Electrophoresis in dentistry is a physiotherapeutic procedure when medicinal substances are introduced into the body through electric current. This method uses special compounds that, under the influence of electricity, disintegrate into ions, accumulate in the pathological area and have a targeted effect on it. Thus, maximum therapeutic effect is achieved.
Indications for the use of electrophoresis in dentistry
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- glossalgia;
- glossitis;
- purulent and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
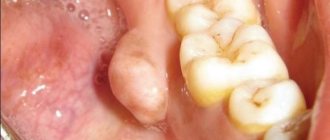
- dental cysts;
- dental granulomas;
- pathology of the facial nerve;
- inflammation of dental cells (alveolitis);
- lesions of the oral mucosa;
- severe pain after treatment or tooth extraction.
Despite the rapid development of technology in dentistry, electrophoresis has been and remains one of the most effective and affordable physiotherapeutic methods for treating hard and soft dental tissues.
Laser benefits
Due to its gentle impact, laser equipment is effective in solving almost all dental problems. It does not always replace a drill, but it successfully complements its work, since it can independently determine the affected areas, including those that are difficult to identify with the naked eye. The fact is that healthy tooth tissue does not contain moisture, and therefore boiling cannot occur in it. Many dental problems are resolved in just a few minutes and do not require a second visit to the doctor.
The beam is very thin and is able to penetrate microcavities that would otherwise require drilling with a bur. The radiation is directed to the desired location through a flexible and very thin quartz-polymer waveguide. The device itself is equipped with a compact, ergonomic head that can be easily operated by a trained physician.
Another advantage of the laser is that the surface processed by it acquires a slight roughness, which greatly improves the adhesion of the filling material. Reliable fixation reduces the likelihood of relapse to almost zero.
Features of electrophoresis for teeth
The procedure is performed in a treatment room and is comfortable and painless. Allows you to quickly relieve pain in the tissues, inside the dental canal, thereby eliminating foci of infection. Medicines are administered slowly, and the therapeutic effect lasts for several weeks. The risk of developing allergic reactions is minimal.
Medicines used in electrophoresis:
- lidocaine;
- iodine;
- vitamin cocktails;
- calcium;
- a nicotinic acid;
- novocaine, etc.
Purified water, dimexide, and buffer compounds are used as solvents.
Drug electrophoresis in dentistry is performed as follows:
- a special pad is wetted in the medicinal composition;
- the element is fixed at the site of inflammation;
- when treating pulpitis, the teeth are pre-treated and the drug is simultaneously injected into the canals;
- the tissues of the oral cavity are exposed to weak current pulses through the pad;
- The patient is given an electric current with a gradual increase in strength until painful sensations appear. Thus, the optimal indicator of the power of impact on the zone is determined;
- the procedure lasts about 10 – 30 minutes.
The average duration of an electrophoresis course is 10-20 procedures, which are performed daily or with breaks of one or two days.
Laser treatment allows you to achieve the following results:
- improvement of metabolism at the cellular level;
- stimulation of recovery processes;
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- increased blood microcirculation, and, consequently, improved tissue nutrition;
- analgesic effect;
- immunostimulating effect.
How does a laser affect a living organism? Low-intensity laser radiation causes local heating of individual sections of macromolecules, without causing heating of the entire cell. Such thermodynamic changes lead to the release of calcium ions from the calcium depot, and a change in the calcium concentration in the cell is a trigger for the physiological reactions listed above, because they are all calcium-dependent.
Contraindications
When prescribing physiotherapy, special attention should be paid to contraindications. They can be general, that is, they are not suitable for any physical impact, and specific - for each procedure there is a separate additional list.
Physiotherapeutic procedures should not be prescribed in cases of detection of these diseases:
- Neoplasms or suspicion of their presence.
- Tendency to bleed.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Heart failure.
- Intoxication.
- Cachexia.
- Skin diseases.
- Systemic blood diseases.
- Individual intolerance.
Exposure to physical factors in the presence of general contraindications can lead to a sharp deterioration in health.
