We have all experienced pain in one way or another. It happens that it is fleeting and does not bring much discomfort, but it happens the other way around. Paroxysmal, recurring or constant. For such indications, pain medication is necessary.
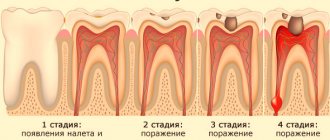
Nimesil is used for toothache
Nimesil is a non-steroidal drug that has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. Nimesil is used as a symptomatic treatment of pain in dental, headache, menstrual, joint, muscle and postoperative pain, as well as in the treatment of injuries to soft tissues and the musculoskeletal system. The duration of the drug's effect is about 6 hours.
Nimesil can be used either once or for systemic therapy, that is, for a long (up to 15 days) course.
What does Nimesulide help with and indications for use?
Before using the drug, consult a doctor.
It is important to remember that Nimesulide does not affect the causes of diseases and does not treat them. This drug is symptomatic and is used to relieve and alleviate clinical manifestations.
The main indications for taking the drug are:
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system with severe pain (arthritis of various origins, including rheumatoid, bursitis, tendonitis, osteoarthritis, myalgia).
- Early postoperative period.
- Headache or toothache.
- Periodic pain in women.
Use for toothache
Powder is poured into warm liquid
The medicine is intended for oral administration.
Any anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended to be taken after meals, which is necessary to accelerate absorption in the intestines.
The tablets are taken by swallowing the drug.
It is recommended to take the medicine with a sufficient amount of liquid. The method of using the powder is different.
Instructions for use:
- The contents of the sachet are poured into a glass;
- The powder is poured with warm liquid (about 1/3 cup);
- The mixture is thoroughly stirred;
- The resulting liquid is taken orally.
As a rule, one dose (100 mg of Nimesulide) is enough to eliminate the unpleasant symptom.
Important to remember! The drug in gel form is not used in the treatment of dental diseases or any other pathologies of internal organs or mucous membranes. The gel is prescribed exclusively for the treatment of joint pain for local application.
Dosages
For toothache, take 1 dose of the drug. If the pain syndrome resumes, re-administration is carried out no less than 6 hours later.
The maximum daily dose is 400 mg (4 tablets). Long-term treatment of toothache with Nimesulide is contraindicated due to possible side effects.
Contraindications
The drug is prohibited for gastric and duodenal ulcers, especially in the acute stage, for bleeding disorders and increased bleeding, Crohn's disease, bronchial asthma, inflammatory processes in the intestines, polyposis of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
Also, the use of Nimesulide is limited in case of individual intolerance to NSAIDs, severe chronic, renal and liver failure, in children under 12 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation.
NSAID gastropathy
In the scientific literature, this problem is called “NSAID gastropathy.” The term was first proposed in 1986 to distinguish specific damage to the gastric mucosa that occurs with long-term use of NSAIDs from classic peptic ulcer disease.
The difference between NSAID gastropathy and peptic ulcer disease can also be traced by the affected area. Most often, ulcers can be seen in the stomach, and not in the duodenum. Plus, the changes are more common in older people than in younger people.
Side effects and overdose
Taking Nimesulide in some cases may be accompanied by the development of unwanted side reactions. These include:
- From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, anxiety, headaches, nightmares.
- Urinary system: decreased amount of urine excreted, hematuria, exacerbation of chronic renal failure.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: dyspeptic syndrome (nausea, vomiting, stool disorders), abdominal pain, flatulence, bleeding, gastritis, ulcerative lesions, jaundice as a result of cholestasis, increased transaminases.
- Skin: increased sweating and allergic reactions of varying severity (itching, urticaria, swelling, Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
- From the cardiovascular system: hypotension, increased heart rate.
- Hematopoietic organs: anemia, pancytopenia, increased clotting time.
- Respiratory system: shortness of breath, spasm of smooth muscles in the bronchi, exacerbation of COPD or bronchial asthma.
- Organ of vision: blurred perception.
Symptoms of overdose are similar to those of adverse reactions. They develop due to non-compliance with doctor’s instructions and uncontrolled use of Nimesulide.
In case of overdose, it is necessary to discontinue the drug, lavage the stomach to clean water and take activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight.
Reviews
In this section you can read user reviews about the drug Nimesulide and its analogues, the effectiveness of the drug, side effects, and features of administration.
Nimesulide is a drug with a pronounced analgesic effect, which occurs by eliminating the inflammatory reaction. The medicine helps eliminate toothache, but has only a symptomatic effect.
To prevent the recurrence of the disease, you need to visit the dentist and eliminate the reason why it occurs.
Interactions
Nimesulide increases the activity of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. Concomitant use of this drug with diuretics reduces their effectiveness, which can lead to edema, especially in patients with hypertension and renal failure.
Nimesulide also increases the toxicity of cyclosporine and methotrexate. And its simultaneous use with GCS and serotonin reuptake inhibitors significantly increases the risk of bleeding in the digestive tract.
