A common reason for visiting a dentist is a lump on a child’s gum. Upon examination, the doctor discovers a round formation of varying degrees of density, painless or with a mild pain symptom.
In most cases, in the area where the pathological element occurs there is a dilapidated or filled tooth. But sometimes the tooth turns out to be intact (undamaged), and the surrounding gum has a normal color. The reasons for the appearance of a lump can be varied. To determine them, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Causes of dental cysts in children
Most parents do not seriously care about the health of their children’s teeth until they replace their baby teeth with permanent ones, arguing that the baby teeth will fall out anyway. This opinion is wrong - it is quite possible for a cyst to appear on a child’s baby tooth.
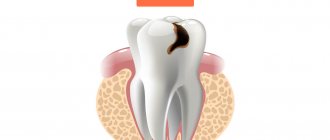
If caries has progressed to pulpitis, and then to periodontitis, then such a tooth becomes a source of infection, and the body, in order to stop its spread, turns on self-defense. To do this, it forms, most often at the root of the tooth, a protective bubble, or granuloma, which then transforms into a jaw cyst.
But not only advanced dental diseases can cause the formation of a tooth root cyst. Any injury, from cracking nuts to a blow to the jaw, can trigger the appearance of a dental cyst in a child. Those parents whose children are young hockey players or boxers need to be especially careful.
Also, if the treatment of pulpitis is poorly carried out, the infection will reach the roots through the canals of the tooth, as a result of which a rare type of dental cyst in children may occur - follicular, which occurs only in 6% of cases. The only thing you can wish for in such circumstances is to approach the choice of clinic and doctor competently and with all seriousness, otherwise your teeth will have to be constantly re-treated.
In addition, there is such a thing as an eruption cyst. It occurs several weeks before the appearance of a new baby or molar tooth. Teething cysts in children can be caused by infection, trauma, caries, or dental abnormalities.
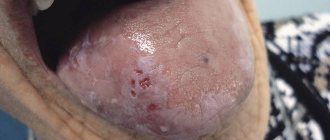
Photo of eruption cyst in children
Causes
The cyst appears as a tumor under the cheekbone, protruding from the outside. If left untreated, inflammatory processes appear, which can lead to the formation of an abscess or phlegmon. The pathology is a rare formation, usually diagnosed before the age of thirty. Place of development - on the lips, cheeks, palate, less often - in the sublingual ducts. Very rare is the pathology of the glands that develops in the parotid and mandibular areas.
The causes of this pathology are:
- injuries, wounds of the mucous membrane;
- mucus plugs that appear in the ducts;
- stomatitis and other inflammatory processes leading to obstruction;
- formation of salivary stones;
- pressure on the ducts;
- scar type narrowing.
Causes also include developmental defects, genetic predisposition, and damage to certain tissue areas. But more often the problem develops against the background of tissue injury and inflammatory processes. Wounds are formed by frequent biting of the cheek or tongue, due to the abuse of rough, spicy food, and hot dishes. In addition, such injuries can cause gland atrophy, so they cannot be ignored.
How dangerous is a cyst?
At first, when a cyst forms, the child may not complain of discomfort, so the cyst increases in size without making itself felt. But at one point, a cyst on the gum of a child’s baby tooth may fester—then, when the shell of the cyst ruptures, all its contents will spill into the bone tissue, opening access to infection.
The child may experience swelling in the jaw and even facial asymmetry. Further spread of pus is fraught with serious consequences - odontogenic periostitis, destruction of the jaw bone, diseases of the digestive system, kidneys, liver, heart, bone marrow damage and the subsequent development of osteomyelitis. The disease may also be accompanied by a fistula on the child’s gum.
Photo of a tooth cyst in a child
Purulent lump
The main reasons for the development of pustules on the gums:
- The most important factor that leads to the formation of a purulent lump or gumboil is periodontitis, which develops as a result of untreated caries. In this case, the size of the carious defect does not matter, and even the smallest lesion can cause a strong inflammatory reaction.
- Also, the cause of the formation of an abscess over a tooth can be an injury received from a fall or blow.
- Sometimes flux is a consequence of tissue damage from sharp objects (for example, if a child has the habit of chewing a pencil or toothpick).
Manifestations
The symptoms of this pathology are quite specific. At the initial stages of development of the purulent process, the child complains of pain and a feeling of fullness in the tooth area. At this time, a red swelling appears on the gum in the projection of the tooth root, which gradually increases in size, and pus accumulates in its center. This lump is soft to the touch and hurts when you press on it. As inflammation progresses, the formation becomes whitish and a white abscess forms.
At the same time, the general condition of the baby may suffer. Children become restless, refuse to eat, and their temperature rises.
If full treatment is not carried out at this stage, then as pus accumulates, the pressure inside the abscess increases and spontaneous opening of the white lump occurs. In this case, a fistula is formed, which connects the surface of the gums with the pathological focus. After the lump bursts, the child experiences relief of symptoms: pain decreases.
As the inflammatory process subsides, the fistulas can close on their own, but this does not mean that recovery has occurred, since the pathological focus itself remains unsanitized. With a decrease in the protective properties of the body, the disease can be activated with the reappearance of an abscess and fistulas.
Treatment
If a purulent lump is detected in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to contact the dentist as early as possible.
If the cause of the formation of an abscess or fistula is a baby tooth, then treatment will be reduced to its urgent removal. It is impossible to leave such a tooth, since the preservation of even a slight focus of inflammation can lead to the death of the permanent tooth germ.
