Glossalgia is a secondary manifestation of a number of diseases and manifests itself in the form of painful sensations in the tongue area. The patient may experience burning, pinching, tingling and other unpleasant symptoms. Symptoms are not related to external stimuli or food intake. Upon examination, the mucous membrane of the tongue is not changed, has a physiological color, and is free of damage. The pain can be quite intense and usually occurs for no apparent reason. Taking painkillers provides only a short-term effect. To radically solve the problem, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the main cause causing these clinical manifestations.
According to ICD-10, glossalgia is one of the manifestations of glossodynia, which is a pathology of a neurological nature.
Reasons for appearance
This disease belongs to the genus of polyetiological ones. This means that a variety of reasons can lead to its appearance:
- injuries to the oral mucosa;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamus;
- nervous system disorders;
- side effects from taking medications.
Mouth injuries
Injured mucous membranes of the oral cavity are called the main cause of glossalgia. Microtraumas caused by foreign objects and sharp edges of teeth lead to impaired blood circulation in the capillaries, which results in stagnation of blood in the mucous membrane.
Endocrinology
Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and their chronic diseases are the second common cause of unhealthy sensations in the tongue. Most often, people with reduced gastric secretion, chronic colitis, cholecystitis, and hepatitis suffer from this.
Hypothalamus
Pathologies of the hypothalamus lead to disruption of all basic functions of the body, including such important ones as: the cardiovascular system and the digestive system. These deviations are also reflected in the state of the tongue.
Nervous system
Nervous disorders, depression, constant stress, overwork, or psychological trauma are another reason.
Side effects
A famous expression says: “everything is medicine and poison.” Some medications, when used in incorrect proportions or when the body is sensitive to taking them, give side effects, expressed in glossalgia.
Other reasons
Other causes include: stomatitis, infectious inflammation of the tongue, salts of heavy metals and other chemical poisoning.
Causes of the disease
There are many types of pain in the tongue area. Most of them are inflammatory or traumatic in nature. Glossalgia is a functional disorder. This means that there is no damage of any kind in this case, and the painful sensations are reflexive in nature.
Glossalgia often manifests itself in combination with other disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Without proper treatment, the pain becomes chronic.
Many diseases can serve as a trigger for the development of glossalgia:
- endocrine disorders;
- mental disorders;
- CNS pathology;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- damage to peripheral nerves;
- encephalitis;
- stroke;
- neurosyphilis.
Symptoms usually appear in the presence of triggers, such as stress.
The tongue has pain receptors. When various injuries occur, they are irritated, an electrical impulse is formed, which is transmitted along nerve fibers to the corresponding parts of the brain. This process creates pain. In the case of glossalgia, there is no effect on pain receptors. False sensations arise due to incorrect perception of signals by the nervous system. Pain is usually a warning signal about problems in a particular organ, but in this situation the brain receives a false signal.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Diagnosis of glossalgia
During the diagnostic process, glossalgia is differentiated from the following pathologies:
- neuritis;
- neuralgia;
- pathological bite syndrome;
- spinal osteochondrosis;
- injuries
The key difference between glossalgia and other pathologies is the absence of deformations of the tissues of the tongue and damage to its epithelium.
Correct diagnosis allows not only to select the most effective treatment program, but also to avoid serious complications of the disease.
Glossalgia of the tongue: symptoms, diagnosis and photos of manifestations
This disease may have the following symptoms:
- burning or painful tingling sensations;
- feeling of discomfort while eating or talking;
- pain of various types;
- numbness of the tip or entire tongue;
- decreased salivation.
The last symptom is observed in more than 30% of patients.
Unpleasant sensations are usually localized on the sides, at the tip, or at the root of the tongue. They manifest themselves especially strongly in the evening after a busy day at work or under severe stress. When eating occurs, symptoms may either intensify or not manifest themselves at all.
Symptoms of glossalgia
The main symptoms of glossalgia are:
- Burning of the mucous membrane, not associated with food intake.
- Impaired taste, metallic taste or bitterness in the mouth.
- Numbness (paresthesia) on the tip and sides of the tongue. In rare cases, numbness can spread to the root of the tongue, lips, palate, pharynx, and esophagus.
- Disappearance of discomfort during eating and intensification during nervous excitement or prolonged conversation.
Most often, symptoms of glossalgia are observed in elderly women and people with weakened immune systems. The problem can be aggravated by the fact that, trying to independently understand the causes of burning tongue, the patient constantly examines the mucous membrane, sometimes mistaking the papillae for neoplasms. This causes even more stress and, as a result, worsening of the condition.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Glossalgia: treatment
If you do not treat it in a timely manner, this disease will never be cured (such cases are rare). It will manifest itself throughout life, either subsiding during positive changes in the body, or intensifying as the diseases that led to glossalgia develop.
