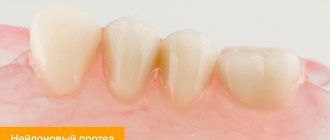
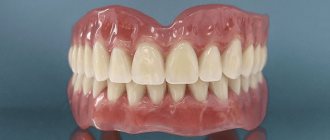
Removable acrylic dentures are a base made of acrylic plastic that imitates gum tissue and artificial teeth inserted into it. The prosthesis of the lower jaw is attached to the gums, and if it is the upper jaw, then it rests on the roof of the mouth. There are 3 types of acrylic dentures:
- Complete denture;
- Partial denture;
- "Butterfly prostheses."
Complete design
, used when there are no teeth in the jaw. Consequently, the prosthesis is attached to the gum.
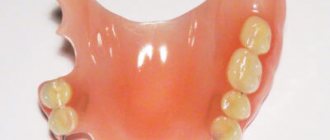
Partial construction
. It is installed when not all teeth in a row are lost. Such dentures rest on the gums and are secured in the mouth with special arms.
"Butterfly Prosthetics"
. This is a prosthesis for one or two missing teeth; it clings to adjacent teeth. It is not necessary to take it off at night.
What is the secret of the popularity of acrylic plastics
Today, plastics are no longer used for veneering crowns and bridges as widely as before. Porcelain and modern composite materials will gradually replace cheap plastic, but will not completely replace it due to economic benefits. The properties of acrylic plastics were overestimated immediately after the material appeared on the market. Over time, a harmful effect on the mucous membrane and low strength of acrylic were discovered.
Despite the development of polymer technology, over the past few decades, materials based on derivatives of methacrylic and acrylic acid have held the lead in orthopedic dentistry. Acrylic polymers are attractive due to their low toxicity and ease of processing - at low pressure and relatively low temperature. These properties bring them to a high competitive level.
Basic rules for caring for acrylic dentures
Most people today know very well how to properly care for their teeth: rinse every time after eating and brush in the morning and before bed with a brush and toothpaste. Despite the fact that acrylic plastic is an artificial material and, it would seem, bacteria are too tough, in reality, you need to care for an acrylic prosthesis no less carefully than for your natural teeth. All principles of care remain unchanged: rinse your mouth after eating and clean your denture with a toothbrush and paste.
On a note
Just don’t use whitening toothpaste - such toothpastes are characterized by increased abrasiveness, and you don’t want to wear off the plastic quickly, do you?
If it is impossible to clean the denture by rinsing the mouth, you can rinse the structure under running water after eating. In addition, there are special solutions for additional hygiene of the prosthesis and maintaining it in good condition.
Do not forget that any problems associated with discomfort after receiving a prosthesis require monitoring by a doctor. It doesn’t matter when they appeared: the next day or a few months later. A mandatory recommendation is to visit an orthopedist once every 6 months for monitoring and possible “correction” of the base or retaining elements of the prosthesis.
Review
“I have been wearing an acrylic prosthesis for 3 years now and I can say that it is both comfortable and affordable. And if I were to get implants, as the doctor calculated for me, then I would have to sell my car, or at least a kidney. Easy to remove and easy to clean. I clean it with a regular toothbrush. The prosthesis does not rub the gums and fits in the mouth like a glove. In short, I have no complaints so far. Let’s hope the prosthesis will last a long time.”
Ivan, Ekaterinburg
Classification of polymers
Polymers used in prosthetic dentistry belong to one of three groups. Each of them is subject to different hygienic, toxicological, aesthetic, and technological requirements.
- Basic, or basic polymers in dentistry are used for the manufacture of artificial teeth and bases for removable dentures.
- Auxiliary - needed for impressions, molding and modeling.
- Clinical polymers include sealants, restoratives, and adhesives.
Can you be allergic to acrylic material?
If, while wearing an acrylic structure, you notice:
- burning in the mouth;
- That your sense of taste has changed;
- Dry mouth;
- Heavy salivation;
- That the tongue, gums and mucous membranes are inflamed.
In this case, you should consult a doctor, as acrylic can cause such a reaction. An alternative to acrylic will be dentures made of nylon or silicone. Acrylic structures are the most affordable and budget type of prosthetics. This type of prosthesis is often used to correct dental defects, mainly in older people. An acrylic prosthesis can be worn either temporarily or permanently, after consulting with your doctor.
Water resistance and water absorption of polymers
Water resistance is the ability of polymers to retain their properties under prolonged exposure to water. If water gets inside the polymer, it swells, its shape is distorted, and its strength indicators suffer. Moisture resistance is resistance to humid air. Due to absorption, water vapor also causes swelling of hydrophilic materials. However, more often moisture accumulates in the surface layer due to adsorption, penetrating into microcracks.
The water resistance of the polymer is characterized by water absorption. This parameter indicates the amount of water that the material is able to absorb when kept at a temperature of 18-22 ° C for 23 hours. Due to water absorption, the geometric shape of the prosthesis base changes, and the mechanical properties deteriorate. The higher the water absorption, the more susceptible the polymer is to the penetration of microorganisms.
The presence of sorption water in the polymer sharply reduces its strength, hardness, rigidity, and indentation resistance. The polymer loses soluble substances, so its properties change.
A few words about the cost of acrylic dentures
The cost of an acrylic denture largely depends on the materials used for its manufacture, as well as on the extent of the dentition defect.
For example, at the request of the client, acrylic plastics from Russian, Czech and even Japanese manufacturers can be used to make the base. Accordingly, the price of the finished product can vary within significant limits, sometimes differing significantly.
The price of an acrylic prosthesis is also determined according to the method of fixing it to the supporting teeth. Acrylic dentures with a small number of artificial teeth can be relatively inexpensive, but it is important to remember that in addition to removable structures, crowns can also be made for abutment teeth, which are charged separately for each crown unit.
In general, the cost of removable acrylic dentures for the entire jaw (upper or lower) usually ranges from 5 thousand rubles to 15-20 thousand, depending on the level of the clinic, the quality of the plastic for the bases, the purchase price of dental sets and some other factors.
Useful video about calluses in the oral cavity caused by acrylic dentures
What is residual monomer
One of the disadvantages of acrylic base polymers is residual monomer. We are talking about the part of the monomer that did not enter into the polymerization reaction. The amount of residual monomer in the polymer depends on the nature of the initiator, the time and temperature of polymerization. Monomers can have a harmful effect on the body, cause inflammation of the prosthetic bed and various allergic reactions, so it is necessary to achieve a minimum content of it in the denture.
In hot-curing plastics there is 0.5% residual monomer, in self-hardening ones its amount can reach 3-5%. The substance has a negative effect on the strength of the material. When this value exceeds 3%, a sharp decrease in strength is observed, water-oil-alcohol absorption increases, and aging accelerates.
Cold curing plastics
Self-curing acrylic plastics are compounds that cure spontaneously at room temperature. The polymerizate, depending on the composition of the compound, can be hard or elastic. Self-hardening plastics are widely used in dentistry for correcting (relining) dentures, repairing dentures, making temporary dentures, splints for periodontal disease2, models, and individual impression trays. Self-hardening plastics have gained a strong place as filling materials. Cold-curing plastics have a number of advantages over hot-curing plastics, but are inferior to them in some respects. The technology for processing self-hardening plastics is simpler, no heating equipment is required, there is less change in product dimensions, less residual stress in products, and repair of the prosthesis can be done quickly in the presence of the patient. In some cases, self-curing materials cannot be replaced by hot-curing plastics. At the same time, self-hardening plastics are inferior in strength and contain a larger amount of residual monomer. Thus, hot- and cold-curing plastics do not exclude one another, but complement each other. The technology for the production of cold-curing plastics differs from the production of hot-curing plastics in that during the synthesis an initiator is introduced into the polymer powder in an amount of 1.5%, and an activator is added to the liquid.
Compound . Powder is a suspension homo- or copolymer, colored and turbid and containing a component of the redox system - usually an initiator.
Liquids of self-hardening plastics have the following composition:
- 1) linear polymers (monomer or mixture of monomers, OBC activator, inhibitor);
- 2) polymers of three-dimensional structure (monomer or mixture of monomers, OBC activator, cross-linking agent, inhibitor).
The production of dental structures from polymer-monomer self-hardening materials proceeds according to the following scheme:
Properties . Self-curing of acrylic compounds used in dentistry is due to the initiating action of the redox system (ORS). The main components of OBC are the initiator and activator. Organic peroxide can be used as an initiator. Benzoyl peroxide is usually used. Various compounds are used as activators: tertiary amines (primary and secondary ones inhibit the polymerization process), mercaptans, sulfinic acid derivatives, ascorbic acid, etc. In addition to the initiator and activator, some OBCs also contain promoters.