If flux has formed over a molar, then all therapeutic measures will be aimed at preserving it. In this case, the dentist will open the lump, clean the cavity from purulent masses and treat it with an antiseptic. Removing a permanent tooth is a last resort and is carried out only when there is significant destruction.
Complications
Despite the fact that purulent bumps are rarely large, their complications can be extremely serious and dangerous.
- The death of the rudiments of permanent teeth leads to edentia. Such a condition in childhood can cause improper development of the maxillofacial apparatus and bite pathology, which will require serious orthodontic treatment in the future.
- Chronic purulent lesions and fistulas in the oral cavity are a source of infection, which can spread and cause inflammation in other organs: tonsils or adenoids.
- The constant inflammatory process changes the activity of the immune system, which becomes more sensitive to the effects of various allergens. In this case, the child may develop hypersensitivity reactions even to those substances to which allergies were not previously observed.
- If the abscess does not open outward, then the pus can spread deep into the tissues with the formation of phlegmon - a severe complication that is life-threatening.
Memo to parents
If you find a purulent lump in your child, then you need to remember several important nuances:
- It is strictly forbidden to try to open an abscess on your own. This can lead to pus entering the bloodstream and the development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
- You cannot carry out any warming procedures: apply compresses or rinse your mouth with hot liquid. This will only worsen the inflammation.
- Cold can be applied externally to the cheek in the area of the lump; this will somewhat alleviate the symptoms and slow down the development of the abscess.
- At the first symptoms of gumboil, you should contact your pediatric dentist for professional treatment.
Treatment and removal of a dental cyst in a child
In a child, treatment of a dental cyst is carried out using surgical methods, depending on the case, cystotomy or cystectomy is used. As a rule, treatment uses anesthesia in pediatric dentistry or sedation. During cystotomy, only the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. This method is the least traumatic, since, for example, it preserves the rudiments of permanent teeth during surgery on a baby tooth.
A cystectomy is an operation that involves cutting the gums and completely removing a dental cyst in a child. If the size of the cyst does not exceed 1.5 cm, then a cystectomy with resection of the root apex is performed. Compared to cystotomy, the operation is more traumatic, but the postoperative period is shorter.
If the causative tooth is permanent –
In this case, the tooth is not only possible, but also necessary to be saved.
If permanent teeth in children have already formed roots, then treatment of permanent teeth with periodontitis will be carried out as in adults. However, treating a permanent tooth with incomplete root formation will present some difficulty, because such teeth may have very wide root canals as well as gaping apical foramina (see photo below). And this poses a great difficulty for high-quality filling. Permanent tooth with incomplete root formation –
Currently, in pediatric therapeutic dentistry, there are 2 main approaches to the treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth with incomplete root formation. The first method is based on temporary filling of root canals with materials based on calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide. This requires a long, months-long exposure of these materials in the root canals (with periodic replacement of the material with fresh portions). This will narrow the width of the apical foramen by creating an osteocement apical barrier, after which it will be possible to perform permanent filling of the root canals.
The duration of such treatment usually ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 years. If a water-based material with calcium hydroxide is used, then it needs to be changed in the root canals monthly, but if it is oil-based - only once every few months. The disadvantage of this method is the need for frequent repeat visits, and the effectiveness is only about 70-90%, because the emerging osteocement barrier has a loose porous structure and does not guarantee 100% reliable sealing of the root canal lumen.
The second method is a one-step technique for forming a barrier in the area of the apical foramen using materials from the MTA group (mineral trioxide aggregate). An example of such material is “Pro Root”. The method assumes that the apical part of the root canal for 3-4 mm will be permanently sealed with MTA. Thus, in this case, only 1 visit is required, but it is best to use this method only in the last stages of root formation (otherwise, it will be best to combine temporary filling with calcium hydroxide-based material for 1-2 months + subsequent permanent filling with MTA) .
Prevention is the best cure
You can detect a cyst in children in the early stages of formation on an x-ray, which is recommended to be taken every six months if the child has diseases such as chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. Cysts are most likely to appear in children aged 7 to 12 years, during the period when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. The cyst forms mainly in the area of the first molars, most often on the lower jaw.
The child must be taught regular, and most importantly, high-quality oral hygiene. If you don’t do this and don’t take your child to the dentist, the consequences can be disastrous. It is also worth taking note of the following: firstly, it is possible and necessary to treat pulpitis and caries of baby teeth; secondly, severely affected by caries is an indication for the removal of a baby tooth, which should be carried out in a timely manner, otherwise they will become a source of infection and subsequently provoke the appearance of a cyst.
You, as a parent and person responsible for the health of your children, must monitor the condition of the entire oral cavity from the first erupted tooth of your child. Remember: the visible part is only 40% of the entire tooth, so you should not assume that its healthy appearance indicates the health of the entire tooth. Don’t forget about going to pediatric dentistry - any disease in the early stages can be treated much easier and more effectively.
Preventive measures to prevent the formation of lumps on the gums
To reduce the likelihood of an abscess to a minimum, a child from childhood should be taught to carefully observe oral hygiene.
The list of the most effective measures includes:
- Brushing your child's teeth twice a day. First, parents should brush their child’s teeth themselves, showing how to do it correctly, gradually giving the child more independence in this matter;
- rinsing your mouth after every meal;
- minimizing sweets in the diet - it is important to ensure that the child keeps caramel and candies in his mouth as little as possible;
- Do not introduce your child to chewing gum (the product is especially harmful if it contains sugar).