First of all, it is important to correctly classify this disease and not confuse it with other ailments of the oral cavity or neuralgia. And not every doctor is capable of this, only a well-trained and experienced dentist or neurologist. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the fact that it rarely manifests itself externally, which is why the experience and professional instinct of a specialist are so important when diagnosing.
After detecting glossalgia, the first step is to carry out preventive work in the oral cavity. Quite often, to eliminate it, it is enough to correct the bite, grind the sharp edges of the teeth, correct or replace implants. In general, work to eliminate objects that cause cuts and microtrauma to the mucous membrane.
To prevent the patient from experiencing pain while the dentist is working, he is injected with painkillers, or a course of rinsing with various tinctures is prescribed.
If work in the oral cavity has given only partial results, the dentist may recommend contacting the following specialists:
- general practitioner;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist;
- psychiatrist.
These specialists will be able to determine the root cause of the disease and begin to eliminate it.
As mentioned above, most often glossalgia is a symptom of endocrinological disorders or problems with the nervous system. The patient should not be surprised if the therapist, after examining the tongue, refers the patient to a psychologist, who, in turn, will prescribe a course of psychotherapy or hypnosis.
It also happens that a comprehensive analysis of the body helps to eliminate the cause of the disease, which shows that the maximum permissible concentration of certain medications is exceeded.
No matter which doctor the patient consults, the course of treatment will not last more than two months.
Author:
Diagnostics
The disease must be differentiated from traumatic and inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane, neuralgia, and clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis.
Glossalgia is supported by the absence of changes in the language, the diffuseness of the pain syndrome, as well as a reaction that does not correspond to the intensity of the stimulus. It should be noted that neuralgia has a specific localization, corresponding to the area of innervation of a particular nerve. With glossalgia, sensations can be diffuse or migrate.
In case of injury, the pain is constant and localized. The consequences of damage are visible on the mucous membrane; the patient’s sensations and the picture visible upon examination coincide. With glossalgia there is no such pattern. Damages in this pathology are present, but they are secondary in nature and do not correspond to the localization of pain.
How to cure glossalgia
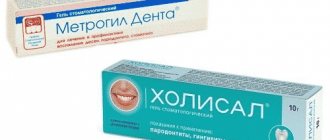
Treatment for glossalgia depends on the cause of the disease. It may consist of:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- replacement of poorly installed dentures, allowing the formation of a correct bite.
The patient is also recommended to consult with a gastroenterologist, neurologist and endocrinologist, and talk with a psychologist.
Pathogenetic therapeutic measures for glossalgia consist of influencing the central and peripheral parts of the pain symptom and normalizing homeostasis. For this, the patient is prescribed:
- valerian;
- bromine preparations;
- mild tranquilizers (“Phenazepam”);
- B vitamins;
- trimecaine blockade of the lingual nerve (allows you to completely restore the functions of the affected nerve);
- iron preparations (“Gemostimulin”, “Ferroplex”, “Ferrocal”);
- local anesthetics;
- mouth baths;
- treatment of painful areas with vitamin A and rosehip oil.
Also, for a speedy recovery from glossalgia, the following can be used:
- hypnosis (hypnotic sleep);
- reflexology;
- physiotherapy.
Surgeries are not performed for glossalgia. Usually, patients manage to get rid of an unpleasant illness with the help of medications, folk recipes and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Glossalgia of the tongue: causes and treatment
Content:
Types of glossalgia
Causes of the disease
Clinical manifestations of glossalgia
Diagnosis and treatment of glossalgia
Prevention of tongue diseases
Doctor's advice
Answers on questions
Treatment of glossalgia of the tongue includes an integrated approach. The following may be involved in therapy: dentist, neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
Glossalgia – what is it? A dental disease, the symptoms of which are discomfort and a burning sensation in the tongue.
Diagnostic measures
It is important to correctly diagnose in order to distinguish between glossalgia and other language pathologies that develop due to trauma, increased pain and sensitivity of the nerves. The specialist will perform a visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity to assess the bite relationship. The main thing is to determine the difference in sensitivity and strength of impact.
In case of trauma, pain sensations are clearly located. With nerve pain, the pain quickly disappears at the point where the nerve passes. In inflammatory processes - on the one hand, and with a change in reactivity.
Treatment methods
Therapeutic measures begin with complete sanitation of the oral cavity:
- filling carious lesions;
- replacement of incorrect prosthetic structures;
- replacement of defective and outdated fillings.
New dentures will help shape the jaw relationship, and visiting highly specialized doctors - a neurologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, etc. will help adjust treatment tactics and achieve better results.
