Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology During the implantation of implants, local anesthesia is usually used, after which there may be no sensitivity in the lower lip and chin for several hours. This kind of insensitivity is normal. However, if after 5-6 hours paresthesia persists, then quite possibly an implantologistwho performed dental procedures, touched one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which are located in the canals of the lower or upper jaw..
Ask a question!
8
We'll call you back in 1 minute
Why does my chin go numb?
Trigeminal neuralgia
The main symptom of neuralgia is painful paroxysms provoked by shaving, tension of facial and masticatory muscles, contact with wind, cold water and air.
Involvement of the trigeminal nerve trunk is characterized by numbness of the entire half of the face, which develops during the chronic course of the pathology. Numbness of the chin is observed with an isolated lesion of the 3rd branch (n.mandibularis). Along with a decrease in sensitivity in the chin area, there is numbness in the lower part of the cheek, lower lip, lower jaw area, buccal mucosa, gums, teeth, lower half of the tongue and oral cavity. The clinical picture is complemented by peripheral paralysis of the masticatory muscles, accompanied by facial asymmetry. Possible deviation of the lower jaw in the direction of the lesion.
In 95% of cases, neuralgia develops as a result of nerve compression. The cause of compression may be a change in the diameter of the adjacent vessel in arterial hypertension and cerebral atherosclerosis. Another provoking factor is tumors of the brain and skull bones. Sometimes the disease is provoked by a narrowing of the bone canals due to chronic ENT diseases, traumatic brain injuries or dental pathologies.
Traumatic injuries
Numbness of the chin due to injuries is caused by a violation of the integrity or compression of the mandibular nerve. The symptom can be caused by damage to the soft tissues of the face in the projection of the small molars - in this place a branch of the nerve emerges from the canal of the lower jaw, providing sensitivity to the chin and lower lip. With bruises and hematomas, compression is usually observed; the symptoms quickly disappear after the swelling decreases.
With open wounds, the branch may be crossed with long-term numbness. When the lower jaw is fractured, compression or rupture of the n. alveolaris inferior, located in the intraosseous canal. The injury is accompanied by pain, swelling, hemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes, articulation disorders, and facial asymmetry. Stepping of the dentition, mobility and dislocation of teeth may be detected.
Fractures of the lower jaw
Osteomyelitis of the lower jaw
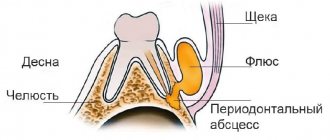
The infectious-inflammatory process develops as a result of diseases of the teeth and gums, purulent wounds, open fractures, boils and carbuncles of the face, some ENT diseases, and the spread of infection from distant foci. Accompanied by pain, fever, discharge of purulent contents from the gum pockets, limited mouth opening, and breathing problems. Chin numbness may be accompanied by a tingling or crawling sensation.
Tumors of the lower jaw
The cause of numbness in the chin is cancer of the lower jaw. The occurrence of the symptom is often caused by nerve sprouting. The pathology is characterized by early onset of pain, rapid intensification of pain to unbearable, impaired closure and opening of teeth, infiltration of the cheeks and floor of the mouth, ulceration, and bleeding. Sometimes the symptom is provoked by some intraosseous or locally destructive benign neoplasia: ameloblastoma, osteoma, osteoblastoclastoma.
Diseases of the cervical spine
In some cases, numbness of the chin is caused by muscle tension and compression of the dorsal roots of the spinal cord against the background of spinal pathologies: osteochondrosis, protrusion, intervertebral hernia, spondyloarthrosis, etc. Pain and forced positioning of the head are observed. There may be numbness of the upper limb on the affected side.
Migraine with aura
One of the variants of aura during migraine is transient loss of sensitivity in the fingers with numbness spreading to the entire limb, half of the neck, face and chin. Subsequently, a typical clinical picture of migraine is formed with pressing or throbbing pain in half of the head, slight dizziness, nausea, and increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
Shingles
The disease develops against the background of persistence of the herpes virus and is diagnosed in people who have had chickenpox in the past. Along with neuritis of the intercostal, facial and trigeminal nerves, skin rashes are observed along the listed nerve trunks. In children, catarrhal inflammation of the upper respiratory tract may be detected. Symptoms of shingles last for 2-3 weeks.
Other diseases
Sometimes numbness of the chin is determined by the following pathologies:
- Multiple sclerosis.
A characteristic feature of the disease is damage to the sensory pathways and individual cranial nerves, including the trigeminal nerve. Paresis, optic neuritis, ataxia, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs are observed. - Pernicious anemia.
Numbness of the chin is combined with sensitivity disorders in the face and limbs, muscle weakness, and changes in gait. Tachycardia, hepatosplenomegaly, and “varnished tongue” are detected. - Mental disorders
. The symptom most often occurs during hysteria. It is found in an unusual context that does not fit into the clinical picture of a certain somatic disease. In some cases, it is observed with depression.
Physiological causes of numbness
Numbness occurs with prolonged immobility. Whatever position we are in, some vessels become pinched, and we risk that the nerve endings, which do not receive proper nutrition, will lose sensitivity. Our body must move, changing the areas that have been subjected to compression, and then we will not be in danger of numbness. This usually happens during the day. But during deep sleep, we can lie in the same position for quite a long time without changing posture. And then, when we wake up, we notice that we have rested some part of our body, for example, a hand placed under our head.
Numbness is caused by exposure to cold. When in contact with cold air, the skin loses sensitivity. Local blood circulation is disrupted, and we cease to feel the nerve endings. If this situation lasts longer, frostbite is possible, but in most cases it is enough to rub the area of skin that has lost sensitivity or return to warmth, blood circulation will be restored and the numbness will go away.
If numbness occurs without an obvious connection with a specific situation, then it probably has a pathological cause.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist. According to indications, the patient is referred to a dentist, maxillofacial surgeon or hematologist. To clarify the cause of chin numbness, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- Neurological examination
. With neuralgia, trigger points are determined at the exit points of the nerve branches. A comprehensive study of sensitivity, reflexes and muscle strength can detect neurological deficits indicating damage to brain structures. - Dental examination
. Informative for injuries, osteomyelitis of the jaw. It makes it possible to confirm the presence of a fracture and identify the disease that provoked the development of a pathological process in the bone. - Radiography
. In case of injuries of the maxillofacial area or osteomyelitis, photographs of the lower jaw are taken. If damage to the spinal column is suspected, an X-ray of the cervical spine is performed. - CT scan
. It is used to clarify the volume and localization of traumatic and inflammatory foci in the area of the skull and lower jaw, and to detect degenerative processes in the spine. Effective in identifying narrowing of the canals through which the trigeminal nerve passes. - Magnetic resonance imaging.
Recommended for cerebral tumors. Visualizes cysts and neoplasms. To confirm the vascular etiology of nerve compression, MR angiography is prescribed. - Lab tests
. For pernicious anemia, a biochemical blood test, tests for antibodies to intrinsic Castle factor and gastric parietal cells are indicated. In case of tumors, a morphological study is necessary to establish the nature and degree of differentiation of neoplasia. In inflammatory processes, culture of the discharge is required to determine the microflora.
Physiotherapy
In what cases should you consult a doctor if you have numbness?
If the numbness has a physiological cause, that is, caused by a temporary disruption of the local blood supply, then it is enough to change the position and rub the numb area, and sensitivity will be restored. If the numbness does not go away, then the cause is more serious and you should consult a doctor.
It is necessary to get emergency medical help if numbness is accompanied by symptoms of damage to the central nervous system:
- headache, dizziness, attacks of weakness, double vision, loss of coordination;
- unexpected bowel movements or sudden urination;
- speech problems.
These symptoms may occur after a head, neck, or back injury.
You should also consult a doctor if:
- numbness occurs periodically and without an obvious reason;
- thermal perception is impaired (for example, the ability to distinguish between warm and cold water is impaired);
- Numbness is preceded by pain and loss of range of motion in one of the joints.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics depend on the causes of chin numbness. Patients with trigeminal neuralgia are prescribed anticonvulsants. The dosage is gradually increased until a therapeutic effect is achieved. Reception is continued for several months, and then the dose is gradually reduced. The regimen is supplemented with antihistamines, antispasmodics, and means to improve microcirculation. Blockades are performed according to indications. Among the effective physiotherapeutic techniques are diadynamic currents, galvanization, and ultraphonophoresis.
To relieve a migraine attack, NSAIDs are used; in severe cases, drugs from the triptan group are used. For repeated vomiting, antiemetics are used. To prevent paroxysms, long-term treatment with antidepressants and anticonvulsants is carried out. For herpes zoster, antiviral therapy is administered with acyclovir. Mental disorders are corrected with the help of psychotherapy, sometimes in combination with psychotropic drugs.
Antibiotics are indicated for wounds, open fractures, and osteomyelitis of the jaw. First, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used, and later the medication is replaced taking into account the antibiotic sensitivity of the pathogen. Patients with pernicious anemia require lifelong treatment with B12 drugs, elimination of conditions that led to the development of vitamin deficiency.
How to tell if you have dystonia
People who live with vegetative-vascular dystonia for quite a long time get used to their symptoms if they do not manifest themselves as crises and do not disrupt the normal course of life.
They learn to live with headaches, endure periodic numbness in their arms or legs, sometimes suffer from rapid heartbeat, and know that when the weather changes, they may experience insomnia. The rest of the time, VSD does not make itself felt and does not cause life-threatening conditions. But some manifestations of dystonia feel truly scary. A lump in the throat and a feeling of lack of air, palpitations and fear during panic attacks, sudden loss of consciousness, pressure changes. If after such an incident you were examined and no dangerous diseases were found, then with a high probability we can talk about VSD.
Numbness of the limbs with dystonia is usually associated with an unpleasant experience. Such a reaction of the body can occur even in anticipation of a pleasant event, from an excess of emotions.
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
If the upper or lower jaw, as well as the lips, tongue and chin, go numb, then the reasons for this phenomenon may lie in an acute lack of B vitamins. With their deficiency, the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted. To replenish the body’s “pantry” with B vitamins, you need to include foods such as nuts, beans, chicken, cheeses and cereals in your diet.
“My lower jaw constantly went numb during pregnancy. I complained to the doctor, but she said that this happens often. Pregnant women have metabolic disorders and slow blood flow, and they are always lacking vitamins and minerals. To correct the situation, I took all sorts of vitamins as prescribed by the doctor, had a massage, and tried to eat right. BUT nothing helped. I already began to suspect some serious abnormalities in my health, I donated blood, but the tests were normal. Everything went away a few weeks after giving birth!”
Alina I., review from babyblog.ru
Lack of vitamins also contributes to jaw numbness
Inflammatory process on the root of the tooth
If you are wondering why the lower jaw is numb, then the first thing you need to pay attention to is the condition of the oral cavity. An unpleasant symptom can be caused by dental diseases such as periodontitis and a cyst on the root of the tooth. Then, in addition to discomfort, a slight tingling sensation may be observed in the jaw and chin area, as well as pain when pressing or chewing food on the causative tooth.
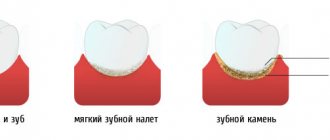
The photo shows a cyst