Neurologist (algologist)
Vasilenko
Marina Gennadievna
Experience 26 years
Head of the Pain Treatment Center, neurologist-algologist, member of the Society of Neurologists and Neurosurgeons, Russian Society for the Study of Pain, Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine, International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP)
Make an appointment
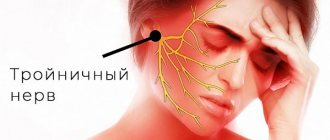
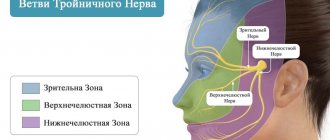
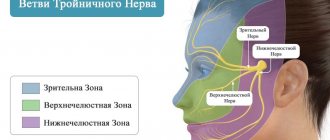
The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the 12 cranial nerves, specifically their fifth pair. It belongs to the nerves of a mixed type and includes very sensitive fibers. This name is due to the fact that the nerve is divided into three branches, providing mobility and sensitivity of the face, mucous membranes of the mouth and teeth. These are the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular branches.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is a serious pathology that causes severe pain in the facial area. Otherwise it is called neuritis. In turn, neuralgia is pain along the trigeminal nerve. It can act as an independent sensitivity disorder, but it often accompanies inflammation, i.e. neuritis.
Symptoms and signs
Acute trigeminal neuralgia causes sudden and very severe pain along the nerve fiber. It manifests itself in attacks and is shooting and burning in nature. On average, the duration of an attack is up to 3 minutes; in approximately 7% of patients it lasts up to 3 days. Their number can reach 200 per day.
Pain from trigeminal neuralgia can be observed in different parts of the face. It all depends on which branch of the nerve was affected:
- if maxillary - in the area of the facial muscles, upper jaw and nose.
- mandibular – the pain will resemble a toothache.
- ophthalmic – in the area of the temples, forehead and above the eyebrows.
Against the background of pain, the patient develops increased anxiety and even phobias. A person strives to avoid those poses and movements that provoke unpleasant sensations in him. Other characteristic symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- facial muscle spasms;
- increased salivation;
- increased or decreased sensitivity of facial skin;
- moderate increase in temperature;
- weakness and muscle pain.
Are you experiencing symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Symptoms
Symptoms of postherpetic neuralgia typically occur only in the area of the body affected by shingles and include:
- Pain (can be sharp, cutting, throbbing, burning),
- Numbness, tingling, itching
- Headaches if shingles is localized to the head or face
- Rarely, muscle weakness or paralysis if the nerve supplying a particular muscle is damaged.
Sometimes patients experience allodynia. Allodynia is a reaction that is not proportionate to the stimulus (that is, the patient reacts to minor stimuli such as a slight change in temperature or the touch of clothing with severe pain).
Causes and risk factors
Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve branch is a disease with many possible causes. First of all, this is compression by vessels: displaced arteries or veins. Inflammation can also be provoked by metabolic disorders and diseases that are associated with them. These are diabetes mellitus, gout and other similar pathologies.
There are other possible causes of trigeminal neuralgia:
- inflammations that occur during dental treatment;
- hypothermia (general or facial area);
- mental disorders;
- purulent diseases of the jaw bones or skull;
- infection of the body with worms;
- chronic caries or sinusitis;
- infectious and viral diseases (herpes, adenoviruses, mumps, pulmonary tuberculosis, herpes zoster);
- very severe allergies;
- brain tumors;
- inflammation of the outer, middle or inner ear;
- multiple sclerosis;
- too narrow canal of the facial nerve from birth;
- injuries or operations on the temporal bone.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
As a rule, neuritis does not affect all branches of the trigeminal nerve. Most often, inflammation occurs in the maxillary region, so pain occurs while eating or brushing teeth.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
- Pain. Shooting, pronounced, paroxysmal. With extensive damage, attacks last several minutes and are repeated at regular intervals.
- Impaired facial expressions and decreased sensitivity of facial muscles.
- Temperature, taste disturbance, lacrimation. These symptoms manifest themselves individually and depend on the form and severity of the disease.
