Usually, the healing of the hole after tooth extraction occurs painlessly and does not cause any sensations in the patient. It would be good if everyone knew how this process works and how to speed it up.
Proper oral care after tooth extraction and following all the dentist’s recommendations will help speed up the healing of the hole and avoid complications.
Stages of socket healing by day
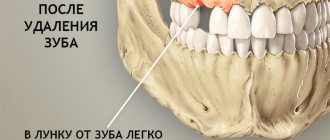
- The bleeding that occurs after tooth extraction stops after a few minutes , and a blood clot is formed that protects the wound from the penetration of microbes. Under the clot, damaged tissue is being restored, so it is so important to maintain its integrity until the hole heals completely.
- Day 1 – the processes of epithelization (healing) of the wound surface begin.
- Day 3 - signs of epithelization become noticeable, healing begins from the edges of the wound and moves towards the center.
- Day 4 - granulation tissue begins to form - a type of connective tissue that is formed in the body only during wound healing by secondary intention, when there is a strong defect in the skin.
- Day 7 - granulation tissue replaces part of the blood clot, it remains only in the center of the hole. Osteoid (bone) beams begin to appear, indicating bone formation. At the same time, epithelial tissue grows significantly from the edges of the gums.
- 14th -18th day - epithelization of the wound is completely completed, its surface is tightened and heals completely. By this time, the hole is completely filled with granulation tissue, and osteoid tissue is actively developing.
- After a month, a significant part of the hole is filled with new bone tissue. By the end of the second, sometimes third month, this process is completely completed.
- 4th month - bone beams in the newly formed osteoid tissue calcify, it matures: it becomes spongy and does not differ from the rest of the bone. At the same time, the edges of the socket dissolve, the alveolar edge in the area of the extracted tooth becomes thinner and lower than it was before surgery.
Stages of socket regeneration
How long does it take for damaged soft gum tissue to heal? It all depends on the individual characteristics of the human body. Regeneration time varies widely - from several weeks to several months. The healing period depends on the complexity of the dental work performed, the type of unit removed (soft tissue takes a long time to heal after the removal of wisdom teeth and elements with a large number of roots), the presence of chronic and infectious pathologies.
How does the hole heal after tooth extraction? There are several stages of healing:
- Formation of a blood clot (after 2-4 hours). At this time, it is advisable to refrain from rinsing the mouth and eating food. Injury to the clot leads to infection of the soft tissues of the gums and the development of alveolitis.
- The stage of formation of granulation tissue 2-3 days after the intervention. This tissue is the basis for the growth of new epithelium.
- The formation of the epithelium begins on days 7-14 after the intervention.
- Formation of the bone tissue of the socket from the edges to the center - 2-3 weeks.
- Mineralization of osteoid – 21 days from the moment of surgery.
- Calcification of bone trabeculae – after 2-3 months.
Stages of socket healing
How long does it take for gums to heal? The answer to the question depends on the volume of damaged tissue. If the doctor had to apply stitches during the intervention, then gum regeneration can be observed only after a week. Complete tissue restoration is observed only after 3 weeks, at the moment when the formation of new bone tissue begins.
After removing the figure eight, the gums will heal only after a month. This fact must be taken into account so as not to waste time fighting natural symptoms. Stress will only slow down the recovery of the extracted tooth socket.
In normal condition, the wound stops bleeding 3 days after extraction. The clot changes its color from burgundy to light or yellowish. This condition is explained by natural physiological processes: gradually saliva washes away hemoglobin from the clot, leading to its discoloration. Despite the change in color, the clot retains its structure and prevents re-bleeding and infection of the socket.
Do not clean the injured area with a brush or touch it with your hands. Failure to comply with these conditions and the dentist’s recommendations may lead to suppuration of the wound and formation of gumboil in the gums. One of the most common consequences of the removal of multi-rooted teeth is alveolitis, manifested by severe pain and inflammation of the operated area. If timely measures are not taken, the disease can be complicated by phlegmon, sepsis and abscess.
