Introduction
In dentistry, since 1971, there has been the so-called two-digit Viola system.
According to it, the units of the upper and lower jaw of a person are divided into four quadrants, each of which has 8 teeth (we recommend reading: how often can radiography of the lower jaw be performed?). Quadrants for adults are numbered as 1, 2, 3 and 4, and for children - numbers from 5 to 8 (see table). Therefore, if you suddenly hear from a dentist that you are undergoing medicinal root canal treatment of 46 or 36 units, do not be alarmed. READ ALSO: structure and anatomy of the human lower jaw
Each unit has its own individual structure. The number of canals and roots depends on where it is located and what function it performs. From this article you will learn what a dental cavity is and why it is affected by pulpitis. Also read about the concept of working length of the root canal. You will learn about methods for expanding dental cavities and their medicinal treatment, and see photos of three-channel pulpitis.
Number of roots and canals in human teeth
Many people often ask the question - how many roots does a molar have? This question is relevant for most doctors. Because the complexity of many medical procedures depends on the number of roots, ranging from treatment, restoration and ending with removal. After birth, after birth, every person begins to grow milk teeth, of which there should be 20 by the age of 3. Then, after 6-7 years, the dairy ones are replaced by radical units, which should already increase by almost 1.5 times - 32. At the same time, dairy units can only have one root, but radical ones grow with several roots.
Number of roots in each tooth
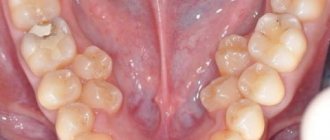
Often the root is located in the area under the gums, below the surface of the cervix and its size is about 70% of the total volume of the organ. The number of chewing organs and the roots present in them is not the same. In dentistry, there is a special system with the help of which the number of roots is determined, for example, in the sixth unit at the top or in a wisdom tooth.
This image shows the side of the upper and lower arch of teeth, which shows the number of roots each tooth has.
So how many roots do adults have? This indicator is different for each person, it depends on various reasons - on heredity, on size, on location, on the age and race of the person. For example, representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races have one more root than representatives of the Caucasian race, and they also grow together quite often.
This system applies to adults. But as for children's milk teeth, their root system has some differences. Many people believe that dairy plants have no bases and they grow without them, but this is not true. Typically, the first teeth appear from the root system; each unit usually has one base, which is completely dissolved at the time it falls out. That's why many people believe that they don't exist at all.
How many channels
The root canal system is the anatomical space inside the root of the tooth. It consists of a coronal space connected to one or more main canals at the root of the tooth.
Features of the number of channels:
- The upper and lower organs may have some differences. Usually in the area of the incisors and canines of the upper jaw there is one canal;
- The central ones of the lower row may have two recesses. But in almost 70% there is only one, and in the remaining 30% there are two;
- In the area of the second incisor of the lower jaw, in almost 50% of cases in adults there are two canals, in 6% of situations the canine has only one recess, and in the rest it has similar properties to the second incisor;
- Dental unit No. 4, also called a premolar, which is at the top, has three sockets. But a three-canal fourth premolar occurs only in 6% of cases, in the rest it has one or two recesses;
- The similar fourth premolar, which is located below, has no more than two, but in most cases there is only one;
- The upper fifth premolar can have a different number of recesses. In 1% of cases there are units with three channels, in 24% - two, and in other cases there is one depression;
- The lower fifth premolar meets a single canal;
- The sixth upper organ has the same ratio of recesses - three or four;
- Below, sixes are sometimes found with two channels, in almost 60% of cases with three, and can also be with four;
- The upper and lower seventh tooth has three canals in 70% of cases, and 4 in 30% of cases.
How many canals does a wisdom tooth have?
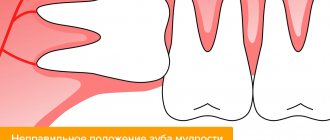
How many wisdom teeth can there be? This is a difficult question, because this organ has a very unusual structure. If it is located at the top, then it can have four and sometimes even five channels. If this tooth is in the lower row, then it usually has no more than 3 indentations. In most cases, when teething and already at the moment of full growth, the figure eight causes unpleasant sensations and severe discomfort. To clean it, it is recommended to use a special brush, which is designed for hard-to-reach places. Typically, wisdom teeth have narrow sockets that have irregular shapes. This property causes great difficulties when performing medical procedures. Often, if improper eruption or other pathological processes occur, the figure eight is completely removed.