The main therapeutic method is the elimination of pain. So, the doctor can prescribe medications with vitamin B, bromine and iron, tranquilizers and sedatives, and nerve blockade.
For dry mucous membranes and a small amount of saliva - Vit A solution (to moisturize and increase salivation). It is possible to use reflexology and physiotherapy.
It is important to be attentive to your mental and emotional state - relaxation and breathing exercises.
Symptoms
Temporarily or permanently marked in the language:
- burning;
- tingling;
- itching
Are common:
- dry mucous membranes;
- fatigue when speaking;
- nervousness.
When eating food, symptoms may decrease or disappear completely. Burning and tingling sensations are felt on the sides or tip of the tongue; the back and root of the organ are less susceptible to them. The pain is widespread over the entire area without clear localization.
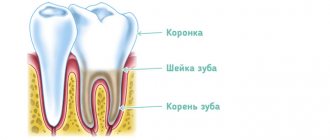
There are no visually detectable changes in the oral mucosa. Some patients may experience swelling or coating on the tongue, or enlarged papillae. Varicose veins occur in older patients.
Many patients are depressed. Excitability and anxiety are sometimes expressed.
Prevention of glossalgia
Prevention of glossalgia involves regular examination of the oral cavity and an annual visit to the dentist. Important:
- timely restoration of damaged teeth and treatment of caries;
- install only high-quality prostheses;
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- Periodically rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions and special antiseptic solutions.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Prevention of tongue diseases
To prevent the development of tongue pathologies, it is important to promptly engage in the prevention of oral diseases. It consists of:
- professional hygiene: removal of dental plaque;
- selection of household hygiene products (brushes, pastes, floss, tongue scrapers, rinses);
- elimination of sharp edges of fillings and failed prostheses.
Regular professional and home hygiene will help maintain the health of your teeth and entire oral cavity.
Clear signs of glossalgia
The symptoms and general nature of a disease such as glossalgia occur in different ways. Some symptoms extend over long years or months. Therefore, in this case, experts diagnose the disease as periodic or general glossalgia. Although the signs of the initial stage of the disease are not very pronounced, they still intensify over time. Due to this, experts identify a systematic series of symptoms of glossalgia, which include:
- tingling, rawness, burning sensation in the tongue area. These unpleasant sensations are both periodic and permanent. The intensity of pain increases when eating spicy food and under the influence of some other external irritants;
- constant dry mouth;
- bulimia, which can progress if treatment for glossalgia is delayed for any reason;
- nutritional increase in body weight, due to the fact that glossalgia disappears for a short time after eating, so patients resort to eating immediately after the pain disappears;
- fatigue during a conversation.
- burning and discomfort on the lateral areas of the tongue or on the root and back of the organ;
- slight swelling;
- plaque on the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- phlebeurysm.
As noted earlier, glossalgia does not have a clearly defined lesion, so the location of the unpleasant sensations may vary. Sometimes glossalgia goes away on its own, but more often patients still require medical attention. After all, as such, changes in the oral cavity and mucous membrane of the tongue are completely absent. However, glossalgia can be diagnosed by some indirect signs. Especially when a patient with glossalgia often begins to become depressed and suffers from excessive excitability, anxiety, suspiciousness, and sometimes autism. At this moment, the patient can pay increased attention to detail, delving into the specifics of his condition. He easily loses his temper and becomes aggressive over the most insignificant reasons. In addition, a patient with glossalgia may suffer from cancerophobia or fear of other serious diseases. Also, the symptoms of glossalgia are aggravated by a neurotic state, which leads to sleep disturbances, cardialgia, and spastic colitis. At the same time, due to changes in mental state, the patient most often refuses the help of doctors or treats glossalgia with folk remedies, which often leads to serious consequences and complications.
Complications
Glossalgia does not pose a major threat to health, but its symptoms greatly reduce the quality of life. If unpleasant symptoms are not treated and ignored, the process may become chronic. Over time, the psyche and emotional expression will be disturbed, with the background development of anxiety, eating and sleeping disorders. If glossalgia and the condition of the body are aggravated, treatment should be performed not only by dentistry, but also by doctors - a neurologist, psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
Possible complications include:
- aphthous stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- gingivitis.
Answers on questions
Is it possible to cure this disease at home?
It is impossible to cure this pathology with any home remedies. The use of pharmaceutical products without a doctor's prescription leads to complications. It is recommended to contact a dental clinic at the first symptoms.
What are the complications of glossalgia ?
The disease does not have serious complications, but significantly disrupts the patient’s daily life. In some cases, eating becomes difficult, and long conversations tire the patient. Headache and sleep disturbance are also observed. In addition, the disease can become chronic: periodically the discomfort goes away, then returns again. Therefore, treatment should not be delayed.