Let us consider the mechanism of action of cold-curing OBC. The radicals that initiate the polymerization process are formed during the decomposition of benzoyl peroxide. As can be seen from the kinetic curves of the decomposition of benzoyl peroxide obtained at different temperatures, the rate of decomposition depends on temperature and begins to decrease noticeably from the moment 65-75% conversion is reached (Fig. 19). For the effective initiating action of benzoyl peroxide, heating to a temperature above 65 ° C is required, at which vigorous decomposition of the peroxide begins. The activator reduces the activation energy for the decomposition of benzoyl peroxide, which is equal to 126 kJ/mol, and the decomposition of the peroxide begins at room temperature. OBC is the most important criterion for the quality of self-hardening plastics. This system should:
- 1) ensure complete monomer conversion;
- 2) do not cause changes in the color of the polymerizate under the influence of solar radiation and endogenous processes;
- 3) not be toxic;
- 4) be stable;
- 5) initiate the polymerization process at minimal concentrations;
- 6) provide the necessary working hours.
To avoid premature polymerization, the activator is usually introduced into the liquid, and the initiator into the powder.
O B C peroxide-amine type. The great practical importance of self-hardening plastics has stimulated a wide scope of research on the creation of cold-polymerized alloys.
Powder-liquid plastics
Tertiary amines were first proposed as activators (dimethylaniline) for cold polymerization in 1943 by Schvebel and Tromdorf. Based on this activator, the first self-hardening plastics AST-1, AST-2, AST-2A and (styracryl) were produced in the USSR (1952). It soon turned out that the use of dimepilaniline and other tertiary amines leads to a change in the color of the polymer. This occurs as a result of endogenous processes , in which the amine is involved. Strubell found that the color and light fastness of the plastic depends on the nature of the tertiary amine. Table 11 shows the effect of the nature of some amines on color fastness.
In the homologous series of dimethylaniline, color fastness increases from dimethylaniline to dimethylamino-p-isopropylbenzene. The most widely used are dimethylparatoluidine CH3•C6H4•N(CH3)2 and N-bis(2-oxyethyl)paratoluidine CH3•C6H4•N(OC2H5)2, which, having a high activating efficiency, are quite suitable for the production of self-hardening plastics used for repairs prostheses, relocation, manufacturing of orthodontic appliances and other works. The color fastness of plastics depends on the purity of the activator. Even the presence of traces of undermethylated products in dimethylparatoluidine (DMPT) causes a decrease in the color fastness of the polymer.
A technology has been developed for the synthesis of DMPT, free from traces of impurities that cause coloration of the polymer product. The completeness of monomer conversion depends on the efficiency of the OBC and the temperature of the polymerizing molding mass. Rice. 20 illustrates the dependence of polymer temperature on time when using some amines. The most effective is dimethylaniline. However, in terms of its set of properties, DMPT can be considered optimal, while compounds based on dimethylaniline are used only for technical needs. In order to increase color fastness, work was carried out to stabilize color fastness. Foreign information about the stabilizing effect of carboxylic acids and their anhydrides has not been confirmed. An increase in color stability was achieved by introducing up to 1% 2-oxide-5-methylphenyl-benztriazole.
OBC based on sulfonic acid and its derivatives. Tertiary amines are very effective activators, but they still do not provide long-term color stability under light radiation conditions. In addition, it is desirable to have OBCs that make it possible to obtain a polymer product with a higher degree of conversion. The search for new activators led to the discovery of the activating effect of sulfinic acids, as reported by Hagger in 1948. Sulfinic acids make it possible to obtain color-stable polymers, but their low chemical resistance and lower activity compared to amines have limited their use. Due to its easy oxidation by air oxygen, sulfinic acid was mixed with silicone oil and stored in a tube in the form of a paste. Before preparing the molding mass, the required amount of paste was squeezed out and squeezed out with filter paper. Sulfinic acid crystals were dissolved in the monomer before mixing it with the powder. In paste form, sulfinic acid can be stored for 6 months.
M. M. Gerner, L. N. Mats proposed OBC based on stable derivatives of sulfinic acid. In addition to residual benzoyl peroxide, stable sodium sulfate is added to the powder, and a small amount of methacrylic acid is added to the monomer. Thus, in this case, the activator and peroxide are contained in the powder. When mixing the powder with the monomer, the reaction occurs: CH2=C(CH3) • COOH + C6H5SO2Na → CH2=C(CH3) • COONa + C6H5SO2H.
Active sulfinic acid C6H5-SO2H forms with benzoyl peroxide an OHS of cold polymerization, and an excess of methacrylic acid and the resulting sodium salt participate in copolymerization with the ether. The introduction of methacrylic acid increases the adhesion of the polymer due to carboxyl groups to various substrates. This OBC is used in the self-hardening plastic noracryl.
