Causes of diseases of the oral mucosa
Diseases of the oral mucosa occur throughout life in an average of 5-10% of the population.
Their cause may be:
- Traumatic damage to the tissues of the oral cavity and other traumatic effects (chemical, thermal, etc.) with the development of traumatic erosion, ulcers, leukoplakia or leukokeratosis (keratinization of an area of the mucous membrane capable of malignant degeneration).
- Infectious diseases that affect the oral mucosa due to the penetration of viruses, spirochetes, bacteria, and fungi.
Quite often, the occurrence of pathological changes in the oral mucosa is associated with disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems of the body: allergies, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, systemic connective tissue diseases, blood diseases, dermatoses, tuberculosis, AIDS and some other conditions. It is often quite difficult to identify the true cause of pathology of the oral mucosa - a lot of experience, high professionalism, and the ability not only to carefully collect information, but also to interpret it correctly and draw appropriate conclusions are required. Experienced medical dentists will quickly understand the intricacies of the existing manifestations of the disease in relation to a specific patient, determine the cause of the disorder and prescribe highly effective treatment.
When to contact a periodontist
Patients who come to see a therapist are most often sent to the periodontist's office. After listening to complaints, collecting anamnesis, examining the oral cavity and identifying symptoms characteristic of gum disease, he gives a referral to a highly specialized specialist who is more competent in solving such problems:
- mucous membranes bleed during hygiene measures after chewing
food ania; - mucous membranes have changed color and are swollen;
- discharge of pus is noticed;
- a putrid smell appeared;
- the sensitivity of units to external stimuli has increased;
- grayish-white spots appeared on the gums;
- The intersegmental spaces have widened and food debris has become more likely to get stuck in them;
- stony deposits have formed on the enamel of the segments, a soft coating in hard-to-reach areas that cannot be removed with home hygiene products;
- there is pain while eating;
- The volume of the gums has decreased, the necks of the teeth have become exposed;
- periodontal pockets have formed;
- the teeth began to loosen;
- the position of the segments in the row has changed.
The periodontist will conduct a thorough examination, determine the periodontal status, make a reliable diagnosis, and prescribe adequate treatment. The duration and range of manipulations depends on the neglect of the process.
After completing therapy, it is necessary to visit the doctor according to the prescribed schedule for a follow-up examination and, if necessary, repeat the course of periodontal intervention. Your periodontist will help you maintain the health of your gums so that your smile can once again be admired by others.
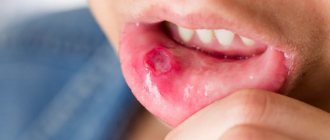
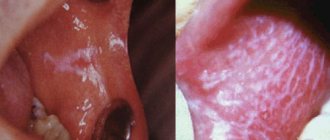
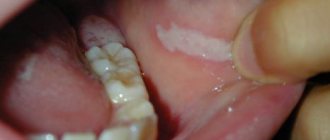
The main manifestations of diseases of the oral mucosa
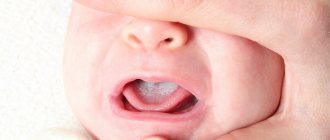
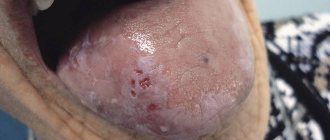
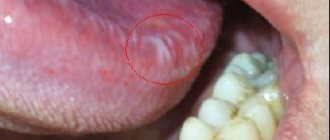
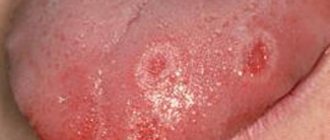
There is a common name for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa - stomatitis. When the pathological process is localized on the tongue, they talk about glossitis, on the gums - about gingivitis, on the lips - about cheilitis. A characteristic manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance on the oral mucosa of foci of redness, blisters, erosions (afts) or ulcers covered with plaque. These lesions are most often detected on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard palate, and tip of the tongue. Often there is pain at the location of erosions and ulcers, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in body temperature. The average duration of the disease is 7-14 days. Stomatitis can recur with decreased immunity, poor diet, hypovitaminosis, infectious diseases, and exacerbations are more common in spring and autumn.
Oral tumors: detection and treatment
REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE
Tumors are divided into two groups: epithelial and nonepithelial.
