The number of cancer diseases is steadily growing throughout the world every year, and the proportion of patients with malignant neoplasms can reach 1.4% of the country's population [1]. According to experts from the World Health Organization, in the next twenty years the number of cases of various types of cancer in the world will increase by 60% [2]. Today in Russia there are about 3.7 million people living with some kind of cancer, which is approximately 2.6 thousand cases per 100 thousand population [3].
Currently, an important indicator of the effectiveness of cancer treatment is improving the quality of life of patients. One of its components is timely dental care aimed at maintaining health and preventing oral diseases.
Causes
Let's look at the causes of dental cancer
:
- Oral injuries of various origins. Poor-quality dentures rub the gums; the presence of piercings in the tongue or lip can cause inflammation
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs).
- Untreated caries.
- Inflammatory diseases of soft tissues.
- Herpes virus, HPV, Bowen's disease.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Hot or spicy foods that constantly irritate the mucous membranes.
- Work in conditions harmful to health (hot workshop, dusty room).
- A history of cancer of the stomach, kidneys and lungs. In this case dental cancer
is a secondary pathology.
To take care of your health, rule out dental cancer, causes
its development must be monitored. Careful oral care, eradication of bad habits, and regular visits to the dentist will reduce the risk of developing pathology.
Stages of pathology development
Dental cancer
Like any cancer, it occurs in the human body through four stages:
- The first stage is when the tumor is within 10 mm. The place of formation is the mucous membrane or tooth germ.
- The second stage is when the tumor reaches 3 cm. The symptoms of cancer become more obvious. Metastasis is found in one of the regional lymph nodes.
- Stage three – the tumor exceeds 3 cm in size. Metastases are detected in several regional lymph nodes.
- The fourth stage is when the process becomes aggressively malignant, affecting the oral cavity, nose, and also the base of the skull. Metastases may be found in the lungs and liver.
Dietary recommendations if cancer is diagnosed
You should limit your intake of simple sugars or replace them with aspartame, acesulfame, sorbitol or xylitol. Consumption of foods with spicy spices that irritate the mucous membrane should be limited. Preferred food is warm and with mild aromas, with minimal amounts of spices. Avoid fruit juices, particularly sour fresh fruits, both because they taste too strong and because of the risk of enamel erosion. Reduce consumption of coffee, tea and thirst-causing foods (dry biscuits, crackers, chips). Alcohol in any form should be excluded from the diet.
It should be borne in mind that maintaining a balanced diet in patients undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy poses specific difficulties. There is a change in taste, difficulty swallowing, and nausea and vomiting may occur. In addition, drugs recommended during treatment have an adverse effect on some food ingredients, drugs such as neomycin reduce the absorption of vitamins K and D, methotrexate, in general, affects the metabolism of vitamins, in particular, it reacts with folic acid and most drugs can lead to anorexia.
Nutritional compositions available in pharmacies, in liquid form, containing a set of vitamins, microelements and amino acids that provide calories and nutrients, should complement the daily diet of cancer patients.
In the case of stomatitis, the most effective drugs are oil-based keratoplasties - aecol, vitamin A, E. But their healing effect is not high, these drugs are nothing more than vitamins.
There is a need to use more advanced and effective specialized drugs.
EGF Epidermal growth factor. Belongs to the group of polypeptides. Only a few of its forms are approved for use in Russia; in particular, it is offered by the Moscow company REPLERY in the form of a spray for application to the mucous membrane or skin. The wound healing effect is very high, as is the cost of the drug. It is still used in medicine to a limited extent, but is very widely represented in cosmetology and is included in many cosmetic preparations.
Palifermin is a recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor, a drug close to EGF, certified and used in the European Union
SUMMARY
Prevention of stomatitis in every patient with cancer should be part of therapy. It has a chance of success only due to the proper motivation of the patient himself, his desire and self-discipline. Of course, if a person has cancer, if the doctor sees symptoms of cancer in the mouth, then a request to replace a filling or install prosthetics causes a sarcastic smile in the patient. In addition to unpleasant sensations, there are also expenses, and cancer treatment itself is not cheap.
And then these dentists start the old boring song about the need to have clean teeth. But it should be recalled that dental problems are one of the provoking factors for the occurrence of cancer. Those. Many ended up at the oncologist precisely because of untreated teeth.
And in our practice, we have encountered similar cases. In particular, I remember a case when we diagnosed a patient with cancer that developed under an old removable denture. This was malignancy of the area of the mucous membrane under the prosthesis with deep ulceration and reaction of the regional lymph nodes, classic leukoplakia. Our diagnosis was subsequently confirmed.
