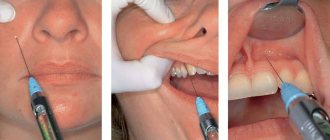
Is caries treatment painful?
Many people are convinced that caries is painful to treat, and therefore are afraid to go to the dentist. The problem goes back to the recent past, when anesthetics were not used in dentistry. Just a few decades ago, no one could even imagine that it was possible to treat teeth with anesthesia, and all manipulations were performed “live.”
In this article
- Is caries treatment painful?
- Is it painful to treat dental caries with anesthesia?
- Is anesthesia always necessary?
- How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
- Is it painful to treat caries on the front teeth?
- What anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries?
- Who is contraindicated for anesthesia?
- Conclusion
Of course, with this approach it was very painful to treat deep caries and other stages of this disease that affected the sensitive parts of the tooth. Fortunately, dental treatment methods have changed, modern safe anesthetics have appeared, and it has become easier to treat with an injection.
Painless dental implantation in Moscow
Some choose an implant for installation based on personal preferences or reviews of other patients, while others choose a specific design, listening to the recommendations of an experienced doctor. If you decide to restore the aesthetics of your smile and restore the healthy functionality of your teeth, we suggest having implantation done in a specialized dental office!
Our clinic employs high-level professionals with extensive experience. The initial consultation examination is free.
When treating and implanting teeth, modern technologies, high-quality materials and safe anesthetics are used to eliminate pain during treatment procedures.
Types and prices of dental implants
You can see the price list on our website. We also offer to leave your feedback on the work of our specialists and receive a 3% discount on all dental services as a pleasant bonus!
Is it painful to treat dental caries with anesthesia?
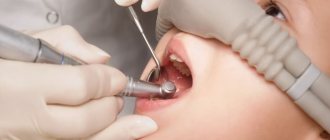
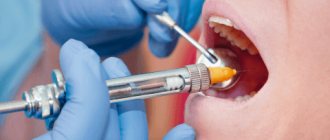
If you treat caries with an injection, anesthesia will be given at one of the first stages of treatment. Once the tooth is frozen, it will no longer hurt. Thanks to anesthesia, tooth sensitivity will noticeably decrease, and even with deep and complex caries there will be no pain. You will feel the touch of dental instruments, perhaps minimal discomfort, but not pain. When the treatment is completed and the anesthesia wears off, your gums will hurt a little for a while after the injection. But this feeling is tolerable and will soon pass.
There are people with intolerance or allergic reactions to anesthesia for whom injection pain relief is not suitable. This does not mean that they will have to endure pain when treating dental caries. For such patients, modern dentistry can offer an alternative painless treatment method - for example, using chemical dissolution of the affected tissue or using a laser.
Is anesthesia always necessary?
When treating caries, there is not always a need for an anesthetic injection. It depends on how badly the tooth is damaged and the individual sensitivity of the patient.
Superficial caries.
For example, early caries on the surface of the teeth resembles a whitehead and can be treated in a non-invasive, painless way. To do this, a procedure is carried out to remineralize the enamel. It is coated with special protective compounds and electrophoresis is performed with fluorine or calcium ions. This method of treating teeth does not hurt at all, so the doctor does not even offer pain relief with an injection.
Average caries.
At this stage, the carious process reaches the upper part of the dentin - the connective tissue under the tooth enamel. At this stage, drilling may be painful, but for many it is tolerable. Therefore, treatment of average caries can be carried out both with and without an anesthetic injection - it depends on the individual threshold of sensitivity and the wishes of the patient.
Deep caries.
This is the most complex form of pathology. If the caries is deep, then the dentinal tubules with nerve endings are involved in the process, and any touch causes pain. It is very painful to treat teeth without anesthesia at this stage, so in most cases the area around the affected tooth is numbed with an injection.
In addition to the degree of tooth decay, the intensity of pain can be influenced by the location of the caries. The lateral one is located on the side of the tooth, away from the neck and, as a rule, does not cause severe pain. The contact tooth is located at the junction of two teeth, and the severity of pain is comparable to average caries. To endure or to give an anesthetic injection depends on the patient’s choice. Cervical caries is located in the most sensitive root zone of the cervix, where many nerve endings are located. Almost always, cervical caries is treated with an anesthetic injection.