OBC based on sulfones. Research by Brederice et al. showed that α-hydroxy and α-aminosulfones can be successfully used as effective polymerization activators, which give more color-resistant polymers. Their effective use is only possible in combination with cocatalysts, monohydric alcohols, compounds of metals of variable valence (Сu2Сl2), etc. Good results can be obtained using N-ethyl-bis-(p-tolylsulfonmethyl) amine (CH3•C6H4•SO2CH2)2• N•C2H5 and N-methyl-bis-(p-tolylsulfonemethyl)amine (p—CH3C6H4SO2CH2)2•N•CH3. Sulfonamines at room temperature without cocatalysts practically do not accelerate the polymerization process. At 40°C, polymerization occurs in 22–26 minutes with a temperature peak of 82–84°C. With the introduction of only 0.01% Cu2Cl2, curing occurs in 7–11 minutes with a temperature peak of 95 °C.
Copper chloride I is introduced into the monomer, and since it is insoluble, the liquid must be shaken before mixing with the powder. When 8% methanol is introduced into the liquid, curing occurs at room temperature. Three-component OBC (1.5% benzoyl peroxide, 8% methanol and 0.01% copper I chloride) provides curing in 5-7 minutes. In Fig. Figure 20 shows curves of the temperature of the polymerizing molding mass versus time for various compositions of sulfone-based OMS. The introduction of a small amount of DMPT up to 1%, which has virtually no effect on color fastness, significantly increases the conversion of the monomer, since the temperature peak reaches 94-98 °C. Cold polymerization does not lead to complete monomer conversion. After polymerization is completed, the polymer contains 3-5% residual monomer during cold polymerization and 0.5% during hot polymerization.
OBC based on mercaptans. Peroxide-mercaptan type OBC is widely used for the vulcanization of rubbers and can be used to cure dental acrylic compounds at room temperature. Self-hardening plastic Orthofil (England) contains OBC of the peroxide-mercaptan type. In the reaction between peroxide and mercaptan, the latter plays the role of a reducing agent.
To create acrylic compounds in dentistry, lauryl mercaptan C12H25SH (synonym: dodecyl mercaptan) is used as an activator. The advantage of these OBCs is the color fastness of the polymer. The OVS currently used cannot be considered perfect. The search for new systems is carried out in two main directions - increasing color stability and increasing monomer conversion.
Preparation of molding mass . The technology for preparing the molding mass of self-hardening plastics is identical to that described. From each batch you can only manage to mold one product. During polymerization, the mass experiences slight thermal expansion, so the pressure inside the mold does not rise as sharply as during hot polymerization. At room temperature, polymerization of most materials occurs in 20-30 minutes. Acceleration of curing can be achieved by immersing the mold in water heated to 37 °C. When preparing the molding compound, it is necessary to take into account that volumetric shrinkage depends on the monomer/polymer ratio and increases with increasing this ratio.
Linear shrinkage (taking into account technological methods) of self-hardening plastics averages from 0.15 to 0.5%.
The powder/liquid ratio recommended by the manufacturer must be strictly followed.
The rate of polymerization of self-hardening plastics depends on the following factors:
- 1) initial temperature of the monomer and polymer; high temperature (above 30 °C) causes rapid polymerization; upon cooling (below 5°C), the process slows down sharply, and at negative temperatures the reaction practically stops;
- 2) the amount and nature of the activator and initiator;
- 3) the degree of dispersion of the powder and its molecular weight: the finer the powder and the lower the molecular weight, the faster the swelling and polymerization occurs;
- 4) monomer/powder ratio. Reducing the monomer/powder ratio shortens the polymerization time.
An excess of monomer slows down the process, but at the same time a higher temperature of the polymer is observed and shrinkage increases, which ends after 3 hours. The polymerization process, as already noted, is exothermic. The heat of polymerization of the MMA monomer is 78.7 kJ/mol.
