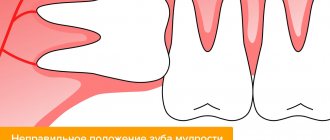
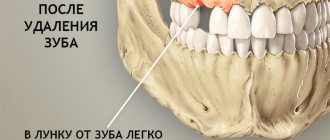
Indications for removal of eighth teeth
wisdom teeth
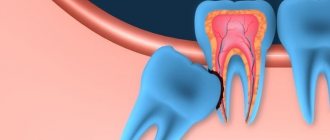
begin to grow much later than other permanent teeth, as a result of which they often do not have enough space in the jaw. Lack of space provokes all sorts of curvature of roots and crowns. Doctors advise removing such molars. Here is another list of problems that may require extraction:
- A pronounced tilt of the figure eight towards the seventh tooth or cheek.
- Hypercementosis (excessive deposition of secondary cement, in which the tooth root thickens and becomes deformed).
- Incomplete eruption of the tooth or its location in the bone (retention).
- Destruction of the crown or roots of the figure eight, as well as neighboring teeth (after injury or caries).
- Granuloma (granulation in the form of cystic sacs with pus located in the periodontium).
- Rotation of the tooth around its axis or horizontal position (dystopia).
- Deformation of the roots (they can bend in every possible way, even twist into a spiral or form an angle of 90°).
- The close location of the roots of the upper eights to the nasal maxillary sinuses.
- In the presence of pericoronitis (an acute inflammatory process in the area of the eruption of the figure eight, accompanied by pain and an increase in ESR in blood tests).
An incorrectly growing 8th tooth can compress the facial nerves and provoke neuritis, which is expressed by sharp pain radiating to the ears, neck, temple, and can lead to facial paralysis.
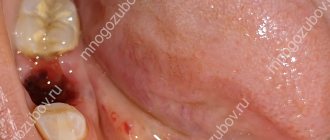
Alveolitis
This condition occurs for various reasons. This usually happens with chronic periodontitis (when the patient has inflamed tissue around the tooth) or if there is a tooth fragment in the wound. This provokes infection of the socket and accompanying inflammation. Typically, symptoms of this condition include bad breath and pain. Over time, the condition progresses, a grayish coating is found in the socket, and the pain intensifies so much that difficulties arise with eating.
If you have such symptoms, it is better to immediately consult a doctor, since only he can prescribe adequate therapy and treat the holes with disinfectants. Self-medication causes unpleasant manifestations in the form of inflammation of the periosteum, pus and phlegmon.
Occurrence of complications
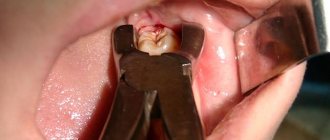
Operations to pull out figure eights are considered complex dental procedures, which are due to:
- difficult access;
- frequent retention;
- unpredictable structure;
- features of the location of the mandibular alveolar nerve.
Such procedures are very traumatic, which creates the preconditions for the occurrence of general and specific types of complications.
Are common
The nature of complications largely depends on the location of the tooth: on the upper or lower jaw. But there are also general complications that arise in almost everyone, regardless of the location of the figure eight and its initial condition. The most common overall effects are listed below.
Painful sensations
Approximately 2-3 hours after molar extraction, you will experience noticeable pain in the gums. This is a normal reaction of the body to trauma, which is dental surgery. During it, soft tissues are torn or cut, the bone is injured (if the tooth is located under it), blood vessels and nerves are damaged. Painful sensations should completely disappear after 2-4 days, and for some people disappear within a few hours. They can be reduced with the help of painkillers prescribed by the dentist. If the pain does not go away, and the cheek is very swollen, it means that the gum healing process is proceeding with complications.
Swelling of the tissues of the face and neck
Often after figure eight extraction, especially impacted ones, swelling of the soft tissues of the gums or cheeks is observed. This is also a reaction to injury, which can be called a normal consequence of a dental procedure. In addition to swelling, the following symptoms may occur:
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- painful sensations during mouth movements, radiating to the ear.
Normally, severe swelling should go away completely in 2-3 days, and if it doesn’t go away, then we can talk about more dangerous consequences. If the condition worsens every day, difficulties arise when breathing, fainting, the temperature rises and the skin becomes covered with a rash, then such swelling is provoked by an allergy and it can lead to anaphylactic shock.
Hematomas
Hematoma due to extraction is usually expressed by minimal bluishness of the cheek, which goes away after a few days. But there are situations when the appearance of a bruise is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and an increase in temperature. In such a situation, medical attention is needed. Hematomas form after vascular damage in people with increased capillary fragility, as well as when the patient has hypertension.
Alveolitis
complications after wisdom teeth removal
Alveolitis is often provoked by non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations after treatment procedures. It is a local inflammation of the gums with the following additional symptoms:
- the gums swell and turn red;
- local pain and headache are observed;
- sore throat;
- the temperature rises, muscle aches appear;
- lymph nodes become inflamed, most often the submandibular ones.
If inflammation occurs, the cause is often the loss of a blood clot from the socket and infection. Various infections that enter the wound due to poor hygiene can provoke extensive inflammation. In advanced cases, the above complication develops into osteomyelitis, which is expressed by:
- increased persistent temperature;
- poor general health;
- severe migraine-like pain;
- nausea;
- other signs of intoxication of the body.
Increased body temperature
A slight increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C also often occurs in the postoperative period. This complication occurs due to a reaction to inflammation. The temperature should completely return to normal within the first day, and if it continues to rise and rise, it means that more serious pathologies have arisen and you need to go to the hospital again.
Bleeding
The dentist will never dismiss a patient with severe bleeding, especially if it is complicated. After removing the figure eight, the bleeding is stopped in the hospital, and then sent home with a gauze pad on the hole. If blood clotting is normal, then the bleeding will stop within 10-15 minutes, after which the tampon must be removed. Severe prolonged bleeding is provoked by:
- rupture of large vessels;
- capillary fragility;
- hypertension.
Damage to the roots of adjacent teeth
Such a complication is observed extremely rarely and only if the patient did not undergo X-ray diagnostics before the procedure. This procedure is mandatory for all people with indications for the removal of figure eights and allows you to fully assess the condition, location, as well as other features of the tooth and its roots.
Flux
Flux in the postoperative period develops in cases where the gums become infected due to the fault of the dentist or patient, after which the infection quickly reaches the periosteum and provokes its inflammation. This complication is not considered normal and acceptable and must be treated. Main signs of flux:
- redness, suppuration and swelling of the gums;
- severe shooting pain;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Others
Among other common complications, the most commonly observed are:
- displacement of the seventh tooth (2 molars);
- mouth rupture; cut gums or cheeks;
- jaw injuries.
In addition, complex extraction of the 8th tooth can cause the formation of a cyst. This is a small tumor located at the root of the tooth and filled with fluid. The cyst often serves as an insulator for infected cells from healthy ones. To prevent its occurrence, the dentist prescribes antibiotics, and the treatment in this case (if the cyst is located at the roots of the tooth) will be resection.
The appearance of bleeding
Immediately after the removal procedure, bleeding appears from the hole. This is quite normal, since the vessels are damaged, of which there are a lot where the teeth are located. After the operation, the doctor takes the necessary actions to stop the bleeding. Sometimes, unfortunately, there are cases where even after several hours the bleeding still stops. Under this condition, the patient applies a tampon to the gum at the site of the extracted tooth and lightly presses it. This should help, but if it does not work, further consultation with a specialist is necessary.
On the lower jaw
Standard and non-standard complications after pulling out figure eights on the lower jaw occur more often than on the upper jaw. The lower jaw has a number of features, and there are many obstacles in the area where the wisdom teeth are located.
Nerve damage
The mandibular and lingual nerves are at risk of injury, since they pass close to the wisdom tooth. Such damage causes paresthesia, which is manifested by impaired sensitivity:
- sensory;
- painful;
- taste;
- temperature
In the most severe cases, nerve damage negatively affects vision, hearing, and also provokes paralysis. Patients compare paresthesia with numbness of the jaw in the area of the removed molar. In most cases, this complication disappears on its own within a few days, but sometimes additional drug treatment is required.
Alveolar ridge fracture
A fracture of the alveolar process of the lower jaw occurs when the dentist does not grip the jaw correctly and applies more force than necessary. This is an unlikely complication as the mandible is quite strong. Treatment is carried out under conduction anesthesia and involves repositioning and fixing the fragment in the correct position.
Jaw damage
snapshot of the jaw
Jaw injuries (dislocations and even fractures) also often occur due to the fault of the doctor if the tooth is pulled out too intensely or abruptly. During surgery, it is necessary to remove a significant amount of lower jaw bone to provide access to the problematic molar. Because of this, the sections of the jaw are weakened, which increases the risk of fracture if excessive force is applied. A crack or fracture does not always appear immediately. It happens that the patient notices the first symptoms in the form of pain, swelling, and impaired mobility already at home. Sometimes it takes a week before they appear. Statistics show that jaw injuries during medical procedures account for no more than 0.2% of all jaw fractures.
Soft tissue injuries
By pulling out a molar, the doctor can injure the soft tissues surrounding the molar. We are talking not only about the gums, but also about the cheek, tongue, lips. Injuries are caused by dental instruments (scalpel, drill, forceps). The lip is also often injured by the thread used to suture the gums. This happens due to the carelessness of the doctor or the restlessness of the patient. To avoid complications, you need to sit quietly in the dental chair and not distract the doctor.
Gum inflammation
At first, the patient does not have any noticeable sensations after the operation. However, after some time, the gums may begin to bleed, fever may occur, and the tooth will become loose and loose in the gum. The pain often radiates to the ear. It is important to start treatment promptly, otherwise an abscess or fistula filled with pus may form. You can’t wait for it to fester - the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance that complications will be avoided.
If pulpitis occurs, the pain radiates to the ear and also to the temple. With this manifestation, it is better to take a pain reliever.
You should not rely on self-medication with traditional medicine - they can further aggravate the situation, since the root cause of inflammation is clear only after examination by a dentist.
Important ! Auxiliaries treat the symptoms, not the cause of the pain.
If you treat symptoms while ignoring the cause of their occurrence, you can start the development of the disease to such an extent that you will have to remove a previously healthy tooth.
On the top
The most common complication of extraction of figure eights in the upper jaw is a puncture of the base of the maxillary sinus (maxillary sinus).
Puncture of the bottom of the maxillary sinus
The dental roots of molars number three in the upper jaw are located too close to the base of the sinus, and sometimes even grow into it. Chronic inflammation of the periapical tissue provokes resorption of the axillary septum, due to which the roots of the molars fuse with the mucous membrane inside the sinus. It is this part that most often ruptures during the extraction of the right or left tooth. This complication can be noticed by the following symptoms:
- nasal sound, bleeding air bubbles;
- blood from the nose on the side of the figure eight.
In such a situation, urgent medical assistance is necessary.
Edema and swelling
This is also a temporary phenomenon, especially often occurring after surgery in the lower jaw. The most severe swelling is observed on the second day - this is normal. Cold compresses or ice should be applied to the patient's cheek.
There is severe pain when opening the mouth after this type of intervention due to inflammation of the mucous membranes. After two or three days the pain decreases. After a week it goes away completely.
A hematoma sometimes occurs on the cheek on the side where the tooth was removed. This is usually caused by mechanical damage due to wisdom tooth extraction. This can be found in patients with arterial hypertension. It goes away in about 3-5 days.
At the dentist
If there are symptoms indicating complications, the doctor must determine the cause of the pathology. He performs the necessary diagnostics and visual inspection. Sometimes an x-ray may be needed.
Treatment methods are usually as follows.
When suppuration , the doctor cleans out the pus through an incision in the tissue; then prescribes antibiotics.
When it comes to trigeminal neuralgia , complex treatment is carried out with the prescription of drugs that help restore damaged nerves, as well as anesthetics.
The pus is cleaned out of the hole, then a tampon with NSAIDs is applied. This is performed if there are complaints of a “dry socket”. In addition to the dentist, it is worth visiting an otolaryngologist to rule out concomitant pathologies.
Important ! For a speedy recovery, it is extremely important to maintain rest, ideally bed rest. It is better to avoid physical activity completely.
The amount of liquid you drink is limited, and it is better not to eat solid food temporarily. In order to reduce pain, you can take a painkiller prescribed by your doctor in the dosage indicated in the instructions.
The total time of therapy is up to several days. However, even after completing the course of treatment, the patient sometimes experiences weakness and mild pain.
Therapy for pain
If there is unpleasant pain radiating to the ear, the patient should not worry ahead of time. It usually goes away after two or even three days.
It is extremely important to contact specialists in whose work you can be confident. Treatment is carried out by qualified doctors in specialized medical institutions. Self-medication and traditional medicine methods can do more harm than good.
When contacting a doctor, be sure to notify him of any drug or other intolerance or allergic reactions. The doctor can select the necessary drug substitute to facilitate therapy. Don't forget to tell your doctor what medications you are taking (regularly and during the week before your appointment).
The dentist will indicate a list of recommendations that must be carefully followed in order to avoid complications.
You should not rinse your mouth, while brushing your teeth, you should not touch the socket with a brush or dental floss, food should be warm and without a lot of salt and spices. These rules must be followed for at least two days after the intervention. Compliance with them will help avoid serious and unpleasant consequences.
People suffering from diseases such as chronic hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, severe liver damage, and HIV infection should pay special attention to their health. In these conditions, there are disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, which is why various kinds of complications arise after any surgical interventions. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out a course of antibiotic treatment under the guidance of the attending physician.
For three days, any alcohol and soda are completely excluded. You only need to chew soft food on the side opposite to the extracted tooth, so as not to touch the wound.
Take painkillers prescribed by your doctor. To avoid increased pain at night, it is recommended to sleep on the side where the tooth was removed.
Fever, increased body temperature to low-grade or higher levels
This usually occurs in the patient in the evening or at night. The reason is the reaction of the immune system to inflammation resulting from a traumatic procedure. This is a protective, not a pathological reaction of the body.
After 5-6 days, most pain symptoms disappear. If the unpleasant condition lasts longer than a week, this may indicate certain pathologies. In order to identify the disease in a timely manner, the dentist prescribes an additional examination to control the situation and acts according to the circumstances, carrying out the necessary therapy.
An immediate visit to the doctor should take place if the following symptoms appear.
- Swelling on the face.
- Bleeding lasts longer than one day after the intervention.
- Severe chills and rising temperature (values above 38 degrees).
- Dizziness, vomiting or nausea.
- The appearance of pus.
- Swelling of the throat, difficulty breathing, or cough.
- Sharp sharp pain.
As a rule, pain appears again after the end of the anesthetic and remains acute. In the future, it, naturally, should gradually weaken until it disappears completely. If everything remains unchanged, you need to consult a doctor.
Therapy for the appearance of “dry socket”
As we have already mentioned, during the normal course of the recovery process after extraction, the formation of a blood clot should occur, which performs protective functions and helps rapid tissue regeneration. If it is washed out or damaged, a “dry socket” appears. This happens when eating solid food that can injure the mucous membranes, as well as when rinsing.
In such cases, the attending physician usually prescribes the application of compresses with antiseptic and healing medicinal compositions that accelerate healing.