Lightening the hole after tooth extraction by 4-5 days
After 5 days, the wound will regenerate, but the patient will experience discomfort for several more days when eating food. If there is no severe pain, then a repeat visit to the dentist is not required. At this time, it is important to thoroughly clean the oral cavity and try to chew food on the healthy side of the jaw.
How many days does it take for the pain to disappear? This is usually observed on day 7-8. Granulation tissues gradually replace the blood clot. Only in the middle of the wound are epithelial particles observed. If by this time the pain does not subside, you should immediately consult a doctor. It may be necessary to re-open the cavity and rinse it with antiseptics. In practice, complications are rarely observed in patients who follow preventive rules after extraction.
What does the wound healing process depend on? Several factors should be noted:
- Age and immune system of the patient. At a young age, the wound heals faster due to accelerated metabolism. In elderly patients, the socket scars for several weeks longer, which is considered normal.
- Type of element to be removed. The hole after the removal of a wisdom tooth is much larger and deeper than after the extraction of other elements. With complex removal of the figure eight, regeneration of soft tissues is observed only on days 7-8. Gums heal worst after removing elements with crooked roots and crumbled crowns.
- Possibility of infection. The main sign of the pathological process is redness and inflammation of the surgical site. After removing a single-rooted tooth, the sign should disappear on the 5th day, after removing units with numerous roots - on the 13th day.
- Oral care. After the operation, the specialist advises the patient about the features of the rehabilitation period, which include rinsing (from day 3), changing the diet, and careful oral care. It is especially important to adhere to preventive measures after extraction of the lateral elements.
To accelerate the regeneration of soft gum tissue, ordinary and cosmetic sutures are used. In the first case, the patient will need to return to the dentist for suture removal. Cosmetic materials dissolve independently in the oral cavity.
Healing of the socket with gum inflammation
If tooth extraction was carried out against the background of inflammation, or the inflammatory process in the gums developed later, epithelization of the wound begins on the 10th -14th day, bone beams appear only by the 15th day. A significant part of the socket is filled with young osteoid tissue only by the end of the second month.
After a complex tooth extraction, when the gums rupture and the walls of the socket are traumatized, the edges of the gums cannot come together for a long time and the epithelization process slows down. Wound healing can only be completed after 1-1.5 months. In this case, the development of new bone tissue is delayed.
What happens to the gums during tooth extraction
To completely remove a tooth from its socket, surgeons have to traumatize the soft tissue of the gums. Before the procedure, the patient is given an anesthetic, since the extraction causes significant pain.
After the onset of anesthesia, the doctor bends the gum away from the tooth and wraps the neck of the element with special forceps. After this, the problematic unit is removed from the hole using rotational and rocking movements.
What happens to the gums after tooth extraction? The blood vessels that fed the pulp rupture, leading to excessive bleeding. Damaged nerve endings signal injury with severe sharp pains that appear immediately after the anesthetic wears off. The symptom worsens when talking and eating. During extraction, the ligaments that fix the root in the jaw alveolus are also damaged.
Surgical intervention is acutely perceived by the body, so the area of the hole begins to be intensively supplied with blood. An inflammatory process develops in the damaged area. This is necessary so that most of the leukocytes can penetrate through the blood vessels, thereby preventing infectious complications.
How to speed up the healing of a hole
To speed up the healing of the hole after tooth extraction, you need to follow these rules:
- Do not touch the blood clot on the socket with your tongue, much less with your hands or a toothpick, so as not to damage it. The presence of a clot is a guarantee of speedy healing of the wound.
- For three hours after visiting the dentist, you should not eat or rinse your mouth. Compliance with this point will also help maintain the integrity of the blood clot.
- · Drinks and food should not be too hot or cold for several days after removal. The food chosen is soft, without coarse inclusions, to prevent injury to the gums.
- You should not engage in heavy physical work for several days to avoid opening the wound and resuming bleeding.