How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
At other stages of caries, teeth are treated approximately according to the same scheme, which includes several stages:
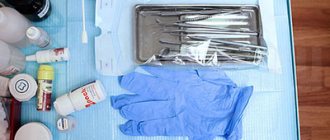
- Cleaning teeth.
The doctor removes tartar and plaque from the surface of the tooth being treated.
- Selecting the shade of the filling.
The dentist selects the material for filling, focusing on the natural color of the enamel of the damaged tooth. To do this, he uses the so-called Vita scale - a plastic strip with samples of different shades.
- Anesthesia.
Anesthesia injections help make the procedure painless and reduce discomfort during the treatment of caries. The type of drug and dose are selected taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the patient. The anesthesia usually lasts from 40 minutes to several hours. Sometimes the gums hurt a little after the injection, but this does not compare with the pain when treating deep caries without anesthesia.
- Isolation of the tooth before treatment.
It is performed by placing a small plate - a rubber dam - on a row of teeth. As a result, one or more necessary teeth are completely isolated from the others. This allows the dentist to do a better job and prevent blood and saliva from getting on the cleaned surface, which guarantees its reliable connection to the filling in the future.
- Preparation of a carious cavity.
Cleansing the tooth of all tissues that have been damaged by caries and parts of the tooth enamel above the carious cavity. If you leave the caries at least partially and install a filling, after a couple of months the problem may recur. And in the future complications may develop - pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Formation of a carious cavity.
The doctor creates the best conditions for installing the filling by forming special support points. It makes indentations, notches, irregularities in the cavity, and smoothes the edges of the enamel. This is required for the filling to fit tightly to the walls of the tooth.
- Washing the cavity.
After the above procedures, the carious cavity is washed and sprayed with a stream of air to remove dentin sawdust.
- Medical treatment of carious cavity.
It is produced using antiseptic solutions to prevent the new development of caries. Then the doctor dries the cavity well so that drops of moisture do not interfere with the close contact of the filling with the tooth tissues.
- Acid etching.
It is performed so that the adhesive, which is applied after etching for a stronger fixation of the filling material, can penetrate deeper into the dental tissue. To do this, use a special gel with phosphoric acid. After etching, the gel is washed off well and the tooth is dried.
- Application of adhesive.
It is applied to the tooth to firmly fix the light-curing filling material; after absorption, it is illuminated using a special lamp.
- Application of a therapeutic and insulating pad.
This step can be performed either before or after acid etching. Spacers are an intermediate layer between the dentin or pulp and the filling material. Therapeutic pads protect the tooth from external adverse influences and help stop inflammation; they are most often used to treat deep caries. Isolating gaskets protect the pulp, the soft connective tissue of the tooth, from the negative effects of filling materials.
- Placing a filling.
The doctor takes turns, layer by layer, applying filling materials and drying each of them with a dental lamp.
- Grinding, polishing.
The restored tooth with filling is ground and polished to perfect smoothness and evenness. This gives it a natural shine and eliminates the smallest imperfections and gaps that cause inconvenience. At this stage, caries treatment ends. Thus, anesthesia with an injection is given at the very beginning of dental treatment, and all other stages are absolutely painless for the patient.
Local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry. Application technique, safety
What is used and how does it affect the body? Why is anesthesia necessary and is it mandatory? I hope you will find answers to these and other questions in this article and, when you bring your child to an appointment, you will better understand the doctor’s decision.
So, let's start, as usual, from the beginning. Local anesthesia is a method of pain relief that blocks nerve impulses from the surgical site by interrupting nerve transmission. For this purpose, pharmacological drugs - local anesthetics - are used.
How long ago did this method begin to be used for dental procedures? Not so long ago, in 1885, infiltration anesthesia for dental treatment was first performed by Landerer, Witzel, and Voltaire in Germany. Novocaine was synthesized in 1905. And in 1921, the first carpule syringe with the ability to conduct an aspiration test was invented in Cook's laboratory. Today, dentists around the world have been using anesthesia using a carpule syringe for 100 years.
