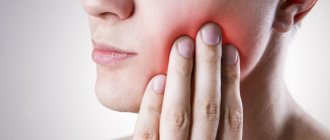
If you are concerned about inflammation of the gums in the area of the mouth where the wisdom tooth is located, it is likely that you are developing pericoronitis
. The essence of this disease is that the gums that surround the tooth become inflamed. This situation usually occurs when eruption is difficult or incomplete. In practice, this disease most often occurs when the lower wisdom teeth erupt.
The pain may increase with chewing, pressing on the tooth, swallowing, or contact with hot, sour or cold foods. A feeling of discomfort may occur when opening the mouth.
Visually pericoronitis
characterized by reddened and swollen gums located near the erupting tooth, while pus may be released from the gums, and the patient’s temperature may rise to 38 degrees.
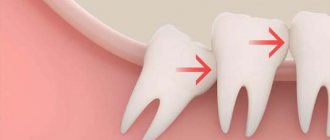
Quite often, the eruption of wisdom teeth is accompanied by complications in people, the cause of which may be insufficient space for its growth or incorrect position of the tooth in the jaw.
If a wisdom tooth does not fully erupt, a kind of hood forms over it, which is a gum that partially covers the tooth. A certain space appears between the tooth and the gum, where there are favorable conditions for the accumulation of microorganisms and food debris, which ultimately leads to the development of caries or other serious diseases.
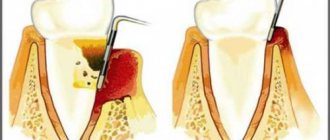
Pericoranitis is treated surgically in a dental clinic. The gum that hangs over the wisdom tooth is incised, and the resulting wound is treated with a strong antiseptic solution. If the dentist believes that such dental treatment will not bring relief to the patient, then a decision is made to remove the wisdom tooth.
Content:
- Why does the gum around the wisdom tooth hurt? 1.1. Pain due to wisdom tooth cutting 1.2. Pericoronitis as a cause of pain 1.3. Dental neck caries 1.4. Other reasons
- Signs of inflammation
- What to do at home
- Treatment
- How to avoid inflammation
If your gums near your wisdom tooth hurt, you need to visit a dentist and undergo a prescribed examination. Self-medication for painful symptoms is usually ineffective, since it is not possible to establish the true cause of the disorder. Consequently, all measures taken will be aimed exclusively at relieving the unpleasant symptom.
The main causes of pain
Painful symptoms from wisdom teeth are caused by the anatomical features of the upper and lower jaw, which are already fully formed in a person at the age of 17-25.
As the figure eight begins to grow, it puts pressure on neighboring teeth, bone and soft tissue. The growth process can last for months and even years, so pain manifestations are temporary, periodically fading and exacerbating.
The pain of tooth 8 can be provoked not only by its growth or anatomically incorrect position, but also by the presence of various pathologies, for example, caries, pulpitis, periodontitis or a wide range of infectious diseases. Note! The lack of timely professional help can provoke a worsening of the situation, which will result in the need to remove the diseased tooth and treat complications.
Why does the gum around the wisdom tooth hurt?
The inflammatory process in the area of the third molar is always accompanied by swelling and pain. This allows you to notice it immediately and begin treatment in a timely manner. Before giving prescriptions to the patient, the dentist finds out the cause of the disorder. This is necessary to eliminate the infectious focus and prevent relapse.
Radiography is used to make the correct diagnosis. In the image, the doctor sees what is happening to the tissues and how far the inflammation has gone.
The main reasons look like this:
- wisdom tooth coming out;
- pericoronitis developed;
- a carious process occurs in the cervix.
Pain due to wisdom tooth cutting
Eights can appear both at 20 and at 50. And each case is a variant of the norm. You can never predict when these units will decide to show up. You can understand that a wisdom tooth is growing by the following signs:
- increase in gum volume;
- compaction and redness of tissues;
- pain when touching the inflamed area.
It happens that a unit does not cut through for a very long time. This is possible when the volume of bone structures is too large, there is insufficient space to accommodate a volumetric crown, or the unit is in a dystopic position (then it grows to the side or at an angle).
Pericoronitis as a cause of pain
The tissue surrounding the third molar may become inflamed. Plaque actively accumulates in the hole through which the figure eight erupts. A so-called gingival hood is formed. It does not allow the unit to “pass” completely and is a suitable place for the growth of bacteria and the accumulation of food debris.
Dental neck caries
The third molar has the same structure as the rest of the oral cavity, so caries on its surface is not uncommon. Then he hurts himself or the gums near him ache.
Due to the peculiarities of the position of the unit, a person usually does not have the opportunity to examine the carious cavity. Therefore, you should visit the dentist's office. Neglected caries leads to pulpitis. Then the treatment will be much more difficult.
Other reasons
Less common causes of discomfort in the figure eight area include:
- burn of mucous membranes;
- mechanical damage to tissues;
- hormonal imbalances, long-term use of hormonal medications, thyroid diseases;
- wearing incorrectly selected or low-quality removable dentures;
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis.
Non-inflammatory pain syndrome -
If the pain syndrome is not associated with the development of inflammation, but is the result of pressure from the wisdom tooth on the teeth in front, this is an indication for taking analgesics from the NSAID group, for example, based on ibuprofen. Of course, there are also pain-relieving gels for topical use (Cholisal, Kamistad, etc.), but the effect of their use in this case will not be long or pronounced. Again, in this case, we recommend contacting a dentist (24stoma.ru).
If the wisdom tooth does not have enough space to erupt, it can cause displacement of the teeth in front, which will lead to crowding of the front teeth. The second variant of the problem is that the pressure of the wisdom tooth when erupting on the 7th tooth can lead to the destruction of the crown of the latter. Therefore, if pain occurs during teething, it is better to immediately assess the need to preserve the wisdom tooth, and in some cases it is better to remove it immediately.