- Since tobacco smoke and alcohol irritate the mucous membrane and inhibit the healing of the hole, you need to stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a while.
- To prevent infection from entering the wound and reduce inflammation after a traumatic tooth extraction, antiseptic baths are used. For them, solutions of chlorhexidine or furatsilin, infusions of sage, chamomile, and eucalyptus are used. The solutions are taken into the mouth, held for several minutes and carefully spat out.
- On the third day after removal, you can carry out antiseptic rinses with the same agents.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs (nimesulide, ibuprofen) will help not only eliminate pain, but also relieve the inflammatory process, which also helps accelerate socket regeneration.
- If the doctor has prescribed antibiotics, you should not refuse them, since eliminating the microbial infection shortens the healing time.
- When brushing your teeth, be careful not to touch the wound with the brush.
- To speed up healing, you can use Solcoseryl dental paste. It enhances intracellular energy exchange, due to which cell regeneration and restoration of damaged tissues are accelerated. Solcoseryl also creates conditions for the growth of granulation tissue. The paste is applied to a previously dried surface, then moistened with water. Before using the medicine, it would be more correct to ask your dentist about when to start using Solcoseryl after tooth extraction and how many times a day to apply it to the gums.
When to see a doctor
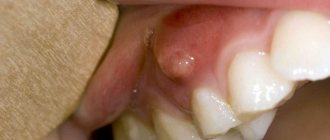
The sooner you see a doctor if you notice signs of inflammation, the easier and faster the problem can be solved. Since, in the normal course of events, pain and swelling disappear within 2-3 days, a good reason to urgently consult a dentist would be an increase in the symptoms present a couple of days after removal. The absence of a clot in the hole, swelling of the tissues, increasing pain and a suspicious-colored coating are the main signs indicating undesirable processes. In such a situation, you cannot hesitate - you need to immediately go to the doctor.
- According to WHO.
What to do when the hole has healed?
After the hole has healed and filled with full bone tissue, it is necessary to take care of restoring the dentition. The absence of even one tooth can lead to displacement of the remaining teeth, changes in bite, diction, aesthetic problems, and resorption (atrophy) of bone tissue at the site of the extracted tooth. A tooth can be restored using implantation, when an artificial root is implanted into the bone and a crown is installed on it. This method of prosthetics is by far the most comfortable and effective for the patient.
If bone tissue atrophy has already occurred, bone tissue augmentation is performed before installing the implant. The procedure allows you to perform high-quality prosthetics and restore the functionality and aesthetics of your teeth.
Causes
Causes of dry socket may include:
- blood clotting disorder;
- incorrectly selected anesthesia;
- severe tissue injury during extraction;
- active rinsing of the mouth in the first days;
- smoking immediately after the procedure;
- a tooth fragment remaining in the socket;
- poor tissue washing, which leads to infection.
Important! If at the time of tooth extraction there are foci of infection in the oral cavity, this will become a factor of alveolitis. Before extraction, professional hygiene must be carried out and inflammatory processes are eliminated.
Cyst and granuloma of the tooth
Previously, it was generally accepted that if a neoplasm on the root of a tooth measures up to five millimeters, it is a granuloma, and if it is more than ten millimeters, then it is a dental cyst. Some dentists also distinguish a certain transitional stage - cystogranuloma, but practice shows that there are granulomas reaching even twelve millimeters, so an accurate diagnosis cannot be made only by the size of the formation and its shape. In addition to X-rays, histological examination of tissues is necessary.
The question often arises of how a granuloma differs from a dental cyst. The fact is that a cyst is a bladder filled with fluid or pus, with a shell formed by connective tissue and lined on the inside with endometrium. Secretory fluid is produced by the membrane, and due to this the cyst increases in size. Granuloma grows due to the growth of tissues containing infected cells.
Treatment of severe dry socket
Symptomatic drugs are used to reduce temperature, relieve pain, relieve swelling
Severe forms of the disease require hospitalization. The patient is prescribed a number of measures, depending on the manifestations.
