From this article you will learn:
- Tooth pulled out, gums hurt: what to do.
- why gums hurt after tooth extraction: reasons,
- How many days should the pain last?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
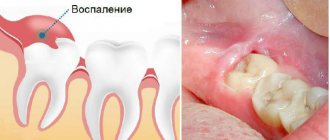
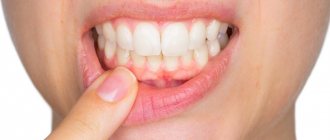
Many patients complain that their gums hurt in the first days after tooth extraction. Pain is the body's normal response to injury, and therefore mild pain that does not last long is normal. However, pain occurs not only as a consequence of injury to the bone and gums, but also because inflammation of the gums could develop after tooth extraction.
According to statistics, inflammation and improper healing of the socket after tooth extraction occurs in 3-5% of cases (but this applies to teeth of any location except wisdom teeth). But the removal of the eighth teeth leads to the development of complications in approximately 25-30% of cases. This article will help you understand the cause of the pain, whether your tooth socket is healing properly, and what to do if it becomes inflamed.
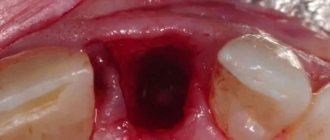
Type of gums after tooth extraction (normal) –
Please note that normally, the socket of each extracted tooth should be completely covered with a blood clot. The surface of the clot should first be an intense burgundy color, gradually becoming yellowish-whitish. What the sockets should look like at different times after extraction - see the article: → “Healing the sockets of extracted teeth: photo”
Why is tooth extraction required?
In certain cases, tooth extraction is the only possible method of solving a particular dental problem. Indications for removal may include:
- Incorrect position of the tooth, when neither the patient nor the doctor can access it (high-quality hygiene and/or treatment is impossible);
- The absence of the main part of the dental material without a chance of its restoration;
- Malocclusions (for example, severe crowding);
- Inflammatory process in the roots of the tooth, which can lead to infection;
- Painful eruption of wisdom teeth.
This is also necessary when preparing to correct your bite using Invisalign aligners. In particular, it is usually necessary to remove the “eights” if they have not fully erupted and can interfere with quality orthodontic treatment. It is worth noting that such a decision should be prepared when there are certain indications and no other option is possible.
Otherwise, when installing aligners, the unerupted tooth hidden inside the gum will prevent the aligner from attaching and pull the remaining teeth in the right direction, leaving them no room to move.
Treatment methods
The choice of a specific treatment method depends on the cause of the problem and the complexity of the situation as a whole. An integral part of therapy in this case is the use of appropriate medications - antibiotics and vitamin complexes, designed to facilitate the rehabilitation period. It may also be necessary to antiseptically treat inflamed tissues and place medicine inside the socket to fight infection.
Treatment of alveolitis Treatment of this disease involves complete cleansing of the socket from inflamed tissue, antiseptic treatment of the cavity, followed by placement of a medicinal product inside. Such compresses can be carried out either one-time or consist of a course of several procedures - it all depends on the severity of the inflammatory process. Additionally, antibacterial drugs and oral baths with antibacterial agents are necessarily prescribed, which promote tissue restoration.
Price:
from 3,000 rubles more about the solution
Treatment of facial nerve neuralgia An unsuccessful tooth extraction can lead to facial nerve neuralgia. Often the problem manifests itself in the form of minor inflammation of the nerve, which is accompanied by numbness in a certain part of the face. To solve the problem, drug therapy is carried out using anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsant drugs, as well as physiotherapy and electrical stimulation. Surgery can be performed to restore the integrity of the nerve, but this is a last resort and is usually necessary in advanced stages.
Price:
from 4000 rubles more about the solution
Why does a pulled out tooth hurt?
The presence of pain after tooth extraction is due to the fact that soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves are damaged during tooth extraction. Typically, the first pain symptoms appear 3-4 hours after surgery. This is due to the fact that this is when the anesthesia stops working.
Also, during removal, the bone tissue of the jaw socket may be damaged. In this case, the pain during the healing period is more intense and prolonged. However, if the removal was carried out correctly, it will soon pass.
How long does it hurt?
In most cases, pain during removal worsens on the second day. On the third day they begin to decrease. By the fourth or fifth day, there is practically no pain. If by this period the pain after tooth extraction does not subside, the patient should consult a doctor, as this may indicate the emergence of complications.
