OPTG or orthopantomogram is a panoramic x-ray of the entire dentofacial apparatus, including the sinuses and soft tissues. Without this research it is impossible to imagine modern dental treatment.
Unlike targeted radiography of an individual tooth, OPTG gives the specialist a complete picture of the condition of both jaws of the patient. Based on this knowledge, further treatment tactics are selected.
The whole procedure takes 10-15 seconds, after which the image is obtained on digital or analogue media. The image quality is high, with good resolution, the doctor can examine the details and notice the smallest changes.
Orthopantomogram - when you need a panoramic image of the jaws and what it gives
A panoramic photograph of teeth or orthopantomogram (OPTG) is a radiographic examination technique that makes it possible to study in detail the anatomical features of both jaws, the condition of soft and bone tissue, dental roots, maxillary sinuses and joints. The study is carried out using equipment with reduced radiation exposure and does not pose any threat to the health of the body. Today we’ll talk about what this is, why a panoramic shot is needed and how often it can be taken.
How often can you do it
According to sanitary standards, the total radiation exposure per person for 1 year should not exceed 1000 μSv. During orthopantomography, the patient is exposed to a dose of 20-30 μSv. Using simple calculations, we calculate that it is possible to take a photo 50 times in a year!
The answer to the question of how often an orthopantomogram can be done is as determined by the attending physician. Calculations show that radiation during OPTG is almost safe. It is allowed to be carried out during pregnancy, bypassing the 1st trimester. In terms of workload, the study is comparable to a 3-4 hour plane flight.
What is OPTG and why is it performed?
Unlike a standard targeted photograph, an orthopantomogram allows you to obtain a fairly clear and detailed image of both jaws at once with the ability to study not only the condition of the teeth and their root system, but also the jaw bones, paranasal sinuses and other important anatomical structures. To understand what this diagnostic technique is, you first need to answer the questions: what does it do and why is it carried out. So, here's what the x-ray shows:
- deviations in the formation of occlusion - defects in bite, position, shape and size of teeth,
- early stages of caries and hidden foci of infection,
- periodontal pockets,
- neoplasms: cysts, granulomas, fibromas,
- hidden inflammatory processes and the extent of their damage,
- condition of the temporomandibular joint,
- impacted teeth that have not yet erupted - including wisdom teeth,
- condition of the root canals after treatment,
- diseases of the paranasal sinuses, for example, sinusitis.
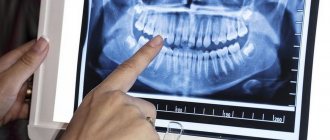
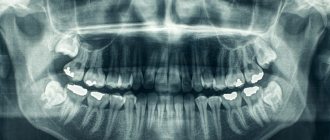
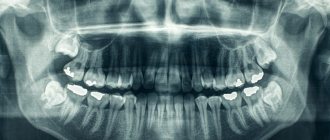
The procedure is mandatory before orthodontic treatment, prosthetics and, of course, implantation. In the latter case, the image gives the doctor the opportunity to carefully examine the condition of the jawbone, select suitable locations for implants, or prescribe a bone tissue augmentation procedure. To understand what the result of OPTG looks like, take a look at the example image below.
The photo shows a panoramic shot
Important! It should be noted that today, within the framework of one-stage implantation techniques, the preparatory stage involves undergoing a computed tomography scan. This is a more modern X-ray method that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the patient’s jaws with the possibility of layer-by-layer study of tissues, without distorting the actual sizes and shapes of the teeth.
OPTG is also performed before treatment or removal of wisdom teeth or “eights”. The image will allow you to identify the exact location and position of the elements, detect hidden carious lesions and make a decision on the need for removal. In general, an orthopantomogram helps to carefully examine the clinical picture, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Description / what dental x-rays show
When performing a pantomogram, the recording program includes not only both dentitions, but also the bones of the nose, lower jaw, both mandibular joints and adjacent soft tissues.
Dental X-ray determines:
- Position of tooth roots.
- Defects in the contact surfaces of crowns.
- Hidden carious spots and cavities.
- Cystic and other neoplasms.
- The course of teeth eruption and growth in childhood.
- Presence of undetected teeth.
- Condition of surrounding tissues (periodontal).
- Defects in jaw closure.
- Bone destruction, arthrosis of the jaw joints.
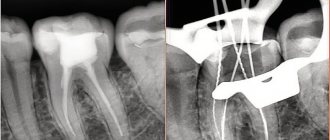
- Quality of fillings, sealed canals.
- Inflammation of the facial nerves, nasal sinuses.
The image is prescribed for prosthetics, orthodontics, complex cases of surgical treatment, for maxillofacial injuries, and ENT diseases.
What equipment is used as part of the study?
This is not a new method - by now, OPTG has been actively used in dentistry for decades. And if earlier film cameras were used to obtain a panoramic image, today they have been replaced by more modern digital devices - orthopantomographs. The image is generated in a special computer program and, if necessary, can be printed on film.
