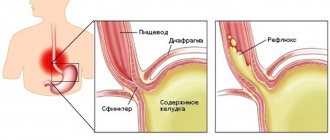
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
is a disease caused by repeated spontaneous reflux of stomach contents (and in some cases, duodenum) into the esophagus.
Our body is designed in such a way that movement must occur in only one direction: food from the esophagus must enter the stomach.
The reverse movement is prevented by a ring of muscle, the lower esophageal sphincter, which provides a barrier that prevents stomach contents from naturally flowing into the esophagus. The digestive process begins in the stomach. Gastric juice secreted to digest food contains aggressive hydrochloric acid. Once in the esophagus, where it is not intended to be located, the acid causes irritation of the mucous membrane, manifested as a burning sensation along the esophagus, which we call heartburn. Heartburn can occur even in a healthy person, but if reflux occurs quite often, irritation of the esophageal mucosa can cause inflammation.
Thus, isolated cases of heartburn are not a disease, but if irritation of the esophageal mucosa occurs often enough, GERD is diagnosed. In this case, endoscopic examination may not reveal mucosal erosion. This form of the disease is called endoscopically negative reflux disease.
.
It accounts for approximately 70% of cases. In 30% of cases, endoscopy reveals mucosal lesions. This form of the disease is called reflux esophagitis
.
Causes of GERD
Reflux (reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus) can occur for the following reasons:
decreased tone of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Sphincter weakness may result from:- consumption of caffeinated drinks, chocolate;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy;
taking certain medications;
- flatulence (which, in turn, can be a consequence of poor nutrition, gastrointestinal diseases, digestive disorders - dyspepsia);
pregnancy;
- hiatal hernia.
For the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease, not only the reflux itself is important, but also some other factors that contribute to the aggravation of the situation, for example:
- depressed state of the esophageal mucosa, in which it is unable to resist damage;
- impaired ability of the esophagus to cleanse itself. Normally, the esophagus should quickly be cleared of the stomach contents that have entered it - due to gravity and peristalsis, and the acidity of the environment should be eliminated by sodium bicarbonate, which is part of the saliva.
Factors that provoke reflux are:
- stress;
- eating too much food (overeating);
- eating foods that cause increased gas formation and other digestive disorders;
- physical activity after meals.
Causes of taste in mouth
Causes of blood taste in mouth
This symptom occurs when you accidentally bite your cheek or tongue until it bleeds. The characteristic taste in the mouth, repeated several times a week, is due to pathological reasons. The main diseases that cause a taste of blood in the mouth are:
- Dental diseases
: gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis. - ENT pathology
: sinusitis, chronic atrophic rhinitis. - Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
: erosive esophagitis and gastritis, peptic ulcer, dilation of the esophageal veins. - Cardiovascular disorders
: hypertension, angina, vasculitis. - Rare causes
: tuberculosis, lung cancer, bronchial asthma.
Causes of bitter taste in mouth
Bitterness is most often felt in the morning, but sometimes the symptom bothers the patient during the day. The bitter taste is accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite, sometimes vomiting with bile, and a specific unpleasant smell of rotten breath. A bitter taste in the mouth can be caused by the following reasons:
- Age-related mucosal atrophy in the elderly
. - Pregnancy
. - Bad habits
: smoking, alcohol abuse. - Liver pathologies
: autoimmune, viral or toxic hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty degeneration. - Damage to the biliary tract
: cholecystitis and cholangitis, bile duct dyskinesia, cholelithiasis. - Gastrointestinal diseases
: functional dyspepsia, chronic gastritis, duodenitis. - Neurological disorders
: consequences of traumatic brain injury, residual manifestations of stroke, Alzheimer's disease. - Iatrogenic conditions
: placement of fillings, dental prosthetics. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: treatment with chemotherapy drugs, antihistamines, antibiotics.
