- What does gum healing depend on?
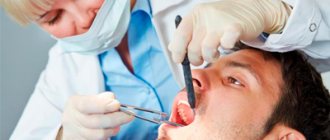
- How is tooth extraction performed?
- Postoperative period
- Stages of healing
- Possible complications
How and how long the gums heal after wisdom tooth removal depends on many factors; myths and facts about third molars can be read here. On average, the wound healing process lasts 3 weeks; after 21 days, you can safely eat all foods and load the gums. But complete filling of the tooth socket with bone tissue occurs only after 4-5 months.
Tooth extraction: main stages
An obligatory stage is preparation for surgery. It includes a consultation and a three-dimensional photograph taken by the dentist, which allows you to assess the position of the tooth, the number and direction of the roots. Only after a thorough visual examination and diagnosis is an appointment for surgery made.
Surgery begins with local anesthesia, selected individually for each patient. In some cases, the operation consists of making an incision in the gum, sawing the tooth into several small parts and their subsequent removal.
Then sutures are placed and a fibrin clot, PRF, obtained by centrifuging the blood, is inserted into the socket, but the oral cavity requires special care even after surgery.
Easy removal
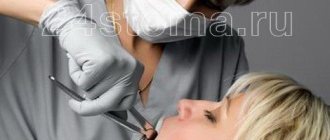
When nothing prevents you from removing the tooth from the socket and cutting the gums with a scalpel is not required, then such removal is considered simple. The procedure is carried out in the following order:
- the doctor orders an x-ray or recommends a CT scan;
- the problem area is numbed with local anesthetics;
- Using forceps, the surgeon first rocks the tooth and then pulls it out of the socket.
After the tooth is removed, the hole is treated with an antiseptic solution, after which a sterile swab is applied to it. If necessary, the wound is sutured. The entire procedure lasts about 10 minutes.
What to do after surgery?
The main thing is to follow the dentist's recommendations. You can remove the tampon left by the doctor 20-25 minutes after the operation is completed. You should not eat until the anesthesia wears off (the doctor will tell you the exact time). Do not rinse your mouth for 3 days after wisdom tooth removal.
Important recommendations for oral care after surgery:
- Within 48-72 hours after the removal of the eighth tooth, it is recommended to avoid hot, as well as too hot and spicy foods;
- Do not play sports for the next 7 days, try to avoid any intense physical activity;
- Gently brush your teeth using a soft brush and being careful not to injure the socket and extraction area;
- To relieve swelling on the first day after surgery, it is useful to apply ice to the cheek every 2-3 hours for 15-20 minutes.
Postoperative period
Very often, patients have gum pain after the removal of a wisdom tooth; you can read more about how dystopic teeth are removed here.
After surgery, the patient may be concerned about the following:
- Pain in the retromolar area;;
- Unpleasant and painful sensations when opening the mouth;
- Discomfort in the oral cavity;
- Swelling and hyperemia of soft tissues;
- Bleeding;
- Swelling and asymmetry of the face;
- Inability to eat food normally;
- Deterioration of general condition: weakness, fever, headache.
What is prohibited after wisdom tooth removal?
The sooner the wound heals, the faster you can return to your normal rhythm of life and forget about restrictions. In addition to recommendations, the dentists of the “V Put” clinic draw your attention to the rules that are strictly prohibited from breaking:
- Under no circumstances try to clean the hole and the surrounding area from food debris using toothpicks;
- It is prohibited to visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, and solariums for 7 days after dental surgery;
- It is strictly forbidden to heat the wound or cheek, or use an ultrasonic cleaning device for the oral cavity.
Indications for removal of eighth teeth
wisdom teeth
- A pronounced tilt of the figure eight towards the seventh tooth or cheek.
- Hypercementosis (excessive deposition of secondary cement, in which the tooth root thickens and becomes deformed).
- Incomplete eruption of the tooth or its location in the bone (retention).
- Destruction of the crown or roots of the figure eight, as well as neighboring teeth (after injury or caries).
- Granuloma (granulation in the form of cystic sacs with pus located in the periodontium).
- Rotation of the tooth around its axis or horizontal position (dystopia).
- Deformation of the roots (they can bend in every possible way, even twist into a spiral or form an angle of 90°).
- The close location of the roots of the upper eights to the nasal maxillary sinuses.
- In the presence of pericoronitis (an acute inflammatory process in the area of the eruption of the figure eight, accompanied by pain and an increase in ESR in blood tests).
