Causes
Why fetid ozena occurs has not been reliably established. The mechanism of its development is based on a violation of the blood supply to the mucous membrane in the nose and its innervation, and this condition can be a consequence of:
- congenital pathologies of the respiratory system (increase in the size of the nasal passages, underdevelopment of the paranasal sinuses, etc.);
- advanced inflammation of the nasal cavity (rhinitis, sinusitis);
- bacterial lesions;
- traumatic injury to the nose and paranasal sinuses;
- diseases of the immune system;
- surgical interventions - removal of foreign bodies, surgery to correct a deviated nasal septum, adenoidectomy, conchotomy (partial or complete removal of the nasal mucosa);
- severe infectious diseases;
- genetic dystrophy of the upper respiratory tract;
- hormonal disorders (most often nasal congestion develops in women during puberty, pregnancy and menopause);
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- poor nutrition;
- climatic influences (fetid runny nose occurs more often in people living in countries with a dry, hot climate).
More than 60% of patients diagnosed with ozena disease are infected with Abel-Levenberg bacillus, a bacterium from the genus Klebsiella. Many patients also have iron deficiency anemia.
Medical causes of metallic taste
If a metallic taste appears in the mouth, this may indicate illness. Their list is very extensive. To make it easier to classify, diseases can be divided into two groups: dental and non-dental.
Diseases that lead to a metallic taste, which are systemic in nature and are not associated with teeth and gums, are as follows:
- diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, otitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- lung diseases (pneumonia, tuberculosis);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, cholecystitis);
- diseases affecting the nervous system (sclerosis, tissue tumors);
- anemia due to deficiency of iron or B vitamins.
It is not uncommon for a metallic taste to accompany diseases that develop in the oral cavity. These include:
- stomatitis (the mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes inflamed, which is often accompanied by the formation of small ulcers);
- gingivitis (inflammation of the gums);
- periodontitis (the disease appears as a result of advanced gingivitis, when the infection no longer affects the external tissues, but the periodontium);
- glossitis (formation of plaque on the tongue, its inflammation).
Another common cause of taste associated with the oral cavity and dentistry is the installation of crowns and dentures. The appearance of a taste in this case is normal, provided that it goes away within 1-2 months. A sign that adaptation to the structure in the mouth has not occurred is unpleasant sensations in the form of tingling of the tongue, burning, and a feeling of dryness.
Ozena symptoms
The disease develops slowly, but has a progressive course. At first, constant viscous transparent discharge from the nose begins to bother you, gradually it becomes yellow-green or brown, an admixture of pus is added, and crusts appear in the nose. A characteristic symptom of ozena is the unpleasant odor of exudate. After removing the crusts, it disappears, but after the formation of new crusts it appears again.
The smell becomes so strong that even those around you can smell it. But the patient himself gradually loses his sense of smell (hyposmia develops), since the olfactory receptors in the nose are affected. The crusts become larger, they are difficult to remove, and therefore make nasal breathing difficult.
Other main symptoms of ozena:
- dry nose;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- headache;
- asthenia;
- prostration;
- sleep disorders;
- violation of taste sensitivity.
Complications
As a result of a person swallowing purulent nasal discharge, problems with the gastrointestinal tract often arise - bloating, nausea, loss of appetite, strong smell of feces.
If there is no treatment for a foul runny nose, sinusitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, blepharitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, otitis, dacryocystitis, and conjunctivitis may develop. There are known cases of damage to the auditory nerve and decreased hearing function.
Due to bone tissue atrophy, deformation of the external nose is possible, the so-called duck shape is formed.
If the atrophic process affects the nasopharynx and trachea, hoarseness and an obsessive cough appear.
Can I delete it myself?
Everyone needs to know what to do if there are purulent plugs in the throat. Self-medication with them is highly undesirable.
Doctors do not recommend performing procedures to remove tonsil plugs on your own. The risk of harm in such a situation is much higher than the opportunity to cure a sore throat. As a result of such manipulations, there is a danger of injuring the lymphoid tissues, which will cause heavy bleeding, which may require urgent medical attention. Also, improper cleansing of the tonsils sometimes provokes the spread of infection throughout the body, which is dangerous to health.
Doctors consider squeezing out with the tongue to be the only relatively safe method of removing plugs on your own. They press on the tonsils, causing the plugs to come out. After this, the throat is gargled to remove them. Swallowing purulent accumulations is extremely harmful. The tongue does not injure the delicate tissues of the mucous membrane and will not exert dangerous strong pressure, at which pus can escape inside, when there is a high probability of developing sepsis. A person will not harm himself during such cleansing.
Also, although doctors do not recommend it, sometimes they do home cleansing of the tonsils using a cotton swab or swab. The method is risky and traumatic, since you can press too hard and provoke the release of pus into deep tissues with the subsequent development of dangerous complications.
If it is not possible to visit a doctor, but you need to clear your tonsils, the procedure is carried out at home. This can be done no earlier than 2 hours after eating. You need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth and throat with an antiseptic solution. A swab made of sterile cotton wool or a cotton swab treated with an antiseptic is applied to the base of the tonsil and pressed upward. There should be no pain during the procedure. If after 3 attempts the purulent plug does not come out, then you cannot continue.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ozena disease is usually not difficult, given the presence of crusts in the nose and the specific odor that occurs only with this form of atrophic rhinitis.
