Herpesvirus infections are a group of infectious diseases that are caused by viruses from the Herpesviridae family, can occur in the form of localized, generalized, recurrent forms of the disease, and have the ability to persist (the virus is constantly present) in the human body.
Herpesvirus infections (HVI) are among the most common human viral diseases. Their infection and morbidity rates are increasing every year. In all countries of the world, 60-90% of the population is infected with one or another herpes virus.
Types of herpes in infants
For babies in the first year of life, herpes comes in different types. The forms in which the herpes virus manifests itself are as follows:
- generalized;
- neurological herpes in newborns;
- localized.
In the first case, the generalized form of herpes in infants has the following clinical picture. The virus affected the internal organs and led to intoxication. The baby has difficulty breathing, he may vomit and belch, and the fever can sometimes be very strong.
With the neurological form of herpes, the virus spreads its influence to the nervous system and brain. If the infection occurred in utero, the child may have the following deviations from normal development: microcephaly, hydrocephalus, and the formation of calcifications. Symptoms here vary and are not always typical. The newborn baby appears lethargic or cries incessantly. In addition, the baby may experience a swollen fontanelle and convulsions. Localized herpes in infants. The virus appears in limited places on the child's body. These are the eyes, nasolabial area, etc.
In addition, herpes can be primary or secondary. Primary herpes in newborns can be a consequence of infection of the baby's mother during pregnancy. In addition to transmission of the virus through the placenta, the infection can be transmitted to the fetus during childbirth, when the baby passes through the birth canal. The method of entry of the herpes virus can also be domestic. A baby can become infected with the disease through the belongings of other children or through airborne droplets, as well as from parents.
How does secondary herpes develop? When an infection has entered the body of a newborn, it may not immediately manifest itself. The virus is suppressed by antibodies that the baby's mother transmits to him along with milk during breastfeeding. If the baby’s immune defense decreases, the herpes virus will be activated. In this case, the infection will spread throughout the body, approaching the skin and mucous membranes; visual manifestations of herpes will be visible as a specific rash.
The worst thing is if herpes in infants occurs on the genitals. In this case, the virus can infect the bladder and ureter. Also, such herpes, and it is called genital, can affect important internal organs, including the heart.
Development of infection
A decrease in the child’s immunity for various reasons contributes to the occurrence of herpes, for example, caused by factors such as emotional and physiological stress, exacerbation of chronic and the appearance of acute diseases. In addition, children under 3 years of age have a physiologically weakened immune system, and therefore are especially susceptible to contracting a herpes infection. The first appearance of symptoms of a herpes infection is possible against the background of a developing or passing cold. And if herpes has settled in the body, then its activity can manifest itself in the presence of other diseases, for example, acute respiratory viral infections, which significantly suppress the immune response.
Symptoms and localization of herpes in infants
Manifestations of herpes can be in different places of the newborn’s body. Depending on what type of herpes virus infected the baby, the distribution of manifestations will be different. So, we will tell you the symptoms in each case in order.
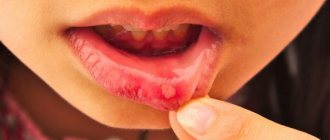
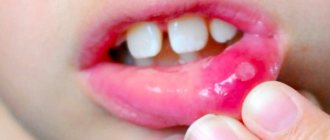
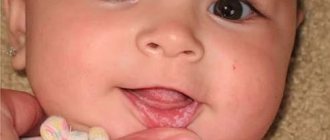
Simple herpesvirus type 1. The manifestation of infection on the lips of the newborn, as well as in the nasolabial area. The rashes are filled with liquid and are small in size. The liquid becomes cloudy over time, and the so-called blisters burst. In place of the burst blisters, wounds appear, which disappear after a while.
The second type, genital. Localization area: genitals, anus. The rashes are small and filled with liquid. The affected area itches and burns. There is also discomfort when emptying the bladder. Lymph nodes enlarge.
The third type is called chickenpox. The rash covers the entire body. They are present not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. This herpes in infants is characterized by an increase in body temperature, the child looks lethargic and weak.
Herpesvirus type 4. If the form is uncomplicated, then there are no symptoms. With the development of infectious mononucleosis, the tonsils and palate are affected. The virus can infect the spleen and liver, and the composition of the blood changes. Symptoms: general malaise, apathy, weakness. In addition, the child has a stuffy nose, a sore and red throat. Lymph nodes become larger in size. The rashes are pinpointed, they look like tiny hemorrhages or pink blisters on swollen skin.
Fifth type. In most cases there are no symptoms. However, there are also characteristic manifestations of this type of herpes in a child. With cytomegalovirus mononucleosis, intoxication of the body begins. This is expressed in a sharp rise in temperature to 39 degrees, a sore throat, and the nasopharyngeal mucosa is red. In difficult cases, infants have pain when swallowing. The child has difficulty breathing, hearing partially or completely disappears. Sometimes internal organs are damaged.
Virus type six. Increased temperature, changes in lymph nodes. The rash is papular-spotty, pink in color. This herpesvirus can cause immunodeficiency in children.