Causes of metallic taste in mouth
An unpleasant sensation is more often observed after consuming untreated tap water that passes through poor quality pipes covered with rust. The taste of iron also appears when cooking or storing food in aluminum cookware. Possible pathological causes of a metallic taste in the mouth:
- Anemia
: iron deficiency, B12 deficiency. - Foreign bodies
: piercings on the tongue or lips, low-quality metal dentures. - Hormonal changes
: pregnancy, menopause. - Chemical poisoning
: mercury, lead, copper, arsenic. - Exposure to radiation
. - Diseases of the urinary system
: chronic glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, renal failure. - Gastrointestinal diseases
: esophageal erosion, bleeding gastric ulcer, esophageal varicose veins. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: taking antiprotozoal, antacid antihypertensive drugs.
Causes of sweet taste in mouth
A constant taste of sweetness is observed in people who abuse confectionery and chocolate. If the symptom is not associated with food intake, unsweetened foods predominate in the diet, this indicates serious problems. The main reasons for which a sweet taste appears in the mouth:
- Diabetes
. - Pregnancy, gestational diabetes
. - Dental diseases
: caries, periodontitis, stomatitis. - Diseases of the digestive system
: chronic pancreatitis, GERD, hyperacid gastritis. - Exposure to pathogenic microorganisms
: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci and streptococci. - Neurological disorders
: damage to the facial nerve, chronic stress. - Pesticide poisoning
.
Causes of acetone taste in the mouth
A sharp chemical taste is often the result of changes in metabolic processes and the accumulation of ketone bodies. This symptom does not occur normally and always indicates serious disturbances in the functioning of the body. The unpleasant smell and taste of acetone in the mouth is caused by the following reasons:
- Following a low-carbohydrate diet
. - Endocrine diseases
: diabetes mellitus and its complication - ketoacidotic coma, thyroid dysfunction. - Kidney damage
: glomerulonephritis, acute and chronic renal failure, necronephrosis. - Liver pathology
: fibrosis and cirrhosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, neoplasms.
Symptoms of GERD
Acid from the stomach can enter the respiratory tract (this usually happens when lying down) and cause a sore throat, hoarseness, dry mouth, and cough. GERD can stimulate the development of bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis, and aspiration pneumonia.
The constant presence of acidic contents in the esophagus leads to scarring of the mucous membrane of the lower part of the esophagus, as a result of which the lumen of the esophagus narrows (this complication of GERD is called peptic stricture of the esophagus). In this case, pain when swallowing and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) may occur.
But first of all, GERD is characterized by symptoms that usually appear an hour and a half after eating. This:
Heartburn
Heartburn is the main symptom of GERD. The presence of heartburn that regularly occurs after eating is the basis for diagnosing the disease.
More about the symptom
Belching
With GERD, belching after eating is typical.
More about the symptom
Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
A sour taste in the mouth means that acid from the stomach has traveled up the esophagus and irritated the taste buds. The taste in the mouth may be bitter if bile enters the esophagus, which normally should not rise above the duodenum.
Chest pain
A burning sensation may be felt behind the sternum (along the esophagus). Often the complaint is formulated as chest pain, so it is important to make sure that the pain is caused by irritation of the esophageal mucosa, and not by heart problems. In the case of GERD, the pain is usually associated with food intake, begins in the epigastric region and only then rises higher. Pain can radiate to the neck, shoulders, interscapular area, and lower jaw.
General description of the anomaly
The sensation of sweetness, present in the oral cavity for a short time after eating desserts, is a natural, transient reaction of receptor zones that has no clinical significance. The need to visit a doctor is indicated only by phantageusia - the presence of the taste sensations in question in the absence of the influence of irritating substances on the analyzers (cells, their microvilli).
The described pathology can be permanent (protracted) or short-term. It is observed only in the morning or throughout the day, occurs in isolation or is accompanied by additional symptoms. Among the latest:
- bad breath;
- the appearance of dense gray deposits on the tongue;
- heaviness, discomfort in the stomach.
Shades of abnormal taste sensations vary from sweet and sour to cloying, milky and bittersweet.
GERD Treatment Methods
Treatment of GERD is carried out by a gastroenterologist. Treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation of the esophageal mucosa, reducing the frequency of reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, reducing the damaging properties of refluxate (the substance that enters the esophagus from the stomach), and increasing the protective properties of the esophageal mucosa.