Currently, Articaine anesthetics with a vasoconstrictor are used. They are the most effective and safe. An allergic reaction to the anesthetic is certainly possible. However, a true allergy to the anesthetic itself is quite rare. Most often, negative reactions are associated with:
- Vasoconstrictor as part of the anesthetic. This is often not an allergy, but reactions such as increased heart rate, “fainting”
- Preservatives and stabilizers in the composition of the drug in the capsule, which are added to extend the shelf life of the anesthetic
In order to cope with the negative reaction that has arisen, there are always medications and first aid supplies in each office. And in order to prevent them, it is enough to carefully collect anamnesis from the parents and, if you are prone to allergies, carry out treatment “under the guise” (having previously taken) antihistamines.
As elsewhere, there are exceptions and there are health features, and they are necessarily taken into account by the doctor when choosing a carpule of local anesthetic and the method of its use.
Treatment for children differs somewhat depending on the age category and the tooth itself that needs to be anesthetized. We will analyze separately milk and permanent teeth, as well as some features of children’s age groups.
So, baby teeth. They have a similar structure to permanent ones; they have a “nerve” inside - pulp and long roots. They differ from permanent teeth in that the layers of hard tissue in them are thinner than in permanent teeth, and the pulp (“nerve”), on the contrary, takes up more space. That is why if caries has developed in a baby tooth, in a short period of time (3 months) it can develop into pulpitis. You need to know all this in order to understand: baby teeth are sensitive! Yes, some children have a high enough threshold for pain sensitivity so that treatment of caries of a baby tooth is painless for them. Often the parents of such children say something close to: “I was treated normally without an injection when I was a child.” In such children, theoretically, uncomplicated caries of baby teeth can be treated without using anesthesia. BUT!
Those “buts” again.
In the 21st century in Russia and not only the standard in the treatment of dental caries (both primary and permanent) is the use of composite materials (light-curing composite). They have many advantages compared to materials that were used previously. However, for their high-quality use, it is necessary to achieve COMPLETE DRYness of the enamel of the tooth being restored. How to achieve it?
- Isolation with a rubber dam (the same “lock” and “handkerchief” on the tooth). This allows you to dry the tooth and it will not get wet either by a child accidentally licking it or by condensation formed during breathing. Installing a rubber dam clamp is quite unpleasant and the gums on all sides of the isolated tooth must be numbed.
- Ensure that there is no leakage of gingival fluid or blood from the adjacent gum. This is exactly what the vasoconstrictor does in the anesthetic. That is, having given anesthesia, we locally constrict the blood vessels near the desired tooth. We get “dry” gums.
Total. To treat caries of primary teeth, we perform anesthesia, MAINLY to ensure the quality of treatment and long-term restoration. In this case, anesthesia of the tooth itself is secondary.
Of course, if we are talking about the treatment of complicated caries (pulpitis), then anesthesia is also needed so that the tooth itself does not feel anything, because in this case we are already working with the pulp (“nerve”).
For the treatment of permanent teeth, the question of priorities changes somewhat, since for most children it is still painful to treat permanent teeth. But in general, anesthesia is needed for the same purposes.
The decision to use or not to use local anesthesia for each child is made by the doctor together with the parent after a detailed clarification of the characteristics of the general health and psyche of the child.
We decided that this was really necessary. How to administer anesthesia to a small child? How do doctors do this? Each child’s psychological maturity is individual. Therefore, the schemes proposed below are only indicative. Up to 3.5 years, the use of local anesthesia has not been studied, therefore, up to this age, treatment under general anesthesia is considered the safest. However, this is another topic.
So:
3.5 - 6 years
To facilitate the perception of all dental procedures, fixate attention on the cartoon and increase the time of “quiet lying” in the chair, the baby can be offered support with nitrous oxide (supplied through a mask, the baby is conscious). This is also a separate topic for conversation, so we won’t dwell on it.
When the child lies in a chair, puts on glasses, watches a cartoon and is mentally prepared for the fact that he has come for treatment, the doctor describes to him the process of administering local anesthesia. Analogies are usually drawn with “freezing”. Initially, we do topical anesthesia, describing it as “I’ll anoint you with magic jam”, “I’ll apply cold gel”. This is necessary to initially reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membrane.