Possible complications
Over time, symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can give rise to neuropathic complications and lead to the development of secondary pain syndrome in the head. In the chronic form of the disease, the auditory and facial nerves are irritated. Without treatment, trigeminal neuralgia can lead to more serious complications:
- dystrophy of masticatory muscles;
- decreased sensitivity of the affected area;
- Sykinesia (cooperative movements in which one nerve controls many muscles);
- contracture and spontaneous contraction of the facial muscles;
- conjunctivitis.
Causes
Postherpetic neuralgia has a specific pathogenesis. Nerves in their structure are similar to electrical wires that run throughout the body and conduct impulses from the central nervous system and back, with information about the state of organs and tissues. Sensory nerves transmit pain, temperature, and tactile sensations.
Postherpetic neuralgia occurs when the shingles virus damages sensory nerves. Damaged nerves begin to function poorly and send pain impulses to the central nervous system. This leads to chronic pain or sensory disturbances in certain areas of the body.
When to see a doctor
If you experience symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia, you should immediately consult a doctor, as it may be a sign of another serious disease. In the treatment of neurological pathologies, accurate and timely diagnosis is extremely important. This is done by a neurologist, with whom you can make an appointment at our clinic in the center of Moscow. The specialist knows not only how to relieve trigeminal neuralgia, but also how to correctly diagnose it in order to prescribe effective treatment in the future.
Diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia
A preliminary diagnosis can be made by a neurologist based on the patient’s complaints, studying the history of his disease and an objective examination of the face with an assessment of symmetry at rest and when trying to smile. Also, during the consultation, the doctor may conduct additional tests, asking the patient to close his eyes, purse his lips, frown, etc.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of trigeminal neuralgia include the following examinations:
- general blood and urine tests;
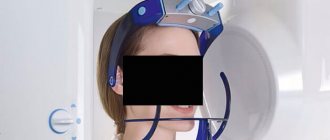
- computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- panoramic radiography of the oral cavity;
- electroneuromyography to determine the localization of inflammation.
All about occipital neuralgia: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment methods
Occipital neuralgia is a disease accompanied by severe headaches in the back of the head. There are 2 types of this disease. If neuralgia develops on its own, then it is primary. If the disease appears as a result of injury, then this is secondary neuralgia.
What are the causes of the development of occipital neuralgia?
As a rule, the described disease progresses against the background of other diseases. Among them it is necessary to highlight:
- Diseases of the cervical spine;
- Acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throat;
- Aneurysm of the vertebral artery;
- Gout;
- Lymphadenitis of the cervical glands;
- Cancer of the brain or spinal cord.
In addition, spinal injuries lead to the development of occipital neuralgia.
Main symptoms
Pinched fibers of the occipital nerve are susceptible to inflammation. For this reason, severe headache occurs in the back of the head. Sometimes it can radiate to the neck, temples, and lower jaw. The patient's condition worsens with sudden turns of the head: nausea appears, and the eyes may hurt.
Inflamed nerves become very sensitive. Lightly pressing on the affected area will make the migraine worse. Because of this, people suffering from occipital neuralgia often tilt their heads rather than holding them straight.
Another symptom of the described disease is a change in skin color in the back of the head. At the same time, the skin looks either slightly red or too pale.
The eyes also react to the development of occipital neuralgia. In this regard, many patients complain of involuntary lacrimation.
If you experience one or more of the symptoms listed above, then be sure to consult a doctor. The doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. In this way, you will protect yourself from disruption of the innervation of the area of the affected nerve.
Briefly about diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by the doctor after a conversation with the patient. In addition, the specialist uses the information obtained as a result of the patient undergoing a palpation examination. It is also possible to use other techniques, for example, MRI, fluoroscopy.
Treatment information
The main goal of treatment is to relieve the patient of muscle spasms and migraines. If occipital neuralgia develops intensively, then the patient should be at rest as much as possible. Moderate pain can be relieved by taking medications and B vitamins in tablets. You should also take muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If headache attacks are incredibly severe, and pills do not help, then corticosteroids and anesthetics should be injected subcutaneously to alleviate the condition. In this case, the effect will not take long to appear, but it will be short-lived.
If the disease has progressed to a subacute period, then warming procedures will bring tangible benefits. For example, you can apply compresses to the affected area. In addition, often the course of treatment for occipital neuralgia includes manual therapy, acupuncture, and massage.
