1604
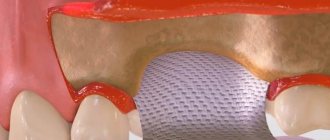
Barrier membranes are a modern surgical thin-sheet material designed to isolate surgical wounds filled with bone substitute for guided osteoregeneration.
Membranes are used to increase the efficiency of bone regeneration, accelerate wound healing, and eliminate bone resorption and postoperative complications.
Barrier films are used in dental surgery for various types of bone grafting, flap periodontal surgery, surgical correction of maxillodental anomalies, etc.
General overview
The American company Osteogenics Biomedical produces barrier membranes of various characteristics from natural and artificial materials.
Resorbable materials are made from natural raw materials - cattle tendons and porcine collagen.
The starting material for non-resorbable membranes is polytetrafluoroethylene. PTFE material can have a non-textured or textured surface, or be modified (hardened) with titanium.
Osteogenics Biomedical Barrier Membranes
| Resorbable | Size, mm | Non-resorbable | |||||
| Untextured | Size, mm | Microtextured | Size, mm | Titanium Reinforced | Size, mm | ||
| Cytoplast RTM Collagen | 30x40, 20x30, 15x20. | Cytoplast GBR-200 Singles | 12x24 | Cytoplast TXT-200 Singles | 12x24 | Cytoplast TI-250 ANTERIOR | 14x24, 12x24 |
| Cytoplast GBR-200 | 25x30 | Cytoplast TXT-200 | 25x30 | Cytoplast TI-250 BUCCAL | 17x25 | ||
| Cytoplast TI-250 POSTERIOR | 25x30, 20x25 | ||||||
| Cytoplast TI-250 XL | 30x40 | ||||||
Non-resorbable polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) dental membrane is an exclusive product not produced by anyone else other than Osteogenics Biomedical.
The material is intended for targeted regeneration of bone and gum tissue during surgical operations in dentistry.
Among the main purposes of Cytoplast GBR-200:
- providing primary wound coverage;
- preventing bone resorption;
- stimulating the growth of bone tissue from osteosubstitute;
- protecting the wound from pathogens;
- acceleration of wound healing;
- simplifying the work of surgeons.
Correction of malocclusions using Vector Tas microimplants and features of their use.
Come here if you are interested in the characteristics and purpose of Bio Oss bone material.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/implantatsiya/metodiki/temperaturyi-posle-zubov.html find out how long the temperature lasts after dental implantation with a positive outcome of the operation, and what indicators indicate the need to see a doctor.
Resorbable collagen membranes
Dental membranes "Bio Vin" (15x20/20x30/30x40) have good biocompatibility and are made from porcine collagen types I and III.
They can be cut into required shapes, are flexible and perfectly adapt to imperfections. Dental membranes “RTM Collagen” (15x20/20x30/30x40) have good elasticity, made from bovine tendon with type I purity. The multilayer membrane design and unique fiber structure provide high strength.
| Name | vendor code | Price |
| RTM Collagen 15x20mm - resorbable membrane | RTM 1520 | 143 $ |
| RTM Collagen 20x30mm - resorbable membrane | RTM 2030 | 182 $ |
| RTM Collagen 30x40mm - resorbable membrane | RTM 3040 | 259 $ |
Main characteristics
Cytoplast Regentex GBR 200 material is a dense polymer film 0.2 mm thick with a smooth surface.
The latter feature is a significant advantage over traditional resorbable membranes, the surface of which promotes retention and invasion by bacteria, causing rejection of the covering material and inflammation of the wound.
The smooth surface of GBR-200 “repels” pathogenic microorganisms, preventing infection and inflammation of the operating area.
The Cytoplast Regentex membrane has a microporous structure with a pore size of up to 1.26 microns, which does not allow bacteria to pass through the film, but at the same time is permeable to proteins.
The plastic-elastic consistency of the material allows it to be stretched and deformed, giving it the desired shape to adapt to the operating area.
Cytoplast has self-adhesive properties to the wound surface. As an additional measure of fixation, suturing the edges of the flap laid over Cytoplast can be used with light, tension-free sutures that do not affect the membrane itself.
The material comes in standard sizes 12x24 mm and 25x30 mm . From these blanks you can cut pieces of any size required in a specific clinical situation with scissors.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Complex one-stage implantation of the lower jaw
Case: there was a loose bridge of 4 front teeth on the lower jaw; after diagnosis, removal of the remaining teeth and complex basal implantation were prescribed.
