Most people attribute discomfort and pain during swallowing to symptoms of a cold. However, inflammatory processes in the throat can affect not only the larynx, but also the small tongue. Often, when visiting a doctor, a patient is diagnosed with uvulitis. What does this mean, what symptoms accompany the pathology? How to treat an inflamed tongue?
Anatomical structure and functions of the small tongue
The uvula is called the palatine uvula and is a conical process that is part of the soft palate. Located in the oral cavity above the root of the tongue. The uvula consists of connective and muscle tissue, is penetrated by a large number of blood vessels, and the surface is covered with a mucous membrane.
In normal condition, the uvula is small in size. Its color matches the color of the surrounding tissues. The process performs the following functions:
- promotes the formation of various speech sounds,
- distributes food and air in the larynx,
- protects the throat from cold air flows,
- regulates gag and cough reflexes,
- prevents the penetration of foreign bodies deep into the respiratory tract,
- reduces the spread of viruses and bacteria.
What is uvulitis?
Uvulitis is an inflammatory pathology of the palatine process. The name of the disease comes from the Latin name for the small uvula – “uvula”. The disease most often begins unexpectedly, is acute and is accompanied by swelling of the soft palate. If not treated promptly, it becomes chronic.
When the uvula becomes inflamed, the size and color of the conical process changes, the throat hurts, and discomfort appears in the throat. With a significant increase, the gag reflex begins to work.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease, swelling and other signs of inflammation are insignificant. Respiratory dysfunction does not develop in patients. Clinically, uvulitis is manifested by a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, a change in voice, and discomfort when swallowing and speaking. The tongue in the throat enlarges and swells slightly. The general condition of the patients remains satisfactory.
Moderate and severe uvulitis manifests itself with more pronounced clinical symptoms. The patient experiences:
- Hyperemia and swelling of the uvula,
- Hanging it to the root of the tongue,
- Swelling and tenderness of the soft palate,
- Fever,
- Weakness, myalgia, arthralgia,
- Dysphonia,
- Hypersalivation,
- The urge to vomit
- Rhinitis.
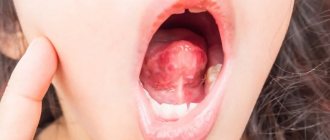
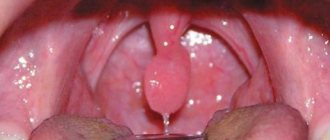
photo of an inflamed tongue in the throat
Symptoms of uvulitis occur when eating food, coughing or sneezing. Persons who have undergone adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy are most susceptible to developing the disease.
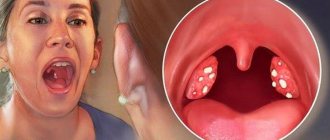
The inflamed uvula swells in the throat, becomes red and increases significantly in size. The uvula appears white when coated. In the absence of timely medical care, it can block the airways, which will lead to the development of asphyxia.
Diagnosis of uvulitis involves conducting a pharyngoscopy examination. In patients, the uvula is enlarged, swollen, and hyperemic. If it reaches the root of the tongue, a gag reflex occurs. In severe cases, the tip of the tongue becomes bluish, becomes covered with a false film, or becomes ulcerated.
Types and symptoms of uvulitis
The causes of pathology are various. Depending on the provoking factors, the following types of uvulitis are distinguished:
- Infectious. Damage to the soft palate by bacteria and viruses.
- Medication. This type of pathology is a consequence of adverse reactions after taking medications.
- Allergic. Inflammation of the uvula can manifest itself as an allergic reaction.
- Traumatic. This category includes inflammation that occurs as a result of mechanical, chemical and thermal effects on the palate and palatine process. The pathology is often complicated by infection.
Despite the different causes of the disease, all types of uvulitis have common symptoms. Chronic inflammation may not appear for a long time. The acute stage of uvulitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
Solutions for inhalation
One of the most effective methods of therapy is therapeutic inhalations. It is necessary to make a decoction based on thyme, eucalyptus oil and pine buds. 20 grams of kidneys are poured into a glass of water and boiled for 30 minutes. Then mix 10 grams of thyme with a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 40 minutes. The decoction and infusion are combined in one container and 20 grams of eucalyptus oil are added. The resulting product is poured into a nebulizer and inhaled at home.
Inhalation with vasoconstrictor drugs is also good for relieving swelling.
Main causes of pathology
Uvulitis most often develops in people with weakened immunity and bad habits - alcohol, smoking, etc. Alcohol abuse leads to drying of the mucous membrane and, as a result, to the development of the inflammatory process.
Factors that may cause the disease include:
- frequent colds and infectious diseases,
- chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx,
- throat surgeries,
- snore.
The reasons for the appearance of uvulitis in children and adults are the same:
- inhalation of toxic fumes,
- violation of tonsil removal technique,
- damage to the surface of the upper tongue with a sharp object,
- eating hot food
- purulent inflammation in the nasopharynx and oral cavity,
- pharyngitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, acute rhinitis,
- carious processes,
- benign and malignant neoplasms on the palate and small uvula,
- long-term use of potent drugs,
- allergen exposure.
Which doctor and when should I contact?
The inflammatory process is often a concomitant symptom of colds and infectious diseases, so it can be stopped by treating the underlying pathology. If the symptoms of uvulitis are not pronounced, there are no problems with breathing or eating, swelling on the small tongue is not noticeable, the disease does not require an additional course of treatment.
Uvulitis sharply worsens, so if the first alarming symptoms occur, you should consult a specialist. The treatment is carried out by an otolaryngologist. Doctor's help is necessary in the following situations:
- the disease gets worse,
- breathing is difficult due to the fact that the appendix is very swollen,
- body temperature increased to 39 degrees,
- profuse vomiting occurred due to the elongation of the uvula,
- the swollen appendage prevents the swallowing of food,
- the patient's age is less than 5 years,
- A purulent coating is noticeable on the tongue.
Diagnosis of uvulitis
During the patient’s first visit, the doctor conducts a survey to identify associated symptoms and the reasons why the appendix is swollen. Pharyngoscopy (a clinical method of examining the condition of the pharynx) is required. In most cases, the diagnosis is made based on the symptoms identified during the initial examination. To clarify the diagnosis during the second visit, the specialist may prescribe laboratory tests:
- General blood and urine tests. Diagnostics allows you to assess the general condition of the body and identify the root cause of the pathology.
- Biochemistry of blood. Allows you to find out how internal organs function and identify factors that provoke inflammation of the appendix.
- Immunogram and allergy tests. They are carried out if an allergic nature of the disease is suspected. They help identify the allergen in order to prevent future contact with it.
- Microflora smear and bacteriological culture. This is done when the symptoms of a bacterial disease are severe. The analysis allows us to identify the type of pathogenic microorganisms and choose the right antibacterial drug.
- X-ray, histological examination, computed tomography. With an enlarged uvula, these examination methods are rarely performed. Procedures are prescribed if the doctor suspects the presence of a tumor in the larynx.
Basic treatment methods
First you need to determine the cause of the disease, and only then prescribe medications. Therapy must be comprehensive in order to eliminate discomfort, remove symptoms and improve the patient’s condition as soon as possible.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Regularly carry out wet cleaning
- Ventilate the premises
- Humidify the air
- Maintain personal hygiene rules
- Use separate dishes
- Follow a diet, namely eliminate foods that irritate the throat
- Quit smoking and alcohol
The disease is treated by otolaryngologists. If the disease is caused by bacteria, then a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary.
Local treatment will help relieve swelling and reduce sore throat. For medications, you can use antiseptic sprays (Derinat, Kameton, Ingalipt), as well as gargle with decoctions of medicinal herbs or a soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per glass of water).
Antibiotics should be prescribed on an individual basis after receiving the culture results. Antibiotics from the group of macrolides, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, have proven themselves well. The most common are Solutab, Azithromycin, Moxifloxacin, Ceftazidime.
Allergic uvulitis is treated with antihistamines (Loratodine, Cetirizine, Eden, Cetrin), diuretics (Mannitol, Uregid, Furosemide), as well as glucocorticosteroids for difficulty breathing (Diprofos, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone).
The speed of recovery depends on the body’s immune system, so it is important to adhere to a proper balanced diet, drink plenty of fluids, take vitamin complexes, paying special attention to vitamin C.
Surgical intervention is possible only with the development of a paratonsillar retropharyngeal abscess, as well as with the occurrence of purulent inflammation in diseases of the dentofacial apparatus.
