Occlusion of the femoral artery is a violation of its patency (blockage).
As a result of the occlusion, arterial, oxygenated blood stops flowing to the lower leg. Ischemia develops (local anemia).
Femoral artery occlusion occurs mainly in men. Persons over 50 years of age account for up to 75% of cases of the disease.
Femoral artery occlusion can be:
- segmental, affecting only a limited area of the artery;
- complete, when the entire artery is affected;
- combined with occlusions of other arteries of the lower extremities.
Causes of femoral artery occlusion
The cause of occlusion of the femoral artery in the majority (75-80%) of cases is obliterating atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a disease in which cholesterol plaques are deposited on the walls of the artery, which over time block the lumen of the vessel. Also, occlusion of the femoral artery can be caused by injury, blood clot, and some other reasons.
Factors contributing to the development of occlusion
, are:
- smoking;
- high blood pressure;
- hereditary predisposition;
- improper diet (fatty foods);
- diabetes.
Facial anatomy
The key to understanding the reasons for the development of complications after filler injections is knowledge of the structural features of the face.
Main 5 structural layers:
- Skin (it consists of epidermis and dermis).
- Subcutaneous fat deposits.
- Facial muscles, SMAS.
- Blood vessels.
- Skull bones.
With any contour plastic surgery, there can be either a standard number of dangerous zones or an increased number - if, for example, surgical interventions were previously performed in the facial area. At the appointment, the cosmetologist asks the patient in detail about diseases and operations previously undergone - this allows him to assess the risks as accurately as possible and reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions to a minimum.
Treatment methods for femoral artery occlusion
With limited occlusion, the body can compensate for the blood circulation of the limb using blood flow through the lateral branches of the arterial system (collateral circulation). In this case, conservative treatment is possible.
With increasing severity of ischemic symptoms, intermittent claudication occurring after less than 100 meters of walking, pain at rest, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment. Such symptoms mean that circulatory compensation is insufficient, and this threatens the development of ulcerative-necrotic changes, gangrene and loss of limb.
Surgery
In the surgical treatment of occlusion, depending on the area of artery damage, the following are used:
- endarterectomy (removal of atherosclerotic deposits from the lumen of the artery);
- femoropopliteal bypass surgery;
- femoral-tibial bypass (if there is concomitant occlusion of the popliteal artery).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Blog
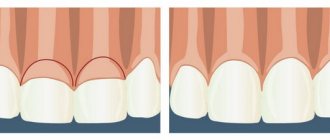
Water continuously rises from the depths of the skin to its surface and then evaporates. If you slow down its evaporation by covering the skin with something gas-tight, the water content in the epidermis will increase quite quickly. This method is called occlusal.
If the film is completely impenetrable, the epidermis will become too wet, which will lead to swelling of the stratum corneum and destruction of the barrier. A so-called “greenhouse” effect will be created.
But a semi-permeable film slows down, but does not completely stop, the evaporation of water. It will relieve the symptoms of dryness without damaging the skin.
Ingredients that slow down water evaporation vary in occlusion strength:
• Mineral oils, petroleum jelly, liquid paraffin are hydrocarbons, petroleum products;
• Lanolin is an animal wax obtained from sheep wool;
• Animal fats – goose, whale, pork;
• Squalene and its derivative squalane are a natural component of human sebum; obtained from shark liver and some plants;
• Vegetable oils rich in saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids. For example: shea butter (karite), mango, prakaxi, cocoa, etc.
• Natural waxes – beeswax, vegetable waxes.
Vaseline and other mineral oil derivatives create too much occlusion, and can slow down the restoration of the epidermal barrier - the cells will not receive a signal in time that the barrier needs repair. Therefore, choose cosmetics that do not contain these components! Owners of combination and oily skin should especially pay attention to this.
Give preference to cosmetics that contain components that create a slight occlusion: natural waxes, vegetable oils and vegetable squalane.
Occlusive creams quickly eliminate dry skin, reduce inflammation and itching in skin diseases. They are necessary for the skin, for example, for protection in winter. However, they should be used only at the initial stage, since they do not act on the cause of skin dehydration - a violation of the barrier function of the stratum corneum.
Components related to the skin will help restore the stratum corneum. These are ceramides, cholesterol and oils, especially rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids Omega-3 and Omega-6. However, you should be patient: the process of restoring the stratum corneum is not quick, but as a result you will get healthy skin that can withstand the aggressive effects of the environment.
Be beautiful and healthy, BFN team.
How to cure occlusion?
Methods for treating occlusion involve drug therapy and surgery. Further recommendations from the doctor on the most appropriate course depend on the degree of advanced disease and the affected area. Conservative treatment is used in the early stages of the disease and consists of taking the following medications:
- antithrombosis drugs;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- aimed at correcting blood pressure;
- anticoagulants;
- improving blood flow;
Surgical intervention to treat occlusion is intended if conservative measures do not bring results. And also in the case of advanced forms, with the threat of death. When the time is counted on the clock. Operations are carried out in the following ways:
- bypass;
- embolectomy;
In advanced cases, when there is death of certain parts of the limb, the only treatment method is amputation.