The wisdom tooth is the last one to erupt; it seems to fight for space in the jaw, often shifting the dentition and causing discomfort. The roots of the tooth have a swirling, intertwined shape, so the root canals of the tooth cannot always be treated.
Interest calculation
Due to the fact that every person is individual and there are no clear norms and rules for determining how many canals are in the teeth, in dentistry data on this issue are given as a percentage. At first they are put off by the fact that the same teeth in the upper and lower jaws are very different from each other. If the first three upper incisors, in fact, in 100 percent of cases have only one canal, then with the same teeth of the lower jaw everything is much more difficult, and they have approximately the following percentage ratio:
- In the first incisor there is often only one channel - this is in 70% of cases from the general statistics, and only in 30% there can be two of them;
- The second tooth can have either one or two canals in virtually equal proportions, or more precisely, a ratio of 56% to 44%;
- The third incisor of the lower jaw actually always has only one canal, and only in 6% of cases can there be two.
Premolars have the largest structure; they are subject to more pressure and overload; therefore, it is reasonable to imagine that there will be more canals in the tooth, but here, too, not everything is so simple. For example, in the fourth tooth of the upper jaw, only 9% of teeth have one canal , in 6% of cases there may even be three, while others most often have 2. But with all this, the subsequent premolar (5th tooth), which seems to receive an even more powerful overload, most often has one channel and only in some cases more (of which only 1% is accounted for by three branches).
With all this, the situation in the lower jaw is completely different - the 1st and 2nd premolars are not found with three canals at all, but most often have only one canal (74% - four and 89% - five) and in only 26% of cases for four and 11% for an A is two.
The molars are already the largest and the number of their canals is increasing. The sixes of the upper jaw can have either three or four branches with equal probability. On the lower jaw, from time to time there may be a two-canal tooth (usually no more often than 6% of cases), but most often there are three canals (65%) and from time to time four.
Posterior molars usually have the following relationship:
- Top seven: 70 to 30% three and four channels;
- Bottom seven: 13 to 77% two and three channels.
Differences in the structure of incisors, canines and molars on the upper and lower jaws - table
As mentioned above, the number of channels is largely determined by the range of the element. The essence is the same: the very last chewing teeth bear the maximum chewing load, so they must be strong and resilient, and for this they need abundant nutrition - this is provided by a developed internal system. The table below shows average data on the number of passages in the tooth roots in the upper and lower jaws.
| Tooth | Number of channels | |
| Fangs | upper | 1 |
| lower | 2 | |
| Incisors | upper | 1 |
| lower | 1-2 | |
| Premolars | upper | usually 2, but sometimes from 1 to 3 |
| lower | first – 1-2, second – 1 | |
| Molars | top first | 3 or 4 |
| second | 3, less often 4 | |
| third | 5 | |
| lower first | usually 3, but can be from 4 to 5 | |
| second | usually 3, but sometimes 4 | |
| third | 3 |
On the upper jaw
The teeth on the upper jaw have their own structural characteristics, and therefore they are somewhat different from their antagonists on the lower jaw. Here are the main distinguishing features:
- second molars (sixes) most often have three canal passages, but in some cases there are 4,
- premolars usually have 2 canals, although in some situations their number can vary from 1 to 3.
The photo shows the teeth of the upper jaw
It should be noted that the roots on the upper jaw usually have a more complex and branched structure. Therefore, upper molars are more difficult to treat, which explains the higher percentage of complications due to incompletely healed cavities.
On the lower jaw
The structure of the upper and lower jaws is different, which is partly due to the peculiarities in the distribution of chewing load. In the lower teeth, as a rule, there are fewer canals, but here much depends on the individual anatomical parameters of the jaw apparatus. Therefore, the patient must undergo an X-ray examination, and with the image in hand, the doctor will be able to begin treatment directly.
The following are the features in the internal structure of the incisors, canines and molars of the lower jaw:
- in the first molars (sixes) there can be from 2 to 4 moves - there is no exact number to focus on,
- the lower second premolar (five) most often has one canal, although in approximately 10% of cases specialists find two canals at once,
- the first premolar usually has only one root, but in about a third of cases there are 2,
- Eights are the most unpredictable - the exact number of roots located inside can only be determined using radiography. As a rule, there are no more than 3 of them, but often during treatment specialists identify additional cavities. This is one of the reasons why wisdom teeth are difficult to treat therapeutically.
The photo shows the teeth of the lower jaw
Regardless of the type and stage of the disease, competent dental treatment necessarily involves preliminary x-ray diagnostics. Otherwise, any wrong move by the doctor can easily lead to serious complications.