The most common tumors are those that develop from glandular, flat, and tooth-forming epithelial tissue. Depending on their location, tumors of the gums, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, hard and soft palate, as well as the salivary gland in the sublingual area are distinguished.
The causes of benign tumors of the oral mucosa are not entirely clear. Based on experience and observations, doctors give the following recommendations to minimize risks:
- Monitor the condition of chronic ulcers and cracks formed due to poor-quality dentures and crowns or injury to soft tissues from chipped teeth.
- Avoid using tobacco in any form. Its long-term use can lead to consequences in the form of a tumor.
- Avoid eating too hot foods, spices, alcohol and foods high in acids. This will prevent burns and irritation of the mucous membrane.
A timely visit to a specialist when the first symptoms are detected can save you from cancer: a dangerous disease that is difficult to treat.
TYPES OF NEW FORMATIONS
Neoplasms arise in various types of tissues of the oral cavity: connective tissues, bones, nerves and muscles. Some tumors cause irritation and discomfort. It is possible to notice them on your own, but often they are discovered only by a specialist during an examination. Benign tumors are divided into several types:
Epithelial:
Papillomas. They consist of stratified squamous epithelial cells localized on the tongue, lips, soft or hard palate. Papillomas resemble a protrusion on the mucous membrane with a smooth surface or papillary growths. Usually papillomas are single, but multiple ones are also found. Over time, they become overgrown with keratinized epithelium and become whitish and rough.
Nevi. In rare cases, they occur in the mouth. They are convex with varying degrees of pigmentation: from pink to brown. Some nevi can transform into melanoma.
Glands of Serres. They are located in the area of the alveolar process, resemble hemispherical dense formations of light yellow color, and can be multiple.
Connective tissue:
Fibroids. Often found in the tongue area, on the palate and lower lip. These are oval or round formations that are difficult to notice: their color blends with the mucous membrane.
Myomas. Usually develop from muscle tissue. Observed in the thickness of the tongue in the form of nodular formations.
Myxomas. They have a lumpy, rounded or papillary surface. Localized in the area of the hard palate and alveolar process.
Epulis. They arise on the gum, growing from its deep layers, as well as from the periosteum and periodontal tissues.
Pyogenic granuloma. It develops from the connective tissue elements of the oral cavity and from the mucous membrane after injury. It grows quickly, has a burgundy color, and bleeds when touched.
Neuromas. They are the result of the proliferation of Schwann sheath cells of nerve fibers. One of the few formations that causes discomfort upon palpation.
Vascular:
Hemangiomas. They are among the most common. They are divided into capillary, cavernous, capillary-cavernous and mixed. They turn pale or shrink in size when touched and may bleed.
Lymphangiomas. Appear due to disorders of embryogenesis of the lymphatic system. Often discovered in infancy. Visually they resemble swelling in the oral cavity, limited or diffuse. Prone to inflammation after injury to the mucous membrane or exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory disease of the nasopharynx.
At the first alarming signs, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and identification of neoplasms.
Tumor in the oral cavity: symptoms
The cause of the appearance of benign neoplasms in the oral cavity can be disturbances in the acid-base balance, neglect of hygiene, mechanical damage and bad habits. These risk factors are a serious reason to see a doctor for an examination.
There are several striking symptoms of the presence of a tumor:
- Discomfort when talking and eating.
- Unpleasant or painful sensations of a constant nature.
- Feeling of the presence of a foreign body.
Tumors do not cause any problems with your health, but you should not ignore the symptoms. Systematic irritation of the affected area can contribute to the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant one.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Oral tumors may be discovered by a dentist during an examination or treatment. Determining the depth of their germination is possible using ultrasound. X-ray examination is necessary to assess the condition of bone tissue. For gum fibromatosis, an orthopantomogram is performed to identify areas of destruction of the alveolar process.
Depending on the type of tumor, the following types of surgical treatment are used:
- Laser removal.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Surgical excision.
- Sclerotherapy.
There are diffuse tumors. They tend to grow rapidly and penetrate into the deep layers of the mucosa. Their removal is carried out in several stages. Fibromatous growths are excised along with the periosteum. Areas of affected bone tissue are treated with a milling cutter and also removed by coagulation (cauterization).
Vascular tumors are sclerosed by introducing special solutions into the tumor vessels. Active substances damage the walls of blood vessels, causing further scarring.