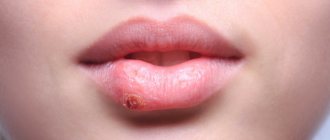
Labial herpes (herpes on the lips, cold sores on the lips)
Labial herpes is a highly contagious and common viral infection caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (less commonly type 2). Most people by the age of puberty already have this virus in their body and are its carriers, even without symptoms. After infection, the virus “sleeps” for some time in the nerve cells of the facial skin, and when activated, it causes a cold on the lips. Exacerbations may be caused by a viral infection or fever, hormonal changes, increased fatigue or stress, prolonged or intense exposure to sunlight, decreased immunity, or skin trauma.
The herpes simplex virus is transmitted through close contact (for example, by kissing), and is contagious even in the absence of obvious rashes on the lips. It appears as small, painful blisters (filled with clear fluid) on the lips (sometimes near the mouth or nose), which are usually grouped together, so the size of the lesion can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
After the bubbles burst, a crust forms in their place. Herpes on the lips usually goes away in 2-3 weeks, leaving no scars.
The disease occurs in several stages. The initial symptoms are tingling, itching or burning in the lips, then blisters appear, which merge and burst over time, leaving small wounds oozing liquid, after which a crust forms in their place. The first episode (manifestation) of the disease may be accompanied by fever, sore throat, sore muscles, headache, sore gums, and swollen lymph nodes. Recurrent infection is usually milder. Symptoms of cold sores most often occur in children between 1 and 5 years of age.
In the typical course of the disease, diagnosis does not require the use of specific studies; it is enough for the doctor to conduct an examination and find out the medical history. Diagnosis is usually based on symptoms.
There are no medications aimed at the cause of the disease. As a rule, herpes on the lips goes away on its own, without treatment. The healing process can be accelerated by using antiviral drugs in the form of ointments or tablets (acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir). Reducing discomfort and pain is achieved through the use of local products containing alcohol (dries and accelerates healing), lidocaine or benzocaine (for very uncomfortable and painful conditions), antipyretic and analgesic drugs (for fever, severe pain). Cold compresses reduce redness and help remove crusts.
Before going outside, lips and face should be protected from the sun (with a product containing zinc oxide) and moisturizing balms should be used.
It is necessary to consult a doctor if herpes on the lips of a child does not disappear within 2 weeks, the disease is severe, there is irritation in the eyes during an exacerbation, relapses of herpes occur frequently, the child has a weakened immune system (due to some disease), there are diseases such as atopic dermatitis.
When to see a doctor
With a primary infection, the child almost always develops a fever. The baby has no appetite, anxiety, crying, and sleep disturbances. If one of the above symptoms is present or if there are several of them, you need to immediately show the newborn to a specialist - a pediatrician (children's doctor) or a dermatovenerologist.
If the infection develops, it can lead to complications, including death. The herpes virus in newborns should be identified as quickly as possible so that treatment can begin without delay. If there are signs of herpes in an infant, you can visit JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) in the center of Moscow. The Pediatrics Department has a staff of highly qualified specialists, new generation equipment and instruments for examination. You can make an appointment with a pediatrician or dermatovenerologist on the website or by calling +7(495)993-00-33.
Prevention of herpes
The basic rules that will help reduce the likelihood of infection with viruses of the herpes family are:
- hand washing;
- limiting contact with sick people;
- nasal instillation with saline solutions during the off-season.
There is now a vaccine against chickenpox. Vaccination helps prevent infection and/or development of severe forms of the disease. “SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary medical institution that provides effective treatment to children facing various diseases. Herpetic infection in any of its manifestations is not a problem. The main thing is to schedule a consultation with our specialists on time. Contact us!
Diagnostics
Herpes has been detected in a child - what to do? You need to undergo examination at a clinic to detect the virus in the body. Diagnostic measures are as follows:
- blood tests - general and chemical;
- taking a smear from the mucous membranes;
- collecting liquid from the cavity of the bubbles;
- scrapings at the affected areas;
PCR is also used to identify the type of herpes virus. If a clinic specialist suspects that the child has damage to the liver, spleen, nervous system and other internal organs, you will be prescribed an MRI, CT scan and ultrasound.
About the disease
Herpetic infection is a collective concept that is used to refer to diseases that are provoked by different types of the virus of the same name.
Traditionally, in pediatric practice, pathology caused by type 1 is encountered. This is the so-called labial herpes (rash on the lips). Its peculiarity is its chronic course. It is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. With adequate treatment of a child with symptoms of labial herpes, stable remission can be achieved. However, at this time the virus “hides” in the nerve ganglia (ganglia), where it can remain inactive for as long as desired. When favorable conditions arise (primarily decreased appetite), it is activated again. Another common form of herpes infection that can occur in children is varicella (chickenpox). The disease is provoked by the herpes virus type 3. It is important to remember that after successful recovery, the pathogen also goes into a latent form and persists in the nerve ganglia. The risk for the patient may be a reoccurrence of the infection. The type 3 virus, when reactivated, can cause herpes zoster, which is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture with a deterioration in the child’s well-being and the appearance of rashes along the intercostal nerves.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have extensive experience in early diagnosis and treatment of all pathologies caused by herpes viruses. Doctors provide the necessary monitoring and quality treatment for children with any form of herpetic infection.
