The cold weather sets in, and children begin to get sick much more often. Parents stubbornly call doctors, and they stubbornly diagnose ARVI.
The structure of acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) includes many infectious agents. Influenza is invariably considered the most terrible and unpleasant, followed by adenovirus infection in children, which can progress to almost any complications. Adenovirus affects the upper and lower respiratory tract, contributes to the development of pharyngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, and is often the cause of pneumonia1.
The disease affects children at any age, but is especially difficult to tolerate up to three years of age. Adenoviral infection can penetrate the body all year round, but the main increase in incidence is observed in the winter-spring period; local outbreaks begin to form everywhere, especially in closed children's groups.
Causes
A child’s cheek hurts for various reasons. This is often due to:
- allergies to foods or body care products;
- teething;
- a piece of food that penetrated into the gum pocket and caused suppuration;
- stomatitis;
- deep caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- an incompletely removed nerve in a dental unit;
- inflammation of the facial nerve or lymph node;
- injury that occurred after a blow or bite from the inside of the cheek;
- sinusitis;
- mumps;
- temporal tendinitis;
- temporomandibular joint disease;
- tumor;
- insect bite.
Any of these reasons cause inconvenience and discomfort. Therefore, it is important to contact a doctor in a timely manner, who will prescribe treatment. This way you can safely and quickly eliminate unpleasant sensations.
Why does a child's cheek hurt? It is difficult to install this on your own. But if such a symptom is present, adults need to take urgent measures to alleviate the condition.
Causes of dental periostitis in children
As already mentioned, this disease is usually secondary and caused by inflammatory processes in the teeth (odontogenic periostitis). What problems can lead to damage to the periosteum?
- dental caries with inflammation of the pulp;
- periodontitis;
- injury to the tooth or jaw.
Inflammation from the soft tissue area spreads deeper, involving the periosteum (fluss = “flow” in German, which perfectly characterizes the infection process).
Types of periostitis of the jaw in children
According to the course of the disease, acute and chronic forms are distinguished. It should be noted that the second is very rare.
Acute periostitis in children is usually purulent in nature - exudate forms under the periosteum, significantly changing the shape of the face, making it asymmetrical. Other symptoms of the disease are described above - increased body temperature, complaints of pain, swollen gums, etc. If the gums are soft and loose, then this is a different case.
Any manifestation of inflammatory processes in the teeth and jaws should be a signal to go to the hospital. And acute purulent periostitis
is a signal to provide immediate assistance
.
The chronic form is manifested by an increase in periosteal tissue, which outwardly looks like a slightly asymmetrical jaw. This usually does not cause discomfort to the child. However, you need to consult a dentist - perhaps dental treatment will help remove the source of inflammation, which will lead to a gradual return of the periosteum to its original healthy state.
Which doctor should I contact for flux?
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including periostitis, are treated by a dentist. You can go to a municipal clinic or a private center. In the dental clinic at your place of residence, you will be provided with assistance under the child’s compulsory medical insurance policy
.
If the flux manifests itself on a day off, find the contacts of on-duty municipal clinics in your city. Typically, several offices in different areas are open on Saturdays and Sundays.
Or go to a private clinic. In this case, flux treatment may be a little more pleasant, since such organizations are equipped taking into account the mental characteristics of children. The child may be shown a cartoon during the procedure. The staff of private clinics is specially trained to work with young patients. Prices for the treatment of periostitis should be clarified by calling a specific organization.
How is acute periostitis treated in children?
Treatment of the acute form of the disease is possible only with a doctor. No folk remedies, lotions or rinses can defeat flux - it can only make it worse. Separately, it is worth mentioning the dangers of warming up. Heating the painful area can increase the rate at which inflammation spreads, leading to unpredictable consequences. Warming up the flux is strictly prohibited!
Treatment of acute, including purulent, periostitis in children includes, first of all, opening the abscess and removing pus. The gums and periosteum are cut, under which exudate has accumulated. In some cases, drainage is required. The tip of a latex strip is inserted into the wound, which prevents the incision from closing quickly and allows all the pus to leak out. The procedure seems unpleasant, but it is well tolerated.
The doctor also carries out manipulations aimed at minimizing the source of initial inflammation.
In advanced cases, hospitalization will be required.
Also, after opening the wound, draining and sanitizing the oral cavity, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial therapy, possibly immune-supporting drugs.
