Why do people not immediately grow permanent teeth?
Adults have 32 teeth, although some have only 28. A child's jaw is so small that so many teeth cannot fit in it. Therefore, the baby grows only 20 teeth, which then change. As the child grows older, the size of the jaw also increases. Permanent teeth begin to emerge at the age of 6 or 7 years. However, they form under the first row of teeth from the birth of the baby. This causes baby teeth to be replaced by molars and fall out.
Milk teeth are a kind of “pioneers”. They “show” the natives where they should go when growing. Over time, they inevitably begin to wobble and fall out. If a baby tooth falls out and a new one does not grow, parents need to take the child to the dentist.
What is the danger of late eruption?
There is a possibility of complications not only in the mouth, but also for the whole body:
- With prolonged accumulation of pus, which has no outlet, soft tissue melts, provoking the spread of infection and the formation of abscesses;
- The bite may be affected;
- If a tooth is cut towards the cheek, chronic injury occurs;
- Clamping of the mucous membrane with teeth leads to the appearance of a long-term non-healing wound and, as a result, ulcers;
- The temperature rises, weakness appears;
- Purulent inflammation eventually spreads to the periosteum.
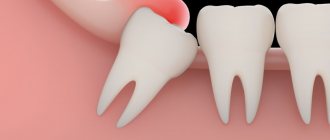
The process is often aggravated by incorrect positioning or impaction of the tooth:
- Pericoronitis develops - the gingival hood becomes inflamed, as food accumulates in it and pathogenic bacteria multiply; in the absence of timely treatment, osteomyelitis and periostitis develop;
- A completely impacted tooth is the cause of neuralgia, facial pain, and cysts;
- With a horizontal direction of growth, the “figure eight” destroys neighboring teeth, causing caries;
- A wisdom tooth can begin to grow after the installation of a prosthesis, causing a lot of inconvenience to a person.
To prevent the development of complications, you should visit the dentist as soon as possible - the doctor will assess the situation and decide what to do.
Timing of eruption of molars
Before you figure out why baby teeth fall out and new ones don’t grow, you need to find out the timing and norms for the growth of molars, established by dentists. This will allow you not to panic ahead of time and consult a doctor in time if necessary.
The rudiments of baby teeth begin to form in the first trimester of pregnancy (at 8 weeks), and at 20 weeks the rudiments of molar teeth are formed. They are located very deep in the baby's jaw. It should be understood that not all teeth that erupt in a little person will fall out in the future. Some of them become permanent immediately.
The baby's first tooth appears at approximately 6 months. By the age of three, all his teeth have grown. When do the molars erupt?
By about 7 years of age, the baby grows molars, which in dental practice are called sixth teeth. At the age of 11 to 13 years, molars also appear, but this time the 7th ones. These teeth do not have milk analogues; after eruption, they immediately become permanent. All other molars gradually replace baby teeth. At the age of 6 to 8 years, the child’s central incisors sprout, and from 7 to 9 years, the lateral incisors erupt. From 10 to 12 years of age, the child begins to grow premolars, which are also called fifth and fourth teeth, according to the dental formula. Molar canines erupt between the ages of 9 and 13 years. Adults develop wisdom teeth, but not always. Considering that the process of changing teeth takes place according to a certain schedule, parents are concerned about why their child is experiencing some kind of delay. Usually they are very worried about why the baby teeth have fallen out, but the permanent teeth are not growing.
What is the danger of premature loss of baby teeth?
Trauma, caries and other dental diseases can cause the loss of a baby tooth. In place of the tooth there remains a “gap” in the dentition, which can cause significant disturbances in the formation of a permanent bite:
- crowding or crowding of teeth;
- dystopia of the tooth, when it erupts outside the dentition;
- horizontal overjet or excessive overlap of the lower front teeth with the upper ones;
- overbite or changing the distance between the chewing surfaces of opposing teeth in the vertical plane.
At the initial stage, changes may be minor. However, over time they begin to progress rapidly.
If a baby tooth is lost prematurely, then it is advisable to “close” the defect in the dentition that has formed in its place with a removable denture. Most often, so-called immediate dentures are used, which in private conversations dentists may call “clothespins.”
It is not only the fact of tooth loss that matters, but also the reason why it happened. Preventing childhood injuries is a good thing, but not always 100% effective. But in terms of prevention and treatment, caries is much simpler. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, initial changes in the enamel can be eliminated with the help of special gels and varnishes, and emerging carious cavities can be cleaned and filled without the use of a drill.
It is not recommended to leave caries unattended, as these are not just black spots on the teeth. This is primarily a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms, an infection whose toxic effect on the body can lead to serious consequences. A reliable connection between caries and pathology of the kidneys and digestive system has been established. Changing teeth cannot solve the problem of caries in a child. Milk and permanent teeth “neighbor” each other for a long time, which increases the likelihood of damage to permanent teeth by the carious process.
Physiological causes of pathology
The primary dentition is not immediately replaced by primary teeth. After a baby tooth falls out, a certain period of time must pass. Only after this does the molar appear. Subsequently, he completely takes the place of his predecessor. But some children, even 3 weeks after the loss, do not even have a hint of teething. Parents are starting to worry. However, this does not always indicate the presence of the disease. There are cases when the dental body began to erupt only after 1 or 2 months. There could be many reasons for this. In addition, there are cases that even adults retain their baby teeth. Only a specialist can determine this.
One of the reasons why a baby tooth falls out and a new one does not grow is the absence of its rudiments. Pathology can be diagnosed using an x-ray. In this case, the patient is given dental plates, and upon reaching adulthood, a new dental body is implanted. There is no other way to solve the problem.
But there are teeth, the formation of which occurs quite late. These are eights. Their rudiments are formed only in adolescence - at 13 or 14 years old.
Parents should remember that they should go to the hospital in a timely manner in all cases if any pathology is noticed in the child’s oral cavity. If more than three months have passed since the tooth loss, and there is also redness and swelling of the gums, then you cannot do without the help of a doctor. Such symptoms indicate that the dental body cannot erupt. In this case, the edge of the gums may acquire a blackish tint. In this case, the specialist must open the gum so that the new tooth can emerge.
When considering the question of why the baby fang fell out and the molar (or other teeth) does not grow, it is necessary to establish the causes of the pathology. They are as follows:
- Infections that affected the formation of dentition rudiments.
- Serious mechanical injuries.
- Incorrect dental treatment.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Unbalanced child's diet.
- The presence of caries, which slows down the development of the permanent tooth.
When there is a need to go to the clinic
Parents should know in which cases it is necessary to visit a doctor’s office in order to be able to respond in a timely manner and provide proper assistance to the child.
- If a toddler's tooth falls out and the wound is bleeding for more than 10 minutes, this is a reason to seek help from a specialist. It is possible that the baby has problems with clotting.
- If the child is already 8 years old, and he is still the happy owner of all milk teeth. It is possible that he will still have them, but consultation is necessary.
- In the case when a child’s tooth falls out early, for example due to injury, it falls unsuccessfully and the tooth falls out. The doctor can install a temporary denture so that the child’s bite does not become disturbed due to the missing tooth.
- After the timely loss of a baby tooth, the molar does not erupt for more than three months.
- The baby experiences all the symptoms of tooth eruption, but it never appears, and this whole process causes a lot of anxiety and even pain.
- Teeth begin to fall out frequently, literally one after another, and permanent teeth never appear.
- It never hurts to visit the dentist. The doctor will be able to determine whether the teeth are growing correctly, whether they are crooked, identify caries at an early stage and prescribe treatment to prevent complications, including those affecting the growth of the molar.
Which doctor should I contact?
When molars do not erupt for a long time, you can contact both a pediatrician and a dentist, whichever is more convenient and comfortable for you. If the problem turns out to be beyond the scope of a specific specialist, you will be redirected to another. So, for example, if the problem is the presence of congenital adentia or retention, the dentist will handle it himself, and if it’s a violation of metabolic processes in the body, the pediatrician will figure it out and prescribe the appropriate recommendations, and if necessary, refer you to an endocrinologist, if your clinic has such a specialist.
