Find out more
Caries
According to a study published in the medical journal The Lancet, 2.83 billion adults and children worldwide have tooth decay.
Cavities typically form when bacteria in plaque combine with sugar to form an acid that erodes enamel.
Treatment:
If you or your dentist catches tooth decay early enough, you may be able to reverse the process with fluoride medications. Otherwise, the classical treatment of caries is provided - filling.
However, if the decay gets so bad that a filling doesn't help, your dentist may crown the tooth or remove it. Again, early detection can prevent tooth decay and loss.
Choosing the right dental restoration
Dental restorations are the various ways in which a dentist can replace missing teeth or restore missing parts of a tooth structure. Tooth structure may be missing due to tooth decay, tooth loss, etc. Traditionally, the following restoration methods are distinguished:
- Fillings are the most common type of dental restoration. There are many options for filling materials. The dentist selects the most suitable one.
- crowns are a tooth-shaped “cap” that is placed over a tooth to restore its shape and size, strength, appearance, and to hold a bridge in place or cover a dental implant.
- Bridges are artificial teeth that are designed to “bridge” the gap formed by one or more missing teeth. Sometimes bridges are fixed on both sides with crowns.
- Implants replace tooth roots. Implants are a small metal rod that is inserted into the jawbone of a missing tooth.
- Dentures are a removable replacement for missing teeth and surrounding tissue. Complete dentures replace all teeth; partial dentures are installed while retaining some of your teeth, which serve as anchors for the denture.
Gum diseases
Some form of gum disease, also called periodontal disease or periodontitis, affects nearly half of adults age 30 and older. Severity ranges from mildly swollen gums to bleeding gums and complete loss of teeth.
Most gum diseases develop in several stages:
- Plaque and tartar build up on the teeth, leading to gingivitis (inflammation of the gums).
- Gingivitis irritates the soft tissue along the gum line, which gradually leads to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis occurs when the gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets. This can lead to further gum infection, requiring treatment with antibiotics, surgery, or tooth extraction.
Treatment:
Like tooth decay, gum disease in the gingivitis stage is highly treatable if detected early. If it can't be corrected, your dentist will likely suggest scaling, a professional deep cleaning to remove all plaque from your mouth. As noted, antibiotics may also be prescribed. If periodontitis is advanced, surgery may be required.
“Periodontal disease is indeed a common problem. If such diseases are left untreated, sooner or later this will lead to the formation of deep and painful periodontal pockets, and ultimately to tooth loss. In addition, the microflora that lives in the mouth is very aggressive. Once it enters the bloodstream, it can spread and complicate the course of chronic diseases of the joints, heart, lungs, and brain, causing disruption in their functioning. The relationship between the presence of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity and diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease has been proven. Getting dental plaque or the contents of periodontal pockets into the lungs when coughing can worsen the prognosis of any acute respiratory viral infection, as well as aggravate the course of COVID-19. Therefore, it is so important to monitor the condition of the periodontium, undergo preventive examinations every 6 months, and have a professional. oral hygiene, remove dental plaque, both hard and soft. When diagnosing gum disease, it is imperative to carry out timely treatment. For prevention, it is important to use simple care methods at home - brushing your teeth with high-quality toothpaste - 2 times a day, and also use dental floss, irrigators, and special rinses for additional hygiene.”
Kalashnikova Oksana Yurievna
dentist, implantologist-orthopedist, gnathologist, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in aesthetic dentistry, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, doctor of integrative interdisciplinary anti-aging medicine Work experience: 30 years
Vitamins that protect the body in general and mucous membranes in particular
Severe deficiency of any vitamin negatively affects the immune response, since each of the essential micronutrients is included in several biochemical cascades at once. For example, deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, B12 – corresponding anemia, which is accompanied by a significant decrease in protective functions. In this context, the optimal means of increasing the body's defenses are multivitamin complexes. However, some nutrients play a special role in the formation of the immune response, let's talk about them in more detail.
