Sterility for materials and instruments
Most dental supplies are disposable and supplied in individual sealed packages. These are masks, gloves, napkins, brushes and applicators for applying varnishes and gels, tablets on which pastes are mixed, elements of saliva ejectors, etc.
Reusable instruments and materials undergo special treatment after each patient. It is performed in several stages:
- disinfection - soaking in solution for 2 hours;
- mechanical cleaning;
- washing (ultrasound can be used to remove all contaminants);
- washing in distilled water;
- drying;
- packaging in disposable sealed bags;
- dry heat or steam treatment (at high temperature).
After the sterilizer, the instrument remains in individual packaging, which is opened only before use in the presence of the patient.
Sanitary standards allow the use of conventional autoclaves in dental offices. In such equipment, superheated steam is supplied under pressure to sterilize accessories. The method is effective, but it does not always completely clean the pores on the surface of the instruments (if any). To increase the reliability of processing, dry heat sterilization is used, the temperature at which is so high that all microorganisms die. Another option is the use of automated autoclaves, with control of the operating protocol. To check the quality of cleaning, chemical indicators are additionally used - azopyram samples. If traces of biological material remain on surfaces, they show this. The results of such checks are recorded in a separate journal.
After sterilization and until use, reusable instruments are stored in special boxes with bactericidal irradiators. However, they are not removed from sealed bags.
Sterilization of dental instruments
Today, almost every person who crosses the threshold of a dental institution knows that everything the dentist touches must be as clean as possible, treated according to all the rules from microorganisms, so the presence of modern sterilization equipment in the clinic has become a guarantee of peace of mind for the patient and, as a result, a fact , increasing the prestige of this clinic. Thus, when choosing a dental institution, it is recommended to pay attention, first of all, to the degree of its equipment for sterilization and disinfection of medical instruments, and only secondly to the merits of the staff and the price of the services provided.
In every dental office, regardless of its functional focus, instruments and materials must be stored in sterile conditions. Usually this is a sterile table set according to all the rules or sets of sterile instruments sealed in bags. Ideally, treated instruments should be stored in sterile, disposable packaging and opened only in the presence of the patient. The presence of sterilely packaged tips and instruments in a dental clinic tells the patient about the level of responsibility of this medical institution and the preservation of his health.
Any dental office must be equipped with a bactericidal ultraviolet irradiator, which is used to carry out quartz treatment. You should also disinfect surfaces in your dental office, including equipment, faucets, and door handles.
Anti-infective protection of a doctor and his assistant during patient visits is largely determined by the correct use of disposable and reusable clothing, caps, gloves, safety glasses, and hand hygiene products that have bactericidal and antiviral effects. Despite the fact that medical personnel always work in disposable sterile gloves, careful hand cleaning is necessary, since a huge number of microorganisms accumulate on them.
So, all instruments intended for medical purposes must be subjected to sterilization, a complex process of destroying all types of microbial flora and viruses using physical or chemical agents. Sterilization can be steam, dry heat and gas. Currently, steam sterilization (in autoclaves) is the preferred method of eliminating the risk of cross-infection from contaminated equipment, recommended by the World Health Organization and the Center for Disease Control for healthcare workers.
For reliable sterilization of dental instruments, advanced clinics use class “B” autoclaves, which allow sterilization of any medical instruments, linen, dressings and where all phases are controlled automatically, there is an interface with a printer and a personal computer for logging the entire process. Moreover, when sterilizing dental handpieces that have a complex structure of internal channels, only class “B” autoclaves are allowed.
Class “B” autoclaves can sterilize all types of medical instruments and materials: solid, hollow, porous, individually or double-packed of any type. They are equipped with a pre-vacuum cycle and vacuum drying at the end of the sterilization process, which reliably eliminates all infections and does not damage the surface of autoclavable instruments.
You can find out about the sterilization equipment of ProfiSmile dentistry here
Treatment of dental offices
Cleaning regulations are determined by sanitary standards. All surfaces must be smooth, easy to clean, without microscopic pores or roughness. They are treated with disinfectants several times a day. Disinfection is carried out for furniture and equipment of walls, floors, ceilings, window sills, etc.
Dental offices must be equipped with special medical furniture. It is made from materials with surfaces that can withstand repeated disinfection and are free of micropores.
After each appointment, additional processing of all items touched by the doctor or patient is performed.
Some infections are transmitted by airborne droplets. To protect against them, dentistry can use bactericidal recirculating lamps (they continuously disinfect the air; they can operate in the presence of the patient), closed-cycle UV emitters, and special filters. A separate ventilation system is installed for surgical rooms. The air passes through fine filters. Access to the room must be through the sterilization department.
Dental equipment
Water supply systems. They are used to cool the tooth tissue during preparation. The jet is supplied through the tip. This treatment can only be carried out with distilled water. The design of the units is such that liquid from the oral cavity cannot enter the line even with a constant change in pressure.
Tips. During treatment, they come into contact with tooth tissue and require especially thorough cleaning. It becomes more complicated because the tips may have hidden cavities in which bacteria accumulate. For high-quality cleaning, the tip is blown twice: to remove mechanical impurities and rinse it with a hot antiseptic solution. Only after this is it sterilized in a disposable sealed bag.
Other tools. Endodontic accessories, burs, and scaler tips are stored in closed containers after treatment. You can only remove them from there with disposable sterile tweezers.
