Lichen planus
If you have problems with the oral cavity, it is important that you consult a periodontist in a timely manner. This is the only way to accurately determine the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the easier and faster the therapy. In the case of lichen ruber, which is flat in nature, the oral cavity is covered with a whitish film. Pathological bubbles appear on the mucous membrane, where an admixture of blood inclusions is clearly visible.
The disease occurs as a result of immune disorders, which causes inflammation. The pathology is provoked by chronic stress, emotional turmoil, digestive disorders, liver and pancreas disorders. Some experts believe that the disease is associated with disorders of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, and hypertension. The disease occurs due to injuries, in patients who come into contact with substances for film development, as well as during long-term tetracycline therapy.
Leukoplakia
This disease usually causes a plaque on the roof of the mouth in an adult. Painful blisters form as the mucous membrane becomes keratinized. White thickenings appear as a result of exposure to pathological agents on the mucosa. This could be alcohol, tobacco smoke, spicy and spicy foods. Sometimes the disease develops as a side symptom of long-term medication use.
Tonsillitis
The development of tonsillitis is associated with the penetration of various infections into the body:
- Staphylococci, streptococci;
- Pneumococci and chlamydia;
- Anaerobic organisms or fungi;
- Haemophilus influenzae and cabsiella;
The acute form of the disease is caused by chronic rhinitis, caries, and chronic pharyngitis.
White ulcer on the oral mucosa: how to deal with the problem
White sores in the mouth appear quite often. Although the problem cannot be called critical, it causes significant discomfort. Difficulty talking, chewing, swallowing and smiling. In some cases there is pain. Therefore, everyone who has ulcerative formations wants to get rid of them as quickly as possible. In this case, you cannot self-medicate. To determine the cause of the ulcers and prescribe effective therapy, it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.
Diagnostics
To cure plaque in the mouth on the roof of your mouth, you need to find out the cause of the disease. To do this, you need to carry out diagnostic procedures. Research begins with a visual examination and medical history. Besides:
- A clinical and sugar blood test is done;
- A scraping is taken from the pathological area;
- Submits urine for analysis;
Blood is tested for viruses and fungi. A biopsy of the affected tissue is performed. Also, the body’s defenses are assessed and the sensitivity of drugs to the pathogen is determined. If there is a suspicion of the development of syphilis, a special Wasserman test is used. Giardiasis is clarified using instrumental diagnostics of the abdominal organs. After laboratory tests, the correct prescription can be made.
Symptoms of ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa
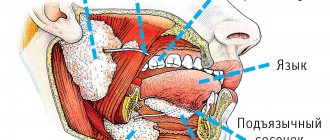
An oral ulcer is a sign of pathological processes occurring in the body. It looks like a round or oval wound with uneven, soft edges and a loose bottom. The tissues swell. Such lesions can be single or multiple. The localization locations are different: under the tongue or on it (especially at the edges), on the cheek, palate, in the throat, on the inside of the lower or upper lip, on the mucous gingival tissues. Symptoms that may accompany the formation of ulcers:
- itching felt in the affected area;
- bad breath;
- pain when eating;
- increased body temperature;
- increased salivation.
Mouth ulcers can occur in adults and children. When they form, the layer that is responsible for restoring the integrity of the gums is affected. In most cases, the ulcers do not reach large sizes and disappear after 2 weeks. Improvement should be observed within 7 days. If unpleasant symptoms do not go away, or their severity increases, you should consult a doctor.
How is oral candidiasis treated?
To begin with, let's say that treatment is necessary, otherwise the infection spreads to the pharynx, tonsils, and gums. Then the disease descends into the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver and causes irreparable harm to them.
When the first signs of candidiasis of the oral mucosa appear, you should contact your dentist or therapist to confirm the diagnosis. When you see your doctor, describe all your symptoms, even those that are not on the list. For example, you have noticed increased anxiety or a tendency to stress lately. Information about the medications you are taking, recent illnesses, and being around sick people is also important. To confirm the diagnosis, it is often enough to take a swab from the oral cavity and carry out the appropriate analysis. If the disease has already spread to other organs, a more thorough examination may be required, for example, endoscopy - diagnosing the condition of the esophagus and stomach using a flexible tube with a camera at the end.
How to treat oral candidiasis? Treatment can be local or systemic depending on the form and stage of the disease. When local, antifungal agents and antiseptics are prescribed. These can be sprays, rinses, gels, lozenges and more. Treatment on average takes up to 3 weeks, as a general rule - until symptoms disappear and another week. Systemic treatment is used for chronic forms or when the infection spreads to other organs. It usually involves the use of more medications that are intended to treat the directly affected areas.
Under no circumstances resort to self-medication! A fungal infectious disease has nothing to do with inflammation, so your actions are more likely to harm your body. In doing so, you can reduce the harmful effects of the infection and make you feel better. To do this, eat natural yogurt without sugar and take probiotics as recommended by your doctor. But these actions are not a complete treatment for candidiasis in the mouth!
