitis, urethritis, abscesses of the glands adjacent to the vagina), infections of the upper parts of the genitourinary tract (endometritis, epididymitis, pelvic inflammatory diseases), infections of other organs and tissues (proctitis, pharyngitis, blenorrhea, pelvic peritonitis and perihepatitis, pharyngeal gonorrhea), disseminated gonococcal infection; meningococcal infection)
- Pseudomonas (skin lesions, abscesses, infection of burn lesions, keratitis, conjunctivitis, otitis of the external ear, meningitis, bacteremia, endocarditis, enteritis, para- and rectal abscesses, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, osteomyelitis and arthritis)
- Flavobacteria (colonize wounded surfaces, respiratory, intestinal tracts, organs of the genitourinary system, severe meningitis of newborns, septicemia, endocarditis, pneumonia).
Intracellular and extracellular bacteria not only get along with each other, but, participating in the cycle, eat what the previous microorganisms destroyed. They can be compared to jackals and hyenas, eating what is left of the victim after a tiger.
Pain after tooth extraction
In some cases, effective treatment of advanced diseases involves the removal of a diseased tooth followed by prosthetics. After tooth extraction, pain, swelling and redness of the gums are a normal reaction of the body to tissue injury. You should be concerned if:
- the intensity of the pain does not decrease over time and is poorly removed by painkillers;
- the hole does not overgrow for a long time;
- purulent discharge appears from the wound;
- severe swelling of the mucous membrane occurs;
- body temperature rises.
The above symptoms indicate the development of an infectious process in the gum tissue. This happens if the tooth extraction technique is not followed or if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations for oral care.