The inlay is a one-piece structure, the lower part of which is similar to a stump (therefore a stump). It takes into account the characteristics of the destroyed tooth, so it can be single, double or triple. In complex cases, it may consist of individual elements. The upper part is made of any shape, in accordance with the impression taken. The inlay can be installed without a crown, completely repeating the shape of the tooth. Such microprosthetics are often used in orthopedic dentistry, because even a severely damaged tooth can be completely restored, obtaining an aesthetic dental unit.
Advantages and disadvantages of tabs
- There is no danger of destruction or cracking - the strength and reliability of the inlays is high.
- Resistance to food dyes, color stability.
- The characteristics of the bite are taken into account.
- The shape of the tooth is completely restored and remains unchanged in the future.
- There are no unpleasant sensations at all.
- The result of tooth restoration is highly aesthetic.
- The possibility of the spread of harmful organisms is eliminated.
Negative aspects may arise if you go to clinics with insufficient equipment or inflated prices. In these cases, patients note the lengthy process of manufacturing and installing the inlay and the high cost.
How to relieve toothache under a crown?
The most important thing is to make an appointment with the dentist. While waiting for this, you can relieve pain in several ways:
- Rinsing helps to get rid of food particles stuck in the crown and somewhat alleviate the discomfort. It is best to use a soda solution or sage tincture;
- massage of active points: above the upper lip, on the tip of the index finger;
- You can take a painkiller that will help relieve pain until you visit the dentist.
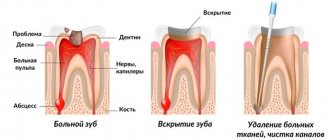
At the appointment, the dentist will remove the crown and treat the tooth for pulpitis, cysts or gumboil, and also correct poor-quality fillings, if any.
If we are talking about an incorrect crown configuration, then it makes sense to replace it with a new one. The main rule of repeated prosthetics: preservation of the tooth. A crown is just a means to achieve this goal.
Indications and contraindications for use
It’s worth putting a tab if there is:
- Extensive caries damage (more than 60%) of the tooth tissue;
- Large cavity size;
- Traumatic tooth damage;
- Hyperplasia, dysplasia;
- Wedge-shaped defect;
- The need for protection against tooth wear;
- Installation of bridges simultaneously with root structures.
The use of inlays is not recommended if the patient has:
- Small tooth cavity;
- Carious processes are active;
- There is no quality oral hygiene.
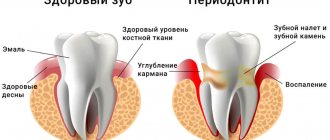
Reconstruction of the functionality of the dentition using an inlay allows you to cope with high loads. This is a great solution, but it can be painful some time after installation. What to do if a tooth hurts under the tab?
The cause of pain may be high sensitivity. If the situation worsens over time, you need to see a dentist and get an x-ray.
If a tooth hurts under the stump tab, then the following reasons are possible.
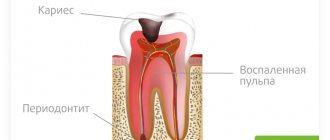
- Pulpitis is damage to the pulp of a tooth with a preserved nerve. When installing the inlay, the pulp chamber was accidentally damaged. After the anesthesia wears off, the pain becomes severe and intensifies with chewing and contact with cold and warm foods. The patient feels pain under the tab.
- Pressing the inlay into the tooth tissue. A bursting, aching pain occurs, which does not allow establishing a specific location.
- The tab is too large. The patient feels pain only when chewing. The pain is dull, there is no reaction to hot and cold food. The sensations are more like discomfort. In the absence of correction, inflammation of the periodontium or gums develops.
- Infection. Before installing the inlay, the doctor cleans the carious cavity to prevent further spread of the destructive process. If at this moment there is already an infection in the tooth, but has not yet been identified externally, after installing the tab the process will spread deeper, to the pulp and to the roots. If left untreated, the pain under the ceramic inlay will become very severe, the nature of the “sensations” will be pulsating and sharp.
Clinical case
A 30-year-old patient came to the clinic with complaints of darkening of fillings. The patient was interested in an aesthetic restoration with a long service life, so it was decided to restore the teeth with ceramic inlays. The initial situation is shown in Fig. 1. After collecting complaints, anamnesis, and conducting an examination, a diagnosis was made: K02.1 Dentin caries of a tooth 3.6, class II according to Black. K02.1 Dentin caries of tooth 3.7, Black class I.
Rice. 1.
At the clinical stage, the tooth was cleaned of plaque. After anesthesia, the color was determined using the standard VITAPAN Classical scale, the color of future indirect restorations is A2.
The preparation and formation of cavities of class I and II according to Black were carried out according to generally accepted principles in compliance with all stages with the obligatory use of a rubber dam to isolate the working field.
A small carious cavity was found on the medial contact surface of tooth 3.6, without destruction of the marginal ridge and without communication with the main carious cavity on the chewing surface. After preparing the carious cavity on the medial contact surface of the tooth, filling was performed using a fluid composite material.