Images taken using digital equipment are more accurate and detailed, which virtually eliminates the risk of making an incorrect diagnosis. Answering the question about how long a panoramic photograph of teeth is valid, it must be said that the information received will remain relevant for several months - a maximum of six months. If more time has passed since the examination, the procedure must be repeated.
This is what an orthopantomograph looks like
Indications and restrictions
The procedure is completely painless, carried out as quickly as possible and without any discomfort for the patient. OPTG is prescribed in the following cases:
- as part of implantation – carried out to study bone tissue, select implant models and places for their implantation. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions about the advisability of building up the jawbone,
- to assess the quality of dental canal treatment, the condition of the roots - before prosthetics,
- before starting orthodontic treatment - before installing braces and other corrective structures,
- before an upcoming operation, complex removal, including wisdom teeth,
- to examine the dental system in children, assess the correctness of its formation and identify possible deviations,
- in order to determine the extent of damage to periodontitis and periodontal disease,
- to identify neoplasms in hard and soft tissues.
This procedure may be required in various clinical cases.
X-ray diagnosis is undesirable in the first and last trimester of pregnancy - it is carried out only in the presence of emergency indications and with the permission of a gynecologist.
Benefits of orthopantomography
- During the study, the patient receives a minimal dose of radiation - the same as he could receive in 30 minutes of travel along one of the trolleybus routes in Moscow.
- A quick and absolutely painless diagnosis has no contraindications.
- After a short period of time required to type the text of the report and print it out, the result is given to the patient.
- If necessary, you can get prompt advice from a specialist on site.
Detailed visualization of bone tissue and teeth makes it easy to diagnose existing pathologies and prescribe adequate treatment for teeth and gums. What information is revealed in the image to a specialist?
Features of conducting OPTG for children
We figured out what is visible in panoramic photographs and why they are taken, and found out that this is a completely safe diagnostic method. Now it should be noted that an orthopantomogram for children is carried out taking into account some nuances. A radiation exposure of 55 μSv (1 shot) is completely safe for a child, so such a procedure is allowed from 5-6 years of age.
The examination requires the patient to stand still for some time, but for young children this task can be quite difficult. When it comes to small patients, the procedure is carried out in exposure mode - the area of exposure is reduced, and the sensor is adjusted to a trajectory of movement corresponding to the small size of the jaws.
“My son also recently had a panoramic photo taken. He's 10, everything went great. Now there are new technologies everywhere, everything is safe. The procedure took less than a minute, and the doctors assured me that there was nothing wrong with it. How else can you start correcting your bite? The orthodontist prescribed OPTG for us. So far I’ve made the plate, but in a couple of years we’ll get braces. There’s no place here without pictures!”
Lyudmila V., Chelyabinsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
In pediatric dentistry, OPTG is used to detect the rudiments of permanent teeth, assess the correctness of their formation, to diagnose adentia and identify malocclusions. Most often, this procedure is prescribed by an orthodontist before starting to correct defects in bite and teeth position.
The procedure is completely safe for the child
Harm and degree of radiation exposure
Let's start with the fact that radiation exposure is measured in micro- or millisieverts - μSv or mSv, respectively. According to the resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the permissible radiation dose within the framework of OPTG for an adult patient should not exceed 55 μSv, and for children under 15 years of age - 24 μSv1. It should be noted right away that only digital X-ray equipment meets these requirements, while film devices provide a slightly higher load. To determine how many times you can take a panoramic photo, you need to take into account that the maximum permissible radiation dose for an adult patient per year corresponds to 1000 μSv.
However, it is still not worthwhile to use such procedures frequently, even despite their obvious safety and harmlessness. X-ray irradiation has a negative effect on a weakened body, especially with repeated examinations. The children's body is more susceptible to this kind of influence, therefore it is strictly forbidden to exceed the permissible dosages when examining small patients.
When contacting the clinic for OPTG, be sure to clarify what type of equipment is used and what the degree of radiation exposure from one image will be. Some private dentistry purchases cheap, outdated equipment, which can produce 2-3 times the recommended dose. The best option where you can take a panoramic photograph of your teeth is a specialized diagnostic center equipped with modern high-precision equipment.
Digital OPTG - description of the process
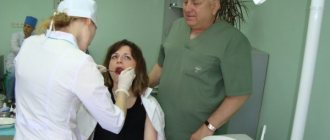
Now let's move on to consider the question of how a panoramic photograph of teeth is taken. To begin with, the patient is asked to remove all metal products from himself so that they do not affect the operation of the equipment and the final result. Next, the patient stands in the place indicated by the specialist, bites down on a special plate that ensures the immobility of the jaws, and after turning on the orthopantomograph, its moving part begins to rotate around the head.
The photo shows the process of performing an orthopantomogram
The procedure takes literally half a minute - the exact duration will depend on the type and newness of the equipment. Next, the resulting image is formed in digital form, that is, in a special computer program, or on film media (outdated version). A digital photograph can also be printed onto film if necessary.
How is it carried out?