Of great importance is:
Drug treatment
Treatment with medications is prescribed by a doctor and must take into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Lifestyle change
Normalization of lifestyle is of great importance. It is necessary to quit smoking, limit, or better yet eliminate, alcohol consumption. You should not eat fatty, spicy, sour foods, as well as coffee, tea, chocolate, legumes, cabbage, peas, and brown bread. It is better to take food more often (4-6 times a day), but in small portions. You should not eat before bed (the last meal should be 2-2.5 hours before bedtime). You should sleep with your upper body elevated to reduce the likelihood of reflux during sleep.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce discomfort, first of all you need to change your diet: limit the amount of sweets, white bread, fatty foods as much as possible, increase the content of protein foods, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is important to maintain an adequate drinking regime. To get rid of the obsessive aftertaste, you can eat citrus fruits and drink water with lemon juice.
Doctors recommend maintaining oral hygiene: brush your teeth thoroughly 2 times a day, and use dental floss or a toothpick after eating. To effectively clean the interdental spaces, use a mouthwash or irrigator. A sweet taste that occurs against the background of abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea or vomiting is an indication to consult a specialist.
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics depend on the cause of the cloying-sweet sensation. Drug therapy is combined with local effects - rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions, medicinal pastes on the area of the dental canals. The treatment regimen for diseases accompanied by a sweet taste in the mouth often includes:
- Insulin
. Hormone replacement therapy is indicated to normalize glucose concentrations in type 1 diabetes. An intensified treatment regimen with a combination of short- and long-acting insulins is selected. For type 2 diabetes mellitus, oral hypoglycemic drugs are taken. - Enzymes
. Enzyme agents are effective for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. They improve digestive function and promote the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates. The drugs are prescribed in long courses; preference is given to drugs containing bile acids. - Antisecretory agents
. Medicines reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, thus eliminating the causes of the formation of a sweetish taste. The most commonly used are proton pump inhibitors, which have minimal side effects and a prolonged effect. - Antibiotics
. Purulent lesions of the oral cavity are treated with antibacterial drugs, which are used both systemically in the form of tablets and locally in the form of ointments and applications to the mucous membrane. To prevent candida infection, antifungal agents are recommended.
Taste of garlic in a child
The taste of garlic that appears in a child’s mouth can occur both after eating a vegetable and in the case of using medications containing garlic (choleretic drugs). In addition, a child’s garlic taste is one of the reasons for poor oral hygiene, which provokes the accumulation of bacteria or dental pathologies.
Children can also provoke a garlic taste:
- sore throat and condition of the tonsils;
- gas formation, stomach cramps;
- problems with urination;
- frequent stress.
If you visit the dentist and there are no oral problems, parents should make an appointment for the child to see a therapist to eliminate adenoid diseases, and also take a urine test.
Due to inflamed tonsils
If there is pathology of the tonsils, the baby will be prescribed conservative therapy or surgical removal of the inflamed cavities.
Treatment always begins with conservative therapy, including:
- washing the tonsils with infusion of chamomile or calendula, or saline solutions;
- the use of nasal drops with a drying and anti-inflammatory effect (solutions of protargol, collargol, albucid);
- taking vitamins C, D and ascorutin;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic treatment (UV irradiation of the nasopharynx, electrophoresis with drugs, laser therapy);
In the absence of positive results, as well as in the case of frequent (more than 4 times a year) respiratory diseases, surgical intervention is performed.
Due to problems with urination
To diagnose genitourinary pathologies, it is necessary to take a urine test, after which the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, or an x-ray to clarify the diagnosis.
After the diagnosis is made, the following is prescribed:
- antibacterial therapy (Amoxicycline, Ceftrianson or Furazidine);
- ibuprofen;
- desensitizing agents (Loratadine);
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
In what diseases is it observed?
It has been established that the smell of acetone can occur in the following diseases:
- poisoning;
- coma;
- kidney inflammation;
- kidney failure;
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- dehydration due to intestinal infections;
- diabetes;
- liver injuries.