Before taking the main impression, immediate dentin bonding was performed according to a traditional adhesive protocol. After polymerization of the adhesive, the undercuts in the area of the cavity walls were closed with a layer of flowable composite. The next step was to apply glycerin to the inner surface of the prepared cavity and illuminate it with a photopolymer lamp to remove the oxygen-inhibited layer in order to prevent possible interaction with the vinyl polysiloxane impression material during impression taking. The final view of the prepared cavity before taking an impression is shown in Fig. 2.
Rice. 2.
Impressions were taken with A-silicone impression material, temporary restorations were made using Clip material.
A follow-up visit took place 1 week later to fix the IPS e.max ceramic inlay. Previously, before admitting the patient, we assessed the marginal fit of the ceramic inlays on dismountable models (Fig. 3-6).
Rice. 3.
Rice. 4.
Rice. 5.
Rice. 6.
The second clinical stage began with cleaning the tooth from plaque. After anesthesia and the application of a rubber dam, the temporary restorations were removed, the cavity was cleaned of temporary cement residues, followed by fitting and preparation of ceramic inlays for fixation (Fig. 7-10). The indirect restoration was cemented using Calibra dual-curing adhesive composite cement (DENTSPLY).
Rice. 7.
Rice. 8.
Rice. 9.
Rice. 10.
After positioning the restoration, excess fixing material was removed in the area of the contact surfaces. Next, excess material was removed from other surfaces of the teeth. After 3 - 4 minutes, the surface of the fixing material was covered with a layer of glycerin and the final illumination of the restorations was carried out from each surface for 20 seconds.
At the final stage, an occlusion check was carried out. The view of the restoration immediately after fixation is shown in Fig. 11.
Ceramic restorations look natural, no different from your own tooth tissue.
Rice. eleven.
The appearance of the restorations 5 years after fixation is shown in Fig. 12.
Rice. 12.
What complications are possible?
An incorrectly installed inlay can result in the development of a cyst. Treatment will be lengthy and expensive - resection of the root apex will be required.
If you have pain under a microprosthesis or the inlay under the crown hurts, contact dentistry at amazing prices. An endodontist will examine the oral cavity and prescribe additional examination.
- X-ray - to assess the condition of the root and surrounding tissue (the image will show whether there is a cyst;
- EDI – Electroodontodiagnosis to assess the condition of the pulp – the doctor has the opportunity to determine:
- The degree of damage to nerve tissue;
- Is it necessary to open root canals, treat or remove the pulp?
Taking into account the results obtained, effective treatment will be carried out.
Causes of tooth pain under a crown or denture
- If you have not had root canal treatment to remove the pulp before getting a crown, pressure on the damaged nerve may cause pain.
- Patients with malocclusion and bruxism may experience pain at night from pressing on ridges or areas of the tooth that are higher than normal.
- If the denture has shifted, exposing part of the tooth, or, worse, is pressing on the dental nerve, then the slightest pressure or change in temperature can send strong pain signals.
- Teeth under a crown are also at risk for all the problems associated with regular teeth, meaning they can become infected, break, and become vulnerable if the enamel wears down. And this can cause pain.
Emergency help
If you can’t see a doctor, and the tooth under the tab hurts, the following measures will help.
- Chewing and temperature stress on the teeth should be completely avoided. Food should be consistent with body temperature and should not require chewing or biting. Broths and pureed soups are the best solution.
- For unbearable pain, take an analgesic or anti-inflammatory drug. The main thing is that the product does not cause allergies. It could be Nimesil, Nise or Analgin.
- If the situation worsens, accompanied by headache and chills, you should contact the nearest medical facility. The staff will call an emergency dentist, and the problem will be solved.
Author:
Mayorov Andrey Mikhailovich
Specialization:
orthopedic dentistry, dental prosthetics, implant installation
Possible difficulties
If you ignore the pain under the crown for some time, it will not go away on its own. There is a 100% chance of complications that will likely require much higher treatment costs:
- the occurrence of a dental cyst. The disorder is sometimes accompanied by swelling of the gum tissue under the crown. But for a long time you may not feel any alarming symptoms at all, except for a slight aching pain;
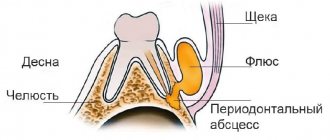
- formation of flux, leading to swelling of the gums and unstable condition of the tooth;
- untreated flux is fraught with the occurrence of a fistula at the base of the crown.
Causes of pain after turning
Discomfort in the oral cavity after partial removal of enamel and dentin is common. If the pulp has not been removed, the prepared tooth may be painful for 3-7 days. Unpleasant sensations worsen when drinking cold and hot drinks, hard foods, sour foods and sweets. This is a normal option, since increased sensitivity is due to thinning of hard tissue.
The cause of pain may be a violation of the teeth preparation technique. If the doctor worked without stopping, tissue overheating could occur. In this case, unpleasant sensations occur throughout the day, and not just in response to external stimuli. Pain can also be associated with removing too thick a layer of dentin and exposing the nerve of the tooth. The only solution to the problem is to remove the pulp.
After grinding, not only the tooth, but also the gums may hurt if a retraction thread was used during the procedure. It pushes back the edge of the gum and often injures it.