Areas of dentistry where physiotherapy is used
An integrated approach and adherence to physiotherapeutic protocols - these are the principles that guide the specialists of the dental department of the Doctor Nearby clinics. They use physical therapy to address the following:
- minimizing or eliminating pain symptoms;
- stimulation of regeneration after implantation and sinus lift surgery;
- eliminating emergency conditions for facial pain of unknown nature;
- treatment of teeth and gums;
- treatment of TMJ diseases;
- restoration of the mucosa after surgery;
- stimulation of muscle tone and nerve conduction.
Material and methods
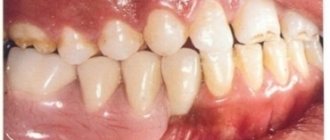
At the Moscow Regional Dental Clinic, 60 people aged 35 to 65 years (12 men and 48 women) diagnosed with moderate CGP were examined and treated.
The examination included a survey and examination, measurement of the depth of periodontal pockets, determination of periodontal indices (modified Muhlemann-Cowell bleeding index (Muhlemann-Cowell, 1975), Silness-Loe hygienic index (Silness-Loe, 1964), PMA index (I Shour, M. Massler, 1947), X-ray examination (orthopantomography and targeted dental photographs) and rheoparodontography (two-channel rheographic attachment RPKA2-01 JSC Scientific and Technical Center MEDASS, Russia). Patients were examined before the start of treatment, immediately after its completion and after 6 months after the end of the course of physiotherapeutic treatment. The course of magnetic therapy was prescribed after complex periodontal treatment, which included the elimination of all traumatic factors, removal of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque. During the treatment, control of oral hygiene and correction of individual oral hygiene skills were carried out.
The patients were divided into two equal groups using simple randomization. Patients in the control group received pulsed carbon dioxide irrigation at an indifferent temperature for 12 minutes in a course of 10 daily procedures. Patients of the main group additionally underwent magnetic therapy with the Magofon-30 device (RU FSR 2009/04946 dated May 28, 2009) No. 10 for 5 minutes on each side on the projection area of the upper and lower jaw using a labile technique.
Laser therapy
At the present stage, physiotherapy uses the most modern methods in dentistry. Along with the traditional treatment of dental diseases using ultrasound, electrophoresis, hydrotherapy, which are not the main type of treatment, laser procedures are widely used.
When the dentist, upon examining the patient, reveals that the course of the disease is advanced and the inflammatory process has taken an acute form, laser treatment may be offered. An infrared laser (5-8 mW) will be directed to the gingival papilla area.
If it is necessary to increase the impact of this device on the affected area, the treatment period can be increased to six minutes. As a rule, this is applied to the surface of the skin in the area of the affected tooth.
Sign up for teeth cleaning at a discount:
— What else can additionally be included in professional dental cleaning?
In addition to the four steps mentioned above, you can clean your teeth with dental floss and special abrasive strips. As a rule, this is done according to indications at the polishing stage.
They also often offer another care procedure that helps prevent caries. If the patient has weak enamel, i.e. the risk of caries is increased, the doctor may prescribe remineralizing therapy
- This is a procedure for saturating tooth enamel with calcium. Remtherapy is most often performed as a course at home. The patient receives special mouth guards and gel at the clinic and applies them independently every day. The duration of such therapy is individually selected by the doctor.
Results and discussion
According to the clinical examination before treatment, there were no significant differences between the groups.