Treatment with medications and folk remedies
The treatment regimen is selected depending on the cause of uvulitis. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the primary pathology and reducing inflammation. The main focus is on relieving swelling, since the disease interferes with normal breathing and is life-threatening for the patient. Treatment of uvulitis is based on complex therapy and includes the use of drugs listed in the table below.
| Group of drugs | Direction of action for uvulitis | Name | Age restrictions | Contraindications |
| Antihistamines | Relieving swelling, eliminating allergic manifestations | Claritin | from 2 years | - breast-feeding, - intolerance to components, - pregnancy, - liver pathologies. |
| Diazolin | at the discretion of the attending physician | - work that requires increased attention. | ||
| Antiviral | Eliminating a viral infection | Arbidol | from 2 years | - high sensitivity to the components of the drug, - diabetes, - pregnancy. |
| Interferon | Treatment of children under one year of age occurs under the constant supervision of specialists | - cardiovascular pathologies, - disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, - severe liver damage, - bleeding in the intestines, - newborns born prematurely. | ||
| Antibiotics | Treatment of bacterial pathologies | Flemoxin Solutab | - liver pathologies, - allergy to components, - impaired renal function, - first trimester of pregnancy. | |
| Azithromycin | from 12 years old | - liver and kidney diseases, - high sensitivity to active ingredients, - cardiac pathologies. | ||
| Hormonal | Relieving severe swelling that interferes with breathing | Dexamethasone | children during active growth | — pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, - viral, fungal and bacterial infections, — AIDS, - cardiovascular diseases at the acute stage, - diabetes, - glaucoma, - severe liver and kidney diseases. |
| Prednisolone | at the discretion of the doctor | - allergies to components, - fungal infections. | ||
| Diuretics | Relieving puffiness | Furosemide | from 3 years old | - kidney disease, - pathologies of the cardiovascular system, - diseases that cause disturbances in water-salt balance, - allergic reactions to components. |
| Hypothiazide | — | - poor urine flow, - diabetes, - violation of water-salt balance, - renal failure. | ||
| Antiseptics | Eliminating infections in the mouth and larynx | Hexoral | from 3 years old | - individual intolerance to components. |
Treating uvulitis at home
Treatment at home is carried out for mild or uncomplicated disease. To do this, use medications prescribed by a doctor (antibiotics, for example), local preparations with an antiseptic, and decoctions for rinsing the mouth.
The following medications help with inflammation and sore throat:
- Hexoral (spray, lozenges). Standard course – 7 days.
- Lizobakt, Lizak (lozenges). They are allowed for children from 3 years old.
- Faringosept, Septefril, Decathylene (lozenges, tablets).
- Gevalex, Chlorophyllipt, Rotokan, Tantum Verde (solutions for frequent mouth rinsing).
It is impossible to quickly cure inflammation; it is important to regularly dissolve lozenges with an antiseptic or rinse the mouth.
The minimum course of such treatment should last at least 7 days. Antiseptic solutions are also available in the form of aerosols for irrigation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat (Ingalipt, Angistop), but they are prohibited for children under 3 years of age and persons prone to sudden laryngospasm and allergic reactions.
Inhalations and homeopathy are not effective in treating acute or chronic uvulitis.
It is highly not recommended to resort to this type of alternative medicine, especially when treating children.
On topic: Rotokan: instructions for use for gargling. Reviews. How to divorce?
Gargling with Chlorophyllipt: instructions. Reviews. How to use the product?
Prevention measures
Uvulitis is one of those diseases that can be easily treated in the early stages. However, advanced pathology poses a threat to the patient’s life. The following preventive measures help prevent inflammation of the uvula:
- timely treatment of dental diseases,
- proper oral care,
- treatment of colds and infectious diseases (including chronic ones),
- Vaccination of children according to the vaccination schedule,
- rejection of bad habits,
- adherence to the principles of proper nutrition,
- contact a specialist if the uvula is swollen.
( 1 ratings, average: 4.00 out of 5)
How to gargle with uvulitis?
Rinsing with folk remedies and medications helps reduce signs of inflammation, relieve pain, and locally fight infection. A banal soda and furatsilin solution has proven effectiveness.
The first is prepared by adding half a small spoon of baking soda to 250 ml of warm water, the second by dissolving 2 furatsilin tablets in 200 ml of water. It is recommended to rinse your mouth every 3-4 hours for at least a week.
Read more: How to gargle with soda? Proportions. Salt and iodine. Full description
How to gargle with Furacilin? How to properly dilute? Instructions and reviews
You can also use the following folk remedies for rinsing:
- solution from onion peels (a large spoon of the raw material is poured with 500 ml of water, boiled, infused for 5 hours and filtered);
- decoctions of sage, thyme, viburnum, St. John's wort;
- chamomile infusion, garlic infusion.
Rinsing with medications (Chlorophyllipt, Gevalex, Miramistin) is highly effective. The treatment regimen is drawn up by the attending physician: as a rule, 4-5 rinses per day after meals, for 7-10 days.
Prevention
In order to prevent the disease, you should avoid contact with infectious patients, observe the rules of personal hygiene, and regularly sanitize the oral cavity. To increase the body's resistance, you should eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and exercise.