Visiting the dentist is a very unpleasant experience. Having headaches after visiting the dental office is a common occurrence. If a doctor removes or prescribes treatment for a diseased tooth, a headache may occur.
The reasons for this may be the following:
- Side effect from medications;
- Severe dental disease;
- Poor oral health;
- A large number of teeth undergoing treatment;
- Poor condition of the body as a whole, the presence of chronic diseases;
- Senile age of the patient;
Most often, pain caused by the cessation of the painkiller goes away on its own. If the pain only gets worse, you need to take an analgesic and consult a specialist for advice.
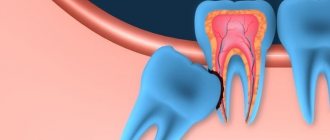
One of the possible causes of headaches may be the removal of a diseased tooth. Headaches occur especially often when a wisdom tooth is removed (the procedure is not always simple). This type of operation tends to damage bone tissue and gums, which leads to pain.
When correcting a malocclusion, headaches often appear. Pain can be of various types:
- Pain in the ear area;
- The occurrence of pain in the temporal part of the head;
- The occurrence of pain in the occipital part;
If you follow clear treatment instructions, this type of headache goes away in a short time.
Pain after tooth extraction
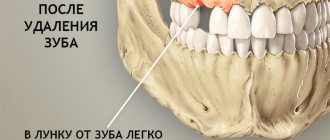
After the tooth is removed and the anesthesia wears off, the patient may experience minor pain, which usually goes away quickly. However, sometimes 1-3 days after surgery a sharp pain appears in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth .
Taking analgesics does not bring relief. This pain most often occurs due to disruption of the normal healing process of the tooth socket. In addition, the pain may be caused by the remaining sharp edges of the socket or by an exposed area of the alveolar bone not covered with soft tissue.
Trigeminal neuritis
Today, traumatic neuritis of the trigeminal nerve is considered one of the most common causes of pain syndromes in the maxillofacial area.
As a complication, it occurs during the removal of permanent molars of the lower jaw, due to damage to the lower alveolar nerve in the mandibular canal. The apices of the roots of the lower molars are in close proximity to the mandibular canal and in some cases may be located in the canal itself. Sometimes, due to chronic apical periodontitis, the bone between the root apex and the wall of the mandibular canal is resorbed. When a tooth is loosened by an elevator, the lower alveolar nerve can be injured, which will lead to partial or complete disruption of the functions of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The result is pain in the jaw, numbness of the lower lip and chin, decreased or absent sensitivity of the gums, decreased electrical excitability of the dental pulp on the affected side. Usually all these phenomena gradually disappear after a few weeks.
Electroodontometry
Electroodontometry is the most effective method for assessing the functional state of the trigeminal nerve when it is damaged. EDI is based on a study of the reaction of the teeth of the lower jaw to electrical stimulation. The method is performed on all teeth of the lower jaw, with preserved pulp both in the affected area and on the opposite healthy side.
S.N. scale Fedotova (1997) to assess the severity of damage to the inferior alveolar nerve based on electrical odontometry data:
- mild degree - reaction of teeth with preserved pulp on the side of nerve damage within 20-40 μA;
- moderate severity – reaction of teeth to currents from 40 to 100 µA;
- severe degree - complete loss of pain sensitivity, reaction of teeth to currents above 100 μA
The use of EDI to diagnose traumatic injuries of the inferior alveolar nerve is impossible if:
- lower jaw teeth endodontically treated
- lower jaw teeth are covered with orthopedic structures
- metal elements of splinting structures are fixed on the teeth
- missing teeth
Locations for measuring electrical excitability of facial skin
Assessment of the area of paresthesia in traumatic neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve
The zone of paresthesia is identified - impaired sensitivity of the skin based on a tactile test, photographed, followed by an assessment of the area of the paresthesia zone: points are drawn on the border of areas of normal sensitivity of the skin, the red border of the lips and the paresthesia zone, which are then connected by a continuous line. Zones of hyper-, hypo- and anesthesia were marked with different colors.
I - vertical lines:
- midline,
- a line passing through the outer edge of the philtrum,
- a line passing through the outer edge of the wing of the nose,
- pupil line;
II - horizontal lines:
- lip line,
- a line running along the lower edge of the red border of the lips,
- the border line between the chin and lower lip,
- a line drawn along the most protruding part of the chin,
- line of the border of the chin and submental areas.
Schematic representation of the areas for measuring facial skin paresthesia.
Each of the 12 resulting squares was assigned a score depending on the nature of the sensitivity disorder:
0-sensitivity is not impaired;
1-skin hyperesthesia
2-hypoesthesia of the skin;
3-anesthesia of the skin.
Next, the sum of points was calculated and divided by 12 (quadrants).
With the results:
3.0-2.1 – severe sensitivity impairment was diagnosed;
2.0–1.1 – moderate severity;
less than 1.0 – mild severity of the pathology being studied
Alveolitis
Inflammation of the walls of the socket.
- In the initial stage of alveolitis, an intermittent aching pain appears in the socket, which intensifies while eating;
- The general condition is not disturbed, the body temperature is normal;
- The tooth socket is only partially filled with a loose, disintegrating blood clot.
With further development of inflammation:
- The pain intensifies and becomes constant;
- Transmitted to the ear, temple, corresponding half of the head;
- The general condition worsens, malaise and fever appear.
How to get rid of pain at home
To eliminate postoperative pain, the dentist will prescribe analgesics and cold compresses on the side of the intervention. Additionally, you can use traditional methods - mouth baths made from tinctures or herbal decoctions. Baths with an antiseptic drug are also allowed (the solution must be held in the mouth for a while and spat out). What is strictly forbidden:
- warm the operated area;
- rinse your mouth intensively (you can wash out the blood clot);
- chew on the injured side;
- “check” the hole using your tongue, fingers, and apply medicine to it.
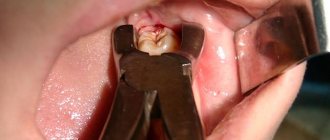
The risk of complications depends on the complexity of the operation to remove a dental unit. Simple extraction is carried out if the tooth does not have strong, intertwined roots, it is intact, and there are no associated problems (cysts, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.).
Extraction of dystopic teeth, which are very crooked, have intertwined, crooked roots, with a destroyed coronal part, and with an inflammatory process, is considered difficult. In such cases, a more extensive operation may be necessary with a preliminary incision in the gum, sawing the tooth into elements, extracting fragments through a hole in the jaw bone, and applying sutures. Molars are usually difficult to remove. If your gums hurt for several days after the removal of a molar, but the painful symptoms are smoothed out, then the wound is healing normally.
Limited osteomyelitis of the tooth socket
Inflammation of the bone tissue in the area of the extracted tooth :
- in the socket of the extracted tooth , and pain occurs in the adjacent teeth;
- Weakness, severe headache;
- Body temperature is 37.6-37.8°C and above, sometimes there is chills;
- Loss of sleep and performance;
- The bottom and walls of the hole are covered with a dirty gray mass with a fetid odor;
- Touching the gum is sharply painful;
- When you tap adjacent teeth, pain occurs;
- The perimandibular soft tissues are swollen, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, dense, painful;
The symptoms of acute inflammation last 6-8 days, sometimes 10 days, then they decrease, the process passes into the subacute and then into the chronic stage.
- The pain becomes dull and weak;
- General condition improves;
- Body temperature normalizes;
- After 12-15 days, the tooth socket is filled with loose, sometimes protruding pathological granulation tissue, which, when pressed, releases pus.
Please note that pain relief during a complication does not mean that the process has begun to heal; perhaps it has entered a chronic, more dangerous stage. As a rule, the surgeon schedules a follow-up examination for the patient after removal; ATTENDANCE IS MANDATORY!
Headaches after using anesthesia
Very often, dentists use local anesthesia when treating teeth. After undergoing anesthesia, many patients experience headaches. There are several reasons for this type of pain:
- Presence of intolerance to anesthesia or incorrect choice of medication;
- Location of the diseased tooth in remote places;
Most often, the headache is aching in nature and tends to increase when moving the head.
If headaches began after the extraction of a diseased tooth, it is necessary to find the cause of the pain; it may be a complication of the operation.
Sharp edges of the alveoli
Socket pain can be caused by protruding sharp edges of the socket, which injure the mucous membrane located above them. Pain appears 1-2 days after tooth extraction , when the edges of the gums above the socket begin to approach each other.
- The pain intensifies during chewing and when touching the gums;
- When you feel the hole with your finger, a protruding sharp edge of the bone is detected, and a sharp pain occurs.
This pain can be distinguished from the pain of alveolitis by the absence of inflammation in the socket area and the presence of an organizing blood clot in it.
Treatment of neuritis
Treatment of neuritis in traumatic injuries must be timely and wait-and-see tactics are unacceptable. For mild damage to the inferior alveolar nerve, decongestant therapy (prednisolone, veroshpirone) is sufficient. In case of moderate severity of damage, drugs that improve the conductivity of the nerve trunk (neuromedin) are added to decongestant therapy. In case of severe damage to the nerve trunk, in the absence of positive dynamics in the restoration of sensitivity within 4 months, the patient should be referred for a consultation with a neurosurgeon in order to resolve the issue of the possibility of restoring the anatomical integrity of the nerve trunk.
Various reflexotherapy methods are widely used in the complex treatment of diseases of the peripheral nervous system. In the complex treatment of diseases of the peripheral nervous system, reflexology methods such as electroacupuncture and transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation are widely used.
Prevention of neuritis
Prevention of neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve is the correct technique for removing teeth, correct diagnosis and correct reading of the radiograph, and a gentle technique for dislocating the roots of teeth in the lower jaw with an elevator.
Toothache after caries treatment
Constant pain after filling can occur for many reasons. A common cause of discomfort is the application of an insulating lining made of glass ionomer cement (GIC) and filling on the same day with a composite. The polymerization times of GIC and composite differ, which can result in displacement of the gasket and its pressure on the pulp.
If the pain is short-term in nature as a reaction to cold, sour or sweet and quickly passes after removing the irritant, it may be due to the fact that during the treatment there was a mechanical effect on the pulp. After 2-3 days, the pulp will return to normal functioning and the pain will stop.
If you experience pain when biting, you need your dentist to grind the filling to fit your bite.
Treatment methods for headaches after dental surgery
If you have a headache for a long time, your dentist will prescribe treatment using the following medications:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - help relieve inflammation;
- Analgesics – eliminate pain;
- Antispasmodics – relieve spasms that cause pain;
If the cause of pain is inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, then the presence of toxins, which are eliminated by the use of antibiotics, should initially be eliminated, and only then the prescribed medications should be used.
Taking such medications must be done under the supervision of a physician. The use of such drugs is contraindicated for patients suffering from stomach diseases.
Diseases that provoke painful pulsation in the tooth
Suddenly got a toothache? At the appointment, the dentist usually diagnoses one of the following diseases.
Caries
First, with carious tooth decay, throbbing pain periodically occurs after eating hot/cold food, eating sweets or sour fruits. This means that the pathological process has reached the dentin (the tissue located under the tooth enamel). As the carious cavity deepens, the intensity of the pain increases, but after 10-15 minutes everything goes away without taking painkillers. If you do not consult a dentist in time, the dental crown will be completely destroyed very quickly. However, at this stage it is possible to save not only the tooth, but also avoid removing the nerve.
Important! Sometimes only a small hole is noticeable in the tooth enamel. However, the carious process spreads inside the tooth. A sign of deep caries (in addition to pain) is bad breath.
For caries, it is not recommended to put analgin into the tooth. This drug, although it effectively relieves pain, instantly destroys tooth enamel. It is impossible to save a tooth that is more than 2/3 destroyed.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the pulp (neurovascular bundle) is a complication of deep caries. During the day, throbbing pain is quite tolerable, it occurs only after eating or inhaling cold air, and is easily relieved with painkillers. By nightfall the tooth begins to twitch.
The worst tactic for pulpitis is to drown out the pain with strong analgesics and again postpone going to the dentist in the morning. It makes no sense to endure pain day after day; in any case, the nerve will have to be removed. However, when the pulp is removed, the tooth stops receiving nutrition, the enamel and dentin become less dense.
Even a filled tooth with the nerve removed is short-lived. Therefore, we recommend that you contact the Matiss Dent dental clinic as soon as painful sensitivity to hot/cold occurs or a small dark spot appears on the enamel.
Periodontitis
If the infection penetrates deeper, a fibrous compaction or granuloma forms at the apex of the root. In this case, the pulsation is usually painless and intensifies when chewing food. The patient feels as if the tooth has lengthened.
With the development of a purulent process, a periapical abscess (cyst) is formed. The throbbing pain in the tooth increases (it jerks more and more), the gums swell, and painkillers only slightly ease the pain. Possible increase in temperature. Sometimes after a few days the abscess forms a white “bump” on the gum.
Important! Under no circumstances should you open a root cyst yourself. Any manipulations at home are fraught with the development of perimandibular abscess and sepsis.
Previously, the cyst was removed along with the tooth. However, modern dentistry makes it possible to preserve the root. The abscess is opened through the root canal (the capsule is scraped out with a curette or dissolved with special substances) or removed surgically in combination with antibiotics. The resulting cavity is filled with a paste that restores bone tissue. The tooth is built up using pins, then a crown is installed. An indicator of successful removal of a periapical abscess is that an x-ray taken 6 months later shows no evidence of new cyst formation.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the periodontium (supporting apparatus of the teeth) is the most insidious dental disease. At the initial stage, the pathology is manifested only by increased bleeding of the gums after brushing teeth, eating carrots and other solid foods.
Over time, degenerative changes occur in the gums: the spaces between the crowns increase, the roots of the teeth become exposed, and a metallic taste is constantly felt in the mouth due to increased bleeding. Even brushing your teeth frequently does not eliminate bad breath. Later, the teeth begin to loosen, ache and throb even after eating soft food. The tissues around the tooth become inflamed, and pus and blood are released from the gum pockets. Body temperature often rises and general health worsens.
When bone tissue is involved in the pathological process, the only treatment method is surgery. After professional cleaning and removal of tartar, a flap operation (gum excision and subsequent plastic surgery) is performed. Implantation of bone tissue substitutes (osteoplasty) is often required.
Pericoronitis
Difficult teething provokes swelling and redness of the gums, painful pulsation, and discomfort when swallowing. Most often, a similar picture is observed during the eruption of wisdom teeth. Severe pain does not allow you to open your mouth wide and eat food calmly. Due to the accumulation of food debris under the “hood”, pus forms. You shouldn't endure pain. The dental surgeon will excise the “hood” in 5 minutes, which will ensure painless tooth eruption.