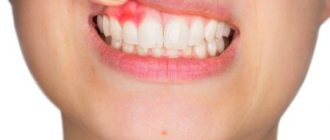
After complex treatment, a significant decrease in the severity of inflammatory symptoms was noted. Complaints of bad breath, bleeding gums when brushing teeth and eating solid food, and itching in the gums were absent in all patients. A clinical study of periodontal tissue revealed a tighter fit of the gum edge to the crown of the teeth, which was expressed by a slight decrease in the depth of pathological periodontal pockets by an average of 0.3 mm and a decrease in the degree of tooth mobility. The gums acquired a pale pink tint, there were no signs of cyanosis. The interdental papillae have become more dense, but in isolated cases their hyperemia has been established. There was no gum bleeding. A significant improvement in oral hygiene was observed in all patients. The Silness-Lohe index averaged 0.16±0.06, which corresponded to a good level of hygiene. Conducting instructions and reminders about the rules of individual oral hygiene helped to keep this index at a low level and thereby eliminate the influence of the personal hygiene factor on the result (Fig. 1). When monitored after 6 months, the patients did not complain of bad breath or itching or soreness in the gums. Complaints of bleeding gums during brushing were noted in 23.3% of patients in the main group and in 36.7% in the control group. No changes in the degree of tooth mobility and the depth of pathological periodontal pockets were recorded.
The values of the Mullemann index (Fig. 2) and PMA (Fig. 3) were significantly better in the main group both immediately after treatment and after 6 months, which indicates a prolonged relief of the inflammatory process.
The values of the indices of peripheral resistance, elasticity and rheographic index at the stage of examination before treatment did not differ significantly in both groups. When examined immediately after the course of treatment and 6 months after its completion, an improvement in these indicators was noted, which was significantly less significant in the control group compared to the main group (see table). It has been established that under the influence of a magnetic field, favorable changes in microcirculation and transcapillary exchange occur in the gum mucosa. There is an increase in the speed of blood flow, the capacity of blood vessels increases, thinning of the blood and an improvement in its rheological properties are observed, and the opening of reserve capillaries, anastomoses and shunts occurs. Changes in the rheoparodontogram indicate the elimination of venous stagnation.
Indications
Physiotherapeutic procedures are absolutely safe for the human body. But only if the physiotherapist correctly selects the type of procedure, power and time of exposure.
A high therapeutic effect will be achieved only in complex treatment. The dentist must build a complete treatment plan for the disease, including physical therapy.
Physiotherapy can be carried out in the following cases:
- Acute and chronic inflammatory processes.
- Poor blood circulation in the oral mucosa and gums.
- Regeneration and degenerative processes of tissues.
- Painful sensations.
- Surgical intervention.
- Decreased muscle tone and nerve patency.
- Prevention and rehabilitation.
- Children's age from 1 year.
The main positive feature is that the procedure does not affect the entire body. Therefore, the results of local treatment are predictable and easily controlled.
Types of physiotherapy and mechanism of action
Under the influence of various physical factors, the physiological processes of the body are activated. With the rational use of physical therapy in dentistry, it is possible to control these processes and obtain the desired result.
Depending on the type of impact factor, there are different types of physiotherapy.
| Physical factor | Physiotherapy |
| Electric current (alternating, direct, high or low frequency, strength, voltage) | Depophoresis Galvanization and electrophoresis Amplipulsetherapy Fluctuarization Darsonvalization Ultratone therapy UHF therapy |
| Light | Laser therapy |
| Warm | Paraffin therapy Mud therapy |
| Ozone Air particles | Ozone therapy Aeroinotherapy |
| A magnetic field | Magnetotherapy |
| Oscillations (mechanical, electromagnetic) | Ultrasound therapy Microwave therapy |
| Pressure | Massage (hydromassage, vacuum, manual) |
Against the background of activation of the physiological processes of the body, the following effects are observed:
- Stimulation of the immunobiological system.
- Desensitization.
- Activation of the endocrine glands (pituitary gland, thyroid gland).
- Regulation of hematopoietic function.
- Improving collateral blood flow.
- Abundant supply of tissues with oxygen.
- Strengthening regenerative processes (fast wound healing).
- Activation of the anticoagulant system.
- Production of endorphins, which has an analgesic effect.
- Activation of proteolytic enzymes and leukocytes in the lesion, which leads to a bactericidal effect.
The method of physical influence should be carefully chosen, taking into account both the local and general reaction of the body. The result for each patient may be different depending on the general condition and clinical picture of the disease.