Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Today, almost everyone knows that teeth need especially careful care. We buy expensive pastes and use special thread. But, unfortunately, when taking care of our teeth, we completely forget about the tissues surrounding them, while the health of our gums needs to be monitored no less carefully.
Many people are familiar with the symptoms when the gums begin to hurt when pressing between the teeth. And many, unfortunately, ignore this unpleasant pain. Let's figure out what can cause it, what these sensations indicate, and how to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of pain in the gums when pressing
Remember, discomfort in your gums is a reason to see a dentist. No matter what kind of pain you feel, relatively mild or severe, you need to determine the cause of the problem as soon as possible and begin treating it.
As a rule, pain in the gums when pressed is provoked by three diseases:
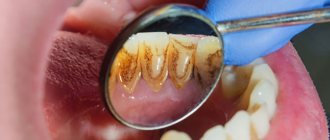
- Gingivitis. This disease is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and bleeding. Inflammation is provoked by microbial plaque, which occurs due to non-compliance or improper oral hygiene.
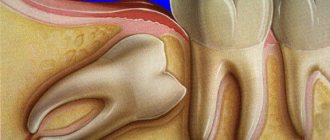
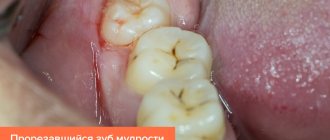
- Periodontitis. The disease, as a rule, is accompanied not only by unpleasant sensations, but also by a general deterioration in well-being. The patient feels which tooth is bothering him, as his “elevation” is felt above the other teeth.
- Periodontitis. The disease occurs due to untreated gingivitis. With periodontitis, the necks of the teeth open, pus oozes from the gums, and the teeth become mobile. The problem affects the entire cavity and can lead to tooth loss.
Other diseases that give similar symptoms
It was already said above that 90% of patient requests fall into one of the three cases already described. But there remains another 10% of calls with the complaint that “the gums are swollen.” Edema or conditions similar to them in appearance can cause precancerous diseases, hormonal changes, cancer itself, HIV infection, diabetes and many other diseases. And with everyone there will be swelling, perhaps there will be pain. Therefore, it is very important if you detect any swelling, growths, or bulges on the gums to consult a doctor to find out the cause of this phenomenon and timely treatment.
Treatment of gum pain
It is important to treat gum disease as soon as possible. Any, even the most harmless pathology, can turn into periostitis with high fever, swelling of the mucous membranes and loose teeth. Moreover, inflammation in the gums releases toxins that provoke the development of blood poisoning.
You should not discount the possibility of pain in the gums when pressing due to illiterate treatment by a dentist. Normally, pain after treatment persists for 1-2 weeks. If the pain continues longer and does not subside, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. It happens that after poor-quality dental canal filling, bacteria appear in the voids, which provoke an infectious process.
The dentist may also leave the edges of the filling uneven, causing damage to the gums. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor so that he can improve his work.
Attacks of pain when pressing on the gums are also common with increased sensitivity of the teeth and gums. However, with proper care, this pain goes away quite quickly. When it occurs, you should use toothpastes and rinses for sensitive teeth.
For example, ASEPTA Sensitive preventive toothpaste allows you to perform oral hygiene without irritating sensitive gums. The combination of 3 desensitizing components - potassium citrate, hydroxyapatite, thermal mud - significantly reduces the sensitivity of teeth and gums.
For more effective prevention of pain in the oral cavity, it is recommended to use ASEPTA gum gel with propolis. In this product, propolis is produced in the form of a gel, which makes it easy to apply to the gums. Prolonged contact with the painful area of the gum allows the gel components to penetrate deeper and promotes rapid healing.
The cause of pain when pressing on the gums can also be various injuries to the gums and teeth, received, for example, when trying to crack nuts or toffee. Such injuries also need to be shown to the dentist as soon as possible, otherwise there is a possibility of an inflammatory process.