There are 2 procedures that help overcome the described illness. The first of these is radiofrequency ablation. This technique is based on heating the inflamed nerve. The second procedure is electrical stimulation. This is a type of physical therapy. It is notable for the fact that it has no contraindications. In this case, the affected area is exposed to electrical impulses that relieve pain.
What can the lack of treatment lead to?
If the occipital nerve is pinched and inflamed, but for some reason the patient decides not to visit the clinic, then he is at great risk.
Left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems. In particular, the development of occipital neuralgia can cause loss of vision and curvature of the neck. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is carried out depending on the severity of symptoms. First, conservative therapy is prescribed. If this does not help, doctors resort to surgical methods. Their essence is to eliminate the cause of neuralgia. This may be compression of the nerve by the vessel. Surgical treatment is carried out using radiofrequency destruction, microvascular decompression or percutaneous surgery.
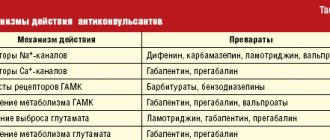
What drugs are most effective for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia:
- antibiotics. Prescribed for infectious nature of the disease;
- glucocorticosteroids. Relieves severe inflammation in the body;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Helps suppress inflammatory processes;
- painkillers. Relieves soreness in the facial muscles;
- muscle relaxants.
To improve metabolic processes in the nervous tissue, the patient is prescribed B vitamins. How to relieve acute pain with trigeminal neuralgia:
- use anticonvulsants;
- provide physical rest, preferably bed rest;
- Apply an anti-inflammatory ointment or a warm compress to the site of pain.
Home remedies
Before treating trigeminal neuralgia at home, you should consult a doctor, since many remedies can only worsen the situation. If the specialist allows it, it is also possible to use various home recipes.
According to recommendations for trigeminal neuralgia, it is worth consuming orally or lubricating the affected side with birch sap. You need to drink 4-5 glasses per day. Heated buckwheat folded in cotton cloth will help relieve pain. The compress is made 2 times a day, keeping it at the site of inflammation until it cools down. At home, it is useful to massage the sore area: rub, stroke and lightly knead the area of inflammation.
Treatment of sciatic neuralgia at home
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, or sciatica. With this type of inflammation, pain occurs in the lower back, back of the thigh or lower leg. Discomfort increases during movement, especially under load. When a person is in a calm state, the pain syndrome decreases or disappears altogether. The cause of the disease, which affects the largest nerve in the human body, is arthritis or pinched nerve roots. An attack of neuralgia can begin unexpectedly, for example, due to an unsuccessful turn of the body, as well as from hypothermia.
A decoction prepared from viburnum flowers, calendula inflorescences, thyme, and horsetail will help relieve the acute phase of inflammation. These plants are taken in equal quantities. After mixing all the ingredients, pour 500 ml of hot water, boil over low heat for 5 minutes, cool and filter. Take 100 g of decoction orally 3 times a day.
Externally, to relieve suffering, the same means are used as in the treatment of intercostal neuralgia with herbs. A decoction of hot chili peppers is especially effective. An extract prepared from birch buds is also used for rubbing. The kidneys are infused for 7 days, first filled with a glass of vodka. The finished product does not even need to be filtered. Rub it into the sore spot before going to bed.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in treatment
Due to the fact that neuralgia does not affect the general condition of the body, many patients postpone visiting a doctor and treating the trigeminal nerve. In fact, this is the wrong approach, since the disease can lead to paralysis and muscle paresis. In addition, it has a significant impact on psychological and social aspects of life.
No less important is the fact that painkillers for trigeminal neuralgia provide only a temporary effect. Over time, anticonvulsant medications may also stop working as they become addictive. Therefore, you should not abuse medications. They only relieve the symptoms of neuralgia, and its cause can only be identified by a qualified specialist.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention against neuralgia. Doctors only recommend eliminating as much as possible exposure to the body of those risk factors that can lead to nerve inflammation. To avoid this, it is necessary to prevent hypothermia of the face, especially in the summer when using fans and air conditioners. It is important to harden yourself and worry less in order to reduce the impact of stress. It is also imperative to treat underlying diseases that are risk factors for neuralgia.