How to remove cheek swelling from a tooth.
Swelling of the cheek can be the result of a great variety of reasons, of which there are more than a dozen, and inflammation, as a result of which the swelling is formed, can be both in the gums and periosteum, and in the salivary glands near the cheek.
Today we will try to find out how to remove cheek swelling from a tooth.
When we say “from a tooth,” we mean that a tumor on the cheek appears as a result of some kind of dental disease. Among these are:
- deep dental caries, which caused inflammation of the gums, and then the mucous membrane of the cheek;
- periostitis (flux), which, being an inflammation of the periosteum, spreads the inflammatory process to the gums, and then can spread to the cheek;
- tooth extraction can also cause the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
There may be several reasons for cheek swelling, but it is always an inflammatory process
If swelling and pain increase, you should consult a dentist as soon as possible. After examining the oral cavity and making a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment and recommend how to remove the tumor from the cheek most effectively.
How to remove swelling when your cheek is swollen from a tooth? This depends on the location of the tooth, the direction in the development of the inflammatory process, as well as its intensity and form of occurrence.
As a rule, antibiotic therapy is carried out first, both general with tablets and local with gels and antiseptic sprays.
However, before embarking on any treatment, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis with a specialist and listen to his recommendations as to whether it is necessary to remove the tooth that caused inflammation of the mucous membrane or whether it is possible to get by with eliminating the inflammation and treating the disease that caused it.
How do you remove a tumor when your tooth hurts and your cheek is swollen? And is it necessary to remove the tooth? Usually, they try to cure a diseased tooth rather than pull it out, so tooth extraction is resorted to only if there is a real threat of blood poisoning.
In other cases, the doctor carries out an antiseptic treatment of the mucous membrane, opens the purulent source of inflammation and draws out the pus through drainage devices.
Home treatments
While the patient is waiting to visit the doctor, he can alleviate his condition by using some home remedies. Among them are:
- an aqueous solution of salt and baking soda to rinse your mouth several times a day;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs such as sage and chamomile, which are used to rinse the mouth;
- a three percent solution of hydrogen peroxide half and half with water also helps in reducing swelling;
- a cold compress of ice on the outside of the cheek, it is important not to chill the tooth.
If after 24 hours the above methods have not had any effect, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
The inflammatory process left untreated can ultimately cause blood poisoning and painful death.
How to remove swelling from the cheek due to tooth disease?
Most people are familiar with toothache. Most often, the patient seeks help immediately after the appearance of unpleasant pain or when swelling appears. In the latter case, you should know what to do, what actions will help relieve swelling. Experts emphasize that in this case you should not self-medicate. The best option is to visit a dentist.
Tumor due to improper treatment
Why else can pathology be observed? Separately, it should be noted the swelling of the cheek, which arose as a result of illiterate therapy. If the cheek is swollen after a complex tooth extraction, then this is a variant of the norm. The symptom disappears on its own after a few days. Typically, such swelling is small in size and does not cause pain to the patient. The situation does not require repeated surgery.
The opposite situation arises if we are talking about an infectious process that has begun after medical care has been provided. Complications are more often observed after the removal of wisdom teeth or a retained element. Such operations cannot be performed without significant damage to soft tissue. Complications arise due to doctor errors or when the patient fails to comply with the dentist’s recommendations during the recovery period.
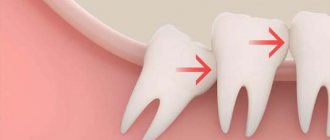
The impacted tooth is located in the deep tissues of the gums due to incomplete eruption or incorrect location
The gums also swell due to improper sanitation of the diseased tooth. In this case, repeated assistance from a specialist is required, followed by taking medications and local treatment of the affected area. After complex removal of an element, swelling can be observed for up to 2 weeks.
Swelling also often develops due to allergic reactions to painkillers used by the dentist during treatment. In this case, additional symptoms are observed (heavy breathing with whistling, shortness of breath), but the tooth does not hurt. A person requires urgent hospitalization to cleanse the body of the allergen.
Causes of swelling
A common situation is when a tooth hurts or a swollen cheek. An inflammatory process begins to develop in the inner part of the tooth. Sometimes the reason lies in incorrect surgical intervention by a specialist.