Next, we inject the needle and inject the first portion of anesthetic, literally “drops”. We describe it as “I’ll put a piece of ice”, “we’ll enchant a microbe like Elsa with the cold”, “I’ll drop a very cold drop”, “we’ll start sculpting Olaf and it’ll get cold.” At this moment, if the child does not cry out and does not turn away, so as not to carry out unnecessary injections, we continue the slow injection of the anesthetic, describing it as “rolling a snowball”, “starting to sculpt a snowman”, “making a cold pad”. If the baby screams and turns his head away, then we limit ourselves to the first drop and calm him down, praise him, explain that “it was the coldest, there was a fluffy snowball left.” After you have calmed down, we continue injecting the anesthetic into the same place where you started. It is no longer so painful, since the first drop has worked.
The following is important at the moment: parents should not use the words “it doesn’t hurt”, “it’s not scary”, “just a prick”, “be patient with the prick”, etc. We believe that many kids can muster the will to endure an injection, just like in a clinic for a blood collection or vaccination.
But we ask you, do not forget, after those injections the baby goes home in 2 minutes! His mother immediately hugs him, praises him and consoles him! And in our chair, the “prick” is just the beginning of treatment. And by asking the child to “just be patient with the injection,” even if he can do it, we give him false hope that after this he will get up right away! That's it, he suffered. He can go. Half of the child’s psychological readiness pool is lost due to one not entirely appropriate phrase.
A child under stress does not perceive the particle “not”. When you say “it doesn’t hurt,” the child hears “it hurts.” Therefore, doctors try to describe what is happening in other words. We replace “painful” with “unpleasant”, “hard”, “cold”. Children vividly imagine these concepts and can handle them much easier than a “prick”.
Dear parents! I hope it is now clear that we do not want to deceive your children, but in order for them to allow us to treat them for 30-40 minutes, we must be extremely careful in our expressions, tactful and sensitive.
6-12 years
In general, the concept of anesthesia is the same. The difference is that children of this age group can ask directly: “Will there be an injection?” In this case, our task is to be honest, but to help the child cope with fear. For this, different comparisons are also used. Here parents can help a lot by whispering in the doctor’s ear, “It’s better not to tell him that this is an injection, play around with it somehow,” or vice versa, “She hates lies, it’s better to show her the syringe.”
12-18 years old
The concept has not changed. Most often, children are prepared for treatment and normally perceive the need for local anesthesia. But in this age category, we can ask the child himself which moment is most unpleasant for him, what to emphasize. Some people do not like the taste of topical anesthetic, and they are willing to endure a more painful needle injection, just not for this taste. Someone asks to treat him “like a baby.” Some people want their assistant to wash it with water at the same time, then it will hurt less, etc.
Let's summarize.
In most cases, local anesthesia is needed to treat children. The child must be prepared for treatment (either adaptation, sedation, or be psychologically mature). Then, acting as a child-parent-doctor team, we can successfully carry out treatment in the most comfortable way for the child. Do not forget that the feeling of numbness goes away from 40 minutes to 1.5-2 hours, so we always remind: “Please watch your lip during this time, do not let the baby bite it!”
Is it painful to treat caries on the front teeth?
Due to their location and structural features, caries on the front teeth is more difficult to treat. If the damage is severe, it is not always possible to put a filling, and then you will have to resort to prosthetics.
There are other features:
- The front teeth, compared to molars and premolars, have thinner and more sensitive enamel. It is easily destroyed, opening access to sensitive dentin, so the central incisors are more sensitive to pain.
- The front teeth, which are used for gripping and cutting food, are subject to high stress and wear out more quickly.
- A large cavity is often hidden under a small chalk point. And often caries is detected already at the stage when it is difficult to cure without pain. Therefore, in most cases, anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries of central incisors.
- Increased aesthetic demands are placed on the front teeth, so the filling must be placed not only reliably, but also beautifully.
That is why the condition of the front incisors - teeth with a small chewing surface area - must be monitored especially carefully.