But even if the disease does appear, oncologists have developed effective treatment regimens and practice has shown that they are successful in most cases. But oncologists themselves admit that it is not always possible to fully carry out therapy due to the occurrence of complications associated with concomitant diseases.
Any therapy for cancer, and indeed all tumors, is based on one basic principle. Tumor cells are in the stage of constant, avalanche-like division and in this state they have one vulnerability - they are sensitive to X-rays and cytostatic drugs.
Unfortunately, epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity are also renewed very intensively. In therapy, they also become targets, although to a lesser extent. There is a chance to keep them intact, eliminating damaging factors.
In conclusion, I would like to warn people against mistakes. The proposed methods of treatment and prevention of complications were found through much trial and error. Medicine is not omnipotent and will never be omnipotent - even if humanity learns to treat all known diseases, they will simply be replaced by new ones and everything will repeat all over again.
But in medicine there are truisms and laws, unshakable axioms. Their fulfillment serves the purpose of recovery. Another thing is that the disease may turn out to be stronger, this is how this world works.
Attempts to reinvent what has already been created and tested by practice are constantly being made; people are ready to believe in a fairy tale, because only a fairy tale always gives hope.
Kerosene with vodka, treating cancer with soda, experiments with excrement - this makes a healthy person smile. But consciousness changes if a formidable illness holds you by the throat. If the doctor sets you up for a difficult and difficult path, then you want to go faster and faster.
If only diseases could be cured so easily, simply by discovering a method.
At the same time, if this is just the beginning of the disease, and the treatment is carried out vigorously and correctly, complete recovery occurs. Diseases are also not omnipotent.
GLOSSARY.
Erythema. Redness of the skin or mucous membranes due to hemostasis in the capillaries.
Erythroplasia (erythroplakia). Red papular or macular lesions of the mucous membrane. Malignancy may occur.
Etiology. Study of the causes of the disease. On the other hand, the cause of the disease.
Scab. A structure formed on tissue caused by cauterization or the application of some destructive substance.
Estrogen. General term for naturally occurring steroid hormones containing the core estrone, estriol estadiol, etc. secreted from the testes, ovaries and placenta; stimulates anabolic protein actions and has a positive effect on nitrogen balance.
Exogenous. Due to external reasons; not occurring in the body.
Fibroblasts. Connective tissue cells; a flattened, irregularly branched cell with a large oval nucleus, which is responsible, in part, for the production and remodeling of the extracellular matrix.
Fibroblast growth factor. A family of growth factors with mitogenic properties for fibroblasts and mesodermal cell types.
Fibronectin. High molecular weight (450 kDa) glycoprotein, consisting of two polypeptides connected by disulfide bonds; the functional domains of the molecule have an affinity for cells and components of the extracellular matrix; found on the surface of cells, in connective tissue, in the blood,
Fibrosis. Fibrous changes in the mucous membranes, especially the gums, resulting from chronic inflammation. Fibrous gums may appear healthy in appearance, masking the underlying disease.
Flow cytometry. Measuring the physicochemical characteristics of individual cells as they move past optical or electronic sensors; can be used to detect specific cells in a mixed population; used to determine the effects of drugs, hormones, chemicals.
General anesthesia. Drug-induced switching off of consciousness, during which patients do not respond to stimulation, even painful stimulation. The ability to independently maintain respiratory function is often impaired. Patients require assistance in maintaining airway function.
Glucocorticoids. A group of corticosteroids secreted from the adrenal cortex (such as cortisol or dexamethasone) that are involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats; which regulate the level of glycogen in the liver and blood sugar levels by changing gluconeogenesis.
Glycosaminoglycan. A polysaccharide chain consisting of hexosamines alternating with another carbohydrate residue. proteoglycan component.
GRAFT GRAFT. Any allograft in the form of granules or xenograft granular material placed for the purpose of increasing bone volume or regenerating a bone defect.
Gram stain. A method of classifying bacteria into two groups based on the color of their cell wall, after they are stained either violet (positive) or pale red (negative). Accordingly, bacteria are divided into gram-positive and gram-negative
Growth factors. A diverse group of polypeptides that play an important role in regulating the growth and development of various organs.
Humoral immunity. The immune response is mediated by the secretion of immunoglobulins (antibodies) produced by activated B cells (plasma cells) against antigens.
Hyperkeratosis. Excessive formation of keratin in epithelial cells.
Hypermineralization. The presence of unusual amounts of mineral elements in calcified tissue.
Hyperkeratosis. An abnormal increase in the thickness of the epithelial layer (stratum corneum) of the epithelium.
Hyperostosis. Localized bone overgrowth. See also exostosis.