→ Indications for saving the eighth teeth
Complications of wisdom tooth eruption –
- Crowded teeth – if there is not enough space for the erupting wisdom teeth, the latter begin to shift the remaining teeth towards the central incisors, causing crowding of the teeth in the frontal area of the dentition. Therefore, it is very important to assess in advance whether the length of the body of the lower jaw is sufficient for the eruption of the eighth teeth. If there is not enough space, it is better to remove these teeth preventively, otherwise you will likely need orthodontic treatment in the future.
- Destruction of the tooth in front - wisdom teeth often erupt in such a way that they have an inclined position, resting the front tubercles of the crown on the seventh tooth in front.
Constant, prolonged pressure will eventually cause the enamel and dentin to break down. As can be seen in Fig. 7, the seventh molar has a darkening in the crown area, which corresponds to the area of tooth destruction. Preservation of the seventh tooth and its full treatment in this case is impossible without removing the wisdom tooth. Figure 8 shows the same picture - number (1) shows a small area of destruction of the hard tissues of the seventh tooth, and number (2) shows the area of bone tissue destruction. In Fig. 9 you can see significant destruction of the coronal part of the seventh tooth (the area of destruction looks like a dark spot against the background of the crown, and is limited by white arrows). At the same time, the amount of destruction of the crown of the 7th tooth indicates that it must be removed.
How to ease the eruption of wisdom teeth -
If the crown of the wisdom tooth is already close to the surface of the gum, then to speed up eruption and reduce symptoms, the gum above the crown of the wisdom tooth is usually excised. That is, they make a so-called “window”. The decision about the possibility of such an intervention should be made by the dentist, taking into account the X-ray data.
In some cases, pain-relieving gels for the oral mucosa can also be recommended, for example:
- Cholisal-gel applications,
- Kamistad gel applications.
Signs of inflammation
Inflammatory reactions at the base of the third molar manifest themselves as follows:
- aching or sharp pain;
- an increase in the volume of soft tissues (they seem to increase in size, become taller);
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of the cheek;
- unit mobility;
- discomfort when pressing;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- bleeding, bad breath;
- pulsation and burning in the mouth on the affected side;
- the formation of fistulas through which pus and bloody exudate come out;
- hyperthermia of the inflamed area.
Often there are no accompanying symptoms. Then the patient complains only of discomfort at the base of the figure eight.
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
Whatever pain relief option you choose, it is important to remember that the absence of pain does not mean the absence of problems. The best option for a person with acute pain is to urgently come to the dental clinic. Moreover, acute pain is a reason for appointment out of turn and without an appointment. Timely correction of the situation - treatment or tooth extraction - will minimize the harm caused to the diseased organ of the oral cavity and the entire body as a whole.
What to do at home
If your gums are swollen and painful, and you cannot visit a doctor in the near future, you should try to reduce the inflammation and relieve the pain. For this purpose it is permissible to use:
- pain medication or NSAIDs, which can be found at the pharmacy;
- anti-inflammatory dental gel (it’s good if it contains an antibiotic);
- rinse solution with antiseptic effect.
If the pain is associated with a removable denture, then it is advisable to remove it. It is important to understand that painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs should never be taken every day. Their use should be regarded as a “one-time action” when you can’t bear the pain, and you can only see a doctor tomorrow.
It is unacceptable to use oral antibiotics to “silence” inflammation without medical advice. These are systemic drugs with a large number of side effects. Only a doctor can prescribe them during an in-person examination.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the degree of inflammation and the severity of the disease. It includes the use of:
- solutions and gels for applications;
- antiseptic compositions for rinsing;
- antibiotics;
- vasodilators.
If it’s all about the hormonal background, then it must be put in order. This process is long. Therefore, in parallel, to relieve painful symptoms, the patient can use local anti-inflammatory gels.
If caries is to blame, then urgent treatment at the dentist’s office is indicated. Often, a carious cavity in the crown of the figure eight is regarded as an indication for its removal. This is due to the difficult-to-reach location of the unit and the inability to carry out full treatment.
For pericoronitis, therapy is simple if a person consults a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. Then antibiotics are prescribed to neutralize inflammation. If pus begins to accumulate in the tissues, the patient suffers from symptoms of general intoxication, and a simple dental operation is performed. The dental surgeon cuts the gum under local anesthesia, rinses the cavity from pus and exudate and installs a drainage tube to drain the accumulated masses. The hood covering the molar is excised so that nothing prevents the unit from erupting completely.
How to avoid inflammation
Preventing a disease is always easier than treating it later. To prevent the figure eight from causing discomfort, you must:
- Maintain good oral hygiene. Getting to the last molar is very difficult, often impossible. You need to use special dental brushes, an irrigator, rinses, and floss.
- Do not take hormonal medications without a doctor's prescription. If long-term treatment with hormones is planned, you need to periodically take blood tests to monitor your health.
- Eat right, eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Once or twice a year, it is advisable to take a course of vitamins and minerals selected by a therapist. Ascorbic acid is very beneficial for gums. It does not allow increased bleeding to develop.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Because of these bad habits, the condition of the oral mucosa worsens, local blood circulation is impaired, and wounds heal more slowly.
- Massage your gums every day. You can do it yourself. First you need to wash your hands, and then use your fingertips to gently massage all areas of the mouth one by one.
- Buy a new brush every three months. Give preference to high-quality and proven pastes.
It is very useful to rinse with plain warm water after each meal. This will allow you to remove food debris in a timely manner.
If the gum tissue becomes inflamed at the base of the wisdom tooth, you should immediately make an appointment with the dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous.