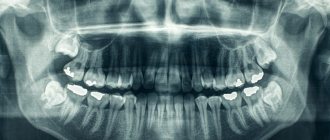
Modern X-ray examinations are used everywhere in dentistry. Knowing how a panoramic photograph of teeth is taken for adults, you can go for this painless and harmless diagnostic procedure without fear. But, if you are interested in delving into the issue of OPTG and finding out what a dental orthopantomogram shows, this article will give the most detailed answers to your questions.
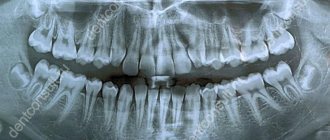
What does a panoramic dental photograph show?
The data in the orthopantomogram image is sufficient for the attending physician to see:
- all possible carious lesions of teeth (including those hidden under fillings or on the contact plane of units);
- various malocclusions (congenital and acquired), including occlusion;
- pronounced pathologies of the dentition as a whole and individual units;
- the condition of previously placed fillings (for medical reasons and during an aesthetic dental procedure);
- foci of acute inflammatory processes (including chronic ones);
- dynamics of changes in the dental system during the use of orthodontic structures (braces, aligners, etc.);
- mechanical damage to bone and soft tissues in the oral cavity (for example, due to injuries);
- impact on the gums of removable and conditionally removable orthopedic structures (any dental prostheses);
- various types of neoplasms (shows cysts, granulomas and malignant tumors);
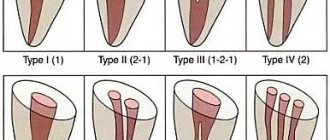
- the number and location of root canals (this information allows you to carry out the procedure for removing nerves and filling canals as accurately as possible);
- condition of the gum bone tissue (especially important before prosthetics and implantation);
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint (for diagnosing arthritis, arthrosis, dysfunction and other pathologies);
- condition (including atrophy) of the alveolar process;
- stage of eruption and position of permanent and milk teeth (buds);
- pathology of the paranasal sinuses;
- position and degree of survival of implants;
- all possible hidden dental diseases.
Also, a panoramic photograph of the teeth is needed to determine the quality of the operations performed. For example, to assess the quality of root canal treatment (to understand whether there are any parts of the instrument, nerves left, and whether there is enough filling material). Such diagnostics are necessary and may be required both during the collection of a clinical picture and at the end of treatment (as a control study).
You might be interested in:
Dental diagnostics
Orthopantomogram of teeth
Pediatric orthopantomogram
Occlusal dental x-ray
The occlusal surface of the tooth is the part from the top of the cusps to the deepest point of the fissure (notch on the surface of the tooth).
Occlusal x-ray of teeth. Alternative diagnostics. This procedure gets its name from the name of the tooth surface.
It is on this plane that the sensor is installed when it is necessary to take a bitewing X-ray. Thus, the sensor-sensor appears between the closed teeth.
Occlusal dental x-rays are used to study the floor or vault of the mouth and the placement of teeth in a specific area of the upper or lower jaw. In such cases, a targeted x-ray of one tooth will not be enough, and an orthopantomogram (panoramic x-ray of the teeth) will be redundant.
The technique allows you to assess the condition of the hard palate, identify neoplasms and stones (stones) of the sublingual salivary and submandibular glands. Also, occlusive dental x-rays allow you to look at the condition of the inner and outer cortical plates of the jaws for the presence of cysts or other neoplasms. This image can also determine the location of the jaw fracture.
It may be necessary to conduct occlusal x-rays of the teeth for the orthodontist if there are dental anomalies. Based on this image, they decide how to correct malocclusions.
Occlusal x-rays are also used when other types of x-rays cannot give an accurate result and an additional picture is needed. Or if there is no other opportunity to conduct research.
Occlusal dental x-rays have two options: x-rays in axial projection and x-rays in isometric projection. In the first case, the sensor is placed perpendicular to the tooth axis.
X-rays in axial projection are used, for example, to identify impacted teeth - those that cannot erupt for a long time without the intervention of a doctor. Or dystopic teeth - those that are difficult to erupt, damaging the soft tissue of the gums and disrupting the bite.
Also in the image in this projection you can determine the location of the roots. Most often, this technique is used to diagnose problems in the lower jaw.
When occlusal x-rays of teeth are taken in isometric projection, the sensor is placed at a slight angle. Such an x-ray will be prescribed if the patient is unable to open his mouth wide, for example, due to a jaw injury. Or when the patient has an overdeveloped gag reflex.
Occlusal x-rays of teeth in an isometric projection are also often used when the patient resists treatment - if this is a child or a person with inadequate motor or psycho-emotional reactions to the doctor’s manipulations in the oral cavity.
The image obtained by this method has significant distortion. But an experienced radiologist can minimize the disadvantages of isometric imaging. To do this, you need to take an intraoral x-ray with an almost parallel beam of rays from a considerable distance.