Before the examination begins, the person removes all metal objects: jewelry, removable dentures, hearing aids. He puts on a protective apron and stands or sits inside the frame of the device. The chin is placed on a special holder, the plastic mouthpiece is clamped with the teeth, and the hands hold the handles of the device. This is done to maximize stabilization of the head during the procedure.
The emitter with the cassette rotates around the person for 10-30 seconds. The result will be recorded on disk, film or paper. The examination is painless and takes 10-15 minutes.
Sign up for the study
Information content of the image and reading (deciphering) technique
If you undergo an examination at a specialized diagnostic institution, the finished image is usually accompanied by an explanation from a specialist with a list of detected problems. Many people are interested in how to decipher an image on their own, how to read it correctly, and whether it can be understood at all. It should be noted here that in order to correctly explain the results of OPTG, you need to have a good understanding of the anatomy of the maxillofacial apparatus, and without the appropriate education, little can be understood. It is better to entrust this task to an experienced, qualified doctor.
Are dental x-rays harmful?
X-ray radiation is potentially dangerous to the human body. But this danger should not be exaggerated; if certain protective measures are observed, this is a completely safe type of research. X-rays in dentistry use a narrow beam and short radiation exposure time. A clinic that conducts dental x-rays and has a separate x-ray room is required to equip everything in accordance with SNiP and train specialists in all necessary safety measures in order to obtain a license to conduct dental x-rays.
If you still doubt whether dental x-rays are harmful, here are some figures: the radiation dose for a panoramic dental x-ray is 0.02 msv, and a person receives about 3.0 msv from the external environment per year (natural background). There are standards for radiation exposure for preventive purposes - the annual radiation dose should not exceed 1.0 MSV. All X-ray examinations performed are entered into the patient’s chart. Thus, if you undergo examinations and treatment in the same clinic, the doctor always knows exactly the total radiation dose you received during diagnosis.
Within reasonable limits, the use of X-ray diagnostics is not only justified, but also necessary, while the use of modern digital technology makes the degree of possible harm extremely insignificant.
Orthopantomogram during implantation
As part of implant treatment, a panoramic image is taken more than once. First, an X-ray examination is carried out at the preparatory stage - the doctor carefully examines the resulting image, assesses the condition of the bone tissue, selects places for implants, and makes a verdict on the need for bone grafting. If we are talking about one-stage immediate loading protocols, then patients are usually sent for a computed tomography scan of the jaw - a 3D image provides more detailed information about the clinical picture.
3D diagnostics makes it possible to study a more detailed three-dimensional image
You will have to undergo a repeat examination after implantation. In this case, OPTG will give the doctor the opportunity to assess the quality of the operation performed, monitor the process of engraftment of artificial roots, and recognize possible complications in the later stages of their development. Several photographs may be required during the osseointegration period of the implants.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of OPTG
An orthopantogram can significantly improve the quality of diagnosis, and today dental treatment is practically not carried out without radiography, except for minor problems. Among the undeniable advantages of the technique, experts highlight the following points:
- speed of the procedure - literally in a couple of minutes the image is ready for study,
- modern equipment makes it possible to adjust the height and trajectory of the emitter, which made it possible to undergo diagnostics for children and wheelchair users,
- minimal radiation exposure and absolute safety for the body,
- high quality and accuracy of the obtained images,
- the ability to zoom in on the area under study and study it in detail on a computer monitor.
An orthopantomogram uses minimal radiation exposure.
If we talk about the disadvantages, the main disadvantage of OPTG is obtaining a flat two-dimensional image. As a result, the image may slightly distort the dimensions of teeth, root canals and bone tissue. Such deviations can vary from 15 to 30%. To obtain a more accurate image, it is better to resort to computed tomography.
OPTG or CT: which is better / what is the difference?
Computed tomography differs from an orthopantomogram in that the output is a three-dimensional image. It can be rotated and laid out into layers, obtaining the most detailed information about the state of the structure of the area under study.
The radiation dose for both types does not exceed SanPiN norms, but there are differences. With a pantomographic examination, the patient receives 20-30 microsieverts, and with a CT scan - 60-70.
A computer image is considered more informative due to the absence of distortions inherent in a two-dimensional image. But it is prohibited to do it during pregnancy. Women who are expecting a child will be offered a pantomogram in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters.
It is up to the dentist to decide whether an orthopantomogram or a CT scan is better in a particular case based on the goals of treatment and the characteristics of the patient.
Approximate prices
How much a panoramic dental photograph will cost directly depends on whether the study will be carried out using film or digital equipment - in the latter case, the cost will be an order of magnitude higher. Approximate prices are given below:
- a photograph on a film camera – about 700 rubles,
- digital photo - from 1000 rubles and 150-200 rubles for printing on film.
We have already mentioned above that today, for a more detailed layer-by-layer study of the tissues of the jaw apparatus, computed tomography (CT) is performed. Essentially, this is the same panoramic photo, but much more detailed and in 3D format. An important advantage of this technique is the accurate transmission of the sizes and shapes of all elements of the dental system.
- Vorobyov Yu.I. New possibilities of X-ray diagnostics in dentistry, 2002.