In general, we can identify the following factors of unpleasant sensations that are localized in the oral cavity:
- changes in pathological illness in the mouth area;
- diseases associated with disruption of the functional functioning of neighboring organs (for example, the maxillary sinus or trigeminal nerve);
- factors of discomfort in the oral cavity include the wrong course of treatment.
Unpleasant sensations may appear temporarily or be permanent. External irritants, such as sweet, hot or cold drinks, also have a huge impact. With slight pressure, an aggravation of this situation is observed.
If you suffer from a swollen cheek, you need to understand the reasons for this process. First of all, this concerns the diagnosis of periodontal disease. As you grow older, your gums lose their former elasticity and bleed constantly. Tooth enamel loses its former resistance to external irritants. This means that teeth and gums are quite easily susceptible to infection.
Sometimes the cheek becomes swollen from this infection. Use medications prescribed by your doctor for the course of treatment. Experts recommend removing the tooth, after which a prosthetic procedure should be performed.
The next disease that provokes swelling is an inflammatory infiltrate. Patients often encounter a situation where their cheek is swollen after dental treatment. For example, after therapy aimed at getting rid of apical periodontitis or pulpitis. A symptom that appears before the onset of swelling is a fairly severe toothache.
The main manifestations of inflammation are characterized by softening of soft tissues, or the gradual accumulation of pus. Subsequently, it penetrates into neighboring areas, and cases of entry into the circulatory system are possible. This process negatively affects the patient’s health and general well-being. In severe cases, death is possible. To protect yourself, you should seek help promptly.
The next option is that the wisdom tooth is growing in the wrong way. Due to the development of the eighth teeth or if the normal process of teething is disrupted, swelling of the cheek is possible. A mucous sac often appears at the site of inflammation. Leftover food often gets into its interior.
It is quite difficult to remove food from this area, so irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. This condition causes discomfort and the patient suffers from severe pain. In some cases, body temperature rises.
If the wisdom tooth grows partially, then the patient may suffer from discomfort while eating. After all, food particles injure the soft tissues of the cheek, and the size of the tumor increases.
There are cases when the cheek becomes swollen after tooth extraction. This situation is explained by unprofessional treatment. For example, if a nerve remains during filling. Even in the absence of pain, this situation is dangerous. If the patient does not take appropriate measures, in most cases he will lose a tooth.
Sometimes swelling may occur as a result of an allergic reaction. If this situation arises, the doctor must promptly remove the filling and replace the material that provoked the allergy with another (more neutral) material.
When the gum is cut, swelling may occur. This surgical intervention is performed if pus is present. At first, the tumor may increase in size.
Separately, it is worth noting the situation when a tooth was removed and the cheek became swollen. To minimize negative manifestations, experts advise not to touch the affected area with your tongue or hands for at least 24 hours. Also at this time it is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages and hot dishes.
It is important to contact a qualified specialist if you notice the presence of one or more symptomatic signs:
- after your tooth was pulled out, your cheek became swollen;
- excess of normal body temperature;
- after you have had a tooth removed, you observe a constant increase in pain;
- swelling gradually expands its boundaries. In the future, if the patient does nothing, this can lead to suppuration.
Why does my cheek swell?
Periostitis of the jaw
It is the most common dental cause of the symptom. Develops against the background of dental diseases: periodontitis, pulpitis, alveolitis, periodontitis, suppurating jaw cyst. It is provoked by open fractures of the jaws, infected facial wounds, operations, and tooth extraction. In some cases, it becomes a consequence of hematogenous or lymphogenous spread of infection from distant foci. Depending on the form, it is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Acute serous periostitis.
Moderate swelling of the soft tissues of the cheek, redness of the mucous membrane, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes are detected. The general condition suffers slightly, sometimes there is an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels. - Acute purulent periostitis (flux
)
.
The contours of the face are sharply changed, the predominant localization of edema is determined by the location of the inflammatory focus in the periosteum. Patients complain of sharp pain radiating to the temple, eye, ear, and neck. General hyperthermia, chills, weakness, headache, and regional lymphadenitis are observed. When examining the oral cavity, an area of swelling with a fluctuation in the center is detected - a subperiosteal abscess. - Chronic periostitis.
Slight swelling of the cheek, thickening of the jaw, and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes are typical. The patient complains of periodic moderate pain. The mucous membrane of the affected area is swollen, hyperemic, with a bluish tint.
Other dental diseases
Other possible dental causes of cheek swelling include the following:
- Perimaxillary abscess.