Modern dentistry has incorporated centuries of experience. At the same time, it is armed with the latest developments in world science. Today, X-rays are performed quickly and with a minimal dose of radiation. The main thing is that the research is carried out on good quality digital equipment.
Such procedures are the most harmless. But there are still some contraindications. Thus, for pregnant women, any type of x-ray, even the most gentle one, is prescribed only in emergency cases, when the woman’s life is on the scale. Irradiation is contraindicated in some chronic diseases.
Be sure to tell your doctor everything related to your health. Only your attending physician should decide which type of x-ray you will need to undergo in a particular situation.
What does a radiologist pay attention to when interpreting an orthopantomogram?
For the specialist who interprets and gives a conclusion, a panoramic photograph of the teeth shows a complete picture of the condition of the dental system. Six key points are explored in detail:
- Fabrics _ Both hard (bone) and soft tissues are subject to examination. This allows you to identify all possible inflammations and consequences of mechanical damage.
- Roots of teeth . A panoramic photograph shows not only the condition, location and defects of already formed roots, but also the root follicles. This makes it possible to assess the state of the primordia, predict the direction of their eruption, etc. That is why x-rays of children's primary teeth are no less important than an orthopantomogram for adults.
- Jaws . Timely examination of the individual characteristics of the jaws allows us to identify possible pathologies and defects. In cases where there are problems with the bite, the degree of abnormal development of the dental system is determined so that the correct orthodontic treatment can be prescribed.
- Crowns and fillings . They have a certain shelf life and may lose their functionality over time. In addition, caries can develop under fillings, and inflammation can develop under crowns. A visual examination alone is not enough to determine the location and foci of the disease, so a panoramic photograph of the teeth is required.
- Temporomandibular joint . An orthopantomogram provides complete information about the condition of the joints, clearly showing existing asymmetry, irregular shape and other defects. Panoramic photography is one of the effective ways to diagnose arthritis in the earliest stages.
- Maxillary sinuses (sinuses) . At the same time, the nasal passages and septum are examined. These orthopantomograms make it possible to determine the exact size and features of the outline of the nasal sinuses and identify even the most minimal curvature of the nasal septum. This is especially important in cases where discomfort and pain in the teeth are the result of ENT diseases rather than dental ones. An orthopantomogram of the teeth shows the cavities on the monitor as a darkened area, and the bony/cartilaginous septa as light areas. Modern equipment allows for a fairly high contrast, which makes it possible to notice even the smallest defects and deviations from the norm.
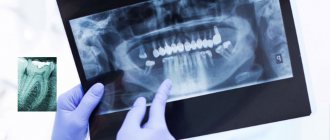
If you still have a question about how to take a panoramic photograph of teeth for adults, ask it at a dentist’s appointment in any of the Smile Factor network of clinics. Our dental orthopantomogram is not only a safe diagnostic procedure, but also the most informative technique that is used before and after treatment in almost all areas of dentistry. What the result of an X-ray examination shows can be seen in 3D on a disk (or sent by email) and in 2D on a printout.
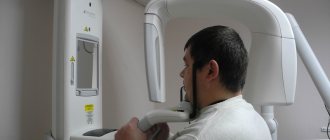
How to do dental x-rays
The procedure is carried out by a doctor in a specially equipped room. The implementation mechanism takes place in 4 stages:
- The patient sits in a chair. The doctor examines the problem area.
- A special apron is placed on the patient to reduce the adverse effects of x-rays.
- The doctor fixes the head of the subject to obtain a clear image.
- On the affected area inside the oral cavity behind the teeth or on the front side, using a digital visiograph, the doctor directs the beam.
The whole process takes 3 minutes. After 15 minutes, you will be given a photograph of your teeth on film or electronically (if necessary).
There may be the following reasons for taking a photo:
- Clarification of the development process of pulpitis, periodontal disease and caries;
- Check after removal of damaged teeth;
- Checking the quality of treated teeth;
- Determining the specific structure of teeth before installing a crown or bridge;
- Checking neoplasms.
During endodontic treatment, at least 3 photographs of the tooth are taken: 1. Photograph of the teeth at the diagnostic stage. It is necessary to determine the condition of the tooth, the shape and number of roots, and the treatment method.
2. A photograph at the stage of tooth treatment with endodontic instruments inserted into the tooth canals. The picture is displayed on the computer screen.
3. Control image after completion of treatment to check the sealed tooth canals.
Permissible radiation dose for dental x-rays
The radiation dose for a targeted photograph for a person is 3-5 μ3v. During the year, an adult is allowed to receive up to 1000 microns. Consequently, a patient can take from 80 to 90 images per year using an X-ray machine. The radiovisiograph will make it possible to take up to 400 images. This indicates the harmlessness of this manipulation.
Read also
What to do if your tooth aches
Sometimes aching pain in a tooth can appear for no apparent reason at first glance.
Why do teeth crumble?
Tooth decay in general, and crumbling in particular, is not an aesthetic problem.