When an unpleasant odor begins to bother you, you should make an appointment with a therapist. After examination, questioning and studying the test results, the doctor will be able to refer you to a specialized doctor - gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, nephrologist.
If such a symptom appears, the doctor will definitely prescribe a blood and urine test for diagnostic purposes. Additionally, nasopharyngeal culture and CT may be required. The research results will help identify the cause and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases
In addition to natural causes, the taste of garlic in the mouth can be caused by the development of intoxication of the body with heavy metals, dental reasons, or gastrointestinal problems.
Poisoning
In case of arsenic poisoning or selenium overdose, it is necessary to isolate the victim, thereby eliminating the risk of further influence of the harmful factor, and then perform gastric lavage:
- water;
- saline solution prepared from 2 tsp. salts mixed with 1 liter of liquid;
- 20 g of suspension of magnesium sulfate, diluted in 1 liter of water;
- 1 tsp Ipecuana syrup.
Lavage is carried out 2-3 times to completely cleanse the stomach. In an unconscious state, this procedure is performed through a probe.
Garlic taste in mouth
If arsenic or large amounts of selenium enter the skin through the skin, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the skin with a soap solution and running water to prevent further intoxication.
For further treatment, the victim is hospitalized in the toxicology department, where:
- put a dropper with an antidote using Unithiol or Dimercaprol;
- restore the body’s water balance with saline;
- carry out oxygen and vitamin therapy;
- in emergency cases, emerging cardiovascular pathologies and renal failure are corrected.
Dental treatment
The appearance of an unpleasant garlicky taste with the addition of rot occurs due to dental pathologies associated with the formation of stony deposits, as well as poor oral hygiene, which provokes the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which become one of the causes of the development of caries and periodontitis.
In this case, thorough sanitation of the oral cavity, including hygienic teeth cleaning, will allow you to eliminate the garlic taste. During the appointment, the doctor will assess the condition of the teeth and gums, remove tartar deposits along with plaque, and then, if necessary, clean out the carious cavity, installing filling material in its place. Additionally, after treatment, the patient will be prescribed a mouth rinse with herbal decoctions or LISTERINE and Sensodyne products.
Treatment of chronic sinusitis and sinusitis
The taste of garlic in the mouth caused by chronic sinusitis requires not only dental, but also ENT treatment, which consists of removing the accumulated pus responsible for the unpleasant symptoms
Teeth cleaning, like sanitation of the oral cavity, is carried out at the initial stage and is accompanied by a thorough examination of the condition of the patient’s teeth and gums for the appearance of carious areas. After this, an ENT doctor is consulted to identify tonsillitis, sinusitis, nasal polyps, rhinitis, which are considered responsible for the garlic taste. For sinusitis and sinusitis, an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity may also be required.
Additionally, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes:
- CT;
- x-ray (panoramic image).
Conservative treatment methods do not solve the problem of unpleasant odor and garlic taste in the mouth, so the patient facing this problem is offered endoscopic sinus surgery, which allows one to carefully remove the pus accumulated in the maxillary sinuses without traumatic punctures. After cleansing, the specialist places a special drainage to prevent re-accumulation of pus, and then the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy with sensitive antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Suprax, Sumamed).
Additionally, for daily hygiene of the sinuses, rinsing with medicinal solutions (Aqua Maris) is prescribed.
Diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies
The taste of garlic in the mouth, caused by disruption of the digestive tract, gastritis or gastric ulcers, requires contacting a gastroenterologist and carrying out appropriate diagnostics, including laboratory tests and gastroendoscopy.
When the diagnosis is confirmed, the following are prescribed:
- acid neutralizers that accumulate in gastric juice (Maalox, Omez and Almagel);
Omez - antibiotics (Flemoxin solutab and Klacid);
- painkillers (No-shpa, Baralgin).
In emergency cases, surgical treatment may be required.
In addition to medications, the patient is prescribed a special diet that completely excludes:
- fried and salty foods;
- smoked products;
- solid food.
Additionally assigned:
- consumption of activated carbon tablets, as well as using it to clean teeth;
- use of mouth rinses;
- Thorough brushing of not only your teeth, but also your tongue every time after eating food.