Simultaneous implantation and removable prosthetics (June 2012)
Case: complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw; at the time of treatment, an old removable denture was used and was to be replaced.
Single-stage removal and basal implantation (September 2012)
Case: destruction of the chewing group of teeth in the lower jaw.
Composition and properties
The GBR-200 membrane consists of one PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon)) - a fluorocarbon compound that is resistant to almost any aggressive chemical agents.
Under human body conditions, PTFE is absolutely insoluble in substances and physiological fluids.
Physico-chemical and biological properties:
- chemical stability;
- extremely low allergenicity;
- self-adhesiveness to the wound;
- gas and light tightness;
- impermeability to bacteria;
- permeability to proteins.
Progress of the operation
Removal of the epiretinal membrane is performed in a sterile operating room using an ophthalmological microscope and other special equipment.
The patient is placed on the surgical table, and the area around the eyes is treated with a disinfectant solution. The anesthesiologist prepares the system for intravenous infusion of the necessary drugs. Blood pressure and pulse rate sensors are attached to the patient. The surgeon performs local, usually retrobulbar, anesthesia, installs an eyelid speculum and begins the operation.
The operation process includes three stages. At the first stage, a vitrectomy is performed - the vitreous body is removed. To do this, three incisions are made through which instruments are inserted. The vitreous body is removed using an aspirator, after which the vitreoretinal cavity is inspected. Next, they begin to directly remove the folds on the macula. First, using tweezers, the outer edge of the film is separated and lifted above the surface of the retina. The surgeon then uses a scalpel or laser to cut through the inner membrane and remove it.
The final stage of the operation to remove the epiretinal membrane is a complete inspection of the intraocular space by the surgeon to identify possible violations of the integrity of the retina or hemorrhages into the cavity. Then the removed vitreous is replaced with a gas mixture, perfluoroorganic compound or silicone oil. The instruments are removed and several sutures are placed on the sclera. Before the end of the intervention, the patient is administered antibiotic solutions, and a sterile bandage is applied to the eye. The anesthesiologist provides postoperative pain relief and the patient is transferred to the observation room.
Advantages and disadvantages
Cytoplast has a number of clinical and technological advantages compared to traditional suture materials, making it very popular among dental surgeons.
Advantages
- There is no need for primary flap closure of the wound fragment (no need to prepare and stretch the flap material).
- Non-germination of epithelium , due to the high barrier properties of the material.
- Elasticity (the membrane stretches in any direction, adapting to the wound).
- Stability of the structure (does not swell).
- There is no need to cover the membrane with anything from above , the film can remain completely exposed. To completely close the wound area, one Cytoplast GBR-200 is sufficient.
- Self-adhesive to the wound due to its special microstructure. There is no need to use complex fixing elements to attach the film to the bone; the edges of the wound do not need to be sutured.
- The absence of any negative consequences and chemical reactions when the material comes into contact with intraoral fluid.
- Fast wound healing.
- Preservation of the shape of the augmented alveolar bone tissue.
- Easy non-surgical removal of the membrane from the wound in 21-25 days. Removal is done through a small hole using a probe.
- Complete absence of any complications.
Flaws
Numerous tests have not revealed any significant drawbacks, which are often observed when using other types of membranes.
No rejection, inflammation, proliferation or other tissue reactions that negatively affected the healing process were noted.
The only drawback is the need for a dental surgeon to have practical skill in using the material , for which he has to undergo preliminary training.
Postoperative period and possible complications
After surgery to remove the epiretinal membrane, the duration of the rehabilitation period is strictly individual and directly depends on the preoperative state of the patient’s visual functions, his age and the presence of chronic diseases. After the procedure, the patient must wear a sterile bandage over the eye, replacing it with a new one every day. After being discharged from the hospital, it is necessary to undergo weekly scheduled ophthalmological examinations and instill reparative, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory eye drops prescribed by the doctor.
To protect your eyes from light, it is recommended to wear dark glasses outside. In addition, you need to stop playing sports and limit general activity. For several weeks it is forbidden to lift weights, visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, and open reservoirs. Avoid eye fatigue when reading, watching TV, or working at close range. By following these simple recommendations, in 80-90% of cases it is possible to avoid possible complications. Vision improvement occurs gradually and reaches the maximum possible within 4-6 months.