Eights - third molars
A wisdom tooth usually has a complex and intricate root system - this is the only element in which the number of roots can reach 5. But this is extremely rare, and more often the figure eight has from 3 to 4 roots, while the lower third molar may not have any. more than 3.
The photo shows wisdom teeth
We are talking about a rudiment that we inherited from our ancient ancestors. Now we do not need to carefully crush very tough foods, such as raw meat. Therefore, there was no longer any urgent need for the figure eight, and due to the reduction in the size of the jaws, there was practically no free space left for it.
Because of this, the tooth almost always erupts with problems, since it initially begins to grow in the wrong position and often half remains under the gum - retention and dystopia. All this significantly complicates the treatment of pathological processes that are localized in this area. Therefore, most often the eight has to be deleted.
How many canals does a wisdom tooth have?
How many wisdom teeth can there be? This is a difficult question, because this organ has a very unusual structure. If it is located at the top, then it can have four and sometimes even five channels. If this tooth is in the lower row, then it usually has no more than 3 indentations. In most cases, when teething and already at the moment of full growth, the figure eight causes unpleasant sensations and severe discomfort. To clean it, it is recommended to use a special brush, which is designed for hard-to-reach places. Typically, wisdom teeth have narrow sockets that have irregular shapes. This property causes great difficulties when performing medical procedures. Often, if improper eruption or other pathological processes occur, the figure eight is completely removed.
The wisdom tooth is the last one to erupt; it seems to fight for space in the jaw, often shifting the dentition and causing discomfort. The roots of the tooth have a swirling, intertwined shape, so the root canals of the tooth cannot always be treated.
The classic method of installing sevens implants
A two-stage protocol involves introducing a two-part titanium root into the bone (separate intraosseous and external parts) using a patchwork method, waiting for its engraftment, followed by prosthetics. The classic method is implemented when there is a sufficient amount of bone tissue. If the alveolar ridge in the area of the former seven is significantly atrophied, osteoplasty operations are resorted to. The bone is built up with artificial material, implants are installed simultaneously or after the material has engrafted.
Pros and cons of the classical method:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| extensive experience in implantology; | long implementation periods; |
| predicted result; | wearing removable dentures for the period of osseointegration; |
| formation of a beautiful gingival contour; | the need to build up bone when it is insufficient. |
| possibility of using implants from various manufacturers; | |
| the ability to eliminate defects in a row of any length. |
In appropriate clinical situations, it is possible to use other treatment regimens—simultaneous or single-stage implantation.
Three-channel pulpitis
Three root canals most often have large chewing teeth - molars, sixth through eighth. Each branch contains connective tissue - the pulp; it contains many nerve endings and vessels. When inflamed, the pulp swells and becomes compressed, which is accompanied by severe pain. Three-channel pulpitis has important features in treatment. Startsmile will tell you more about them.
The number of canals in each tooth varies, usually one or two, in molars – most often three. There are record-breaking patients in whom up to eight processes were discovered during treatment. Three-channel pulpitis, as the name implies, is diagnosed in a tooth that has three channels. Inflammation of the pulp or, as is often said, the dental nerve, manifests itself in severe pain.
- The doctor spends an hour to an hour and a half on a multi-channel tooth;
- under a microscope - about two hours.
This is due to the fact that 3-channel pulpitis requires treatment in each process.
The dental canals are very thin, tortuous, no more than 1 mm in diameter. The microscope magnifies them to 2.5-3 cm. The dentist does not treat blindly, under magnification he clearly sees all the branches and foci of inflammation. Treatment of pulpitis of the 3rd canal takes place in good lighting. The patient lies down, the doctor looks not into the mouth, but into the microscope camera. This has a calming effect on dentophobes. The microscope reveals the most difficult to reach areas for the doctor. This is especially true for patients who have hidden dental canals that are not visible to the human eye.
And during endodontic treatment, it is important to remove all foci of inflammation to avoid relapse
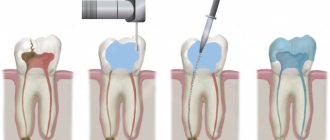
To treat three-channel pulpitis, the vital extirpation method is used. The pulp is removed, the canals are thoroughly cleaned, disinfected and sealed. Let's look at each stage of treatment of root pulpitis 3 in detail.
Pain relief using local anesthesia.
Expansion of the mouths of three canals and removal of pulp.
Flushing the canals with sodium hypochlorite as an antimicrobial treatment.
Drying and filling the canals and installing a temporary filling on the crown of the tooth.
The main treatment takes place during the first appointment. A break is needed so that the filling material in the canals hardens well. The second stage will take less time: the tooth will be processed again and a permanent filling will be placed.
The number of appointments may increase to three if it is impossible to immediately remove the pulp from the canals. In this case, the nerve will be “killed” by a special paste. It will be added to the cavity and left until the next visit. Soviet patients said this: “They put arsenic.” This substance is not used in modern toothpastes, but many, out of habit, believe that the dental nerve is removed with the help of arsenic.
Prevention after healing
After the procedure for healing the root system you should avoid putting stress on the treated tooth for some time; moreover, you should not eat food earlier than two hours after therapy (therapy is a process to relieve or eliminate the symptoms and manifestations of the disease)
, otherwise the filling is not completely hardened It might just fall out. But the same thing can happen if the doctor uses low-quality drugs or performs incorrect treatment (for example, the canals were over-dried or not dried before filling).
Also, after filling, for some time (up to several days) the tooth may feel pain (an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage) when pressed, or simply ache, cause discomfort, or have excessive sensitivity. This is usually a common condition if pain (physical or emotional suffering, painful or unpleasant sensation)
powerful, you can take painkillers.
If pain (physical or emotional suffering, painful or unpleasant sensation)
does not go away after a certain time, this may also be an indicator of disgusting healing (insufficient cleaning of infection
(The term means various types of interaction of foreign microorganisms with the human body)
or infected pulp, leaky filling, introduction of low-quality pharmaceuticals or materials).
From time to time, there are cases of allergic reactions , which are also accompanied by incessant pain, and from time to time itching and rashes appear on the body. It may be caused by a reaction to a pharmaceutical product or the material that was used for the filling. In this case, it must be changed to something else that will not cause allergies.
In all these situations, it is imperative to consult a doctor as soon as possible for a re-examination and dental prophylaxis in order to identify the cause of the defects.
Temporary filling
This type of procedure involves filling the canal with special compounds for a certain period of time. Why do they do this?
- To achieve a disinfecting effect.
- To stop the inflammatory process during periodontitis.
- To protect the dental canal from various infections and external influences, when it needs to be treated over several visits to the doctor.
Sometimes temporary filling is done to protect the dental canal from various infections.
Temporary filling is done for the following problems:
- acute/chronic periodontitis;
- traumatic injuries;
- perforation of walls.
Therapeutic non-hardening pastes for temporary use include antibiotics and antibacterial agents.
Products that are injected into the root canal contain antibiotics and antibacterial agents
Upper canine
It is the longest tooth in the mouth, averaging 26.5 mm (range 20-38 mm). It is extremely rare to have more than one root canal. The pulp chamber is relatively narrow and has only one horn; it is much wider in the vestibulo-oral section than in the mediodistal section. The root canal is type I and becomes round only in the apical third. The apical constriction is not as pronounced as in the incisors. This fact, and the fact that often the apical part of the root is significantly narrowed, causing the canal to become very narrow at the apex, makes it difficult to determine the length of the canal.
Upper canine
The canal is usually straight, but sometimes at the apex it bends towards the distal (in 32% of cases) and, less often, the lateral side. In 13% of cases, vestibular deviation of the canal was recorded. The frequency of occurrence of lateral (side) canals is about 30%, and additional apical ones - 3%. The apical foramen is located in 70% of cases in the range from 0 to 1 mm in relation to the root apex, and in 30% in the range of 1 - 2 mm.
Channels in baby teeth
There are as many nerves in baby teeth as there are in molars—one. In addition, temporary units are similar to permanent ones in the structure of the root system. That is, a milk tooth such as the upper six or second molar has a canal system similar to its molar brother, the second premolar.
Nerve endings perform standard functions:
- signal about developing caries;
- responsible for the growth and development of teeth;
- control the flow of water and nutrients to dentin and enamel.
The root canals of baby teeth are also treated and filled, but the tactics of their treatment depend on how long ago they erupted. Under the temporary units, permanent ones are formed, so treatment should be aimed at preserving them. Milk teeth can only be removed if the permanent teeth are ready to emerge.
Read also: How to treat a broken jaw
The roots of permanent incisors, canines and molars do not form immediately, but over the course of about 3 years. Treatment of permanent teeth with unformed roots also differs from the standard one. The canals in the teeth of patients four, five, six years old (depending on the rate of formation of the dentoalveolar apparatus) are filled with a special paste with calcium and fluoride, which helps close the roots.
Healing
The development of modern medicine and dentistry in particular now makes it possible to increasingly preserve those unhealthy teeth that only yesterday had to be removed due to the impossibility of healing. The procedure for healing root canals in teeth is in itself quite difficult, because they are filled with soft tissue (a collection of different and interacting tissues that form organs)
- pulp, which contains a huge number of nerve
endings (an animal organ that serves to transmit important information for the body to the brain) , blood vessels and other connective tissues. Now this is dealt with by a separate branch of dentistry - endodontics, the development of which makes it possible to improve the condition of a person’s teeth and cure even complex problems in more than 80% of cases, preserving the tooth itself.
The goals of this healing are:
- Removal of developing infection (The term means various types of interaction of foreign microorganisms with the human body)
from inside the root system; - Preventing pulp decay or removing it;
- Removal of infected dentin;
- Preparing the canal for filling (giving it a suitable shape);
- Increasing the effect of pharmaceutical drugs.
The difficulty of such healing of the root system is that it is quite difficult for the dentist to get to the unhealthy canals and supervise the progress of the procedure. After all, if you do not remove even a microscopic part of the infection (The term means various types of interaction of foreign microorganisms with the human body)
, after a while it will be able to develop again.
One of the main characteristics of such healing is the inflammatory process, which leads to damage to the soft tissue of the pulp inside the canals. Most often, this is caused by various diseases (disturbances in normal functioning, performance)
such as caries and pulpitis, but canal healing can also be useful for periodontitis.
The first symptoms (a symptom is one individual specific complaint of the patient)
the need for such healing is pain
(physical or emotional suffering, painful or unpleasant sensation)
in the tooth or swelling of the gums.
But it is worth considering that in the event of a disease (impairment of normal functioning, performance)
to an acquired stage, pain
(physical or emotional suffering, painful or unpleasant sensation)
may not be observed, but the disease develops and will ultimately lead to tooth loss . This is why it is so important to have regular dental checkups.
How to find out how many canals there are in a tooth, and what is it for?
Knowledge of the topography of the tooth cavity is important for correct endodontic treatment. During depulpation, the canal cavity is cleaned, the main passage is formed and hermetically sealed
At the same time, a barrier is restored that prevents the penetration of carious infection and bacteria into the bloodstream.
In ordinary life, the patient does not need to know how many roots and canals he has in his tooth. However, if the units are destroyed or hurt, an x-ray will be taken when visiting a doctor. It will show the degree of tissue damage, the number and length of the dental canals, their branches and structural features.
If narrow and long canals are detected, a computed tomography scan can be performed, which helps to accurately determine the configuration. In addition to the number and length of the canals, which is determined instrumentally, the doctor needs information about their patency:
- with a curvature of up to 25 degrees, they are considered instrumentally accessible;
- curvature within 25–50 degrees can be difficult to pass;
- a change in direction over 50 degrees is inaccessible for instrumental intervention; if the angle is located near the mouth, specialists can try to improve patency.
It happens that the doctor does not find the canal at all, which is due to its narrowing or overgrowing as a result of a long-term inflammatory process. Another reason why cavities are difficult to detect is age-related changes and incorrect dental treatment in the past.
The complex anatomy of the canals causes difficulties in their treatment. The instrument entry cavity may be curved. It may contain pathogenic microorganisms that are resistant to traditional antiseptic drugs. A highly qualified dentist can overcome these problems and provide high-quality root canal treatment for complicated caries, pulpitis and periodontitis. His arsenal includes the necessary diagnostic equipment that will show how many roots are present in the tooth, and tools for canal treatment.
Patency of dental canals
In addition to the number and length, important information is the patency of the root canals, which depends on the degree and location of the curvature. If the curvature is less than 25 degrees, then the canal is easily accessible instrumentally, from 25 to 50 degrees it is inaccessible (the so-called difficult tooth canals), above 50 degrees it is difficult to access. When the curvature is localized near the mouth of the canal, there may be an expansion of the outermost and improved patency.
If the examination reveals a very narrow, deep canal in the tooth, a CT scan may be required to clarify its configuration (Computed tomography is a method of non-destructive layer-by-layer examination of the internal structure of an object)
. Healing complex teeth requires particularly careful work, which can be facilitated with the help of a microscope.
From time to time, the doctor cannot find the canal in the tooth. This situation is usually associated with obliteration (narrowing or overgrowing) of the canals due to an inflammatory or tumor process, incorrectly performed healing in the past, and age-related changes.
Remember that only a specialist can assess the condition of the root canals and, depending on their structural features, find a healing strategy.