However, it is important to remember that complete healing of the hole occurs only in the second or third week after the procedure. Until this time, the gums and bone tissue are vulnerable, so if they are irritated, pain may also occur. To prevent this from happening, you should follow your doctor's recommendations.
Headache
The recovery period after tooth extraction may be accompanied by headaches of varying intensity. They are associated with damage to the nerve fibers that go to the brain. Such symptoms should not frighten the patient, since as the wound heals, they will also pass.
Another cause of headaches during this period may be hypertension. The patient must notify the attending physician about the presence of such an illness. In this case, the surgeon will be able to select appropriate medications that will reduce pain.
Ear pain
For the same reasons, a patient may experience unpleasant or even painful sensations in the ear after tooth extraction. Most often they have a shooting character. This symptom is also normal and goes away in the coming days after the intervention.
Ear pain may worsen if, after the procedure, the patient does not properly care for the oral cavity and tries to chew solid food.
Pain in the gums
Pain in the gum is associated with its direct damage. In this case, not only the soft tissue suffers, but also the nerves, which are also located in the gums. Depending on the degree of damage, pain can last for different times and occur with greater or less intensity.
Increased pain in the gum may indicate the presence of fragments in its tissues, as well as the occurrence of one or another complication. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a specialist.
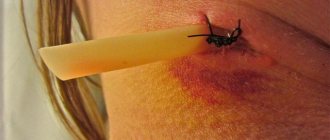
Hematoma
In addition to alveolitis, another complication such as hematoma and suppuration of the hematoma occurs. At the same time, we see normal healing of the socket, but there is pronounced swelling and pain in the soft tissues (cheeks, along the transitional fold).
The main signs of a hematoma are:
- swelling of the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth or at the site of anesthesia;
- pain when touching the cheek;
- the cheek is warmer than the surrounding tissues;
- cyanosis appears on days 3-4;
- the temperature may rise.
There can be many reasons for the formation of hematomas, but the main ones are:
- vascular injury during anesthesia or removal of tooth fragments. All people have different vessels, and the surgeon cannot say with certainty where the vessel will go;
- problems with blood clotting (diabetes, leukemia).
Hematomas also cannot be treated at home. You definitely need to see a surgeon.
If the hematoma is relatively small and there are no signs of suppuration, then drugs are prescribed to resolve the blood. If the hematoma is large and there are signs of suppuration (fever, sharp pain, redness of the cheek and increased skin temperature, tissue tension), then an incision is made along the transitional fold, pus and excess blood are released, and drainage is placed in the wound. After a week, the wound heals, leaving a scar.
Home treatment of hematomas is fraught with the formation of abscesses and phlegmons, which may require external incisions and subsequent cosmetic surgeries, and in advanced cases can cause serious complications for the body as a whole.
Will the site of the extracted tooth stop hurting on the second day?
Patients often believe that the pain at the site of pulled out teeth should go away after sleeping on the second day, and they get scared when it becomes even stronger. This situation is normal, since after a certain time the damaged gum tissue begins to swell, thereby pinching the nerves. All this leads to pain becoming more intense.
You need to be prepared for this. Today there are a large number of analgesics and other medications that can reduce inflammation and eliminate pain syndromes.
The treated tooth hurts when pressed after canal filling
Working with roots requires precision and accuracy from the doctor. If he incorrectly assessed the depth of the canals, then the following complications cannot be excluded:
- a tooth without a nerve hurts when pressed if the filling material extends beyond the apex of the root, gets into the gum and puts pressure on it;
- when the channels, on the contrary, are not completely filled, inflammation may begin in the voids over time. If a lot of time has passed after visiting the doctor, and the tooth aches and hurts, then the problem is the unsatisfactory filling of the canals.
The site of tooth extraction hurts after a week, what should I do?
The holes in which the extracted teeth were located are usually completely healed by the end of the first week. Final healing still needs to wait, but the pain should have passed during this period. If, after a week, the area continues to hurt after tooth extraction or any other symptoms appear, such as bleeding, the patient urgently needs to see a doctor.
Under no circumstances should you try to relieve pain on your own. If it continues to bother the patient, this may indicate the development of inflammation or an abscess process in the gum. If they are not eliminated in time, the consequences can be very serious.
Doctors providing this service
December 6, 2018
Of all the teeth in the mouth, wisdom teeth are the ones that most often have to be removed.