A tumor is a formation consisting of cells that have lost the ability to grow under controlled conditions. A separate branch of medicine—oncology—is devoted to neoplasms. This science studies the development, diagnosis and treatment of both benign and malignant tumors. A dentist can refer you to an oncologist to make an accurate diagnosis.
Extrodent specialists have a common goal: to preserve the health of patients in all available ways. This is possible thanks to high-quality technical equipment and the professionalism of the clinic’s doctors. Complex clinical cases are their area of interest and competence, so the result of their work is always successful.
We will take care of your health and give you a full life!
Diagnosis of oral diseases
Diagnosis of stomatitis and other diseases of the oral cavity is based on a thorough clinical examination of the patient by a dentist, which makes it possible to determine the stage of the pathological process and its prevalence, and the presence of a general reaction of the body to inflammation. It is very important to establish the true cause of the disease (trauma, infection, allergy, pathology of internal organs, hypovitaminosis, etc.), because the effectiveness of treatment and the absence of exacerbations in the future will depend on this. To do this, in a medical clinic, when recurrent stomatitis is detected, if necessary, a thorough additional examination is carried out with the involvement of relevant specialists - an allergist-immunologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist, endocrinologist, and laboratory and instrumental studies are performed.
Treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa
- Etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease (antiviral, antibacterial therapy for the infectious nature of stomatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, vitamin therapy for hypovitaminosis, treatment of the underlying disease that caused the appearance of a pathological process on the oral mucosa);
- Local treatment aimed at eliminating local traumatic factors, the main symptoms of the disease and the rapid healing of existing erosions and ulcers;
- A general strengthening treatment that stimulates the body's defenses.
An early visit to a dentist when identifying the first signs of pathology in the oral mucosa is the key to a speedy recovery!
What diseases does a periodontist treat?
The area of expertise of a periodontist includes the treatment of gum diseases that have developed in periodontal tissues. The most common pathologies:
- Gingivitis is an inflammatory process of the periodontal soft tissues that occurs without disruption of the periodontal ligaments.
Only the gums are involved in the pathology. The first signs of the disease are bleeding and pain in the tissues surrounding the teeth. The pathology can occur in an acute form, which is also characterized by swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, and itching. The chronic course of gingivitis causes virtually no discomfort, so a person is in no hurry to see a periodontist. Despite the asymptomatic course, the inflammatory process gradually progresses, complications arise - ulcerative-necrotic lesions, gum hypertrophy, detachment of mucosal areas, and others appear. The main cause of gingivitis is insufficient oral hygiene, which leads to the proliferation of bacteria. The periodontist usually prescribes conservative treatment, including removing plaque from teeth, using antiseptics, and antibiotics. - Periodontitis. Inflammatory periodontal disease, predominantly of an infectious nature. With periodontitis, destruction of the dentogingival ligaments occurs, and destruction of bone tissue develops. As the disease progresses, teeth begin to loosen and fall out. The disease is classified as polyetiological, since various reasons can lead to its development. Most often, the pathology develops due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. In addition, periodontitis can occur due to poor heredity or gum injury. It often accompanies diabetes mellitus and is detected in hormonal disorders and other pathologies. A periodontist dentist, examining the mouth and jaw area, identifies the presence of periodontal pockets, bleeding, redness, swelling of the mucous membranes, and a heavy odor from the mouth.
- cavities. There is plaque on the teeth. Pus may be discharged from periodontal pockets. There is an exposure of the cervical zones of the segments, displacement of the teeth in the row, and their loosening. Treatment in the early stages is conservative, later - invasive.
- Periodontal disease. Non-inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues, characterized by a chronic course. The pathogenesis is based on circulatory dysfunction in the vessels supplying the periodontium. Violation of tissue trophism leads to the development of atrophic processes in the gum and bone tissues. Other causes of periodontal disease: malocclusion, smoking, decreased local immunity, hormonal imbalance, disruption of periodontal innervation, etc. The clinical picture of periodontal disease depends on the stage of the disease. Main symptoms: gum recession, pallor of the mucous membranes, increased spaces between units, their loosening. Bleeding gums are not typical for periodontal disease.
Treatment is aimed at strengthening the periodontium with the help of hygienic measures, drug therapy, and physiotherapy. If the degree is significant, the periodontist will suggest the surgeon
logical, orthopedic correction.