When mixing powder with liquid, the resulting molding mass retains its plasticity and the temperature does not increase noticeably. The induction period at point A (Fig. 21) turns into a rapid process of development of the polymerization reaction, and the temperature quickly rises. After curing is complete, the temperature of the polymer decreases due to heat transfer to the environment. The temperature jump and the duration of the induction period, which determines the viability of the compound, depend on the mass of the polymerizing polymer-monomer mixture, the redox system and the initial temperature of the liquid and powder. With an increase in mass to 50 g, a sharp increase in the temperature jump is observed. The dependence of the thermal effect on the size of the polymerizing mass results in a higher monomer conversion in the thick parts of the product (prosthesis, etc.). This means that thin sections of the product have relatively lower mechanical strength because they contain more residual monomer. Due to the fact that the temperature during polymerization of self-hardening plastics is below 100 ° C (the boiling point of the monomer is 100.3 ° C), the polymers are distinguished by the absence of pores and cavities caused by boiling of the monomer. Depending on the type of work, the molding compound is used at various stages of swelling.
- Stage I - sand. It appears immediately after mixing the powder with the liquid and, depending on the ambient temperature, can last from 30 s to 5 minutes or more. At a temperature of 10 °C it lasts about 5 minutes, at 15-18 °C - 3 minutes, at 18-22 °C - 1-2 minutes, and at 25 °C it ends in 0.5-1 min. In the sand stage, the monomer-polymer mixture is unusable.
- Stage II - viscous, stretchy threads. The initial period of this stage is characterized by the appearance of stretchy threads, stickiness of the mass, high plasticity and fluidity. At the beginning of the second stage of swelling, the molding mass is used for work requiring adhesion. The molding compound applied to the prosthesis base forms a strong connection after curing.
- Stage III - dough-like. The molding compound in this swelling stage is characterized by loss of stickiness, good ductility and less fluidity. In this state, the molding mass can be conveniently formed on plaster models, producing protective palatal plates, replacing, shaping and obturating dentures, Porta splints, individual trays, orthodontic devices and other dental structures. The mass can be used for relining dentures in all cases, as well as when it is necessary to obtain an imprint of the relief of the prosthetic bed in conditions of functioning dentures, when significant chewing pressure can develop.
- Stage IV - rubbery. At this stage, the molding mass retains its given shape even with minor short-term mechanical impact on it. When relining, the denture is removed from the oral cavity when the molding mass is already in the rubber-like stage. In the case of relining partial dentures with the presence of converged and diverged teeth in the oral cavity or teeth with well-defined equators, the dentures are removed from the oral cavity only after reaching a rubber-like state. Removal at stage III of swelling will result in distortion due to tension. If you skip stage IV, the plastic will harden and the prosthesis cannot be removed from the mouth without sawing. When monitoring the curing of the polymerizing mass, it is necessary to pay attention to the thinner areas of the prosthesis, since they cure more slowly than the thick ones. It should be noted that the polymerization of the monomer-polymer system from the beginning of mixing to curing is a continuous process without sharp interstage transitions.
Optimal pressing mode for products made from self-hardening plastics . The main method of processing self-hardening plastics, which ensures the production of a high-quality product, is pressing. For self-hardening plastics, an important processing parameter is determining the moment of application of pressure. If pressure is applied before the required time, the product is obtained with large shrinkage and unsatisfactory surface quality. Products with the required accuracy can be obtained only with a sharp increase in specific pressure. The working time of self-hardening plastics is significantly affected by changes in ambient temperature even by 2-3°C, and this circumstance causes difficulties in determining the moment of application of pressure (see Fig. 21). The methods used for manufacturing dental structures from self-hardening compounds at room temperature without pressure are not optimal. The polymer is less dense and has lower physical and mechanical properties.
One of the possible options for optimizing the technology of pressing products from self-hardening plastics is to carry out the final stage of polymerization under compressed air pressure. In Fig. Figure 22 shows an apparatus for polymerizing products made of self-hardening plastics. It is a hermetic vessel, inside of which a pressure of 0.3-0.5 MN/m2 is created by air heated to 40-45°C. Inside the apparatus there are shelves on which products are placed for polymerization. Control and maintenance of the set temperature is carried out using a thermocouple interlocked with a temperature relay and an electric heater. The device can be made by converting the ultrathermostat UT-15.
A rack is placed in a preheated apparatus, on which plaster models with products made from self-hardening molding mass, which is in a rubber-like stage, are installed. The device is sealed and a pressure of 0.3-0.5 MN (3-5 atm) is created. The pressure is controlled using a pressure gauge. If the pressure exceeds, the safety valve is activated. After 15-20 minutes, the finished products are removed from the apparatus.