Treatment
If herpes is detected in a child, the following treatment is prescribed. These are antiviral drugs (tablets and ointments), immunostimulants, and interferons are also prescribed. The method of use - tablets, ointments or even injections - is determined exclusively by the attending physician. The dosage is prescribed individually for each little patient. Self-medication in this case is extremely dangerous and can lead to tragic consequences. You must strictly follow all doctor's instructions to avoid further complications.
Let's talk in detail about medications that can be prescribed to infants:
- drugs to suppress infection;
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants;
- antipyretics and pain relievers (suppositories, suspensions);
- antihistamines;
- antiseptics;
- antibacterial agents if microbial infections have joined the virus;
- To heal and dry wounds and ulcers on the body, brilliant green and sulfur-based ointments are prescribed.
Also, if a child has symptoms such as convulsions due to herpes, then anticonvulsant medications are prescribed. To relieve itching on a child's skin, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used. This is chamomile, calendula. You can also use rosehip oil, etc. Such products will not only remove discomfort on the skin where there is a rash, but will also help the wounds heal faster and relieve inflammation.
The baby needs to drink plenty of fluids. If a mother feeds her baby with breast milk, then she needs a balanced and proper diet. You should consume foods rich in vitamins and microelements. As auxiliary measures, isolation of the newborn from contact with strangers and maintaining the personal hygiene of mother and baby at a high level are used. Care must also be taken to ensure that the baby does not scratch the affected areas. To do this, use clothes that cover the baby's fingers. It is sold in special stores for newborns. They also use so-called scratch pads, hand pads, etc.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy 1 element | 700 rub. |
| Setting up functional tests | 190 rub. |
| Excision/removal of cutaneous/subcutaneous elements and formations (1 element) | 2550 rub. |
| Removal of milia of one unit using electrocoagulation | 350 rub. |
Complications of herpes in infants
What are the complications of herpes in a child? In infants, herpes can be complicated by the following types of diseases:
- the cardiovascular system is affected;
- cerebral palsy;
- paralysis;
- disturbance in the hematopoietic process;
- encephalitis;
- herpes eyes;
- meningitis;
- hepatitis;
- eczema Galoshes.
To prevent the development or occurrence of the disease, it is worth making sure that the baby’s immune defense is at a high level. It is necessary to carry out hardening procedures and ensure that the child spends enough time in the fresh air. It is important to maintain a certain temperature and humidity in the nursery.
During the prenatal period, expectant mothers need to be screened for the herpes virus. Pregnant women should also take precautions to avoid infection. For example, do not communicate with people who carry this virus, do not use their things, etc.
Therapy for herpes infection
Herpes in children requires the most careful treatment. It includes:
– prescription of antiviral drugs that inhibit the reproduction of the virion, destroy and remove the virus from the body (for example, acyclovir, Zovirax),
– correction of the immunological status (alpha-2b interferon preparations), responsible for containing viral aggression towards the child’s body,
– symptomatic therapy (anti-inflammatory, disinfectants, painkillers, detoxification agents), the need for which is higher, the younger the child’s age, the prevalence of herpetic rashes and the worse the general health.
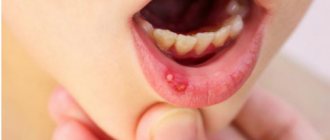
Herpes aphthous stomatitis
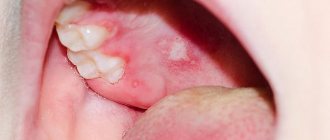
In children under 5 years of age, herpes simplex can affect the mouth, gums, and tongue (herpes aphthous stomatitis). In this condition, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity turns red, swells, the child begins to drool, small superficial ulcerations (aphthae) appear once within 1–2 days - single or grouped, the child becomes irritable, his gums swell, he complains of pain, loses appetite. The temperature usually rises (can reach 40°C) 1-2 days before the above symptoms.
After 3–14 days from the onset of symptoms, the child’s condition returns to normal, the temperature decreases, aphthae heal, inflammation and pain decrease, and appetite appears. With a more severe course, a repeated increase in temperature, aphthae may appear again, and the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged. Recovery in this case may take up to 10 days. A complication of herpes aphthous stomatitis can be the transition of the disease to a recurrent form. The addition of a bacterial infection can cause otitis media, bronchitis or pneumonia.
Treatment of herpes aphthous stomatitis is aimed at eliminating symptoms (lowering temperature, pain relief with paracetamol or ibuprofen, drinking plenty of fluids, rest). Rinsing with aseptic solutions, the use of local anesthetics, antiviral ointments for treating aphthae (acyclovir), steroids in the form of gels and pastes are prescribed. Local treatment with lidocaine-based anesthetic ointments should not be administered to young children.