Nimesil and alcohol
Nimesil and alcohol are incompatible; taking them together is strictly prohibited. Why? Both alcoholic drinks and Nimesil reinforce each other and are hepatoxic, that is, they affect the liver and can lead to severe disorders of its functioning: the development of granuloma, acute hepatitis and cirrhosis. Also, the combination of the drug and alcohol provokes fluid retention in the body and high blood pressure. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is also disrupted. Alcohol irritates the gastric mucosa, causing gastritis and ulcers. Internal bleeding may occur as a result of perforation of the wall of the stomach and intestines.
Do not take Nimesil with alcohol
They try not to prescribe Nimesil to patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system and blood. Ethyl alcohol causes vasospasm, which increases the load on the heart, and simultaneous use of the drug can lead to acute heart failure or death. For patients who suffer from alcohol addiction, Nimesil is contraindicated, since the body is weakened, the risk of complications increases significantly. Also, the suspension is not recommended to be taken during a hangover.
Myths that we encounter in daily practice
Myth 1. Using NSAID drugs in the form of suppositories is less aggressive for the stomach than taking pills
This is 100% a myth. The pathogenic, destructive effect of the drug is realized through the blood, delivering it through the vessels to the stomach.
Myth 2. Medicines from the group of antacids - Rennie, Maalox, Phosphalugel and H2-blockers (Ranitidine and Famotidine) can be used as “gastroprotectors”
In this case they are not effective.
Myth 3. You can't take proton pump inhibitors regularly
The fact is that if an elderly person has been prescribed an anti-inflammatory drug for life, it is absolutely pointless to prescribe gastroprotection for a month. In such cases, medications should be taken strictly in parallel.
Myth 4. Food products (jelly, etc.) can act as “gastroprotectors”
We will leave this myth as absolutely fantastic without comment.
Dangers of taking Nimesil
Many patients confirm the high effectiveness of Nimesil for relieving toothache. However, according to several studies conducted on this medicine, it can cause a number of negative effects caused by toxicological effects on the kidneys and liver. Therefore, the sale of Nimesil was banned in the United States, and in European countries the drug is sold with a mark prohibiting its administration to children.
Data from various studies have shown that negative consequences from the action of the drug occur only if the specified conditions of administration are not observed and if the prescribed dosage is exceeded.
When purchasing the drug, you should be advised about the specifics of use and contraindications of Nimesil.
Dentists recommend taking Nimesil to relieve tooth pain only in cases where other medications that have a safe effect on the body are not able to eliminate the pain. In addition, the drug is contraindicated for long-term use, since the liver is subjected to severe stress.
During studies of the drug's effect, no other negative effects were identified. Only a number of subjects refused to continue taking the medication due to the fact that they were diagnosed with disorders of the digestive system. Moreover, cases of severe liver damage have not yet been reported in medical practice.
Possible side effects
Nimesil in some cases provokes the appearance of many side effects, manifested in the form of:
- Attacks of headaches and dizziness
- Problems with stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increased sweating
- Allergic reaction in the form of skin rashes
- Anemia
- Decreased vision
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased nervousness
- Insomnia
- Shortness of breath
- Stomatitis and hepatitis
- Urinary retention
Basically, the negative consequences that occur when taking Nimesil are associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Side effects manifest themselves in the form of diarrhea, constipation, pain localized in the abdomen.
HOW PNEUMONIA DEVELOPES
In conditions of reduced respiratory and motor activity, when mucus moves less through the bronchi, against the background of intoxication of the body and decreased immunity, bacteria from the nasopharynx descend into the lower parts of the respiratory tract and can begin to multiply there.
Thus, bacterial bronchitis can be caused first, then bronchopneumonia with transition to pneumonia. The development of bacterial pneumonia can also be facilitated by the patient being on a ventilator for a long time. Despite compliance with all the strictest disinfection measures, ventilators are risk factors for the occurrence of ventilator-associated pneumonia.
What can replace Nimesulide?
There are a huge number of drugs on the pharmaceutical market with the main active substance – nimesulide. In fact, these are synonymous drugs that have the same composition and indications. Minor differences may only be in the list of excipients. So, in addition to the drug of the same name, the following drugs based on nimesulide are available:
- Nise;
- Nimesil;
- Nimulid;
- Mesulide;
- Novolid;
- Aponil;
- Flolide;
- Aulin et al.
The listed drugs are available in various forms and dosages, so you can choose the best option for each case. When choosing what is best to use - Nimesulide, Nimesil, Nise or another substitute drug from the above list, you can be guided by the financial availability of these drugs or personal preferences.
In some cases, it becomes necessary to replace Nimesulide with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In this case, the safest drugs are selected, the effects of which are comparable to the effects of Nimesulide. The following analogues of the drug in question are most often used:
- Diclofenac;
- Meloxicam;
- Amtolmetin;
- Indomethacin;
- Diacerein, etc.
It is worth considering that these drugs are also available under different trade names. The choice of an analogue drug should be made only by the attending physician.
Nimesulide or Meloxicam – which is better?
Nimesulide or Ibuprofen – which is better?