Causes of lesions in the mouth
To determine how to treat a pathology, you must first find out why it appeared. In most cases, ulcerative lesions occur against the background of reduced immunity, lack of vitamins and microelements, in particular iron and folic acid. The most common causes of ulcers:
- Different types of stomatitis. The aphthous form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of white or yellow lesions in the center with a red border. Such wounds are 0.3–1 cm in diameter. Pain during the disease is often moderate, in some cases it is severe. If large wounds form, a careful approach to treatment is needed. With candidal stomatitis, caused by fungi of the genus Candida, the ulcers are covered with a characteristic cheesy coating.
- Injury to the mucous membrane. Various factors can provoke a pathogenic process: mechanical influence (with an incorrectly installed filling, caries, improper fitting of dentures, etc.) or thermal (eating hot food), chemical (smoking, exposure to caustic drugs). Even a simple bite of the cheek or tongue injures the tissue. In a child who frequently sucks his thumb, ulceration may occur on the soft palate. The habit of biting nails and pencils also provokes the formation of microtraumas. When they get infected, inflammation develops.
- General diseases of a systemic or chronic nature (disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, tuberculosis, syphilis and HIV, blood diseases). In rare cases, the cause of their formation is oral cancer. Viral diseases also provoke ulcers. Sore throat and tonsillitis can cause lesions on the tonsils.
White sores on the oral mucosa are sometimes a consequence of taking certain medications. They are also formed when there is insufficient saliva production. The problem can be provoked by the use of toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate and triclosan.
Preventive actions
Professional oral hygiene plays an important role. The procedure is carried out in a dental office at least once every six months. You should spend more time in the fresh air, eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, and alternate rest with moderate physical activity. Hardening has a positive effect on the body. The main thing is that the patient follows a number of simple rules:
- Chewing organs should be cleaned morning and evening;
- Rinse aids should be used after meals every time;
- Food that is too hot should not be consumed;
- Enrich your diet with useful microelements and vitamins to improve immunity;
It is necessary to avoid stressful situations, give up bad habits, and regularly diagnose the body. Such actions prevent the development of inflammation and diseases of the oral cavity.
What to do if a white sore appears in your mouth
If ulcerations are detected, you should contact your dentist, especially if they do not heal on their own. The doctor will tell you how to treat the wounds, comparing the problem with the causative factor. The following drugs are most often prescribed:
- Antiseptic solutions for rinsing: “Chlorhexidine” 0.05%, “Miramistin” 0.01%, “Furacilin” (a prepared preparation that does not require dilution). It is important to take into account the concentration of the active substance so as not to get a burn to the oral cavity.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate white ulcers in the mouth, alcohol tinctures from medicinal plants are used. For example, “Chlorophyllipt”, “Stomatophyte”. If a white sore appears in a child, gels (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal) are prescribed, which also have an analgesic effect.
- Antibacterial agents. Prescribed if ulcers are caused by bacteria (tuberculosis bacillus, streptococci, etc.).
- Antifungal agents. Fluconazole and Ketoconazole effectively combat fungi.
Any medications can be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can cause complications! To speed up the action of drugs, electrophoresis, phonophoresis or laser treatment methods are prescribed.
In addition to the complex of drug therapy, you can rinse using decoctions based on medicinal herbs (chamomile, oak bark, sage, calendula). Sometimes a course of vitamins and immunostimulating drugs is also prescribed, especially if the ulcers are chronic.
Treatment
Correctly prescribed treatment will quickly eliminate symptoms. Complex therapy will be the most effective.
- Local treatments are recommended for healing ulcers. Special gels and ointments prevent the proliferation of pathological bacteria.
- Soreness and fever are relieved with the help of painkillers and antipyretics.
- Those factors that provoke the disease are eliminated.
In addition, the diet is selected, the bite is corrected, and concomitant diseases are treated. Drugs prescribed:
- Against candidiasis - “Chlorhexidine”, “Stomatofit”, “Rotokan”;
- Rinse solutions;
- Combined-action medications, for example, Cholisal-gel.
- Vitamins to strengthen the body's defenses.
- Calcium supplements to reduce allergic reactions.
- Iron supplements.
Special recommendations for the treatment of white ulcers on the oral mucosa
To quickly get rid of unpleasant ulcerations in the mouth, you need to follow a diet. Your diet should include vegetables, fruits, red meat, and fish. It is important to avoid spicy and sour foods, such as citrus fruits, until complete recovery. Any rough food (nuts, etc.) that can injure the mucous membrane is also excluded. Sweets (cakes, jam, chocolate), crackers, chips, coffee are also prohibited.
It is important to pay attention to the quality of the water consumed. The heavy metal salts and other impurities it contains can cause constant bleeding from the gums and contribute to infection. If the pathology is provoked by some disease, it is necessary to eliminate it.
Question No. 7. Are there effective prevention measures?
- try not to injure the oral mucosa: if this happens, be sure to disinfect the damaged area with an antiseptic,
- avoid the accumulation of plaque on teeth, the transformation of soft deposits into hard ones: to do this, carry out thorough hygiene at home every day and professional cleaning at the dental clinic twice a year,
- visit the dentist annually for preventive examinations and elimination of existing pathologies at the initial stage of development,
- do not eat too hot or spicy foods,
- boost your immunity, and during seasonal illnesses, be sure to take vitamin and mineral complexes,
- If possible, stop smoking and drinking strong alcoholic drinks.