Undesirable reactions when removing the epiretinal membrane can occur both during the operation and in the long term after it. Surgical complications include hemorrhages into the inner space of the eye and under the retina; it is also possible to disrupt the integrity of the retina and a sharp increase in IOP. In the postoperative period, there are infectious lesions of the organ of vision, as well as retinal detachment. Complications of the long-term postoperative period include the occurrence of cataracts and the development of glaucoma. In 10-12% of cases, a relapse of the disease occurs, accompanied by the growth of a new membrane of even greater density.
Indications
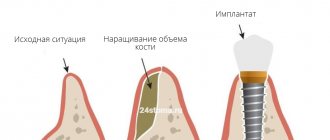
The GBR-200 membrane is recommended for use in dentistry in all cases associated with directed bone regeneration:
- After tooth extraction to restore the bone tissue of the alveolar process.
- Before installing an implant if the bone volume is small.
- During or after installation of the implant - to close the wound.
- For augmentation in a wide variety of clinical cases.
- For peri-implantitis (inflammation of bone and soft tissues adjacent to the implant, their resorption and loss of the implant).
- For flap operations in the oral cavity, plastic surgery and gum recession.
- When restoring jaw proportions (for example, with a planar osteotomy, accompanied by replanting of bone tissue between separated fragments of the jaw bones).
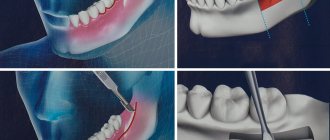
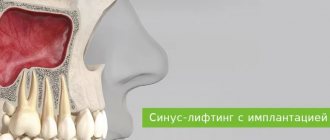
- During sinus lifting (Cytoplast is placed on the bottom of the maxillary sinus to eliminate the risk of penetration of the osteosubstitute into the sinus through perforations in the mucous membrane).
Let's discuss together the pros and cons of dental implantation in comparison with other prosthetic methods.
In this publication we will tell you whether you need to take antibiotics after dental implantation and why.
Follow the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/implantatsiya/metodiki/rashozhdeniya-shvov-posle-zubov.html to find out when the sutures are removed after dental implantation.
What are barrier membranes?
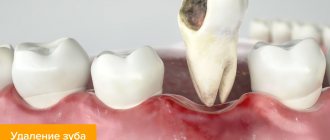
The barrier membrane is one of the most modern and successful inventions in dental practice. Such designs are actively used in almost all surgical interventions. Barrier membranes for bone grafting during implantation can prevent atrophic phenomena in the alveolar process and contribute to the immediate successful fixation of artificial roots. The membrane affects the regenerative abilities of the bone, increasing them, does not allow osteoclasts that are dangerous to bone cells to enter, and minimizes the risk of penetration of pathogenic agents. Thanks to the barrier membrane, graft engraftment is accelerated, as is the overall treatment of the patient.
The membrane for bone grafting is a very thin and fairly elastic plate that is attached to the bone with titanium pins. In this way, the gums are separated from the bone material during the formation of natural jaw tissue.
Types of membranes
There are two types of barrier membranes that are widely used in dentistry:
- Resorbable. This structure gradually dissolves. It does not require separate removal, that is, additional surgical intervention, which means it causes less trauma.
- Non-resorbable. Membranes of this type do not dissolve on their own, which is why patients need an additional stage of treatment - removal of the structure. In most cases they are made of titanium. Such membranes are attached in the presence of a serious deficiency of bone tissue, filled with granules of osteogenic material. Once the alveolar bone and soft gum tissue have recovered, the barrier membrane is removed.
The dentist independently selects the optimal membrane for a specific clinical case. He must take into account that resorbable structures do not fix the grafts well enough, so they are used only for minor atrophies.
Technique of use
After filling the surgical wound with a bone substitute, Cytoplast GBR-200 is placed on top of it, overlapping the edges of the wound by 2-3 mm. In addition to self-adhesiveness, the film can be fixed to the wound using light, tension-free suturing of flaps placed on top of the Cytoplast.
The membrane is removed 21-25 days after the operation. The deadline is 28 days. Repeated surgery to remove Cytoplast is not required.
If a flap has been placed and sutured over the membrane, the material is extracted (pulled out) using a probe through a small hole . In most cases, anesthesia is not required (in extreme cases, topical anesthesia is used), bleeding, as a rule, does not occur.
After covering the surgical wound under the Cytoplast, bone and secondary epithelium begin to quickly form. Fusion of the flap with the newly formed epithelium usually occurs a month and a half after the operation.
In the video, watch the technique of using the Cytoplast membrane.