Individual dental kits. They include masks, gloves, aprons, and caps for the doctor and assistant. Special bags are used for waste materials. The standard set includes tips for a vacuum cleaner and a saliva ejector. If anesthesia is performed, the carpule and needle are disposable.
The described sterilization and disinfection protocol is used at the DentoSpas clinic and complies with the AntiAIDS and AntiHepatitis program. It ensures the safety of the patient during a dental appointment and eliminates infection and infection.
Rules for processing rotary dental instruments
Rotary instruments in dental practice include burs, cutters, polishers, abrasive heads and other accessories for processing hard and sometimes soft tissues of the maxillofacial area.
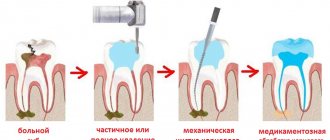
In accordance with the provisions of Chapter V SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”, all dental instruments that come into contact with the wound surface, blood or injectable drugs, as well as those that come into contact with the mucous membrane during operation and can cause its damage must be consistently subjected to disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization. We tell you how to correctly implement all stages.
Disinfection
The task of this stage is to destroy pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms that contaminate the instrument during its operation.
Procedure and necessary equipment.
Products should be disinfected immediately after use so that contaminants on them do not have time to dry. Immerse the instruments disconnected from the tip into the disinfection solution so that a layer of liquid 1 cm thick remains above them. To do this quickly, prepare the solution in advance by mixing the disinfectant concentrate with water in the proportions specified in the instructions. A graduated measuring cup or a disposable syringe will help you accurately measure the volume of concentrate.
All containers with working solutions must be tightly closed with lids and have clear labels with the name of the product used, as well as its concentration, date of preparation, purpose and expiration date.
What means should be used?
To disinfect dental medical devices, you will need drugs with a wide range of antimicrobial activity, including bactericidal, virucidal, and fungicidal effects. The choice of modes is made between viruses or fungi of the genus Candida. To work with tuberculosis patients, you will need regimens in which disinfectant solutions are also active against tuberculosis microbacteria.
Disinfectants containing aldehydes can fix organic contaminants on the surface of the instrument, so we do not recommend their use. Steel and carbide burs cannot be treated with products containing hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide, because they can deteriorate the properties of the materials. Also, such burs should not be kept in one container for a long time, because surface corrosion may occur.
Pre-sterilization cleaning
The task of this stage is to remove protein, fat, mechanical contaminants, as well as remnants of drugs and filling materials from the surface of rotary instruments. This is necessary to reduce overall microbial contamination and facilitate subsequent sterilization.
Methods and equipment.
Tools are washed manually or using special equipment. The manual method is relevant for solutions that involve manual cleaning with brushes or gauze wipes.
For effective pre-sterilization cleaning of products sensitive to mechanical stress, we recommend using ultrasonic washers. The supersonic frequency causes vibrations of the aqueous solution, as a result of which all areas of the instrument are cleaned of the surface layer of contaminants using the “microscopic brush” principle.
After disinfection and cleaning, rotating instruments should be rinsed in running water for the time specified in the instructions for the detergent. Then desalting in distilled water and drying is necessary. Your instruments are now ready for sterilization.
How to check the quality of pre-sterilization cleaning?
To evaluate this stage, you can perform an azopyram (or amidopyrine) test. This will detect any residual blood. If you used working solutions of products with a pH greater than 8.5. You will need to check your tools for traces of alkaline components. For this purpose, a phenolphthalein test is used. The result of the control is recorded in a special journal.
What means are suitable?
The most convenient option is disinfectants for simultaneous disinfection and pre-sterilization washing of rotary instruments. The preparation process will be speeded up by drugs that are already ready for use and do not require dilution.
If you still process instruments in stages, then enzyme-containing products are well suited for pre-sterilization cleaning. Enzymes are capable of destroying the bonds between cells of biological fluid and breaking down biofilms on the surfaces of products.
Sterilization
The task of this stage is to completely eliminate pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms, including their spore forms, from the instrument.
Methods and procedure.
To choose a safe and effective sterilization method, you need to rely on the recommendations of the manufacturer of a particular instrument. In most cases, modes with temperatures above 160°C are not recommended, because the structure of the abrasive layer of the rotary tool can be disrupted. Then, instead of air and glasperlene sterilization, it is better to use steam. Modern autoclaves provide almost all modes, so settings for any type of instrument are available.
First you need to pack your tools. They will be stored in the same packaging after sterilization, in accordance with the shelf life indicated on the packaging material. Equipment you will need is a sealing device and rolls of bags for sterilization.
Unwrapped rotary instruments can only be sterilized if they are used immediately after sterilization. This is possible if portable sterilizers are used in a decentralized processing system. Sterile instruments without packaging should be stored in bactericidal chambers or for no more than six hours on a sterile table.
The sterilized rotary instrument is placed on the dentist’s table in a sterile tray or on a sterile napkin immediately before working with the patient.
Sterilization quality control.
During each cycle, chemical test indicators are used and installed at control points. A modern test helps to evaluate two critical sterilization parameters simultaneously and make a conclusion about the suitability of a sterile batch of products for use. This should also be recorded in the sterilizer operation control log. Printers for autoclaves help quickly and clearly document sterilization protocols and apply markings.
If a dental clinic has more than three dental chairs, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization are carried out in specially designated rooms, divided into “clean” and “dirty” zones.