Treatment will be aimed at eliminating complications - abscess, phlegmon, cysts.
Physiotherapy is prescribed - electrophoresis, UHF, ultraviolet radiation. Patients are kept on bed rest.
Symptomatic remedies are used to lower the temperature, relieve pain, and relieve swelling.
For fibrosing alveolitis, glucocorticoid drugs are prescribed. If they are ineffective, the doctor prescribes immunosuppressants and Penicillamine. Without treatment, rapid replacement of epithelial tissue can lead to respiratory failure.
For toxic and allergic inflammation, glucocorticoids are also indicated. To speed up recovery, the doctor recommends special breathing exercises, physical exercise, and taking vitamin complexes.
Possible forms
The table shows the forms of alveolitis:
| Form | Features of the flow |
| Acute inflammatory process | Pain, swelling of the gums, no discharge, body temperature is normal |
| Chronic inflammatory process | Granulations are present, the pain is mild, droplets of pus may be released, the general condition is unsatisfactory, there is weakness, malaise |
| Purulent-necrotic inflammatory process | There is a sharp pain radiating into the ear, a strong increase in body temperature, swelling of the gums, a dark coating is revealed at the bottom of the socket, pus is released when pressed, and there is a persistent bad breath. The most complex form, often requiring surgery |
Treatment of dental granuloma: what to do?
Today, therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma is successfully carried out; in some cases, dental granuloma is treated with a laser, which does not require tooth extraction. As a rule, it is necessary to carry out high-quality endodontic treatment of the canals: cleaning, rinsing with an antiseptic and filling. They must be carefully sealed so that infection cannot enter from the oral cavity. Subsequently, the dentist monitors the condition of the tooth and the tissues around it. After five to six months, an x-ray should be taken, and if the tumor decreases in size or disappears, the therapy is considered successful. If it continues to grow, this makes it possible to diagnose not a granuloma under the tooth crown, but a dental cyst and re-treatment, which is carried out by a surgeon.
Treatment of dental granuloma with antibiotics and physiotherapy
Dentists often suggest treating dental granuloma with antibiotics. As a rule, this is only a temporary solution to the problem, since it does not eliminate the source of inflammation, and after some time the disease will return. Dentists successfully use physiotherapeutic treatment methods. For example, depophoresis works great for curved or complex tooth canals. Its action consists in the effect of a weak electric current on a suspension with copper hydroxide, which relieves inflammation, penetrating into all corners of the tooth.
Doctors providing this service
Modern surgical dentistry makes it possible to avoid tooth extraction in most cases, but tooth extraction is still sometimes necessary.
An operation to remove a tooth should be performed only as a last resort, when other methods to save the tooth are no longer possible or when the tooth may cause other, more serious complications.
Indications for tooth extraction
A fairly common indication for tooth extraction is the need to sanitation the oral cavity in the presence of chronic periodontitis in the acute stage, when it is impossible to eliminate the inflammatory focus at the apex of the tooth.
In some cases, tooth extraction is performed to avoid more serious complications. For example, if you have teeth that can cause a cyst, inflammation or neuritis of the trigeminal nerve. If a tooth constantly injures the tongue or the mucous membrane of the cheek, and also interferes with a normal bite, it is also better to remove such a tooth. Multi-rooted teeth, which are the cause of odontogenic osteomyelitis, are removed. When fitting a removable denture, sometimes it becomes necessary to remove teeth, but there must be strict indications for this.
Surgical operations to remove a tooth are performed under effective anesthesia, taking into account all contraindications.
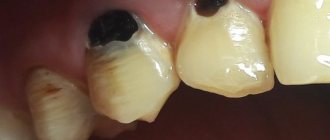
Teeth are removed when they are severely damaged by caries, affected by advanced periodontal disease (“sick gums”), have been broken so that they can no longer be restored, are incorrectly positioned in the mouth (for example, an embedded wisdom tooth), or in preparation for orthodontic treatment.