How to treat swollen gums, how to relieve swelling
Before taking any action, you need to determine the cause of the swelling (edema). This is important, since treatment tactics will be different in each case and those actions that are necessary in some cases may cause a worsening of the condition in others.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
Symptoms
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the bone associated with infection entering the root canals of the tooth and its further spread into the bone. In conditions of decreased immunity (against the background of acute respiratory infections, seasonal cold snaps, severe general diseases), inflammation in the bones can go from chronic to the acute stage, which is accompanied by an increase in the amount of pus. As a result, pain and swelling appear on the gums. Periodontitis can occur either in a previously untreated tooth or in an already treated tooth with filled canals (if the canals have not been cleaned somewhere or additional canals have not been found).
With an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, the following symptoms may occur (not necessarily all, there may only be some from the list):
- swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth;
- The swelling is small at first, but it increases over time, the mucous membrane becomes more “tense”, after a while a fistula may appear - a white bubble against the background of swelling. The fistula opens over time, pus flows out, and the swelling gradually decreases;
- pain when pressing on the gum with a finger and/or when biting on a tooth;
- the causative tooth does not respond to cold, warmth, or sweets;
- a carious cavity in the tooth (or, if the tooth has been previously treated, a large filling);
- possible increase in body temperature.
Pain and swelling with periodontitis appear due to the accumulation of pus, as soon as the pus is released (through the fistula - if without treatment, or through the root canals - if the patient went to the dentist), the pain goes away.
If the fistula has opened, the swelling has gone away, and there is no more pain, this does not mean that the problem is solved. There is still an inflammatory process in the bone and you need to see a dentist.
How is periodontitis treated in the acute stage?
It is necessary to consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis. The dentist will take an x-ray to determine the location of the inflammatory process and its size. In the future (depending on the location of the process and its size), the doctor can offer three options for further action:
- Conservative treatment is dental treatment that creates an outflow of pus through the root canals, followed by filling.
- Surgical treatment – tooth extraction and cleaning of the socket.
- Combined treatment (if there is already a large tumor, but the tooth is planned to be saved) - the tooth is treated and an antiseptic is applied under a temporary filling, and at the same visit a loosening incision is made through which the pus will come out.
Which method will be used and in what case is decided by the dentist. The treatment method depends on the location and size of the process, the condition of the tooth, further possible prospects for tooth restoration, general health and many other factors.
In parallel with each of these interventions, procedures that need to be carried out at home can be prescribed:
- rinsing with a soda-salt solution (1 teaspoon of soda and salt per glass of water);
- taking antibiotics (most often lincomycin 0.5 grams 3 times a day – 5-7 days);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (most often nimesil - 1 packet 2 times a day for 3 days).
What to do before the patient can see the dentist?
- Do not warm the swelling area under any circumstances (do not apply heat, do not apply anything);
- soda-salt rinses (the more often the better - about 10 times a day);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (nimesil);
- You should not start taking antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription - you may end up with a blurred picture of the process and the doctor will not be able to decide on the correct treatment tactics in this case;
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs should not be mixed. If you have chosen one drug, then you do not need to take others at the same time - this can be dangerous to health and even life.
Acute gingivitis, exacerbation of periodontitis (gingivitis)
Causes
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums, periodontitis is inflammation of the gums involving bone tissue. These processes occur only in the tissues surrounding the tooth, without affecting it. With gingivitis and periodontitis, the teeth themselves usually do not bother (except in cases of parallel progression of gum disease and dental disease). There are many causes of gingivitis (most often it is tartar, untreated carious cavities, incorrectly installed fillings and orthopedic structures, and bite characteristics). Gingivitis can be acute or worsened chronic; periodontitis most often has a chronic course with periods of exacerbations. Exacerbation may occur due to the following factors:
- injury to the gums with sharp objects (cuts, punctures with fish bones)
- foreign bodies in periodontal pockets (chipped tartar, bones, fibrous food)
- acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, other systemic diseases,
- frequent exacerbations of gingivitis in diabetes, diseases associated with decreased immunity,
- taking drugs that reduce immunity (corticosteroids and others).