Timing and stages of healing
On average, gums heal for 21 days after surgery. This means that after 3 weeks you will be able to eat any food and not worry about the condition of your gums. Complete healing will occur 4-5 months after surgery.
The exception is particularly severe cases (for example, when complications occur). Then healing of the wound will take from 3 to 5 weeks or more.
Healing stages:
- 24 hours after the intervention : gradual formation of a blood clot that closes the hole and provides protection against infection;
- after 3-4 days : a white film will appear on the wound, indicating the development of epithelial cells;
- after 7-10 days : the formation of a whitish coating, under which granulation tissue gradually forms;
- after 18 - 25 days: the wound heals and heals, after which bone tissue regeneration begins.
Healing of the tooth socket after extraction
Tooth extraction is a surgical intervention with the formation of a wound after extraction, therefore, as after any intervention, the wound formed at the site of the tooth must also undergo a healing process, and its tissue must recover and fill the voids. This process lasts for 4 months. The stages of tooth socket healing are as follows:
- a blood clot forms immediately after removal;
- 2-3 days - epithelization of the hole begins;
- 3-4 days - the first signs of granulation tissue formation appear;
- 7-8 days - part of the blood clot is replaced by granulations, gum cells begin to form an epithelial layer; the process of bone tissue formation begins;
- Days 14-18 - granulation tissue completely fills the socket, and the socket itself is completely covered with new epithelium. New bone cells are actively forming on the walls of the socket;
- 1-2 months - active process of bone tissue formation;
- 2-3 — filling the hole with bone tissue; tissue saturation with calcium;
- 4th month - bone formation ends, the structure becomes spongy.
If, when a tooth is removed, a blood clot does not form in the socket, the healing process of the socket occurs thanks to its walls - they are the ones who contribute to the development of granulation tissue. Otherwise, the further stages of healing are the same as those described above.
Healing after removal of an inflamed tooth
We have described a 4-month process of tissue restoration, however, they are restored so quickly only if there is no injury, inflammation or infection in the tooth and surrounding tissues. If the listed processes take place, tissue regeneration does not proceed so quickly. As a rule, it is prevented by the formation and course of the inflammatory process, the time period increases and the stages of healing look like this:
- epithelization and formation of granulation tissue occur in 10-15 days instead of 3-5 days;
- Bone tissue formation begins only on the 15-16th day instead of the 7-8th.
- closure of the hole by the epithelium is 2 times slower and ends only on the 30th or 50th day;
- only at 2 months the hole is completely filled with osteoid cells, which then become full-fledged bone;
The process of epithelium and bone formation can be even longer if the walls of the socket and/or gum tissue were severely damaged during tooth extraction.
Possible complications
Since tooth extraction is a surgical procedure, unpleasant consequences may arise after it is performed—complications of various kinds. In this case, the causes of such complications can be either the patient’s negligence in hygiene after surgery or the incorrect actions of the surgeon. Another category of etiology of adverse consequences is the complex course of the operation (with increased bone strength, non-standard shape or size of the tooth root).
Alveolitis
Alveolitis often forms when, after removal, a blood clot does not form in the socket for some reason. Without a clot, the socket is deprived of a protective barrier from external influences and is therefore susceptible to the appearance of an inflammatory process. The first and main symptom of this disease is pain immediately after removal or after 2 days. There is swelling of the gums, inflammation of the edges of the socket, due to the fact that a blood clot has not formed, the cavity is filled with food, which further contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. Other characteristic signs: temperature, unpleasant odor from the hole, poor health, pain and swelling of the mucous membrane at the extraction site.
The etiology of the development of alveolitis is considered to be an infection caused by oral microbes entering the socket. The body is not able to form a protective barrier in the hole, so inflammation rapidly develops in it.
The following causes of alveolitis are distinguished:
- chronic inflammation in the tissues of the oral cavity, its exacerbation;
- high degree of tissue trauma due to complex tooth extraction;
- a blood clot did not form during or after the operation (for example, due to the patient’s violation of the doctor’s recommendations);
- disorders in the immune system, chronic fatigue, chronic diseases;
- long removal process (longer than 40 minutes).
Treatment of alveolitis
Depending on the severity of alveolitis, both local and general treatment can be prescribed. Local methods are usually used using antiseptic rinsing and treating the socket with an antimicrobial agent. In addition to this treatment, vitamins and antibiotics may be prescribed.
In the case of general treatment, physiotherapy is also added, and the overall period of treatment and healing of the hole is increased.
Socket bleeding
Bleeding can occur both immediately after the operation and some time after the operation: from 1 hour to 24 hours or more. The period of manifestation of alveolar bleeding varies depending on the reasons that cause it. An earlier manifestation may be caused by vasodilation, later - due to injury to the socket by the patient after surgery. However, the etiology of the complication may also include injuries during removal (gums, alveoli, blood vessels) and diseases of the body (sepsis, hypertension, leukemia, the first 2 days of the menstrual cycle in women, taking aspirin and its analogues, diabetes).
The process of preventing bleeding depends on what causes it: local causes are eliminated by applying sutures to the rupture sites or applying cold, using a tampon. If the bleeding is caused by low blood clotting, medications are used to increase clotting.
Paresthesia
Sometimes after tooth extraction, patients complain of numbness in the oral cavity. Symptoms can be expressed over a period of 1 to 30 days or even more. The cause of paresthesia lies in nerve damage. Dentists can speed up the restoration of damaged tissue by prescribing vitamins B and C to the patient in combination with injections of galantamine and dibazole.
Neighboring teeth change position, Popov-Gordon effect
The body does not tolerate emptiness, therefore, after a tooth is removed and there is no analogue in its place for a long time, the neighboring teeth (and the tooth on the opposite jaw) tend to fill the resulting space, leaning towards the socket. Obviously, in such a situation, the dentition changes, which leads to curvature, changes in chewing load and bite.
The problem can be solved by replacing the missing tooth with an analogue after the hole has healed and tissue restoration: an implant, a prosthesis.
Communication of the oral and nasal cavities
When extracting molars and premolars of the upper jaw, the floor of the maxillary sinus may be injured, which will lead to the formation of a connection between the oral cavity and the nasal cavity.
It is noteworthy that this complication occurs even if all actions were performed correctly by the dentist. Its causes are usually:
- absence of a bone septum or close adherence of the roots to the sinus;
- bone destruction due to chronic inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root;
The complication requires surgical intervention by a specialist, since the entry of food and drink into the nose through the oral cavity usually leads to inflammation in the sinus (sinusitis), which in itself is a very unfavorable consequence and requires long and complex treatment.
Intervention is not carried out only if acute purulent sinusitis of the upper jaw has developed.
Other complications
Other complications are caused by: incorrect actions of the doctor and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
First category of reasons:
- improper use of forceps and, as a result, damage to the crest of the alveolar tissue;
- erroneous extraction of a tooth germ due to the ignorance of the doctor during milk extraction;
- injuries to adjacent teeth due to careless work of a dental surgeon;
Second category of reasons:
- weak or defective teeth located nearby may break during surgery on the causative tooth;
- low strength of the causative tooth, which causes its fracture and the need to remove parts;
- weak jaw tissue, which increases the risk of fracture and complications;
- individual features of the structure of the roots, jaw and location of nerves.
Rules of care
To prevent complications due to the patient’s fault, it is very important to follow all the dentist’s instructions, namely:
- The first day after surgery: keep the installed tampon in the mouth for 30 minutes, do not eat for 2 hours; do not load food and do not touch the socket area with your tongue or toothbrush;
- 2-3 days after surgery, minimize the load on the teeth located in the extraction area, limit the intake of solid and hot foods, giving preference to soft and liquid foods;
- Refrain from smoking (to prevent a vacuum from occurring in the socket) and try not to drink alcoholic beverages;
- Buy a soft toothbrush to gently clean the area of the extracted tooth a few days after the operation; in the first days it is better not to brush the injured area at all;
- The next day after the operation, make oral baths for the socket (do not rinse under any circumstances) with warm salted water (but not with special rinses).
- Do not exercise for 2-3 days;
- Do not take a hot bath on the first day after removal;
- Do not take aspirin and its analogues.
What determines the speed of gum healing?
Removing the figure eight is a complex operation that is important to entrust to professionals. The chief doctor of our dental clinic tells more about why it is important to carry it out here. The difficulty of the operation is that the eighth teeth are located anatomically incorrectly in 8 out of 10 cases.
Criteria affecting the speed of gum healing:
- traumatic operation,
- size and position of wisdom teeth,
- patient's age,
- existing chronic diseases,
- taking medications,
- state of immunity,
- individual characteristics of the body.
Consequences of the operation
In the first 6-8 hours after surgery, the gums hurt and swell; swelling is possible, which does not require self-treatment. To relieve pain symptoms, you must take painkillers (exclusively as prescribed by a doctor).
Minor bleeding is also normal. It usually occurs within the first hours after tooth extraction. Saliva may remain pinkish for 2-3 days after surgery. A slight increase in body temperature (up to 36.8-36.9 °C) is possible.
These effects are normal and should not cause you concern.
Normal and pathological signs
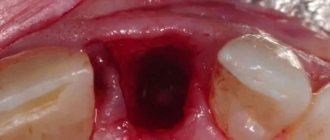
What should the wound look like after extraction? It is necessary to consider which symptoms are normal and which are pathological. Normally, on day 3, the wound is covered with a white film, which signals the healing process. By 4-5 days the entire hole becomes light. If a coating of any other color forms on the surface of the wound, and an unpleasant odor emanates from the mouth, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sign indicates that an infectious process has begun.
Photo of the hole after removal
A normal reaction of the body after extraction is inflammation and swelling of the gums. The signs are due to the fact that during the intervention, damage to soft tissues, blood vessels and nerve endings occurs. Pain after surgery is also normal, but only if it lasts no more than 5-7 days. After removal of sixes, sevens or wisdom teeth, an unpleasant sign radiates to the ears and joints. In the latter case, it becomes difficult for a person to chew. All of these symptoms are normal and usually do not get worse over time. Dentists recommend taking painkillers for 5 days to avoid discomfort.
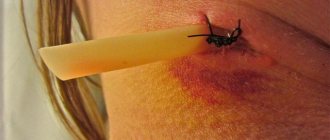
Bruise on the cheek after tooth extraction
Pathological signs of socket healing after tooth extraction:
- increased pain;
- pulsating nature of pain;
- temperature increase;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- aching sensations in the area of neighboring elements, manifesting itself for more than 2-3 hours;
- rise in temperature;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- the hole does not overgrow.
An alarming sign after the intervention is the appearance of severe swelling of the cheeks and gums in the first few hours. To reduce the intensity of the symptom, you can apply a cold compress to the problematic side. If the inflammation intensifies or spreads to the chin and neck, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. The symptom indicates the rapid progression of an infectious complication.
Photo of a swollen cheek after tooth extraction in the socket
A physiologically normal symptom after tooth extraction is bleeding for several hours. The intensity of bleeding varies for several hours after the intervention. Heavy discharge is observed within 15-30 minutes, after this time the symptom should appear less intensely. The bleeding stops completely after 2 hours.
If the bleeding does not stop, then it is necessary to apply a gauze swab moistened with an antiseptic solution to the damaged area. A doctor is consulted when the performed manipulations do not produce results. An additional symptom that is a reason to consult a doctor is a temperature above 38 degrees.
Possible complications
Many factors, including food getting into the socket, can cause complications after surgery. To avoid them, it is important to follow all recommendations and rules of oral hygiene.
If they are not followed, the following complications are possible:
- alveolitis,
- bleeding,
- formation of pus,
- osteomyelitis,
- paresthesia.
In case of severe and prolonged pain, severe swelling, numbness of the upper and lower jaw, as well as increased body temperature (more than 38 ° C) - these are the most common signs of complications, if they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Causes of the disease
Traumatic tooth extraction.
Alveolitis is often caused by a traumatic dental procedure. Injury can occur if a tooth is removed in fragments (parts). During the operation, sometimes the gums are damaged or the bone walls of the socket are partially destroyed. In this case, healing takes longer compared to uncomplicated removal and is often accompanied by the appearance of alveolitis.
Foreign particles entering the hole.
Sometimes pain after tooth extraction occurs as a result of the contents of the carious cavity, dental plaque, fragments of the extracted tooth, or bone fragments of the alveoli entering the socket. In addition, the cause of pain and alveolitis can be the destruction of a blood clot.
Failure to maintain socket hygiene.
Healing of the alveoli occurs due to the formation of a blood clot. This biological barrier protects the socket from infections and inflammation. After some time, the clot is replaced by newly formed bone tissue. It is not recommended to eat rough, hot or spicy foods within 24 hours after a dental procedure, as this can destroy the blood clot. In addition, brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with caution. Failure to follow the dentist's recommendations can lead to blood clot disruption, alveolitis and pain after tooth extraction.
Presence of infection.
Sometimes the cause of dental surgery is chronic periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues that surround the root. If you have had a tooth removed and its socket hurts, this may be caused by an infection getting into it.
Up to contents