Before starting tooth extraction, the dentist examines the oral cavity, takes x-rays of diseased teeth, and evaluates their condition.
After a tooth is removed, the teeth adjacent to it begin to gradually shift, sometimes quite significantly, and this can greatly affect the general condition of the teeth. Removing even a single tooth can create serious chewing problems. To avoid these complications, the dentist will recommend replacing the extracted tooth with an artificial one.
Considering all the advances in operative surgery today, most patients prefer to replace the existing dentition defect by placing a dental implant (advantages of using dental implants), dental bridges or removable partial dentures.
Wisdom teeth removal
The removal of wisdom teeth is due to slightly different reasons. Naturally, the above reasons for tooth removal also apply to the removal of wisdom teeth, however, this case has its own characteristics.
Problems with wisdom teeth often arise as soon as they erupt. They erupt at the age of 18-25 years (sometimes much later), when the dentition is formed by 28 teeth, which leads to incorrect placement of wisdom teeth in the dentition (the lower wisdom teeth are more often displaced), immersion (incomplete eruption with a tilt in the vertical, horizontal, distal or medial direction). In addition, misaligned wisdom teeth can cause damage to adjacent teeth, putting pressure on them and causing root damage and resorption, as well as displacement and malocclusion.
There are no dental rules determining the most acceptable age for wisdom tooth removal. However, practice shows that the sooner you get rid of these teeth, the fewer complications you can expect from them in the future.
If the wisdom tooth is in the wrong position or has not fully erupted, this leads to pericoronitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth), because Part of the tooth is located under the gum and food debris accumulates in the gum pocket, which is an excellent breeding ground for various microorganisms. Wisdom teeth are often affected by caries, because... Between it and the second molar, food debris also accumulates and plaque forms due to the fact that this space is difficult to clean with a toothbrush. In this case, caries affects not only the wisdom tooth, but also the second molar adjacent to it.
- refrain from eating for 2-3 hours after removal;
- do not drink alcohol or take a sauna on the day of surgery;
- do not touch the hole with your tongue or any objects;
- do not eat hot food;
- do not rinse your mouth.
Treatment
Treatment methods will depend on the severity of alveolitis:
- Light - rinsing with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Medium - taking antibacterial agents, filling the hole with medicine.
- Severe - hospitalization, therapy, depending on complications, recovery includes physiotherapy, ultraviolet irradiation.
Important! Antiseptic rinses and antibiotics only temporarily eliminate the symptoms of inflammation, so curettage (cleaning the socket) will be the only effective method of treatment.
Treatment at home
Treatment at home is carried out for mild inflammation
Treatment at home is carried out for mild inflammation.
For this purpose, the drugs Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, and potassium permanganate solution are used.
The mouth is rinsed with the products after each meal.
Additionally, you can use decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula, and oak bark.
The doctor may prescribe Solcoseryl dental paste. It has an analgesic effect and promotes the healing of damaged tissue.
It is introduced into a hole pre-washed with an antiseptic. The paste gradually dissolves, so there is no need to remove it. Periodically it needs to be added to the hole.
Dental care
Stages of dry socket treatment at the dentist:
- Anesthesia.
- Removing food particles and necrosis from the hole.
- Washing with an antiseptic.
- Drying and filling the hole with iodoform turunda.
Important! Without removing the necrosis, any other therapeutic measures will be useless.
After curettage, the dentist prescribes medications and gives recommendations on how to care for the hole. The medicine in the hole needs to be changed every 3-5 days. You will have to visit the dentist at least 3 times.
Treatment by creating a secondary clot
When the cavity fills with blood, the dentist applies an anti-inflammatory agent and places several stitches
Treatment by creating a secondary clot involves curettage of the socket to provoke bleeding.
When the cavity fills with blood, the dentist applies an anti-inflammatory agent and places several stitches. After the procedure, you need to take antibacterial drugs.