How many canals are there in the 5th, 6th, 7th and other teeth of the upper and lower jaw, what is the length
| Tooth formula | Upper jaw, mm | Lower jaw, mm |
| 1 | 13,0 /- 1,7 | 12,8 /- 1,6 |
| 2 | 12,9 /- 1,6 | 13,7 /- 1,6 |
| 3 | 15,9 /- 2,4 | 15,3 /- 2,1 |
| 4 | 13,6 /- 1,8 | 13,7 /- 1,7 |
| 5 | 14,4 /- 1,9 | 15,2 /- 1,8 |
| 6 | 13,3 /- 1,7 | 14,5 /- 1,7 |
| 7 | 13,0 /- 1,8 | 14,1 /- 1,7 |
| 8 | 12,2 /- 2,0 | 12,8 /- 1,9 |
With an accuracy of 60-97%, the length is determined electrometrically (by changes in the electrical resistance of tissues) using an apex locator.
The tactile method is based on slowly immersing the probe into the canal until it jams.
According to the patient’s sensations (a slight “prick” when moving the instrument past the root apex), during treatment without anesthesia, the length of the canal is also determined approximately.
Using a combination of several approaches is effective.
The key to high-quality endodontic treatment is the accurate determination of the tooth canals: their number, length, shape.
Typically, the deeper a tooth is in the mouth, the more canals it has. The number of canals in the teeth of the upper and lower jaws differs: the upper teeth have more of them.
It is statistically impossible to answer the question of how many canals there are in a wisdom tooth: for the upper ones, the number varies from one to five, for the lower ones – about three.
The exact number can only be found out when opening the tooth or based on the results of radiography (targeted, for a specific tooth, or orthopantogram, to assess the condition of all teeth).
What is their topography and anatomy? How many nerves are there in the cavity of the molar located on top, and how many in the one on the bottom? Working length of the root canal - what is it? These questions are also relevant for doctors, because the process of their treatment, restoration or removal depends on the number of canals and roots.
Introduction
In dentistry, since 1971, there has been the so-called two-digit Viola system.
The root canal is the space inside the root. Complex anatomical branches can connect different channels to each other. At the tip of the horse there is an apical foramen. A feature of the tooth root system is that one hole can serve as an exit for several canals. Also, the channel sometimes bifurcates, ending in two exits. No two root systems are alike. Therefore, the doctor cannot do without an X-ray examination.
In general, you can rely on the following data:
- canines and incisors – usually 1 root;
- premolars 1-2 roots;
- molars have 3-4 roots;
- Wisdom teeth have up to 5 roots.
The teeth located on the upper jaw are very different in the number of canals from the lower ones. The situation is simpler with incisors. The 1st, 2nd and 3rd incisors usually have only 1 canal. The fourth tooth is a little more complicated: in 85% of cases it has 2 canals, in 9% 1, and in only 6% 3 canals. In the fifth tooth, statistics give the following result: most often (75% of cases) there is 1 channel, less often (24%) - 2 and only 1% of cases - 3 channels.
In the sixth tooth, dentists find 3 and 4 canals, respectively, in 57 and 43% of cases. Among the “seven”, 3 channels are more common (57%), less often – 4 (43% in total). The doctor obtains the exact result in each specific case through direct examination or with the help of an image.
The “six” and “seven” have a more branched structure. In the sixth tooth, 3 (65%) or 4 (29%) canals are most common, 1 canal is least common - 6%. In the “seven” the dentist usually finds 3 canals (77%) and 2 canals (13%). It is very rare, but even in it you can find only 1 channel. This result shows only 1% of cases.
How is root canal treatment performed?
An important step in the process of treating root cavities is determining the working length of these canals. Not everyone knows the definition of tooth root length. So, the working length of the root canal is the distance from the edge of the frontal units to the apical constriction preceding the apical foramen. There are several methods for determining the working length of the root canal. The most commonly used are the calculation method, x-ray and electrometric methods.
Endodontics treats tooth root canals. When an endodontist treats a root canal, he performs the manipulations in the following sequence:
- diagnostics;
- X-ray;
- preparing the dental cavity for treatment;
- anesthesia;
- chemical treatment of instruments;
- opening of the tooth cavity;
- determination of the working length of root canals;
- medicinal treatment, cleaning and expansion of root canals along the entire working length;
- filling a tooth cavity.
READ ALSO: What should be the sequence and pattern of teething for children?
Diagnostic methods
The first stage of tooth root canal treatment is diagnosis, which will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis and decide on a treatment method. To do this, the patient needs to undergo an x-ray to examine the part of the crown that the doctor cannot see. This procedure allows you to understand how many roots and canals the tooth cavity has. If the X-ray examination is ignored, then the cavity of the diseased tooth will have to be opened again (we recommend reading: X-ray of a child’s jaw: is it possible to take an X-ray with baby teeth?).
INTERESTING: How many teeth should an adult healthy person have?
https://youtube.com/watch?v=aar2229bPhg
Preparatory procedures
After the X-ray of the dental cavity has been carefully studied, the diagnosis has been made, and the stages of the upcoming therapy have been planned, it is necessary to tell the patient about everything in detail. Next, you need to obtain documented consent for the opening and further treatment of the tooth cavity.
An important point in preparing for root cavity treatment is for the doctor to obtain information about the presence of allergic reactions in the patient to anesthetics. If such information is not available, an allergy test is performed. At this stage, chemical treatment of the instruments with which the manipulations will be performed is carried out.
Administration of anesthesia and application of anesthetic
Before treatment begins, the patient is anesthetized in the area of the jaw where the intervention will be performed. Anesthesia can be superficial or in the form of an injection. The first type of anesthesia blocks sensitivity not only in the dental cavity, but also on the mucous membrane. It is usually used to numb the area where the doctor is about to inject an anesthetic.
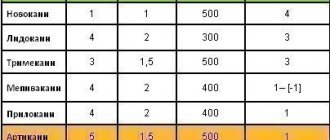
The following drugs are used for superficial anesthesia:
- 0.5% Promecaine ointment;
- Anestezin;
- Lidocaine;
- Dicaine.
Opening a molar tooth
What is the opening of a tooth cavity? In order to remove the pulp and clean the root canals, the dentist needs to provide good access to them. Opening the tooth cavity can begin immediately after grinding the caries and removing sawdust from the dentin. The process of opening the tooth cavity begins with the smallest bur, after which a large spherical one is used.
INTERESTING: the structure of the human oral cavity and the functions of the organs that are located in it
Medicinal treatment of canals
Canal treatment is divided into mechanical (scraping out the contents using special tools) and chemical (medicinal treatment of root canals with disinfectants injected with a thin needle). Today, the following scheme for medicinal treatment of the root canal is used: sodium hypochloride is applied after using each instrument and completing mechanical cleaning, then hydrogen peroxide, and after that distilled water. Drug treatment of root canals is carried out immediately after the opening of the dental cavity is completed.
Sealing
The final stage of tooth root canal treatment is sealing the cavity. The root cavities are filled with a special filling material (usually gutta-percha). The filling helps the tooth remain strong and prevents pathogenic bacteria from entering its cavity.
Filling a tooth cavity can be:
- temporary;
- permanent.
With temporary filling, the tooth cavity is filled with a non-hardening paste that has medicinal properties. This type is used in cases with advanced three-channel pulpitis or periodontitis.
Process and stages of channel healing
The root canal healing process has a clear sequence of steps:
- First you need to make a correct diagnosis of the disease (disturbances in normal functioning, performance)
. In complex cases, the dentist sends the patient for an x-ray. - After this, the doctor carries out the necessary preliminary oral procedures for healing.
- Healing canals is a rather painful procedure, so the tooth must be numbed by injecting anesthesia (usually into the gums near the diseased tooth).
- After this, complete asepsis of all instruments is carried out and the unhealthy tooth is separated from the others using a special rubber film (caffedram).
- Next, the unhealthy tooth is opened with the help of a drill, providing maximum access to the unhealthy canals, after which their initial cleaning is carried out, the infected pulp is removed, and at the same time the canals are treated with special pharmaceutical products.
- Afterwards I dry them and seal them with special materials.
How many canals in teeth, location table and detailed description
Root canals are a complex system that requires special treatment methods. The main problems are their large number, tortuosity, and difficulties with access, especially when it comes to third molars. How many canals are there in a tooth, what are they for and what are their features?
The difficulties of treating wisdom teeth are caused by several factors:
- They often erupt incorrectly because they do not have enough space in the already formed jaw.
- Often, figure eights do not fully erupt. Bacteria accumulate under the “hood” that covers them, which leads to inflammation.
- The brush does not reach hard-to-reach places, so caries is a common occurrence.
Untreated caries develops into pulpitis, requiring root canal treatment. Due to the fact that there are many of them (especially if it is a tooth of the upper jaw), they are uneven and difficult to navigate, endodontic treatment of third molars is difficult.
In most cases, when teething and already at the moment of full growth, the figure eight causes unpleasant sensations and severe discomfort. To clean it, it is recommended to use a special brush, which is designed for hard-to-reach places. Typically, wisdom teeth have narrow sockets that have irregular shapes.
The wisdom tooth is the last one to erupt; it seems to fight for space in the jaw, often shifting the dentition and causing discomfort. The roots of the tooth have a swirling, intertwined shape, so the root canals of the tooth cannot always be treated.
The figure eight or wisdom tooth is quite unique and
and statistics. The upper one can have a completely different structure with channels from one to five. The lower eight is most often found to be three-channel, however, often upon opening during treatment additional branches may be discovered.
Among other things, a wisdom tooth differs from others in that its canals are rarely of the correct shape, often very curved and with a narrow passage, which greatly complicates their treatment and filling.
This organ, in addition to its inconvenient location, which causes discomfort during oral hygiene, has other differences. Thus, the upper third molar is the only unit whose number of canals can reach 5. It is worth noting that this happens extremely rarely, mostly wisdom teeth have three or four canals. The bottom eight has no more than 3 indentations.
Number eight is often the cause of the development of dental pathologies. For example, incorrect placement of the third molar can contribute to impaired growth of adjacent units. In such cases, its removal is required. If the figure eight does not bother or hurt, there is no need to pull it out. The only indication for removal is the presence of pain and the negative impact of the third molar on other units of the row.
To avoid problems with the figure eight, dentists advise adhering to the following rules of oral care:
- due to the inconvenient location of the figure eight, it is necessary to use a special brush;
- Owners of a third molar should visit the dentist for a routine examination at least 2 times a year.
A special feature of the cavity in the tooth is the presence of branched nerve endings in it, grouped into branches. The number of nerve endings directly depends on the number of roots and canals.
Purpose of dental nerves:
- influence the development and growth of dental units;
- thanks to the nerves, the organ is sensitive to external influences;
- The dental nerve makes the masticatory organ not just a bone, but a living unit of the oral cavity.
The peculiarity of the wisdom tooth is that it has a distant location and an irregular curved shape, which complicates the process of treatment procedures. The structure of the third molar is very fragile and thinned, so this chewing organ is most susceptible to the development of pulpitis.
Eights on the upper jaw are equipped with five canals, on the lower jaw - three. The root cavities are characterized by strong curvature, which causes inconvenience to the attending physician when diagnosing the condition of the canals or filling them.
Wrong worldview
Because a tooth consists of roots and a pre-coronal part, from time to time there is a misconception that there are as many canals in teeth as there are roots . This is far from true, because the canals quite often branch off and bifurcate near the pulp. Moreover, several channels can run parallel to each other in one root. There are also cases of their bifurcation at the apex, which is why it turns out that one root has two apexes and this, naturally, complicates the work of doctors when filling similar teeth.
Taking into account all the individual characteristics of the teeth, dentists need to be very careful when treating (the process of alleviating, removing or eliminating symptoms and diseases)
and filling, so as not to miss any branch. Indeed, from time to time, without an x-ray, it is very difficult, even during an autopsy, to identify how many canals are in the teeth.
Prevention of the development of diseases of the root system of teeth
In order to avoid any dental diseases, it is necessary to take good care of oral hygiene, as this will help preserve your teeth for as long as possible. Factors affecting the masticatory organs:
- Some dentists do not recommend brushing your teeth more than twice a day, as this can cause the enamel to become thinner.
- You should not clean immediately after eating; it is better to wait 20 or 30 minutes.
- To avoid the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the mouth, it is worth rinsing your mouth either with special rinses or decoctions of chamomile, oak bark or sage.
- Do not forget that cleaning the chewing organs should be for at least two minutes and in a circular motion.
For any, even the smallest dental problems, seek medical help so as not to aggravate the situation and contribute to the development of more serious diseases associated with the oral cavity and masticatory organs.
Dentists' tips for disease prevention
The development of dental pathologies can be prevented only by following the advice of trained doctors and observing the rules of oral hygiene.
So, for prevention purposes, dentists advise:
- do not abuse the rules of hygiene, brush your teeth only in the evening and in the morning. The most common effect on tooth enamel is its abrasion;
- hygiene procedures must be carried out half an hour after eating;
- use rinses to destroy bacteria remaining in the mouth after cleaning;
- Cleaning should be carried out for at least 3 minutes, performing radial movements.
The basic rule is in case of detection of the first signs of the disease (disruption of normal functioning, performance)
, you must contact your dentist immediately. This will help prevent the upcoming development of pathology and preserve teeth.