If caries affects the front teeth, due to the thin enamel and dentin, it very quickly passes into the middle and deep stage, affecting the sensitive pulp. If you do not know whether it is painful to treat deep caries of the front teeth and doubt whether you need anesthesia, we recommend that you definitely agree to an anesthetic injection. Of course, in the absence of contraindications to the anesthetic. Because treating caries on the front teeth is painful.
Types and benefits of dental implants
In modern dental clinics, high-quality implants from world manufacturers are used to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the dentition. All designs are divided into several groups.
Types of dental implants: description
, indications for installation:
1. Root-shaped - the most popular dental implants are cylindrical in shape with threads. The main design is a titanium pin. The implant takes root quickly, the risks of postoperative complications are the lowest. Installed when there is sufficient bone tissue.
2. Plate implants have a porous plate with a pin. Can be used if the bone tissue is too thin, when installation of a root-like structure is considered impossible. They are not designed for heavy loads, so they are mainly used to restore front teeth.
3. If there is a lack of bone tissue, subperiosteal implants, implanted into the space between the bone and the gum, are also effectively used. Recommended for installation after long-term absence of teeth.
4. Mini-implants are the optimal design for installation in patients who are contraindicated for full dental implantation. Such implants are used in single quantities and are not suitable for restoring a whole series.
On the dental implant market, global manufacturers present a wide variety of designs for restoring lost teeth, each with its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Before carrying out a surgical procedure to implant an artificial tooth, it is very important to choose a high-quality implant with good performance characteristics and rapid healing.
What anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries?
To remove tooth sensitivity and treat it painlessly, the dentist selects the appropriate type of anesthesia for each patient.
The most common are three types - application, infiltration and conduction:
- Application involves pain relief without injections. A gel or solution of an anesthetic is applied to the oral mucosa, which reduces the sensitivity of the tissues in this area. Most often, topical anesthesia is performed when treating or removing baby teeth. It is also used to numb the injection site.
- Infiltration is anesthesia with an injection of an anesthetic, which is injected relatively shallowly and affects the peripheral nerves. This type of anesthesia is often performed in the treatment of caries and pulpitis. After the injection, the patient does not feel pain and feels comfortable in the dental chair.
- Conduction anesthesia acts on large nerve canals and trunks. With its help, you can remove the sensitivity of half the jaw. It can be used for caries, which is complicated by a serious inflammatory process, during surgery.
The type of anesthesia, as well as the drug used to numb the teeth, is selected by the dentist.
Why do they give the injection?
Even a small intervention requires maximum calm and relaxation from the patient, so care must be taken in advance to ensure that no pain occurs during the specialist’s work. Simple and complex removal of teeth, pulp, cleaning and filling of canals, as well as treatment of caries of varying degrees of complexity can cause discomfort, especially with increased tissue sensitivity.
It is important to note that another purpose of the injection is to introduce antibiotics and certain anti-inflammatory drugs into the gums. This is especially common during the treatment of diseases such as gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Most often, dentists perform local anesthesia, this allows them to achieve a targeted and quick effect. When medications are administered intramuscularly, the body reacts after a longer period of time, so the dentist’s appointment may be delayed. Anesthesia has contraindications: age under 3 years, period of pregnancy, allergies, presence of serious diseases or oncology.
Who is contraindicated for anesthesia?
There are three main contraindications to the use of local anesthetics during dental treatment in the clinic:
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system (stroke and heart attack, after which less than six months have passed).
- Endocrine diseases in the stage of decompensation - thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus. It is recommended that patients of the first and second groups treat caries and other dental diseases only in a hospital.
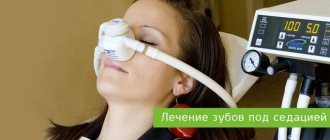
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia and anesthetic components. In this case, it is recommended to conduct allergy tests and find out which drugs you are allergic to. If it is selective, caries can be treated with an anesthetic injection - but only one to which you are not allergic. If the tests show a reaction to all anesthetics, you will have to treat your teeth without pain relief or look for alternative options. Sometimes the solution for allergy sufferers may be sedation, which puts a person into a state of half-asleep and partially disables reactions. In this state, the pain is felt much less.