This method of treatment is possible only in 2 cases: when the patient seeks help immediately after a clot has fallen out, and in case of indolent alveolitis without pronounced symptoms, provided that the hole is filled with granulation.
Medication assistance
After cleaning the hole, the following medications are prescribed:
- painkillers based on NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Nise, Diclofenac;
- antibiotics - Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Unidox-solutab;
- Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% for rinsing.
Why complications arise
Removal of a wisdom tooth performed by an experienced surgeon in a healthy person rarely leads to complications. There may be some discomfort, but it goes away quickly. Serious consequences can occur for various reasons. The most common is improper care. Provoking factors may be:
- Dental diseases. Caries on neighboring teeth, inflammation of the mucous membrane and other diseases can lead to the transfer of pathogenic microflora into the socket. As a result, the wound becomes inflamed.
- Reduced immunity. Removing a wisdom tooth is a surgical procedure. When immunity decreases, recovery takes longer.
- Systemic diseases. Hypertension, blood clotting problems and other cardiovascular diseases can lead to various problems, such as bleeding from the socket.
Medical errors can also lead to complications after wisdom tooth removal:
- Violation of operation regulations.
- Violation of antiseptic rules.
- Not completely removed root, etc.
Removing a wisdom tooth is a complex operation, so you should not trust your health to an inexperienced dentist. Our clinic employs highly qualified surgeons. Therefore, you do not have to worry that serious pathologies will develop due to medical errors.
Is it possible to put a crown on a granuloma on the root of a tooth?
Dental prosthetics imposes special requirements on the doctor and the patient. If we are talking about installing a crown on a tooth of which no more than 1/3 remains, that is, only the root, then it must be carefully prepared: the canals are sealed, the infection is eliminated. A granuloma under a tooth is an indicator that an inflammatory process is occurring in the tooth, and before dental prosthetics it is necessary to get rid of it, or sooner or later the granuloma will still have to be treated, since it can become inflamed under the crown. So why not do this right away, before installing a denture?
Occurrence of complications
- difficult access;
- frequent retention;
- unpredictable structure;
- features of the location of the mandibular alveolar nerve.
Are common
Painful sensations
Swelling of the tissues of the face and neck
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- painful sensations during mouth movements, radiating to the ear.
Hematomas
Alveolitis
complications after wisdom teeth removal
- the gums swell and turn red;
- local pain and headache are observed;
- sore throat;
- the temperature rises, muscle aches appear;
- lymph nodes become inflamed, most often the submandibular ones.
- increased persistent temperature;
- poor general health;
- severe migraine-like pain;
- nausea;
- other signs of intoxication of the body.
Increased body temperature
A slight increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C also often occurs in the postoperative period. This complication occurs due to a reaction to inflammation. The temperature should completely return to normal within the first day, and if it continues to rise and rise, it means that more serious pathologies have arisen and you need to go to the hospital again.
Bleeding
- rupture of large vessels;
- capillary fragility;
- hypertension.
Damage to the roots of adjacent teeth
Flux
- redness, suppuration and swelling of the gums;
- severe shooting pain;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Others
- displacement of the seventh tooth (2 molars);
- mouth rupture; cut gums or cheeks;
- jaw injuries.
Associated symptoms
Dry socket may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- High temperature accompanies acute and purulent inflammation, a dangerous symptom that requires immediate attention from a dentist.
- Swelling of the cheek indicates the accumulation of pus, the development of a dangerous purulent form of the disease.
- Severe pain is an obligatory companion of alveolitis and increases with exposure of the bone and purulent inflammation.
Recommendations after removal
Regardless of which tooth you removed or just its root, you must follow the rules of the rehabilitation period. Then healing takes place quickly and without complications.
- Do not eat for 2-3 hours after surgery.
- Eliminate hot and solid foods from your diet for 7 days.
- Carefully walk around the socket when brushing your teeth.
- Do not pick out the blood clot and try not to disturb the hole with your tongue until it is completely healed.
- Don't rinse your mouth.
The Vimontal Clinic carries out operations of any complexity using advanced equipment. This allows you to provide assistance with maximum comfort and safety.
Main consequences after wisdom tooth removal
- Dry socket is a consequence that occurs due to the doctor using anesthetics and vasoconstrictor drugs at the same time. As a result, the arteries become spasmed, and a blood “sac” (clot), which is required for natural wound healing, does not form in the socket. .
- Pain in the socket area is a common condition that can last up to five days. If the pain does not go away, and after five days it becomes more active, you should urgently consult a doctor.
- alveolitis - inflammation that occurs due to the presence of infection in the oral cavity, tooth fragments;
- pointed edges of the alveoli are a consequence of unprofessional removal of the “eight”;
- osteomyelitis of the socket is a consequence of poor wound treatment in the first hours and days after surgery;
- exposure of the alveolar zone - an injury against which part of the bone is exposed;
- neuropathy of the alveolar nerve - when, during the elimination of the “8”, the nerves of the lower jaw were affected.
- The formation of abscesses and phlegmon is a common phenomenon that develops as a result of infection during surgery or wound treatment. An acute inflammatory process develops in the tissues, and a sac with purulent contents forms. The patient feels severe pain, the tissues in the surgical area become denser, the pain becomes throbbing and acute, the body temperature rises, the head feels dizzy, and the cheek puffs out.
Frequent complications after removal of a wisdom tooth in the upper jaw: alveolitis (inflammation of the socket), hematomas (when the doctor damages a vessel), bleeding (this area is abundantly supplied with blood), damage to the bottom of the sinus. jaws, swelling and inflammation of tissues.
Common complications after removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw: gumboil, damage to adjacent nerve endings, bleeding, stomatitis, cysts, etc.
Signs of complications after wisdom tooth removal:
- the wisdom tooth socket becomes brown, sometimes acquiring a bluish tint;
- increased pain;
- swelling;
- increased body temperature;
- heavy bleeding;
- dry socket;
- weakness;
- weak appetite;
- pain when swallowing food and drinks;
- difficulties opening and closing the mouth, etc.
In case of all the complications listed above, you must definitely contact an experienced, trusted dentist. The doctor will conduct an examination, determine the problem and prescribe adequate treatment.
Wisdom tooth removal
Wisdom teeth are considered full-fledged elements of the oral cavity. They are involved in chewing food (if they are located above each other and have contact), and can act as a support for bridges and removable dentures in the future. There are specific indications for extraction in their case. For this reason, the decision about whether wisdom teeth need to be removed is made only by the attending physician.
The most common problem with eighth teeth is their growth. Only some teeth form and grow completely without complications, but often these processes are accompanied by a number of difficulties:
- semi-retinated or impacted elements that have formed in the bone tissue, but have not erupted or only partially erupted. Their position can be vertical, horizontal, or with their roots outward. Because of this, neighboring elements suffer, constant pain appears;
- violation of position (dystopia). Since wisdom teeth erupt without predecessors (baby teeth), and the jaw bone is already formed and does not develop, the position of the elements is often incorrect. They injure the mucous membrane, overlap other crowns, and put pressure on neighbors. This leads to inflammation. The doctor will determine whether the position can be restored with orthodontic treatment or whether it is better to remove the wisdom tooth;
- appearance of a gingival hood. When slowly cutting through the mucosa, an area is formed in which bacteria and food debris accumulate, which are difficult to clean. This leads to acute inflammation, which can provoke the appearance of pus;
- destruction, caries. Elements may appear immediately underdeveloped with carious lesions.
The doctor determines whether wisdom teeth should be removed or not based on complaints and the clinical picture. Problems with even one or two teeth interfere with the normal functioning of the entire dental system. Pain appears when opening the mouth and chewing. The bite and position of the incisors may even change.
How a wisdom tooth is removed depends, as in the case of permanent elements, on the condition of the dental system. In the absence of contraindications, manipulation is carried out with ordinary forceps.