Comparative characteristics of hot and cold curing plastics . Self-hardening plastics are inferior to hot-curing plastics in a number of indicators, but this is compensated by their exceptional ease of use and better dimensional stability. Polymerization of self-hardening plastics is accompanied by lower monomer conversion, so they contain 5-10 times more residual monomer. This leads to faster aging of the polymer and a decrease in strength characteristics. As a result of leaching of the monomer from the surface of the product, the structure of the polymer is loosened, which leads to a change in a number of properties of the product. Thus, when the monomer content in the polymer decreases from 8.5 to 0.9%, the heat resistance increases from 52 to 130°C, and the Brinell hardness increases from 70 to 194 MN/m2. Self-hardening plastics (linear) exhibit higher hygroscopicity (water absorption>0.7 mg/cm2) than hot-curing plastics and contain large amounts of residual benzoyl peroxide, monomer, activator, which is a prerequisite for the deterioration of their physical and mechanical properties over time. Research has shown that the main factor distorting the size and shape of the prosthesis is not polymerization shrinkage, which is compensated by technological methods, but thermal shrinkage that occurs when the prosthesis is cooled from the polymerization temperature to room temperature. Since the polymerization of self-hardening plastics occurs at lower temperatures than hot-curing plastics, dentures and other dental products made from self-hardening plastics are more accurate and are better fixed in the oral cavity. In addition, less stress occurs in them, although they are inferior in strength to hot-curing plastics, but they are more flexible. Their modulus of elasticity is 2•20-3 MN/m2, and for hot-curing plastics it is 3.8•103 MN/m2 (Table 12). With additional heating and holding for several hours, the physical and mechanical properties of products made from self-hardening plastics can be somewhat improved by reducing the content of residual monomer. The domestic industry produces self-hardening base material protacryl-M.
Heat resistance and thermal conductivity
Heat resistance is understood as the maximum operating temperature of a polymer at which the material can withstand a certain load for a given time, maintaining its geometric shape after cooling. Operating temperatures for the use of plastics, grinding and polishing must occur within the heat resistance range, otherwise mechanical changes will occur.
Thermal conductivity, or the ability to transfer heat, depends on the polymer matrix and filler. The indicator increases with increasing molecular weight. These two thermal characteristics affect the shrinkage of the material, the occurrence of defects in the production of prostheses, and comfort during use.
Various physical and chemical processes affect the aging process of polymers. Destruction in them occurs due to exposure to biological media, mechanical stress and strong temperature changes. Destruction causes fragility of dental dentures and loss of their functionality.
Why here?
- We introduced the technology for the production of such prostheses several years ago and have already achieved all possible milestones. Now we know exactly what needs to be done for excellent quality.
- Your prosthesis will be made by specialists who have trained specifically in this technology for a long time.
- We spare no expense to purchase the best materials for the manufacture of eco-prostheses, and we do not try to reduce costs through savings. An example is plastic. We purchase the best plastic in the world: Acre F 711. It is very expensive, but the result is worth it!
- Our own dental laboratory opens up wide possibilities: speed, continuous interaction between the doctor and the dental technician, precision of execution, quick correction. Under certain conditions, we can produce such a prosthesis in one day!
- All accumulated experience is at your service. We have been doing dental prosthetics for many years; this is one of the most important and favorite areas of our work.
- You won't be abandoned if you have problems, even after the warranty period has expired. You can be sure that during the warranty period (1 year) all corrections are carried out free of charge, and during the entire period of wearing these prostheses, the correction of your prosthesis will be 50% of its normal cost.
New trends in the production of base polymers
In the last few years, there has been a tendency to introduce aesthetic fibers into the structure of hot-curing base polymers. They look more advantageous, but they are inferior to the standard ones in terms of physical and mechanical properties. “Veins” in the structure of polymers lead to the formation of microvoids and reduce the density of the material. Oxygen in microvoids increases the number of monomers. Therefore, such polymers with improved aesthetic characteristics should be used only when indicated - in rare cases.
Despite certain disadvantages, acrylic plastics remain the most common material for the production of removable denture bases. Their main advantages are low price, manufacturability and lack of need for expensive equipment.
Advantages of acrylic dentures
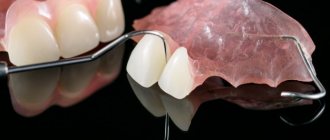
Before highlighting the positive aspects of acrylic dentures, let's first clarify some details. Today, as a rule, certain pros and cons of prostheses made of acrylic plastic are contrasted with the characteristics of nylon prostheses, which are positioned as more modern. And the key question that interests many people in this regard boils down, in general, to the following: which denture is better, acrylic or nylon?
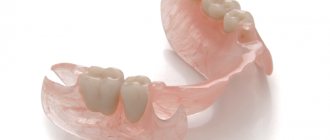
The photo below shows an example of a partial nylon denture for the upper jaw:
So, from a professional point of view and strictly speaking, the best is the one that is not only indicated in a specific clinical situation, but will also allow you to solve a maximum of problems in the future with minimal negative impact. And asking a dentist which prosthesis is better is like asking the manager of a car dealership which car is better: the one that is cheaper or the one that is more expensive. The financial component when choosing in both cases should be taken into account, if not in the first place, then not in the last place.
However, often not entirely conscientious orthopedic doctors speculate on the advantages of expensive structures, specifically highlighting the disadvantages of cheaper acrylic prostheses. More precisely, they take the negative property found in this design out of context, warning the patient about a non-existent danger for him. As a result, methods and materials that have been proven over the years begin to give way under the onslaught of products that are “pushed” to patients and that are more convenient for the doctor’s wallet.
Meanwhile, a simple truth is quite obvious: there is no universal ideal dental prosthetics. Some here may object: how can it be that they made me such and such a prosthesis, and I use it without any problems. In fact, every successful case is the result of correct diagnosis and an individually selected orthopedic treatment plan. Simply put, for one grandmother an ordinary acrylic prosthesis will be enough for a comfortable life and wallet, while for another grandfather the most advanced nylon prosthesis will not be suitable, but his neighbor in the country will be perfect.
Now let's move on to specifics.
The main advantages of acrylic dentures:
- Relatively low cost. For many people, the low price of a prosthesis may be a reason to doubt the quality of the design, but in the hands of a skilled doctor, an acrylic prosthesis can solve its problems to the fullest, both functionally and aesthetically. As a result, you can get artificial teeth for little money, and in some cases even for free (thanks to the compulsory medical insurance program, pensioners and certain social categories of people have the opportunity to receive partial or complete acrylic dentures for free on a first-come, first-served basis);
- Ease of use. A properly made acrylic denture is easy to put on and take off, and caring for it is not much more difficult than caring for your natural teeth;
- Lightness and strength of the material;
- Possibility of production in one visit;
- Acceptable or even excellent aesthetic characteristics in the case of proper selection of the color of artificial teeth;
- Possibility of repair after breakdown;
- Adequate distribution of load during chewing.
Review
“Now even young people walk with prosthetics and it’s fine. So I decided, I will put a denture on the lower jaw. What will happen will happen, I have already prepared the mouth, there will be crowns in front, and an acrylic prosthesis in the back. My friend has had this denture for 2 years now, she likes it all, she says it’s like her own teeth, she doesn’t even notice it and doesn’t even take it off at night. But I have no other options, so I can only hope that everything will be fine...”
Galina, Moscow
Pros and cons of designs
There are no universal dental structures; each of them has its pros and cons. The advantages of acrylic dentures are as follows:
- Convenience. If acrylic dentures are made correctly, they are very easy to remove and put back on.
- The material is durable yet lightweight.
- Speed of production.
- Good aesthetic characteristics if the color of the crowns is chosen correctly.
- Even distribution of the load when chewing.
- Low cost.
However, acrylic products have many disadvantages. Among them the most mentioned:
- Risk of allergic reactions. They can be caused by both the acrylic itself and the additives included in the base - dyes and others. Allergies can be prevented by modern surface treatment of the product - for example, glass transition.
- Plastic is a porous material, and therefore dangerous from the point of view of bacterial growth. Acrylic absorbs organic substances from food, as a result of which it becomes covered with bacterial plaque. To minimize the risk of its occurrence, careful care is necessary.
- Increased fragility: the structure may break when chewing hard food or falling.
- If clasp fixation is used, the hooks that wrap around the teeth do not always look aesthetically pleasing.
Important! In their reviews, patients often complain that wearing a prosthesis is uncomfortable, it falls out, rubs the gums and can even cause a gag reflex. However, it is not the material itself that is to blame for this, but poor-quality prosthetics, when the orthopedist or dental technician made mistakes.
Acrylic often causes allergic reactions.
Possible defects during operation and their repair
Most damage to acrylic dentures can be repaired without the expense of producing new structures.
Repair is required in situations such as:
- an artificial tooth is built in place of the removed supporting tooth;
- if an artificial dental organ falls out or is chipped, it is replaced with a new one;
- the lock that secures the prosthesis is attached to the supporting teeth has failed;
- the prosthesis does not fit well to the gum, and the base needs to be adjusted;
- the base is broken, it is repaired, or replaced if it is severely damaged.
Dentures have their own warranty period. Most often it is determined in one year.
Advantages and disadvantages
Acrylic dentures, like other types, have their pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Affordable price compared to other types of prostheses. It consists of the complexity of execution, the amount of material spent, installation difficulties and other factors. When ordering not just one crown, but a bridge or removable prosthesis, the price for each tooth is significantly reduced.
- Lightweight material. The lightness of acrylic makes it quite simple and quick to get used to the design.
- High reliability and wear resistance. The service life of acrylic dentures can be up to eight years.
- Distribution of the load not on the supporting teeth, but on the gums. Therefore, acrylic products help preserve the enamel of a living tooth.
- Such designs are easy to manufacture. Thanks to the properties of the material, it is easy to obtain the desired shape, color and size.
- The result of using such prostheses is highly aesthetic.
- Plastic products are easy to care for.
- The installation takes place in one visit to the dentist.
Acrylic products have much fewer disadvantages. Let's look at their main disadvantages:
- Risk of injury to soft tissues during operation of the structure in the form of herpes, chafing, and so on.
- Possibility of tooth injury when fixing the prosthesis with special devices. Wear or destruction of the dental organ is possible.
- The material may contain methyl ether, making the product toxic. After installation, the patient may experience an allergic reaction.
- The porosity of the surface of the product promotes the development of microorganisms.
Answers to frequently asked questions
How to properly store the product?
At first, the patient undergoes adaptation to the prosthesis, so he should not take it off at night. After the adaptation period is completed, the device must be removed from the mouth before going to bed and placed in a special container with disinfectant liquid.
The container can be purchased at a pharmacy or specialty store.
What foods are best not to eat?
Patients wearing acrylic dentures do not need to make any significant changes to their diet. However, doctors recommend avoiding products that are too hard, which can damage the product, as well as products that are too viscous and stringy, sticking to the teeth.
Which designs are better - nylon or acrylic?
An alternative to acrylic products is nylon devices. To understand which ones are better, you need to study the pros and cons of each type.
| Nylon | Acrylic | |
| Material | Has high elasticity, allowing for a tighter fit to the gum | Quite hard material that does not adhere to the gum so well |
| Form | Due to its softness, nylon may become deformed during wear. | The structure retains its original shape and does not deform |
| Structure | Nylon has a dense structure, so it does not accumulate odors and microorganisms | The structure of acrylic is porous, so it easily accumulates foreign odors, and also becomes a favorable environment for the development of microbes |
| Harmfulness | Non-toxic | Moderately toxic |
| Price | Has a fairly high cost | Has a low cost |
| Fixation | Additional use of cement or glue is prohibited | Possibility of using cement or glue to improve the quality of fixation |
Types of plastic products
Plastic structures can be of the following types:
- Made by casting, which makes them as similar as possible to natural teeth and completely repeating the shape of a living dental organ.
- Obtained by pressing. This production is much simpler, and therefore the price of such products is lower.
- Removable plastic products are very common, as they can replace dentition with complete or partial edentia.
- Crowns placed temporarily while another permanent prosthesis is being made.
- Permanent dentures that play the role of a lost tooth.
- Full or partially removable structures are quite affordable.
Installation of acrylic dentures
Before installing a prosthesis, it is important to examine the oral cavity and treat possible diseases, if any. It is also important to examine the patient for contraindications.
Installation steps:
- First stage. The oral cavity and lips are disinfected with special means.
- Second phase. An impression is taken and a primary prosthesis is made based on it. They try it on and reconstruct it if necessary.
- Third stage. Having received the most suitable temporary product, a permanent acrylic prosthesis is made from it.
The installation procedure usually takes place in one visit to the dental clinic.
Adaptation period
Having decided to install an acrylic structure, it is important to understand that it will not be possible to immediately gain complete comfort from the newly acquired teeth; for this, an adaptation period must pass. The material is quite hard, initially it will put pressure on the gums, causing discomfort and even pain. Changes in sensation of temperature and taste are possible.
The average adaptation period lasts from 1 to 2 months. During this time, the prosthesis is adjusted to more comfortable sizes. The patient gradually gets used to it. You will have to visit the doctor several times during this time.
Note: If you wear the structure as much as possible, despite the discomfort, adaptation will go faster.
First, it is recommended to wear it continuously for two hours, then rest for 10 to 15 minutes, then even longer. During the adaptation period, it is better not to remove the structure at night.
When the patient is more or less accustomed to the prosthesis, it is removed at night and stored in a disinfectant. To quickly restore diction, you need to speak or read out loud as much as possible.