Lack of vitamins also contributes to the problem.
If you do not want a white spot (a scattering of spots) of unknown etiology to appear inside on your cheek or in another place in the mouth, then you must adhere to the recommendations listed. If the problem cannot be avoided, do not delay contacting a doctor.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
prevention
- Akbarov A.N., Shoakhmedova K.N., Sabirov M.A. The influence of chronic kidney disease on the condition of the oral cavity // Scientific research. – 2020.
- Latysheva S.V., Budevskaya T.V. Clinical aspects of leukoplakia of the oral mucosa // Modern dentistry. – 2013.
Expert “Very often the cause of injury and the appearance of such a symptom are dental pathologies: abnormal bite, chipped and disease-damaged teeth, incorrectly installed and poorly manufactured orthopedic (orthodontic) structures.” Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Tarabanovskaya Marina Igorevna
Specialization: Dentist therapist, periodontist Experience: 10 years
Causes of white plaque on gums
Candidiasis
The most likely cause of such symptoms is infection with microscopic fungi of the genus Candida, relatives of common culinary yeast. Candida is an opportunistic organism that is present in the microflora of healthy people and animals. However, if the concentration of the fungus on the surface of the mucous membranes exceeds a certain critical threshold, its vital activity leads to the appearance of a number of unpleasant symptoms. One of the main manifestations of candidiasis is the formation of a white coating, which can cover both small and large areas of mucous membranes. This plaque consists of fibrin, bacterial mass, waste products of microorganisms, and pseudomycelium of the fungus Candida. When it is scraped off, areas of ulceration and maceration (softening) of the mucosa are revealed.
A white spot on the gum is not the only manifestation of this disease; the fungus can also affect the mucous membranes of the palate, the inside of the cheeks, the tongue, the corners of the lips, and the bottom of the mouth. In addition, candidiasis is often accompanied by the appearance of such unpleasant symptoms as burning, dryness, and soreness in the mouth; Systemic signs of infection may also occur - fever, nausea, headaches, general weakness and malaise.
Treatment and prevention of candidiasis include the use of antifungal and antiseptic drugs, agents that accelerate the regeneration of damaged epithelium. Good results are achieved by regular use of rinses with disinfecting components - for example, chlorhexidine and benzydamine, which are part of the ASEPTA rinse, are active against a wide range of pathogens. The use of such remedies helps get rid of inflammation and bleeding, reduce the risk of developing a secondary infection and speed up recovery.
Leukoplakia
If the gums turn white in an adult, especially a smoker, this may be a sign of leukoplakia. Leukoplakia is not a disease in the literal sense of the word - it is only a pathological condition, which, however, often precedes the development of cancer. As a rule, this condition occurs as a result of constant exposure of the mucous membranes to one or another irritant - chemical, mechanical, temperature. As a result, hyperkeratosis occurs - keratinization of the upper layer of the mucous membrane. The appearance of white plaque is one of the signs of hyperkeratosis. Leukoplakia plaque is difficult to scrape off even with considerable effort.
Leukoplakia can be caused by exposure to chemicals contained in tobacco, the atmosphere, liquids or food, irritation of the mucous membrane due to contact with the sharp edge of a tooth or denture, too cold or hot food, galvanic current in the mouth due to the presence of metal fillings. Such processes occur in the mouth when it contains dentures containing various metals.
Treatment consists primarily of eliminating traumatic factors. Patients are also advised to use agents that accelerate tissue regeneration. One of these products is ASEPTA gel with propolis. Its regular use helps reduce itching and pain symptoms and quickly restore damaged mucous membranes.
Stomatitis
A white spot on the gum may be a sign of stomatitis, an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity. This spot is caused by the activity of one or another pathogenic microorganism. Most often, stomatitis manifests itself in the form of small white dots or spots, which over time can degenerate into ulcers. It is easy to cope with this disease at the initial stage: often it is enough to use antiseptic rinses and special medicinal gels.
For this purpose, we recommend using ASEPTA and ASEPTA Fresh rinses. They contain broad-spectrum antibacterial components, as well as substances that help eliminate inflammation, bleeding and other unpleasant symptoms of stomatitis. No less effective is the adhesive balm ASEPTA, which has a long-lasting effect on the affected areas of the mucous membranes. ASEPTA balm is also excellent for the treatment of other inflammatory diseases, periodontitis and gingivitis, which in some cases can also lead to the formation of white spots and spots.
Neoplasms
If a white spot on the gum hurts when pressed, it may be a sign of neoplasms such as a cyst or wen. In most cases, these formations do not pose a serious health hazard, but sometimes they have to be removed surgically. In children, there are also Bohn's nodes and Epstein's pearls - small cysts formed from the remains of the salivary glands, dental plates, and various epithelial inclusions. They most often do not cause unpleasant symptoms and go away on their own without special treatment.