It occurs as a result of infection of the soft tissues of the perimaxillary area due to boils, tonsillitis, wounds, abrasions, and some dental diseases. Swelling is preceded by toothache, which gets worse when biting. Then dense swelling appears, the temperature rises, and appetite disappears. After spontaneous opening of the abscess, the condition improves, but subsequently the pathology may recur. - Vincent's stomatitis.
Develops when immunity decreases due to diseases, injuries, and stressful situations. The leading symptom is the formation of multiple ulcers on the mucous membrane. Swelling of the cheek is detected in severe cases of the pathology. - Noma.
An area of ulcerative-necrotic lesions of the lip or oral mucosa appears. Necrosis covers the gums, tongue, cheek tissue, and facial bones. The tissues around the area of necrosis are swollen; in severe cases, swelling from the cheek spreads to the chin and infraorbital area. - Salivary gland adenoma.
The parotid gland is most often affected. Local swelling with clear boundaries forms on the outer surface of the cheek, in the parotid zone, and spreads to the angle of the jaw, the area under the earlobe. Characterized by slow growth, painlessness at the initial stage, progression of discomfort and dry mouth as the formation increases. - Tumors of the salivary glands.
Along with adenomas, benign connective tissue neoplasia, intermediate and malignant neoplasms can form in the area of the salivary glands. The area of swelling is located in the same place as with adenomas. The swelling slowly increases in benign tumors and spreads quickly in malignant ones. - Purulent parotitis.
Swelling occurs in the parotid area, which spreads to the adjacent part of the cheek. There is severe pain, difficulty when trying to open the mouth, severe intoxication, and severe hyperthermia.
Cheek swelling
Traumatic injuries
All facial injuries are accompanied by rapidly increasing soft tissue swelling, spreading to adjacent anatomical structures. Swelling of the cheek of traumatic origin can occur with the following injuries:
- Injury.
Swelling without clear boundaries. Along with edema, pain, hyperemia, and sometimes hemorrhage are detected. The pain intensifies when opening the mouth and active facial movements. Speech and the ability to eat were preserved. - Hematoma.
Formed against the background of a bruise. A compaction appears in the area of diffuse swelling, which, as a rule, resolves on its own within 1-2 weeks. - Fracture of the upper jaw.
The most pronounced swelling is observed in Le Fort type 1 fractures, combined with neurological symptoms, hemorrhages in the conjunctiva and periorbital area. Type 2 is manifested by edema, hemorrhages in the periorbital zone, and changes in facial parameters. In type 1 fractures, swelling is more noticeable in the area of the upper lip and medial cheek. - Fracture of the lower jaw.
Injuries to the ramus, lateral and angular fractures of the bone body are characterized by swelling of the lower or outer edge of the cheek. Facial asymmetry, hematomas, bruises, articulation disorders, and stepped dentition are observed. - Fracture of the zygomatic bone.
Swelling appears in the cheekbone area, quickly spreads down the cheek, up the infraorbital region. Bruises and hemorrhages form in the conjunctiva. Along with pain, victims are sometimes bothered by nosebleeds and double vision.
Allergic reactions
Swelling of both cheeks is observed with angioedema, combined with swelling of the eyelids and lips, and breathing problems. The condition develops acutely, within a few minutes, less often – hours. It is provoked by contact with an allergen, insect bites. Along with the listed symptoms, angioedema in children may be accompanied by abdominal syndrome, and sometimes by neurological symptoms.
The cause of swelling of the cheek from the oral cavity may be an allergy to prosthetic materials. The pathological condition occurs several months or years after the installation of prostheses and is characterized by a burning sensation in the area where the prosthesis is fixed, tongue, cheeks, soft palate, changes in taste sensitivity, thirst, and dry mouth. When using metal products, a metallic taste may appear.
Ophthalmic diseases
In patients with acute dacryocystitis, swelling of the lacrimal sac area is complemented by swelling of the cheek, eyelid, and dorsum of the nose. In the chronic form of the pathology, swelling is noticeable along the upper inner edge of the cheek and covers the inner edge of the lower eyelid. Cellulitis of the lacrimal sac is characterized by sharp pain and swelling along the inner edge of the eyelid, combined with fever, weakness, weakness, headache, swelling of the cheek and paranasal area.