Hyperplasia. An increase in the size of the tissue structure due to an increase in the number of cells.
Hypophosphatasia. Hypophosphatasia: An inborn error of metabolism characterized by a deficiency of alkaline phosphatase in serum and bone tissue, resulting in the formation of defective bone and cementum.
Hypoplasia. Defective or incomplete development.
There is a flap on the leg. Any flap that is mobilized to a new location using lateral incisions but retains its natural connection at the base to preserve its blood supply.
Autograft graft. Bone chips from the donor site to the recipient site within the same individual. Also known as autogenous graft.
Block graft. Graft. An autogenous or allogeneic bone graft in the form of a block, used to augment bony areas.
Foreign body. an unusual substance in the tissues or body cavity.
Foreign body reaction. Granulomatous reaction around foreign material in a tissue or organ; often characterized by the appearance of giant cells. This can manifest as acute or chronic inflammation of the gums and can lead to inflammation or purulent lesions.
Bridle. A fold of mucosal tissue that attaches the lips and cheeks to the alveolar mucosa (and/or gingiva) and underlying periosteum.
Fistula. Stoma. A pathological canal connecting the cavities of two hollow organs or into an organ cavity with the surface of the body.
Hydroxyapatite (HA). An inorganic compound, CA(P04)6(OH)2, found in the matrices of bones and teeth, which provides rigidity to these structures. Synthetic forms are used in medicine to replace intraosseous defects, as well as to coat dental implants.
Hemostatic instrument. A tool that can be used to stop bleeding. Clamps, clips.
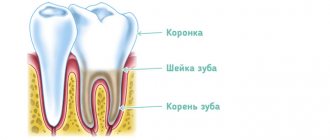
Symptoms of tooth cancer
Oncology in the initial stages has hidden symptoms and can develop over years and decades. Gradually the symptoms begin to manifest themselves:
- A formation of soft consistency to the touch appears on the jaw, convex in shape, increasing in size over time.
- The dentition may become deformed and the teeth become mobile.
- Pain sensations increase. It becomes difficult for a person to eat, chew, and swallow.
- Regional lymph nodes increase in size.
- A man loses weight.
- Low-grade body temperature, which periodically rises.
- Fistulas in tissues.
- When pressing on the tumor area, the doctor may feel a crunching sound.
- The enamel becomes fragile and is destroyed very easily.
In the prevention of dental cancer symptoms
may not appear, but it is important to visit your doctor regularly. Identified disease in the early stages provides a better prognosis for treatment. Late stages are dangerous for metastasis to other organs.
Treatment of tooth cancer
When the doctor confirms dental cancer, symptoms
which prompted you to come to the appointment, it is necessary to begin treatment as soon as possible. The most effective method is surgical removal of the tumor within healthy tissue. In the early stages of the process, the tumor is removed along with the teeth and part of the jaw.
In other cases, the jaw is resected completely or partially, and regional lymph nodes are removed. Based on the results of diagnosing the type of tumor and the stage of the process, chemotherapy or laser therapy is prescribed before surgery in order to reduce the tumor in size.
In the first and second stages, the prognosis is favorable: 80% of people survive the 5-year mark. In the third stage of the disease, more than half of people survive five years. In the fourth stage, only 15% reach the five-year survival mark. Regular preventive examinations and adherence to healthy lifestyle standards can reduce the risk of disease.
Dental treatment for oncology
Dental treatment for cancer is associated with difficulties. During chemotherapy and radiation therapy, the body suffers from various side effects. Dental treatment becomes additional stress for a person. The gold standard before starting cancer therapy is oral hygiene, as the body will be less able to resist bacteria during cancer treatment.
Main side effects of chemotherapy drugs
Use the quick links to find out about the side effect you are interested in:
- Hair loss
- Anemia
- Change in appetite
- Skin and nail changes
- Memory changes
- Constipation
- Weakness and fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Effect on fertility in women
- Effect on fertility in men
- Mouth and throat
- Diarrhea
- Edema
- Nerves
- Urinary disorders
- Bleeding
- Infection
Treatment and removal of teeth in cancer patients
In cancer patients, during the treatment of the underlying disease, favorable conditions are created in the oral cavity for the proliferation of pathological microorganisms. Irradiation inhibits cell growth, including in the oral cavity.
The task of a dentist in the treatment of teeth and oncology
the patient is not to harm him. Despite the fact that the body is weakened by a serious illness and no less severe therapy, caries must be treated so that it does not turn into pulpitis. Due to weakened immunity in cancer patients, inflammation progresses rapidly if left untreated. When treating teeth, it is important that the doctor knows the number of leukocytes, blood coagulation status, uses low-traumatic techniques, and coordinates the procedure with the oncologist.
Chemotherapy and tooth extraction
Teeth that cannot be restored are subject to removal. Although patients receiving chemotherapy have a weakened immune system, the consequences of refusing to remove an inflammatory tooth are much more serious than the side effects of anticancer therapy. It is advisable to remove teeth before starting chemotherapy.
in dental treatment
is taken into account, the doctor takes into account the patient’s condition when choosing an intervention technique. Treatment by a dentist during chemotherapy is not advisable, but if there is an emergency and the patient is already taking chemotherapy, the intervention of a doctor will avoid big problems. Removal should be done as atraumatically as possible.
Dental problems and dental treatment for oncology
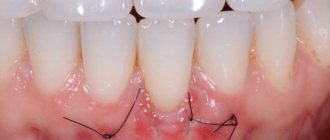
After chemotherapy, many are faced with the fact that they develop caries, gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease, cysts begin to form, gums become more sensitive and bleed.
This condition creates additional difficulties for the dentist, but does not mean that you need to refuse dental treatment, cancer
not prevent. It is important to tell your dentist about your diagnosis and that you are currently undergoing treatment for cancer. This will allow him to choose the most gentle methods for solving dental problems.
You need to know that when treating teeth, oncology
does not progress and the disease itself is not a contraindication to dental intervention. Dental treatment will remove the source of infection, prevent its further spread, and defeat cancer.
Pain therapy methods
Medications
In most cases, pain after chemotherapy can be reduced by taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), especially pain in the joints and bones. Neurogenic pain in the legs is sensitive to ketoprofen from the NSAID group; they respond less well to other drugs in this group. As a rule, the need for weak narcotic drugs may arise only in case of breakthrough pain; one dose may be sufficient to relieve the syndrome. In all cases, pain treatment begins with tablets, and only if there is no effect, injections are resorted to.
Multimodal therapy
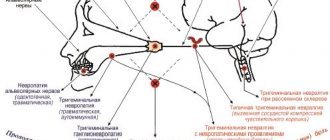
Pain after chemotherapy is most often acute and goes away within a few days, in most cases it is controlled with medications. For neurogenic pain, medications alone may not be enough. To treat polyneuropathy, several groups of drugs are used, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures and drug blockades of nerves and plexuses.
For severe chronic pain, neuromodulatory techniques are required with the introduction of narcotic analgesics into the spinal space in combination with electric current therapy of areas along the nerve endings, as well as acupuncture with acupuncture.
Relieving chronic neurogenic pain is a complex task that requires the participation of different specialists and many therapeutic techniques in the treatment process, which is called a multimodal approach.
Non-drug therapy
For severe and prolonged pain, technologies for neurodestruction have been developed—destruction of the nerve. Preference is given to non-invasive methods - without penetration into the body, but it is fundamentally possible to introduce alcohol and other chemical compounds into the nerve.
For chronic pain, radiofrequency ablation of the nerve trunk blocks the transmission of pain impulses through it without damaging motor neurons. The effect lasts for several weeks, and there is no risk of destruction of surrounding tissue due to infection.
As a rule, radiation therapy is not used for pain after chemotherapy, but for intense pain in a large joint, a single low dose of radiation can help.
Psychosocial measures
Each person feels pain in his own way, which is determined by the psychological characteristics of the individual. It's no secret that you can learn not to feel pain or at least not perceive it as a physical disaster. Psycho-emotional practices, taught to the patient by a psychologist specializing in oncological pathology, help “harden” against pain.
Our Clinic uses all methods of pain relief after chemotherapy; our chemotherapists prepare each patient for special treatment according to an individual program, helping to quickly cope with adverse reactions.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Blank M.A., Korytova L.I., Rozengauz E.V./Synchronous combination therapy in the palliative treatment of cancer patients//Palliative Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2002; No. 2-3.
- Zvatrau E.E., Medvedev I.O./Modern directions of pharmacotherapy of chronic pain syndromes//Gedeon Richter in the CIS, 2001, No. 1(5).
- Kidwell KM, Yothers G, Ganz PA, et al. /Long-term neurotoxicity effects of oxaliplatin added to fluorouracil and leucovorin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: Results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project trials C-07 and LTS-01// Cancer, 2012; 118.
- Mols F., Beijers T., Lemmens V., et al. /Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy and its association with quality of life among 2- to 11-year colorectal cancer survivors: Results from the population-based PROFILES registry// J Clin Oncol, 2013; 31.
- Quasthoff S., Hartung HP/ Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy// J Neurol, 2002; 249.