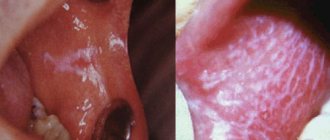
Infectious diseases
An infection of the oral cavity leads to the development of a disease in which the mucous membranes become inflamed. The pathological process can involve the teeth and gums. Symptoms of infections in the mouth are often hidden, but sooner or later they appear.
Online training in Anti-Age medicine Learn the intricacies of anti-aging medicine from anywhere in the world.
For the convenience of doctors, we have created the Anti-Age Expert online training platform: Lectures from our educational programs are consistently posted here, and are accessible 24/7. Doctors can study the materials as many times as necessary, ask questions and discuss interesting clinical cases with colleagues in special chats. Find out more
Causes of infectious diseases of the oral mucosa:
- Uncontrolled medication use.
Treatment of any disease should be under the supervision of a doctor. Improper use of antibiotics, antibacterial and other agents leads to consequences, including diseases of the oral cavity.
- HIV and AIDS.
Infectious diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity often occur against their background.
- The occurrence of infections in the oral cavity
may be associated with a weakened immune system.
- Poor nutrition.
If the mucous membrane is exposed to aggressive food, it injures it. Thus, the mucous membrane becomes more vulnerable and susceptible to infection.
In addition, smoking and alcohol provoke oral diseases. Those whose bodies are dehydrated or experience hormonal imbalances also face similar problems.
- Stomatitis.
There are many bacteria living in the mouth, and due to a decrease in immunity, they are activated. Thus, an infectious disease develops. One of the most common is stomatitis. It usually develops in people who brush their teeth incorrectly or not thoroughly enough. The disease can also occur due to tonsillitis or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. There are several types of stomatitis:
- Catarrhal.
It is manifested by swelling of the oral mucosa. As catarrhal stomatitis progresses, plaque appears on the tongue.
- Ulcerative.
In this case, the lymph nodes become enlarged. This stomatitis is manifested by dizziness and weakness. May occur in people with stomach ulcers or enteritis.
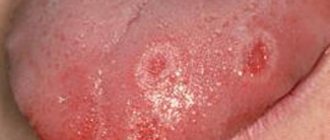
- Aphthous stomatitis.
Leads to damage to the oral mucosa, on the surface of which erosions form. Aphthous stomatitis is associated with an imbalance in the gastrointestinal tract. Signs of aphthous stomatitis: swelling of the oral mucosa, malaise, erosion in the mouth.
- Diseases caused by viruses.
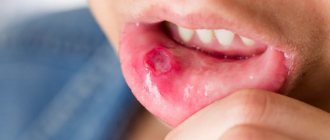
The best known oral infection is herpes, clinically known as herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). It is often found in children between 6 months and 5 years of age.
Once HSV-1 enters a child's body, he will carry the virus throughout his life. It is estimated that 50-80% of adults live with herpes simplex, either dormant or active.
The herpes virus manifests itself as rashes around the mouth. As the disease progresses, ulcers form in the mouth: they are localized on the inside of the lips and cheeks. Herpes can also infect tissues near the teeth.
After the first attack of oral herpes, the body produces antibodies to fight the virus and its effects. This way, your subsequent outbreaks of HSV-1 may not be as severe or the virus may remain dormant.
Otherwise, taking antiviral drugs may help.
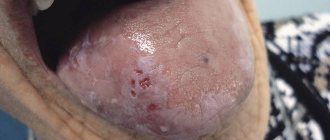
- Candidiasis.
This is a manifestation of a fungal infection. Candida fungus microorganisms live in the mouth and are activated under the influence of unfavorable factors. Candidiasis occurs in people with weakened immune systems. To avoid illness, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and avoid hypothermia. There are several types of candidiasis:
- Pseudomembranous.
It occurs in an acute form. As the pathology progresses, the mucous membrane of the cheeks begins to dry out, and the same thing happens with the lips and tongue. A coating of curd consistency forms on the tongue. Pseudomembranous candidiasis causes discomfort when chewing and itching. The disease can occur in people with a weakened immune system, as well as against the background of blood pathologies. Other causes of pseudomembranous candidiasis are diabetes mellitus and hypovitaminosis.
- Atrophic candidiasis.
In this case, the mucous membrane of the mouth becomes red and dry. The chronic form of the disease develops in those who use dentures for a long time.
- Hyperplastic candidiasis
may be acute or chronic. In chronic cases, plaque forms on the mucous membranes, including the tongue. When you try to remove it, the mucous membrane becomes more inflamed. Brushing your teeth may cause bleeding.
- A disease that occurs due to HIV.
Secondary immunodeficiency is characterized by the active proliferation of pathogenic flora in the oral cavity. Early diagnosis will allow faster initiation of treatment and improve the prognosis of immunodeficiency.
It is important to note that diseases of the oral cavity that occur against the background of HIV often become chronic.
Vitamin D
Another fat-soluble vitamin that has a significant effect on the functioning of the immune system is vitamin D. It is known that it [4]:
- stimulates the activity of macrophages;
- induces differentiation [maturation] of immune cells;
- increases monocyte proliferation;
- increases the activity of T-regulatory cells, which regulate the strength and duration of the immune response;
- reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines;
- increases the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides.
It has been proven that with a vitamin D content of more than 50 ng/ml in the blood plasma, the likelihood of developing respiratory infections is 27% lower than with severe deficiency [vitamin D level less than 20 ng/ml] [5]. At higher concentrations of the vitamin in the blood, the risk of developing influenza, respiratory syncytial virus infection, and pneumonia is reduced [6]. The decrease in the likelihood of developing the latter is associated with the beneficial effect of vitamin D on the respiratory tract: it reduces the production of cytokines in epithelial cells, reducing the severity of inflammation, and blocks the proliferation of smooth muscles of the respiratory tract [7].
The daily dose of vitamin D is 600-800 IU. For pregnant and lactating women it reaches 800-1200 IU, and for people over 50 years old 800-1000 IU.
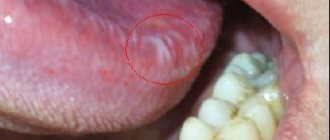
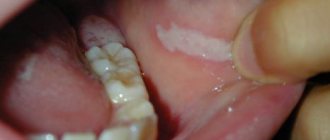
Oral cancer
Oral cancer most often affects the tongue, tonsils, gums and oropharynx. Since its various types often do not cause obvious signs and symptoms in the early stages, regular dental examinations are the most important method of detecting them.
Your dentist may also test you for oral cancer during your exam, especially if you have any of these symptoms:
- Persistent pain in the mouth or lip;
- Red or white spot in the mouth;
- Loose teeth;
- Painful swallowing, constant pain in the mouth or ears.
Treatment:
Depending on the type and stage of oral cancer, treatment may include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
The main dental diseases in humans: what they are and how to treat them
Modern medical practice, implemented in the Dentika dental clinic, actively uses innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment. Almost any disease can be eliminated provided that you seek help in a timely manner, as well as follow all doctor’s prescriptions and prescriptions. Among the measures used by dentists are:
- filling;
- surgical intervention;
- prosthetics;
- implantation;
- aesthetic correction.
In addition, professional hygiene methods are used: bleaching, restoration, etc.
Prevention
Maintaining oral health is not difficult if you follow simple recommendations:
- Eat a balanced diet.
The diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein foods, as well as foods containing amino acids, trace elements and vitamins. Carbohydrate foods, on the contrary, are best consumed in small quantities.
- Careful oral hygiene.
It is important, for example, to use dental floss and brush your teeth with toothpaste or gel twice a day.
- Use of vitamins and nutritional supplements (as prescribed by a doctor).
This will make up for deficiencies in the body that affect oral health.
- Regular visits to the dentist.
You should visit your dentist for a checkup at least once a year. Even if there are no complaints.
Developmental and eruption disorders
What are the different dangerous dental diseases? Perhaps the most serious problems are caused by congenital or hereditary causes. In these cases, the exacerbation does not begin due to pathogenic bacteria, pathogens or other factors. Such pathologies, as a rule, play a symptomatic role. They signal about malfunctions occurring in the body and force you to take immediate action.
Edentia
A pathological process accompanied by the loss of individual units or complete rows. In extremely severe stages, complete tooth loss occurs. The disease begins to develop during intrauterine development. The main factor is poor heredity or serious illnesses suffered by the mother while carrying the fetus. Due to jaw overload, even healthy teeth can become loose.
Superset
A disease in which excess elements appear in the oral cavity, which have an extremely negative effect on the state of the bite, and provokes additional speech and chewing problems. Dentists recommend removing such units, and the sooner the better.
Fusion and Merger
A rather rare deviation, expressed in the connection of tooth buds with dental cement. The main processes unfold during the formation of elements. Only 1% of people are prone to this disease. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed as part of a temporary dentition. In adulthood, pain is approximately 5-6 times less, so patients often do not suspect the presence of a problem until a visit to the dentist.
Spear-shaped teeth
A disease that affects crowns. It is considered infrequent - it occurs in one case in a thousand. It causes both aesthetic, psychological and physiological inconvenience. Usually it is a consequence of chronic injury to the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, and tongue. In some patients it is accompanied by hypoplasia.
Impacted teeth
An ailment in which the teeth are unable to fully erupt. As medical practice shows, the problem begins to bother people due to the gums being blocked by bone layers. Another reason is premature loss of elements.
Dystopian teeth
A disease in which the incorrect location of units is recorded. The displacement occurs as a result of deviations of the alveolar ridges from the norm. It causes psychological discomfort, disrupts the beauty of a smile, and interferes with the correct functioning of the masticatory muscles.
Macrodentia and microdentia
Congenital hereditary anomalies that determine the specifics of development. Manifested in improper formation and scaling of teeth. They have a negative impact on the bite and the aesthetics of the smile. They are also extremely rare - in every 20 people (in the context of not a single state, but the whole world).
Brief conclusions
- The most common oral diseases are tooth decay, gum disease, infectious diseases and oral cancer.
- Caries and gum disease are highly treatable in the early stages.
- The causes of infectious diseases of the oral cavity vary - from viruses to poor diet and uncontrolled use of medications.
- For prevention, it is important to review “life hygiene” and regularly visit the dentist.
Anti-Aging Medicine Seminars Gain knowledge based on evidence-based medicine first-hand from the world's leading experts. As part of the Anti-Age Expert Modular School, in-person two-day seminars are held every month, where the intricacies of anti-age medicine are revealed to doctors of more than 25 specialties
Find out more
Let's sum it up
Dentistry studies the etiology, symptoms, and treatment features of the most common dental diseases. There are a huge number of reasons that provoke oral problems. Some of them are easily eliminated, others are subject to only partial correction. However, for both cases the rule is true: the sooner you start working on dental treatment, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. That is why it is important not to let things take their course and undergo regular medical examinations.
Feature of carrying out independent hygiene procedures
A full range of hygiene procedures includes:
- Using a toothbrush.
They are traditional (manual), electric and ultrasonic. It is believed that an electric brush is more effective in combating deposits and removing plaque. Many people are concerned about the issue of gum trauma. However, if the replacement head fits tightly on the brush and there are no chips on its body, it will not cause harm to your teeth and gums. In any case, in order for the cleaning process with any type of brush to be of high quality, it is important to devote at least 2-3 minutes to it.
- Using toothpaste.
Rospotrebnadzor identifies 4 types of the most effective pastes:
- Fluorine-containing. Reduces the risk of developing caries and demineralization of enamel.
- Whitening;
- Desensitizing. Reduces tooth sensitivity;
- With triclosan. They have an anti-inflammatory effect. It is desirable that the paste does not contain sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium cocosulfate, fluorine, or titanium dioxide.
- Using brushes and dental floss.
They remove food debris stuck in the interdental space.
- Use of rinses.
Essentially, these are antiseptic solutions that reduce the number of microbes in the mouth and also eliminate unpleasant odors.
- Using an irrigator.
This is a device that uses water to help clean teeth from food debris. The percentage of oral cavity cleansing is 99%. An irrigator is an intermediate step between home and professional cleaning. But if you want to spend as little money as possible on a dentist and enjoy your dental health as much as possible, then you can’t do without it.