Neurological pathologies
Local symptoms of cavernous sinus thrombosis are exophthalmos, blurred vision, swelling and pain in the eyeball, swelling of the temple, part of the forehead, cheek, upper lip, and mastoid process. The clinical picture also includes headache, nausea, vomiting, and in case of infectious genesis of the pathology - hyperthermia, intoxication syndrome.
Swelling of the cheeks can be detected with one of the types of angioneurosis - rosacea. There is constant redness of the cheeks, nose, forehead, chin, and the formation of spider veins. The cause of swelling is persistent dilation of blood vessels, which, with a long course of pathology, leads to skin changes.
Skin lesions
Minor swelling of the cheek may result from simple contact dermatitis. The severity of the symptom increases against the background of prolonged contact with the irritant and secondary infection. With allergic dermatitis, the swelling is more noticeable and is combined with itching of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by mild swelling combined with the formation of vesicles.
Due to the abundant blood supply to the face and the structural features of the soft tissues, a boil on the cheek is accompanied by significant swelling. In the center of the swelling area there is a limited round or cone-shaped formation with a black rod in the center. After the boil has matured, yellowish pus appears around the shaft. Increasing twitching pains are noted.
In young children, swelling of the cheeks is often provoked by superficial pyoderma and occurs against the background of pustular rashes. A severe form of facial skin lesions in adults and children is erysipelas. The disease manifests itself with itching, bloating, and a burning sensation. Subsequently, the cheek swells, and a focus of clearly defined hyperemia with uneven edges, reminiscent of a geographical map, forms on it. Fever and intoxication syndrome are observed.
ENT diseases
Slight swelling of the cheeks is possible with the development of acute sinusitis or exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. Other symptoms include pain, impaired nasal breathing, nasal discharge, weakness, fever, and signs of intoxication. Patients with large odontogenic cysts of the paranasal sinuses are bothered by a feeling of tension and heaviness. Objectively, diffuse swelling of the cheek on the affected side and protrusion of the bottom of the nasal cavity are detected.
Other reasons
Swelling of one or two cheeks is observed with the following pathologies:
- Myxedema.
The swelling is bilateral, uniform, covering the forehead and chin, making the face look puffy. In severe cases, swelling spreads to the entire body. Symptoms of hypothyroidism are observed. - Parotitis.
Due to inflammation of the salivary glands, the perimaxillary area, the outer part of the cheeks, swells. The deformation is bilateral, often uneven. The disease manifests itself acutely, accompanied by fever, chills, and signs of general intoxication. - Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
The leading manifestation is periodic swelling of the lips. Possible swelling of the tongue, cheeks, eyelids. Neuritis of the facial nerve is often detected. - Phlebolith.
Stones in the veins of the cheek are often asymptomatic, but can manifest as pain and swelling, and sometimes inflammation of the affected area.
Other provocateurs
In addition to diseases and pathological changes that cause swelling of the cheek from the tooth, there are a number of other causes.
If an infection enters the patient’s body, medications that have an antibacterial effect should be taken. Thanks to this, you will get rid of the main cause, that is, infection, and the consequence - swelling. With inflammation of the lymph nodes in children, this situation often occurs.
The presence of a sebaceous gland cyst provokes changes in the facial part. In this case, surgical intervention will be required.
The cause is identified as neurological diseases. In addition to swelling of the cheek, the patient may suffer from congestion in the ear canal and discomfort in the throat area. To find out the reasons, you need to consult a neurologist.
A similar situation occurs with injuries or bruises. You can reduce the size of swelling by using a cold compress.
With a pathological change in the condition of the internal organs, swelling of the cheek is observed. To find out the reasons, you should consult your doctor.
It is important to know what to do if your cheek is swollen. Here are some tips to help reduce unpleasant symptoms:
- Often, after you have a wisdom tooth pulled out, you may experience swelling. To get rid of this, you should rinse your mouth with chamomile or sage. Chlorhexidine is perfect for these purposes.
- A fairly effective remedy is a saline (soda) solution. Rinsing with these products relieves pain and produces an antiseptic effect.
- While a wisdom tooth is coming out, it is worth using the help of special ointments and creams. Their use helps to minimize unpleasant symptoms.
- If your cheek is swollen after a wisdom tooth has been pulled out, you should use Kalanchoe or aloe juice. To do this, soak a cotton pad in the medicine, then apply it to the painful area.