Children who have undergone treatment for periostitis are advised to drink plenty of fluids, rest, and eat right.
The diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein, vitamins, minerals - calcium, magnesium, iron and others.
Treatment of chronic periostitis in children
This form of the disease is extremely rare in minors. Treatment of chronic periostitis in children is aimed at removing the source of inflammation, reducing tissue proliferation by activating immune processes. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed; in advanced cases or if conservative therapy is insufficiently effective, surgical intervention is possible.
Diseases of teeth and gums
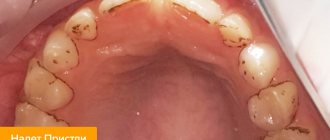
When examining a child's mouth, pay attention to the teeth and gums. Often their pathologies lead to pain in a given place. Black holes in the tooth enamel may be visible. Even if they are small. Caries develops deep inside, but on the surface it will be little noticeable. This process develops from dietary fibers stuck between the teeth and causing inflammation of the gingival papilla. Hard food often remains between the teeth and gums, leading to putrefactive processes.
Various dental ailments lead to both a violation of the integrity of the teeth and a change in the color of the enamel. If a child’s cheek is swollen and painful, this may be due to this particular problem. There may also be itching, bad breath, severe redness of the soft tissues. With flux, a bubble of pus is observed.
If a child has a tooth filled or removed, but pain persists for more than 2-3 days, most likely the procedure was performed incorrectly. This leads to pathologies in the gums. If a child has a sore cheek and a fever, as well as a headache, then there is a risk of periostitis. The presence of pain when swallowing food with swelling indicates inflammation of the tonsils. To prevent diseases of teeth and gums from causing pain, they must be treated in a timely manner. This way you can avoid complications.
How is pressure regulated?
Gas exchange constantly occurs on the mucous membrane of the middle ear. Gas is absorbed onto the surface of the mucous membrane of the ear, creating vacuum (negative pressure) conditions. This is a normal process, and opening the eustachian tube allows an additional portion of air and gas to be released into the ear to equalize the pressure in the ear with atmospheric pressure. Studies note that this function in children is much weaker than in adults, which also explains the frequent occurrence of otitis media in children.
Negative pressure leads to:
- retraction of the eardrum;
- increasing its blood supply and, as a result, reducing transparency;
- passive transport of fluid from the bloodstream to the ear and the formation of serous otitis media;
- result “C” on tympanometry. This result often causes fear and panic among parents. Tubotit? Eustachitis?
Don't panic ahead of time. Tympanometry does not make diagnoses; it only allows indirect assessment of the function of the auditory tube.
Result “C” in children is a normal variant associated with immature function of the auditory tube.
Literature data show that these problems normalize by 7 years, with the exception of a certain percentage of children (1-7%) who continue to have dysfunction of the auditory tube.
Injuries
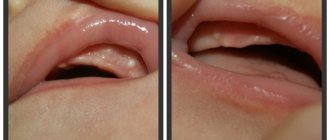
When a child’s cheek hurts, it may be due to injury to the oral mucosa or teeth. If no damage is found on the external part, it is possible that the cheek was damaged from the inside by the dentition. Bruises, abrasions, and swelling are noticeable on the inside. Or the mucous membrane and gums may be scratched. Then the wounds will be noticeable. Trauma is considered a common cause of pain, especially if the child is very active.
It also happens that due to an impact, a piece of enamel breaks off and the stem of the tooth breaks. In the latter situation, the tooth may be intact, but slightly loose. These damages are detected upon inspection. You won’t be able to get rid of the problem on your own; you need the help of a dentist. If the child’s cheek not only hurts inside, but also dizziness and nausea are observed, you should urgently call an ambulance. An ambulance is also needed if there is severe bleeding in the mouth.
Infection
If a child’s cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, then the cause may be fungi, bacteria and viruses. Because of them, stomatitis appears, in which painful ulcers appear in the mouth. Soft tissues also become inflamed. The infection enters the mouth with unwashed hands, toys, and dirty dishes. Its activation occurs with seasonal weakening of the immune system or colds. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the baby’s health so that no unpleasant symptoms appear.
If there is swelling not only on the cheek, but also on the neck, and there is also dry mouth, high temperature (38-39 degrees), then there is a risk of mumps or mumps. Due to pathological infections, sinusitis may occur, which involves inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. The pain from this disease can radiate to the tissues of the cheeks, nasal congestion is observed, and by night the general malaise may intensify.
