Allergic stomatitis
The occurrence of allergic stomatitis can be associated with the penetration of an allergen into the body or direct contact with the oral mucosa. In the first case, allergic stomatitis will serve as a manifestation of a systemic reaction (to pollen, medications, mold, food, etc.); in the second, a local reaction to irritating factors in direct contact with the mucous membrane (toothpaste, dentures, medicinal lozenges, mouth rinses, etc.).
The development of contact allergic stomatitis is most often associated with increased sensitivity to materials used in dentistry: preparations for topical anesthesia, metal fillings, braces, orthodontic plates, crowns, acrylic or metal dentures. In acrylic dentures, allergic factors, as a rule, are residual monomers, and in rare cases, dyes.
When using metal dentures, an allergy to alloys containing chromium, nickel, gold, palladium, platinum, etc. may develop. In addition, caries, chronic tonsillitis, as well as pathogenic microorganisms and products that accumulate in the denture bed play a certain role in the pathogenesis of allergic stomatitis. their vital functions, which irritate the mucous membrane.
Risk factors
Contact allergic stomatitis is more often observed in patients suffering from chronic gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis, dysbacteriosis, helminthiasis, etc.), endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, menopausal disorders, etc.). This is explained by the fact that organic and functional disorders in these diseases change the body’s reactivity and cause sensitization to contact allergens.
The development of severe forms of stomatitis is facilitated by other allergic diseases: drug disease, food allergies, rhinitis, urticaria, eczema, Quincke's edema, asthmatic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, etc. Allergic stomatitis does not always occur in isolation; sometimes it is included in the structure of systemic diseases - vasculitis, hemorrhagic diathesis, erythema multiforme exudative, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, Behçet's disease, Lyell's syndrome, Reiter's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, etc.
Content:
- Description of the disease
- Manifestations of the disease
- How does allergic stomatitis develop?
- Why does it occur
- Establishing diagnosis
- Fighting the disease
- How to reduce the risk of developing the disease
A dental disease in which the integrity of the oral mucosa is damaged - allergic stomatitis - occurs quite often in medical practice. It comes in different forms, so a person cannot always understand what caused the disease and what factors caused its negative symptoms.
Prevention
The best way to prevent any type of stomatitis is careful oral care. The absence of untreated teeth, gum disease and other damage, although it does not completely eliminate the likelihood of allergic stomatitis, does reduce the risk of its formation to a minimum. Preventative visits to the dentist will help you promptly remove unwanted deposits, adjust uncomfortable dentures, and polish the sharp edges of dental crowns.
Nutrition correction is also an excellent way to prevent the occurrence of allergic stomatitis. Potential allergens should be excluded from the diet by adding foods rich in minerals, vitamins and nutrients. In addition, maintaining a healthy lifestyle includes stopping smoking, which negatively affects the condition of the gums, oral mucosa and the whole body.
How to reduce the risk of developing the disease
If stomatitis has already occurred, the likelihood of it reoccurring is very high. To avoid illness, you should follow the recommendations:
Pay maximum attention to oral hygiene. It is unacceptable to brush your teeth only occasionally. This should be done in the morning after meals and in the evening before bed. After each snack, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To prevent plaque from accumulating in the interdental spaces, they need to be cleaned daily with dental floss or an irrigator.- Strengthen immunity. During the cold season, you need to take a vitamin-mineral complex. Proper nutrition is of particular importance. The diet should be enriched with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Give up bad eating habits. You need to stop consuming large amounts of spices and alcohol.
- Combine medications wisely. If you need to take antibiotics for a long time, it is advisable to include antihistamines in the course - drugs that reduce the likelihood of developing allergic reactions.
- Have professional oral hygiene every year. This is a general strengthening measure. It keeps teeth and gums healthy for many years.
Regular visits to the dentist allow you to detect all dental diseases at the earliest stages. Therefore, even if nothing bothers you, do not forget to visit your doctor once every six months.
Establishing diagnosis
If there is a suspicion that the patient has allergic stomatitis, he must be examined by a dentist. If necessary, allergists, immunologists, dermatologists, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, rheumatologists and other specialized specialists are involved in the diagnosis. The attending physician must collect a detailed medical history to understand what caused the disorder and what substance acts as an allergen.
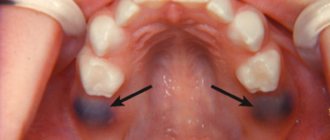
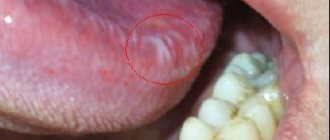
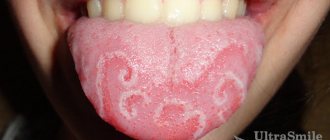
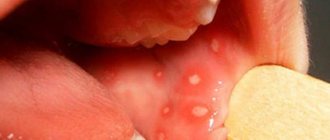
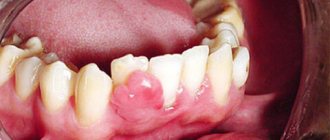
During an examination of the oral cavity, the dentist observes reddened and swollen mucous membranes. In some places, round ulcers are visible on it, covered with a white or gray coating. Saliva is usually very thick.
The specialist pays attention to the condition of the existing prostheses and finds out how long ago they were installed. To study the electrochemical processes occurring in the oral cavity, a saliva test is taken from the patient. It is important to determine the pH of biological material and evaluate the content of microelements in it. Allergy diagnostics involves conducting special tests - skin tests, provocative tests, etc.
If allergic stomatitis is suspected, it is important to differentiate it from a deficiency of vitamins C and B, herpes, candidiasis, leukemia, and HIV. With all these diagnoses, changes in the structure of the oral mucosa are also observed.
Description of the disease
With the diagnosis described, the oral mucosa is damaged, the tissues become very susceptible to all irritants. The incubation period is long. This means that a lot of time passes from the moment the first signs of allergy appear to the manifestation of the disease itself. Because of this, the patient is unable to track the relationship between the symptoms that bother him.
Allergic stomatitis occurs in both children and adults. More often it is diagnosed in people who live in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions.
What it is
Allergies can arise in a person out of nowhere, in the complete absence of any reactions to food, medications, dust, pollen and other irritants in the past. This happens due to failures of the immune system, as well as changes at the genetic level. Blood cells responsible for the formation of antibodies to infections at some point perceive a substance that has entered the body as an “enemy” of the immune system. A response begins, which is accompanied by typical allergy symptoms.
A person can calmly eat honey for half his life, drink chamomile tea, and be treated with penicillin. And at one point, any component of normal life can become a strong allergen, which can lead to a powerful reaction, anaphylactic shock and even death. Approximately a third of the world's population is susceptible to one or another manifestation of allergic reactions, and on average, in 20% of this number, allergies manifest themselves as rashes on the oral mucosa. So if you are faced with stomatitis, allergies may be one of the reasons for its occurrence.
Manifestations of the disease
The disease negatively affects the functioning of the entire body. It doesn’t just cause inflammation of the mucous membranes—it also causes migraines, elevated body temperature, and lethargy. Many people notice dry mouth, severe pain when chewing, which is present even when the integrity of the tissues has not yet been compromised.
Saliva thickens, becomes viscous, more like foam. The gums, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks may swell. All these symptoms deprive the patient of the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle.
You shouldn’t wait for the disease to clear up. The sooner her treatment is started, the sooner her health will be normalized.
Ulcerative necrotic stomatitis, cheilitis, glossitis
This disease usually develops against the background of general severe allergic reactions affecting the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs. It develops acutely and is characterized by salivation, a pronounced bad breath with a sweetish taste. The mucous membranes show severe hyperemia and swelling with yellowish-gray foci of necrosis. Necrosis of the interdental papillae is observed, the mucous membrane is covered with a dirty gray fibrinous plaque, after removal of which an ulcerative, bleeding surface is exposed. The disease occurs against a background of general weakness; children experience headache, loss of appetite, pain in the mouth, which worsens when eating and talking, and sometimes increased body temperature. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful.
When examining blood, an increase in the level of leukocytes - eosinophils and ESR is noted.
Treatment is based on the abolition of the drug that caused the allergy, the prescription of antihistamines, and in severe cases, corticosteroids, Hemodez, Poliglyukin, etc. are prescribed. Local treatment includes antiseptic treatment, removal of necrotic masses through the use of proteolytic enzymes, painkillers, keratoplasty.
Fighting the disease
What therapeutic regimen the doctor will offer the patient depends on the cause of the disease and the type of provoking factor. The first thing to do is to completely eliminate contact with the allergen. But to do this, you must first establish what exactly this allergen is. If there is no answer to this question, the patient is asked:
- stop taking medications he was previously using;
- follow a strict diet;
- change your toothbrush and toothpaste;
- stop wearing dentures.
In this way, the doctor tries to eliminate the influence of the most common allergens.
Drug therapy involves the patient taking antihistamines. They are always used for allergies. The use of vitamin-mineral complexes is also indicated. It is especially important that they contain folic, nicotinic and ascorbic acid, and B vitamins.
Affected areas should be treated regularly:
- special dental anesthetics;
- corticosteroid gels;
- enzyme compounds;
- drugs that accelerate regenerative processes.
If stomatitis is a consequence of recent dental treatment, you should consult a dentist again as soon as possible. It is possible that you will have to replace the installed fillings and crowns.
Among the folk methods that are effective for stomatitis, rinsing with cabbage juice, aloe infusion, diluted sea buckthorn oil, and chamomile decoction help. You can also apply grated raw potatoes to the wounds.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis in adults and children is carried out according to the same scheme. The only difference is in the medications prescribed: not all formulations for adults are suitable for children, and vice versa.