- This manifestation is also possible with an insect bite. In this case, a decoction of chamomile, combined with aloe, helps.
Experts advise taking vitamin complexes daily to help improve the protective function of the immune system. It is better to reconsider your diet, in particular this concerns reducing the consumption of sweets. You can perform a light gum massage for preventive purposes.
By following basic rules of personal hygiene and regularly visiting the dentist, you will prevent complications and the development of pathological conditions.
Dental disease and its treatment is an unpleasant phenomenon that many adult men and women try to avoid or delay until an emergency. But the most dangerous thing about far-fetched fear is that while a person waits for the disease to become unbearable, destruction of teeth and gums occurs, which in the initial stages could be treated with fairly simple, almost painless and inexpensive methods. In this article we will talk about gumboil, how to get rid of it, and how to help the patient at home.
Tip #1: go to the doctor immediately if you suspect purulent pathologies
If certain pathologies are detected, you should not hesitate to seek professional help, because This can lead to serious health problems, as well as the fact that you will have to say goodbye to a bad tooth forever.
So, your cheek is swollen from a tooth. What to do? First of all, try to understand what led to the problem. We list the reasons, if suspected, you should urgently go to the doctor:
- flux, or periostitis: due to this disease, according to statistics, most often the cheek, and not just the gums, swells greatly,
- fistula: a small lump with a hole in the gum through which pus oozes,
- alveolitis: occurs due to infection or injury to the wound of an extracted tooth,
- cyst: can develop next to a living tooth or be located near a pulpless tooth if there is a filling or crown on it,
- periodontitis: often a consequence of advanced pulpitis, or occurs in treated teeth if they have incorrectly manufactured and installed crowns, as well as in the case of poor-quality cleaning and treatment of root canals,
- osteomyelitis.
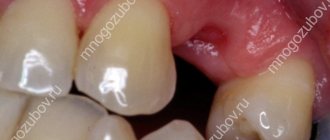
The photo shows the procedure for removing pus.
Click on the links on the names to read more about each disease. And if the symptoms are confirmed, then immediately go to the doctor, because... Without opening, draining and removing purulent masses, treatment will not bring positive results. Trying to help yourself at home will only waste valuable time and increase the likelihood of complications. The infection can quickly spread through the blood and lymph to internal organs and even cause sepsis.
What is flux?
Purulent inflammation of the tooth root is called gumboil. It is formed as a result of advanced caries or its complications, dental injuries or an inflamed pocket between the gum and tooth. A damaged tooth accumulates food debris that is not easily removed by regular brushing with a toothbrush. Under the influence of microorganisms they begin to rot. The accumulated pus seeks a way out and spreads through the dental canal. An obstacle in its path may be the periosteum or the lower jaw. As a result of stagnation, it collects in one place, forming an inflammatory process in this localization. Patients complain of significant swelling in the mouth and face, pain, and also note an increase in body temperature.
It is strictly prohibited to treat flux yourself at home, since the purulent focus can burst and form a fistula. Pus can enter the meninges or blood, which can lead to the development of sepsis. Treatment of this disease should be carried out by a dentist after examination and diagnosis. Only a qualified specialist can choose the most optimal method.
Comments
Just a week ago I had a routine examination at the dentist, they took an X-ray of my jaws... the doctor did not find any problems. There was nothing to treat. A day ago my cheek was swollen, but there was no toothache. With what it can be connected? Maybe the doctor made a mistake?
Dina (12/23/2019 at 05:32 pm) Reply to comment
- Dear Dina, sometimes swelling of the soft tissues of the face can be associated with diseases that have nothing to do with teeth. For example, this phenomenon occurs with ENT pathologies, otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis, and sinusitis. First, seek help from a therapist.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (12/28/2019 at 09:14) Reply to comment
what should I do if my cheek is swollen due to a tooth and I am 13 years old but the tooth does not hurt
Nastya (05/09/2020 at 14:29) Reply to comment
I have clean canals in my tooth, but the pain is terrible when tooth comes into contact with tooth, and the gums are swollen, the doctor prescribed an antibiotic, if that doesn’t help, then remove the tooth)) funny)) if they see that the tooth is no longer viable, why bring my condition to constant pain for 5 days?
Irina (09/03/2021 at 20:52) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Swelling of the cheeks and gums
Swelling of the cheeks and gums can be caused by any of the reasons mentioned.