If your baby needs dental retainers or develops an abnormal bite, you will need to see an orthodontist.
Other causes of deviations
Worried about why a baby tooth has fallen out and a new one is not growing, many parents think about physical pathologies. They do not realize that there are some other reasons that contribute to the disruption of the development of permanent dentition. Negative factors include:
- Poor environmental conditions.
- Eating foods that are harmful to the body.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Eating cereals and purees too often.
What can be done to improve the situation
If you find that your child has lost a baby tooth and a new one is not growing, you can influence the process of tooth development. Firstly, care must be taken to ensure that an infectious disease does not develop. Secondly, it is necessary to develop the child’s diet in such a way that he has enough vitamins and calcium. If there is an injury to the oral cavity, you must contact a medical facility. It is necessary to promptly restore the functionality of the gums even before the development of molars. If we are talking about a complex case, then radical treatment methods will be required.
Only a dentist can determine at what stage of development a particular molar is. Remember that the front baby teeth of the lower row must fall out first.
If the cause of the pathology is an infectious disease, it is necessary to restore the child’s immune system. It is also advisable for the baby not to worry and avoid stress.
How to take care of your teeth?
From the period when the very first teeth appear, parents must constantly ensure that daily dental care is carried out correctly. But daily care is especially important after the first permanent teeth erupt. After all, initially the enamel of such a tooth is not sufficiently mineralized, and caries can develop with a high probability. Therefore, you should brush your teeth with a toothpaste containing fluoride. It is advisable to teach your child to rinse his mouth with clean water after every meal. This will help clean your teeth. But it should be understood that the more a child snacks on sweets and other foods harmful to teeth, the higher the risk of caries will be.
If it is difficult for a child to tolerate changing teeth due to severe itching or pain in the gums, then a consultation with a dentist is necessary. Sometimes there may also be high sensitivity of the enamel
.
By the way, during the period of teeth growth, parents should make sure that the child consumes as many foods containing calcium as possible. vitamin and mineral complexes
from time to time . But such drugs can only be taken after a doctor’s prescription.
Prosthetics
Typically, older children are referred for prosthetics. After all, doctors need to wait until the child’s jaw is formed. This will allow you to do the procedure once and not have to perform repeated manipulations. If adentia is characteristic of only one tooth, this does not mean that others will not erupt. It is important not to panic, since modern medicine can cope with the problem without consequences for health. Thanks to this, the child will be able to lead a normal life.
How to get rid of the problem
When wisdom teeth erupt, many try to solve the problem on their own - with the help of medications or traditional methods. Rinsing and pain relief on your own are acceptable measures, but only after visiting the dentist’s office and receiving medical advice.
The following options can be used:
- medications to relieve pain and inflammation;
- surgical solution;
- use of traditional medicine.
It is often most effective to use all options.
Who to turn to for help
If your child has lost a baby tooth and a new one is not growing, he may have a metabolic disorder. It is best to contact your pediatrician to prescribe the appropriate examinations and tests. Further, long-term hospital therapy will be required if we are talking about a complex case. If necessary, the doctor will write out a referral to an orthodontist. This specialist will install dental plates and also explain why the baby tooth has fallen out and the permanent tooth has not grown in for a certain time.
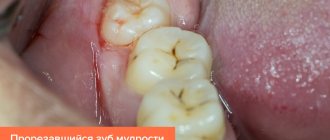
Negative consequences of late eruption of “eights”
The inconvenient location of these teeth for cleaning leads to the accumulation of bacteria and the development of caries, which spreads to neighboring teeth.
Late growth promotes the formation of tumors and cysts.
Maybe:
- Excessive tissue growth that will have to be removed surgically;
- Mechanical displacement of adjacent teeth in the process of freeing up space;
- Violation of the position of the jaws;
- Headache;
- Uneven distribution of load when chewing;
- Formation of traumatic nodes and gingival hood;
- Overhang of the mucous membrane, under which bacteria accumulate.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the pathological process will spread, affecting adjacent teeth, cheeks, tongue, chewing muscles, jaw bone and periodontium.