What is the temporomandibular joint - TMJ
We use this joint while talking, chewing, yawning, laughing - very often. Around it are muscles and tendons that allow the jaw to move in different directions for different purposes.
TMJ problems occur for many reasons:
- violation of the dental system, for example, congenital anomalies of teeth, gums or bone tissue, malocclusions, injuries, poor-quality prosthetics;
- congenital anatomical abnormalities of this joint;
- increased or decreased tone of muscle fibers around the TMJ;
- active conversational load, for example, among actors, singers, speakers;
- central nervous system problems;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- excessive tension of the jaw muscles, for example, due to the bad habit of biting nails.
What is the temporomandibular joint and why do problems arise with it? Detailed and clear - in the video:
Actors and singers with active oratorical articulation are at risk for TMJ arthrosis
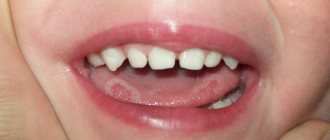
Teething
If a child's cheek hurts on the inside, this may be a confirmation of teething. During this process, swelling of the gums appears, and maybe fever. Through the translucent gingival tissue, whitish dental units and bluish hematomas can be seen breaking through to the top, which appears during teething. Children become capricious, sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
Painful sensations appear when sharp fangs or molars with a wide chewing surface grow. Pain in the cheeks sometimes occurs in older children, especially during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. This phenomenon occurs in almost all children. Parents need to monitor the child’s condition, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, seek help from a doctor.
What is the auditory tube?
The auditory tube is an organ that belongs to the middle ear system, connecting it to the nasopharynx. In the literature, its three main functions are distinguished:
- Regulating or equalizing pressure in the middle ear.
- Isolation and evacuation of fluid constantly forming in the middle ear.
- Protection of the middle ear from contents (viruses and bacteria, allergic substances, food) in the nasopharynx.
Unfortunately, these functions work very poorly in children.
Severe pain
Pain can be both moderate and severe. In any case, it causes inconvenience, so it is better to get rid of it as soon as possible. If the pain is severe, it may be due to:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- temporal tendinitis;
- Ernst syndrome.
When the buccal nerve is inflamed, there is loss of movement of the painful cheek. Much depends on the children and parents themselves. It is important to spend time on hygiene and follow preventive measures.
When visiting a doctor, he first examines the oral cavity. The specialist also asks about complaints and symptoms. Depending on the problem, a referral to a specific specialist may be provided.
Help
When a child’s cheek hurts, what should you do? If you have not yet been examined by a doctor, without a diagnosis and prescription of therapy, assistance must be carried out carefully. We must not allow the pathology to worsen. And for this it is prohibited:
- unauthorized use of antibiotics and other drugs that are sold in pharmacies only with medical prescriptions;
- perform warming up using lamps and warm compresses;
- give your child sweets and solid foods;
- feed cold or hot foods, give sweet, sour, fizzy drinks.
First aid can be performed using pharmaceutical drugs and traditional methods. They will improve the child’s condition, but then you still need to visit a doctor.
Primary chronic
It's rare to see a form like this. Typically, this disease is caused by weakly active microorganisms. They penetrate from teeth affected by caries. They are the ones who maintain inflammation for a long time.
This form of osteomyelitis is characterized by a productive nature, since the processes of destruction observed in bone tissue are weakly expressed. However, during this process new bone is actively formed.
If we study the clinical picture of primary chronic osteomyelitis, then the acute period is omitted. The child's condition generally remains the same, only fatigue, pale skin, and weakness appear. As for local signs, the area of the causative tooth hurts a little, the jaw bones and their thickness increase, and also symptoms of lymphadenitis appear in the lymph nodes. There are no fistulas on the skin or mucous membranes.
At an early stage, the productive form of the disease can be easily treated with conservative methods. If you choose the right means, you can achieve positive results quite quickly and without consequences. If the case is advanced, then surgical intervention will be required. It is used to remove too much bone tissue, as well as dead tooth germs. After that, they model the correct jaw contour.
Medicines
If a child’s cheek hurts on the inside, then painkillers with ibuprofen (Ibuprofen, Nurofen), paracetamol (Calpol, Panadol), which can also relieve fever during teething, help.