In addition, gum problems may be associated with gingivitis, teething syndrome, herpetic stomatitis, parulis, periodontal disease, malnutrition, ill-fitting dentures, and viral or fungal infections. It is also known that pericorinitis (inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums) leads to swelling of the gums and cheeks.
With this type of swelling, the affected area may be numb and painful when chewing. To reduce swelling, you can try applying a cold compress, rinsing with a saline solution, and using antifungal medications.
Read also: How to treat gums
What medications will help relieve pain and reduce swelling?
Before visiting a specialist, you should try to relieve the pain and stop the spread of the inflammatory process. This can be done by rinsing with antiseptics, for example, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin or Miramistin.
Antiseptic rinses will help relieve pain
Applications using local drugs, including Levomekol, Cholisal or Metrogyl Denta, will help reduce swelling. Like cooling anti-inflammatory gels (Troxevasin, Fastum Gel), these drugs are best used after consultation with a doctor.
All of the above recommendations are only part of symptomatic therapy. It is impossible to eliminate the source of inflammation and restore the affected tissue without the participation of a dentist. Do not self-medicate to avoid serious complications later.
1Barer G.M. Therapeutic dentistry, 2008.
Causes of cheek swelling
There are many reasons that lead to cheek tumors. Here are just a few of them:
- Toothache . The development of caries can cause the formation of flux, which causes swelling. Swelling may occur after tooth extraction. Antibacterial drugs are taken for treatment. If the treatment process was carried out correctly, the swelling will disappear within 2-3 days.
- Salivary glands . Swelling may appear due to inflammation of the salivary gland ducts.
- Sinusitis . Inflammation of the nasal sinuses and the accumulation of purulent fluid in them may be accompanied by swelling.
- Lymphatic system . The process of inflammation occurring in the lymph nodes is one of the common causes of edema.
- The facial nerve became inflamed . Neuritis can occur with a cold. This is a one-sided process, which is accompanied by disturbances in facial expressions and movements, as well as pain. To get rid of the disease, you should consult a neurologist.
- Mumps . A viral, infectious disease that affects the salivary glands and leads to swelling of the cheek. Swelling can form on one side of the face or appear on both sides.
- Infectious mononucleosis . The disease is very similar in symptoms to ordinary sore throat. It is acute. Treatment can only be prescribed by the attending physician.
- Diphtheria . A disease of the tonsils associated with the penetration of the Loeffler bacterium into the body. The disease is accompanied by high fever and plaque formation on the tonsils. Taking antibiotics is ineffective, so treatment is carried out using a special anti-diphtheria serum.
- Injuries . Damage to the cheek, traumatically. After injury, the healing period will last 2-3 weeks.
- Allergy . Intolerance to certain foods, medications and hygiene products. Taking anti-allergy medications will help get rid of this swelling.
Read also: Fistula in dentistry
The cheek is swollen inside - what to do and how to treat it?
What to do when your cheek is swollen, but your teeth don’t hurt
Every person wants to have an attractive appearance. Therefore, special attention is paid to facial care. But what to do if the aesthetic appearance of your face is spoiled by a swollen cheek? This problem cannot be hidden with the help of cosmetics such as powder and foundation.
There are many reasons why cheek swelling occurs. In a matter of hours it can become quite noticeable. Why does this happen and how to resist the disease? In this article you will find answers to your question.
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Sometimes the swelling is located on the inside of the cheek. This can be caused by most of the reasons already mentioned - dental problems (decay and infection), ulcers, swollen salivary glands, mouth and cheek ulcers, trauma, infections (bacterial or viral), tooth abscess, lymph node problems (especially preauricular, submandibular nodes and tonsillar lymph nodes), mumps.
Additionally, various procedures such as fillings, oral surgery, tooth extractions, cheek piercings can also lead to swollen cheeks inside the mouth.
This problem occurs in both adults and children and can be accompanied by numbness in the cheek. Treatment for a swollen inner cheek will depend on the underlying cause of the condition.
Swelling of the jaw
Swelling of the cheek, jaw, and neck area can be caused by any of the causes of cheek swelling discussed above. It may be accompanied by pain or numbness depending on the underlying cause of the swelling.
Common causes include blunt force trauma, dental surgery, oral surgery, corrective jaw surgery, chin surgery, dental problems, salivary gland infections, and others. They can affect both the cheeks and jaw.