The disease develops quickly and has serious consequences. To prevent occlusion, it is necessary to follow a healthy diet and exercise regimen, as well as quit smoking and avoid stressful situations. It is also necessary to visit a phlebologist at least once a year
Symptoms of thrombosis of the central vein branch
In more than 60% of cases, it is not the central retinal vein (CRV) itself that is thrombosed, but one of its large branches. The patient, as a rule, does not experience pain or any other physiological discomfort, but pays attention to a sharp deterioration in vision (which may be limited, for example, only to distinguishing fingers on an outstretched hand), illusory fog or a veil before the eyes, as well as the appearance one or more scotomas (scotoma is a local “blind” area in the field of view). In most cases, it is these complaints that bring a patient to an ophthalmologist, although the so-called the prethrombotic stage begins to develop much earlier and can be detected during an ophthalmological examination, for example, a preventive one (all that remains is to draw reasonable conclusions from this information).
Treatment of central retinal vein thrombosis
The main and mandatory condition for a favorable prognosis is the immediate initiation of responsive therapeutic measures when thrombosis begins, and even better - in the prethrombotic phase.
In addition to the above-mentioned Lucentis injections and laser coagulation, such measures may include the following prescriptions. Streptokinase and hemase in injections have a partial thrombolytic and good fibrinolytic (resolving hemorrhages) effect. Antihypertensive eye drops are used to stimulate retinal circulation.
Swelling is relieved with injectable dexamethasone and/or diprospan.
However, one of the most important tasks remains the cessation of neovascularization and the hemorrhages caused by it; here the first choice means are laser coagulation of the retina, injections of Lucentis or Ozurdex.
Possible complications: how they manifest themselves and what to do
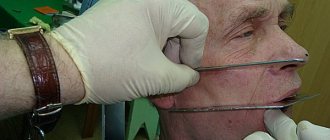
Any change in skin tone immediately after administration of the drug may indicate vascular ischemia. Symptoms of arterial and venous occlusion are complete discoloration of the epidermis or its darkening to a bluish-gray tint, reticular erythema, ecchymosis, severe headaches. The main thing in this case is to start blood flow processes in the affected area. Ways to do this (done by a doctor!):
- applying a compress (it should be warm);
- massage aimed at dilating blood vessels and uniformly dispersing the drug;
- the use of stimulant drugs to dilate external blood vessels;
- taking aspirin;
- hyaluronidase injections (if problems are caused by hyaluronic acid preparations);
- corticosteroid injections (anti-inflammatory/immunomodulatory drugs);
- taking systemic antibiotics;
- antiviral therapy (indicated when there is a threat of necrosis in the perioral zone).
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and a course of laser procedures may be prescribed several months after the injection of filler and the development of occlusion. Although this complication is very rare, it is worth knowing about. To avoid damage to the vessels of the retina, fillers are not injected into the area of the glabella and the upper part of the nasolabial folds.
Upcoming events
2021-09-01BASIC COURSE ON DENTAL IMPLANTATION WITH DR. FRIEDMAN FOR STUDENTS AND RESIDENTS (Annual course)
2022-02-05International Implantology Congress
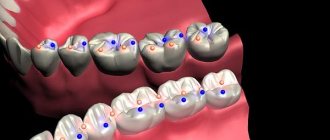
Rice. 7.The force vector is oriented in the orthograde (natural, physiological) direction along the axis of the implants. It should be noted that the central fossa (Fossa) of the lower molar is additionally shifted in the lingual direction, i.e., lingualized.
Diagnosis of acute vascular occlusion of the extremities
The diagnostic algorithm for suspected acute occlusion of the vessels of the extremities involves conducting a complex of physical, laboratory, and instrumental studies. Palpation of the pulse at typical points (on the dorsal artery of the foot, in the popliteal fossa, on the posterotibial and femoral arteries, etc.) reveals the absence of pulsation of the artery below the occlusion and its preservation above the affected area. Important information during the initial examination is provided by functional tests: marching (Delbe-Perthes test), knee phenomenon (Panchenko test), determination of the zone of reactive hyperemia (Moshkovich test).
Laboratory blood tests (coagulogram) in acute occlusion of the vessels of the extremities reveal an increase in PTI, a decrease in bleeding time, and an increase in fibrinogen. The final diagnosis of acute occlusion of the vessels of the extremities and the choice of treatment tactics are determined by ultrasound data (duplex scanning) of the arteries of the upper or lower extremities, peripheral arteriography, CT arteriography, MR angiography.
CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches. Complete occlusion of the lumen of the left internal iliac artery
Differential diagnosis is carried out with a dissecting aneurysm of the abdominal aorta and acute thrombophlebitis of the deep veins.