Ibuprofen is a widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used in the treatment of various rheumatic pains and inflammatory processes in the musculoskeletal system.
It is characterized by good tolerability and effectiveness. However, in comparison with Nimesulide, it is worth noting the more powerful anti-inflammatory properties of the latter.
Ibuprofen is great for menstrual pain by reducing intrauterine pressure and uterine contractions.
Nise or ibuprofen: which is better and what is the difference (differences in composition, reviews from doctors)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used by specialists in all areas of medicine to relieve pain and inflammation. Only a doctor can prescribe Nise or Ibuprofen, choosing the drug that will cause the least harm to the patient’s health. The choice of remedy will depend on the age of the patient and the nature of the disease.
Only a doctor can prescribe Nise or Ibuprofen, choosing the drug that will cause the least harm to the patient’s health.
Characteristics of Nise
The active ingredient of the drug is nimesulide. Auxiliary:
- microcrystalline cellulose;
- corn starch;
- calcium hydrogen phosphate;
- sodium starch glycolate;
- magnesium stearate;
- anhydrous colloidal silicon and purified talc.
The active ingredient of the drug is nimesulide.
Nise is produced in the form:
- tablets;
- gel;
- suspensions for children.
Nimesil or Ibuprofen - which is better?
Of the variety of NSAIDs (painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs), these drugs can be called one of the safest.
Ibuprofen is traditionally considered optimal in terms of the ratio of effectiveness and frequency of side effects, and therefore is the drug of choice for high fever and moderate pain in childhood.
Although Nimesil is not used until the age of 12, it also compares favorably with other similar NSAIDs in its selectivity of action. Let's compare their advantages and disadvantages.
There are contraindications, consult a specialist
The main active ingredient of Italian Nimesil is nimesulide. This is a fairly powerful anti-inflammatory agent with a moderate analgesic effect.
Due to its selective effect on enzymes responsible for pain and inflammation, Nimesulide is much less harmful to the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines compared to non-selective NSAIDs.
The duration of action is similar to ibuprofen, but according to clinical studies it begins to act faster.
"Nimesil" 100 mg (30 pcs.)
Most often used for joint pain (arthralgia) of various origins and injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
The selectivity of Nimesil's action allows it to be taken for a long time by people with chronic joint diseases (arthritis, osteoarthritis), however, periodic monitoring of kidney function is necessary.
Parallel use of gastroprotectors is also advisable if long-term symptomatic treatment with nimesulide is necessary.
Sachet bags with Nimesil granules
Available in the form of separate bags with granules for preparing a solution. Among the direct analogues of Nimesil are such drugs as: Nemulex - also granules (Russia), Nimulid - tablets (India), Nise - tablets or gel (India).
Ibuprofen is the most popular antipyretic after aspirin and paracetamol with a good analgesic effect. Has extensive experience in use in medicine and pediatrics in particular.
Unlike his opponent, he cannot boast of selective action, but he himself acts softer. In children's practice it can be used from a very early age in the form of suspensions.
For adults, the standard dose per dose is 200-400 mg.
Increased dosage of ibuprofen for adults (400 mg)
The scope of ibuprofen is much wider. Most often used as an antipyretic. Available in a variety of forms under many trade names (see 5 Popular Ibuprofen Products).
Ibuprofen tablets 200 mg
What's stronger?
The strength of the analgesic effect of both drugs is average, but there are still differences. Thus, several European independent studies compared the analgesic effect of nimesulide or ibuprofen tablets after removal of teeth and tonsils.
The results showed approximately similar pain-relieving ability, but nimesulide had a faster onset of action (about 15 minutes) in dentistry, and the recovery period after tonsillectomy (surgery to remove the tonsils) was slightly faster. We can conclude that Nimesil will be preferable for adults, in particular for toothache. For children under 12, the clear choice is ibuprofen.
Is it possible to take ibuprofen and Nimesil at the same time?
It is not advisable to take different NSAIDs orally together. Thus, Nimesil is strictly contraindicated for use with paracetamol due to its toxic effect on the liver.
There is no exact compatibility data for ibuprofen, so their parallel use is also best avoided. If there is an urgent need, you can wait until the half-life of nimesulide passes - about 5-6 hours and take Ibuprofen after Nimesil.
However, if you have chronic stomach problems (gastritis, ulcers), then doing this is highly undesirable.
Method of administration
Nimesil is used for tooth pain only after consultation with a doctor and with his direct participation. One of the main advantages that the medicine has is its release form.
The suspension is prepared from powder according to the instructions
Nimesil is produced in the form of a powder intended for the preparation of a suspension. This solution is quickly absorbed, resulting in relief within 30 minutes. During this period, the concentration of the active substance reaches 50% of the maximum possible.
Before you start using Nimesil, it is recommended that you read the attached instructions. The drug is approved for use subject to a number of conditions:
- The patient's age is over 12 years
- The product is taken only after meals
- The prepared solution is not intended for long-term storage
- The powder is dissolved in half a glass of warm water
The drug is taken daily no more than twice a day. At least 12 hours must pass between each dose.