To confirm the diagnosis, rhinoscopy, cytological or histological studies are performed, during which the following disorders are revealed:
- expansion of the nasal cavity;
- the presence of a thick, purulent secretion;
- thinning of the mucosa;
- reduction in the number of mucous glands;
- underdevelopment of cavernous tissue.
The bone tissue of the walls and turbinates of the nose becomes thinner and can be replaced by connective tissue.
Bacteriological culture allows to identify ozenous Klebsiella. A clinical blood test is performed to determine iron levels. In some cases, the doctor additionally prescribes a computed tomography or radiography of the paranasal sinuses.
Bad taste in the mouth
(bitter, sour, metallic)
An aftertaste in the mouth may linger for some time after eating very sour, spicy or overcooked foods. But if unpleasant sensations bother you with frequent frequency and are not associated with dietary habits, there is a reason to consult a gastroenterologist - perhaps this is the way the digestive tract signals its problems.
Causes of taste disturbance
Different tastes may indicate different disorders. Bitterness in the mouth is usually caused by:
- Pathologies of the liver, biliary tract (stones, cholecystitis, dyskinesia). In these diseases, the movement of bile through the ducts is disrupted. Bile stagnates, then is thrown into the stomach and further into the esophagus, from where it enters the oral cavity.
- Lazy bowel syndrome. Accompanied by a slowdown in the process of digesting food. Food is retained in the gastrointestinal tract, and with it digestive juices, including bile.
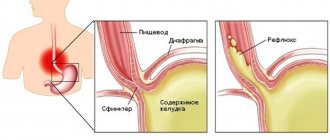
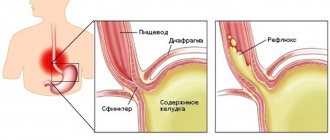
A sour taste often indicates problems with the stomach:
- ulcer,
- hyperacid gastritis,
- reflux esophagitis.
These diseases are characterized by increased formation of hydrochloric acid, which can rise up the digestive tract, reaching the oral cavity. Patients experience especially severe discomfort when lying down.
A metallic taste may be a sign of:
- Xerostomia (insufficient salivation). Accompanied by a pronounced feeling of dry mouth, burning sensation on the tongue and difficulty swallowing.
- Hemorrhagic gastritis. Small ulcers form in the stomach, from which blood periodically oozes. It is this that creates a specific taste in the mouth.
- Foreign body in the stomach. The condition can also be complicated by bleeding.
- Galvanose. This problem sometimes occurs in people with metal dentures in their mouths.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the appointment, the gastroenterologist asks the patient about complaints, clarifies the presence of accompanying symptoms and conducts a general examination. To confirm the diagnosis you may need:
- general and biochemical blood tests,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity,
- gastroscopy,
- pH-metry,
- analysis for Helicobacter pylori.
Therapy is selected based on the results of the examination. Patients with signs of bleeding are subject to mandatory hospitalization.
You can get a consultation with a gastroenterologist and undergo the necessary tests at the Spectra clinic. We have experienced specialists who will help determine the exact cause of the disorders and select effective treatment. Reception is by appointment only.
Treatment of ozena
There is no way to completely cure atrophic rhinitis yet. But carrying out symptomatic therapy can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and increase the duration of the remission period.
Foul-smelling crusts must be regularly removed, for which purpose rinsing the nasal passages with antiseptic agents is prescribed. You can cleanse the nasal passages with a 0.9% solution of sodium chloride (saline), chamomile or calendula decoctions, and soda solution. Ozena medications based on sea salt give good results: Marimer, Aqualor, Aqua Maris, Physiomer, Apicold Prolo.
Before rinsing the nasal cavity, to facilitate the removal of crusts, it is recommended to soften them - introduce turundas with proteolytic enzymes. High efficiency is shown by the introduction into the nasal cavity of Lugol's solution, silver nitrate solution, and oily vitamin solutions.
If a pathogenic pathogen is detected, only a doctor can decide how to treat ozena. He takes into account the sensitivity of the bacterial infection and prescribes local antibiotics for ozena: Baneocin, Bonderm, Bacitracin, Tetracycline, Levomycetin, etc. In some cases, systemic antibacterial therapy is required.
To prevent overdrying of the mucous membrane, you should use moisturizing drops, sprays, gels, for example, Afrin, Isohydronic, No-Sol.
To reduce the atrophic process, oil drops and emollient ointments are used - naphthalene, vaseline, lanolin.
Clinical recommendations for ozena include physiotherapeutic treatment methods: medicinal electrophoresis, short-wave ultraviolet physiotherapy, laser therapy.
In severe cases, the only option is surgery aimed at reducing the width of the nasal passages.
FAQ
Why does ozena appear?
The exact cause of the disease is unknown. There are a number of risk factors that can provoke the development of ozena. The most common are injuries to the nose and paranasal sinuses, advanced inflammation in the nasal cavity. The causative agent of ozena can be a bacterium from the genus Klebsiella.
What are the first signs of ozena?
Ozena is characterized by the formation of crusts, the appearance of viscous discharge with an unpleasant odor, and severe dryness in the nose.
How long does it take to treat ozena?
Fetid runny nose is a chronic disease that has a wavy course. Methods to completely cure it have not yet been developed. Depending on the severity of symptoms, the course of treatment may take up to 20–30 days.