A little history
Among the methods of treating retinal pathologies, operations to remove epiretinal membranes are considered relatively new. Such interventions are usually performed as planned and are classified as high-tech. They require modern, expensive equipment and highly qualified surgeons, which makes it possible to carry out such operations only in large specialized medical centers.
Performing effective operations in the retina became possible only with the development of vitreoretinal surgery. Therefore, diseases accompanied by the formation of epithelial membranes in the macular zone until the middle of the last century were the cause of blindness.
The method of removing the epiretinal membrane was first proposed by the American ophthalmic surgeon, Professor Charles McCamer in the 70s of the last century. Subsequently, the technique of this operation was constantly improved and today it is successfully used even with large-area growths in the macula area. Today, removal of the epiretinal membrane can be performed by two methods - classical, using an ophthalmic scalpel, and innovative, using laser radiation. The use of a laser to excise the macular fold is more gentle and effective. However, the high cost of the operation significantly limits the spread of this technique.
Clinical results
In order to determine the effectiveness of the GBR-200 membrane, the developer conducted studies of the material on a group of 10 patients in 3 clinical cases:
- tooth extraction;
- tooth extraction with implantation of a bone substitute;
- tooth extraction with implantation.
The following conditions for the operation were provided:
- the membrane was cut out using scissors according to the shape of the defect;
- when applied, the membrane overlapped the hole by 2-3 mm;
- adherence of the material to the wound was ensured by stretching and pressing with fingers and an instrument, taking into account the configuration of the alveolar process;
- The cytoplast remained on the wound for 21 days, after which it was carefully pulled off with tweezers.
Research results
- In no case of use of the GBR-200 material did an inflammatory process, cell proliferation or other negative tissue reactions occur.
- None of the membranes were rejected.
- All films were easily removed from the wound after 21 days without the use of anesthesia.
- On the wound surface, which was under the membrane, there was no resorption of surrounding tissues or epithelial growth. Only in some places along the edges of the wound were there migrating small areas of epithelium.
- The wound surface after removal of the Cytoplast was a newly formed bone structure.
Based on the results of the study, it was concluded that when Cytoplast GBR-200 was used for 3 weeks, a reliable barrier was created on the surface of the wound, which prevented the germination of epithelial tissue.
Treatment of epiretinal membrane of the eye
For almost all nosological forms of retinal pathology in the area of the vitreomacular interface, which includes the epiretinal membrane, treatment is carried out mainly surgically. Removal of the retinal membrane is performed through microinvasive vitrectomy followed by removal of the retinal film, which eliminates the manifestations of the disease and restores visual functions.
For epiretinal membrane of the eye, surgery can be performed on any category of patients, however, surgical treatment is performed only in cases where the doctor is confident in the effectiveness and safety of the operation.
Clinical manifestations of the disease may slightly reduce the quality of vision; over time, patients get used to these minor changes, which do not in any way affect the quality of life. That is why each case of epiretinal membrane of the retina requires adequate examination, as well as an assessment of the risks and benefits of the upcoming treatment.
Reviews
The use of barrier membranes during surgical interventions is a new, modern technology that has not yet received the distribution it deserves.
If you have undergone surgery using Cytoplast barrier membranes, share your impressions of this material with other visitors to our site, leave your comment at the bottom of the page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: implantation, implantation methods
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Should I save or remove a tooth in case of purulent periodontitis?
Next article
Universal trainer I-3 for the correction of malocclusions in children
Indications for surgery and possible limitations
Surgery to remove the epiretinal membrane is only necessary if there is a significant decrease in visual acuity or serious distortion of visible objects. The indication for its implementation is the rapid growth of the macular fold, when there is a threat of irreversible changes in the retina. Contraindications to removal of the epiretinal membrane are retinal tumors and diagnosed optic nerve atrophy. Restrictions to surgical intervention are:
- Acute infections of the eyes or eyelids.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Relapses of chronic diseases.
- Feverish conditions.
In this case, the operation may be postponed for a certain period.
Causes
An epiretinal membrane can develop in humans against the background of certain ophthalmological diseases. Such diseases include:
- Diabetic retinopathy;
- Retinal tear;
- Vitreous detachment;
- Retinal vein thrombosis.
This process can be activated by hemorrhages and inflammatory processes in the eye. True, in most cases, the epiretinal membrane is an idiopathic phenomenon, the origin of which remains unclear. It is known that it contains retinal pigment epithelial cells, fragments of the vitreous body, collagen, as well as fibrocytes and macrophages and macrophages.