Symptoms
With gingivitis in the acute stage, the following are observed:
- pain and swelling of the gums near a group of teeth (localized gingivitis) or the entire jaw (generalized gingivitis);
- pain when brushing teeth and eating;
- bleeding gums at the slightest impact (brushing teeth, eating hard foods);
- the gums are red, sometimes bluish;
- possible reaction to hot food;
- pain when pressing on the gum;
- the teeth are partially covered by swollen gums.
With periodontitis, these symptoms are similar and the difference will be that with gingivitis there are no radiological changes in the bone, but with periodontitis there will be a decrease in the height of the interdental septa and their pattern is not clear. Also, with periodontitis, exposure of the roots of the teeth is observed, but in the acute stage, due to edema, the roots can be covered with soft tissue.
Treatment
Gingivitis and periodontitis also need to be treated by a dentist.
The following events are held in the office:
- removal of hard and soft dental plaque (possibly using anesthesia), polishing the surface of the teeth and exposed roots;
- correction of fillings, removal of traumatic elements of orthopedic structures;
- removal of foreign bodies, if any are found;
- treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions;
- applying anti-inflammatory drugs under the bandage;
- in severe cases, patch surgery may be required - exfoliation of gum tissue, cleaning of teeth, roots, bone from stone and affected tissue, followed by suturing.
In combination with this, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and antiseptic rinses can be prescribed.
Before you have the opportunity to visit the dentist, you can take the following measures:
- rinsing with a soda-salt solution (1 teaspoon of soda and salt per glass of water) and antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, furatsilin - according to the instructions);
- Be sure to brush your teeth. They use anti-inflammatory pastes and pastes to relieve bleeding gums (Paradontax, Lakalut Active, Thebodont and others), it is advisable to use thread;
- treating the gums with anti-inflammatory drugs (the most famous is Metragil Denta) 3 times a day, after brushing the teeth and rinsing;
- if it hurts to brush your teeth, you can treat the gums with an anesthetic before brushing (Dentol and other products used in babies when teething).
If after 2-3 days there is no improvement, then you need to consult a doctor, since gingivitis can become chronic or the situation may worsen - the formation of an abscess.
Periodontal abscess
An abscess is a localized area of inflammation characterized by the accumulation of pus under the gum. In fact, this is a cavity filled with pus, which looks like a hemispherical formation on the gum. The size of an abscess can reach the size of a walnut.
Causes
The causes of periodontal abscess can be different, but the most common are:
- release of pus from chronic periodontitis in the acute stage;
- accumulation of pus due to periodontitis;
- deep trauma with a foreign object, in which the infection entered deep into the tissue (an injection with a fish bone, in which a piece of bone remained in the gum, for example).
Symptoms
- A convex semicircular formation in the gum;
- when pressing, pain, elastic tense tissues, a symptom of fluctuation (when pressing on the formation, the movement of fluid inside is felt);
- swelling of surrounding tissues;
- swelling may spread to the cheeks, causing facial asymmetry;
- possible increase in body temperature.
Treatment
Treatment of an abscess in Samara depends on the cause of its appearance. If it develops as a result of injury (as in the case of a bone), then the treatment is exclusively surgical - opening the abscess, removing purulent contents, installing drainage. If the cause is periodontitis or periodontitis, then measures are taken in parallel to treat the causative disease.
After surgery, antibiotics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines are prescribed, and after 3-4 days, when the swelling subsides and the drainage is removed, epithelializing drugs are also prescribed. This treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Need to know:
- If you notice symptoms similar to an abscess, you should immediately go to the doctor. Delaying treatment can lead to the formation of phlegmon - diffuse inflammation, which usually ends with cuts on the outside of the face, and can also lead to sepsis - blood poisoning.