Of all the teeth in the mouth, wisdom teeth are the ones that most often have to be removed. There are a number of important reasons for this:
- the remote location of wisdom teeth makes their hygiene difficult, ultimately contributing to the fairly rapid destruction of the enamel;
- often wisdom teeth do not have enough space in the jawbone, and they erupt unevenly, “into the cheek,” or rest against neighboring teeth, contributing to their destruction;
- if one of the wisdom teeth has been removed, its antagonist begins to move towards the missing one, deforming the dentition;
- inflamed tissue and pain in the gum near the wisdom tooth.
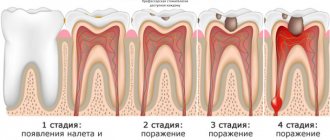
Stages of socket healing
The holes in the place of pulled out teeth heal in several stages. The first one lasts about a week. At this time, the wound heals, its surface becomes smoother. The patient can return to his usual lifestyle - eat regular food, brush his teeth, etc. Usually, during this period, a blood clot remains on the surface of the hole, which in no case should be torn off, as this can lead to bleeding and will slow down the final healing process.
Complete healing of the wound ends by the end of the second week. At this time, the clot disappears, and residual pain goes away. The last stage, that is, complete healing, ends by the end of the third week. If the intervention was very serious, this period may last 4 weeks. By this time, the nerve fibers and blood vessels are completely restored, and the gums become completely smooth.
Complications after removal
In some cases, tooth extraction can cause complications. They can be associated both with poor quality of the procedure itself and with illiterate oral care during the healing period.
The main complications that may arise during tooth extraction include the following:
- an abscess that appears as a result of infection in open wounds in the sockets where teeth used to be;
- bleeding, which may be a consequence of injury to the gums during the healing period, and may also occur due to the presence of hypertension or poor blood clotting in the patient;
- paresthesia, characterized by numbness of the gums or part of the jaw in the place where the tooth was pulled out.
One of the most serious complications is osteomyelitis. It is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process in the bone and bone marrow. This disease can occur when the patient has an infection of the bone tissue against the background of a general decrease in immunity. This disease requires immediate treatment.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a complication after tooth extraction is increased pain after the 5th day of healing. If by this period they do not subside, then you need to contact a specialist to find out the reasons. This could be either inflammatory processes or the presence of tooth particles that went unnoticed after the procedure.
Another symptom is a strong increase in temperature, sharp cramps in the head that last more than 5 days. This can also cause your gums to swell. If this happens, it means that the swelling cannot go away for some reason. This, in turn, is a sure sign of a complication.
Reasons for the development of complications
There can be a large number of reasons for the appearance of one or another complication. In addition to medical errors and improper oral care, these include the presence of certain physical diseases in the patient, which can lead to the development of inflammation or frequent bleeding.
To prevent such situations from arising, the patient must warn the doctor about all his ailments, even if he is sure that they will not affect the outcome of the procedure. After this, the specialist will be able to select certain medications that will reduce the risk of complications and make the wound healing process more comfortable.
What happens if you ignore pathological pain
The appearance of pain always signals a problem in the body. If the tooth was removed long ago, and the pain persists or increases, this is evidence of a complication. Pain may be associated with:
- Increased body temperature;
- severe swelling, redness of the mucous membrane;
- halitosis;
- purulent discharge from the socket;
- white or gray coating on the mucous membrane;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- pain while swallowing;
- restriction when opening the mouth.
In this situation, you should see a doctor immediately.
Ignoring alarming symptoms is fraught with serious problems, such as abscess and osteomyelitis. These are serious pathologies that require timely, qualified treatment.
What to do after removal?
After tooth extraction, it is important to maintain proper oral hygiene and also slightly limit your diet. The main recommendations are:
- You can apply a cold compress to the damaged gum, which will reduce the pain;
- if the bleeding does not decrease, you can firmly press a cotton swab between the teeth in the area of tooth extraction;
- For disinfection, rinses based on natural herbs should be used;
- It is better to eat only warm and soft foods without solid particles.
Medications can also be used to reduce discomfort. However, you can only use those medications prescribed by your doctor. He should also tell you how long to rinse so as not to damage the wound.
If at any stage of healing the patient feels an increase in pain symptoms or discomfort that is not normal, he should immediately inform the doctor.
How to get rid of discomfort after molar extraction
To remove painful sensations, you need to understand their cause. If the issue is a mistake made by the surgeon, then measures are taken to eliminate the adverse consequences. If the hole is infected or an inflammatory process has developed, mouth rinses with an anti-inflammatory drug and oral antibiotics are prescribed. The same is done for “dry socket” and clot displacement.
Timely treatment can quickly normalize the situation - speed up regenerative processes and relieve the patient from painful toothache. Therefore, there is no need to self-medicate.