Older children (from 12 years old) are given medications with nimesulide (“Nimesil”, “Nimegesic”). The use of “adult” painkillers (“Analgin”, “Ketanov”) is permitted from the age of 14. But you still need to read the instructions for the medications. And it should be borne in mind that giving a child painkillers without consulting a doctor for more than 3 days is considered dangerous.
During the treatment of wounds in the mouth, ulcers, and inflammations, gels, ointments, and oils are used that have an antiseptic effect and stimulate recovery. These are Acyclovir, Cholisal, Karotolin. Sprays are used - “Ingalipt”, “Miramistin”, as well as balms and solutions intended for rinsing - “Rotokan”, “Vinilin”, “Chlorhexidine”. But it must be borne in mind that these are only temporary measures that cannot replace professional help. Even if it seems that the disease has subsided, you still need to consult a doctor.
ethnoscience
If a 5-year-old child has a sore cheek, traditional medicine can alleviate the condition. Cold compresses are considered effective, in which ice must be wrapped in a cloth and applied to the sore area. This allows you to relieve discomfort. Instead of ice, you can apply half a raw potato with the cut side to the skin.
Antiseptic rinses with a baking soda solution help. For this, 1 tsp. The product is dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water. Herbal infusions based on chamomile, calendula, green or black tea, oak bark and other herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects. Preparation is carried out by brewing 2-3 tbsp. l. raw materials with a liter of boiling water.
Diagnostics
It is based on X-ray examination. When the disease is just beginning, the images may show symptoms of osteoporosis (in the area where the inflammatory process occurs). And after a few days, radiographs already show foci of destruction. After another 2-3 weeks, bone necrosis is already visible, as well as the places where sequestra have formed.
Dentists' recommendations
Dentists may advise following simple rules to prevent cheek pain:
- Do not use hot compresses.
- Do not self-medicate.
- If your cheek is swollen, you should not disturb it. At this time, you should not eat very hot or cold foods, nuts, spicy foods, or toffees.
- You should not self-prescribe antibiotics.
You should not delay treatment, especially if a tumor appears. If it increases, then this is considered a sign of the development of a purulent process in the cheek. In the absence of professional help, the situation can only worsen.
Classification
Osteomyelitis can be classified according to location, route of penetration, and severity of the process.
If we talk about the course of the disease, then there is an acute or chronic type.
If we are talking about how the bone tissue became infected, then it is worth noting three types of osteomyelitis - post-traumatic, hematogenous, odontogenic.
If we take into account the localization of the purulent process, then it is worth distinguishing between the disease of the lower jaw and the upper jaw.
Prevention
To prevent your child from having a sore cheek, you need to take care of prevention. It is necessary to adhere to simple hygiene rules. It is important to brush your teeth regularly (as soon as you have them). At first, this is done not with a brush, but with a finger with gauze wrapped around it. It is necessary to teach your child to rinse his mouth with boiled water after each meal. From 6 years old, you can floss.
You should examine your child’s mouth at least 2 times a week. If you find food particles stuck between your teeth, they should be removed with a toothpick. The children's menu should consist of apples, carrots, and crackers. Calcium-fortified dairy products and vitamin-rich greens are also needed. This is necessary to strengthen dental tissues. The child should drink clean water, as it is the basis for the production of saliva that washes the mouth. It’s better to exclude sweets.
Do not allow your child's face and ears to become hypothermic. In very cold weather it is better not to walk. Colds in the facial nerve, colds, sinusitis, and mumps should not be allowed to occur. You should visit the dentist twice a year (even if there are no complaints).
Treatment
Here it is necessary to carry out certain measures that will help eliminate foci of inflammation and restore those functions that have been impaired.
Every case of childhood osteomyelitis must be treated urgently. To do this, you should call a doctor and admit the child to the hospital. If surgical intervention is performed on time, then we can talk about a positive prognosis and outcome.
In the case of odontogenic osteomyelitis, the tooth that provoked the inflammatory process should be quickly removed. When it comes to children, teeth can be removed, both baby and permanent teeth. After tooth extraction. the hole acts as natural drainage. However, sometimes the bone marrow spaces are opened to improve the drainage of pus.
After the tooth has been removed, the subperiosteal abscesses are opened or a periostotomy is performed.
During sanitation, they not only open, but also thoroughly clean the destruction cavity and remove necrotic masses from there. Antibiotics and antiseptics are used for washing, and drainage is also done. As for conservative therapy, special drugs from the groups of immunostimulants, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial are used.