- Inflammatory processes should not be heated. When heated, microorganisms multiply more actively, and this can also lead to rapid progression of the process.
How to relieve pain when pressing on the gums
Remember, only a dentist can help eradicate the pain experienced when pressing on the gums or teeth. It is important to quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and prescribe proper treatment. However, to eliminate discomfort before visiting a doctor, you can try the following methods:
- Take painkillers, such as paracetamol or analgin. The main thing is not to overdo it with such drugs, as they can be addictive and negatively affect the functioning of internal organs.
- Brush your teeth properly, trying to free the inflamed cavity from plaque and food particles.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of baking soda, furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Remember, it is strictly forbidden to warm your cheeks and gums or apply warm compresses to the sore spot. Heat can trigger more severe inflammation. Also, you should not take antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
It is also prohibited to put analgesics into the cavity of a diseased tooth. This popular method is far from safe: you can not only cause an infection, but also get a serious burn to the mucous membrane.
Treatment for gum pain
The treatment tactics for pain in the gums when pressing depends on the cause of the disease. If the pain appears due to problems with the teeth, the canals are filled or refilled. The doctor removes the source of inflammation. Advanced stages of the disease are treated with surgery and removal of the diseased tooth.
If the cause of pain in the gums when pressing is their inflammation, it can be relieved with medications prescribed by the dentist. As a rule, in such cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or other penicillin drugs. Rinse must be prescribed.
Folk remedies – decoctions of medicinal herbs – also help relieve pain and inflammation. Oak bark, chamomile, and sage perfectly remove unpleasant sensations. A solution of baking soda with a few drops of iodine also helps relieve inflammation.
Other popular methods for treating inflammation at home are:
- Propolis tincture
has antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. To prepare it, dilute a teaspoon of tincture in 200 ml of water. You need to rinse your mouth with propolis up to five times a day. - Massage with oils
has a beneficial effect on the gums. It is not at all difficult to do: apply a few drops of tea tree, eucalyptus, juniper or fir oil to the pads of the thumb and index fingers of one hand. You need to massage the gums gently for 5-10 minutes. After the massage, you should not rinse your mouth. - Aloe
also contains many anti-inflammatory components. For gingivitis or stomatitis, you can chew a fresh leaf of this plant a couple of times a day.
Treatment of gum swelling
The choice of treatment for gum swelling depends on the root cause of the problem. For example, if the gums are swollen due to caries, the disease should be treated as soon as possible. For gingivitis, the main measures are aimed at reducing the number of pathogenic microorganisms. For this purpose, tartar and plaque are removed, and then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
It is important to note that whatever the cause of the swelling, the first thing you should do is visit a dentist. Self-medication only aggravates the problem and complicates subsequent treatment. In addition, by postponing a visit to the clinic “for later,” the patient risks getting a serious complication.
Nutrition: prevention of inflammation
If gingivitis is the cause of pain when pressing on your gums, it is important to review your diet by including healthy foods in your diet. To prevent future diseases, first of all, you need to consume plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables:
- Apples and pears contain a lot of pectin, which helps accelerate tissue regeneration.
- Citrus fruits are a real storehouse of vitamin C, which also helps reduce bleeding and inflammation.
- Black currants, blackberries, and raspberries contain a large amount of minerals and vitamins that increase the body's resistance.
- Carrots, cabbage and zucchini are valuable fiber and vitamins that enhance metabolic processes in the body and accelerate tissue regeneration.
To prevent gum inflammation, professional teeth cleaning is also recommended. The procedure is carried out by a dentist and allows you to eliminate all accumulated deposits and tartar.
So, now you know the most common causes of pain in the gums when pressing. Remember: when your gums or teeth bother you, you should never put off visiting the dentist. The sooner the doctor determines the cause of the problem and begins treatment, the greater your chances of saving your teeth, gums and avoiding possible complications.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk