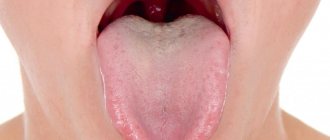
The tongue in the throat is a small process that in its natural state is not felt at all. The situation when the tongue in the throat is swollen takes on completely different symptoms. The person feels discomfort and severe pain.
Swelling of the tongue in the throat (pathology uvulitis) is a clear symptom of infectious diseases, burns, injuries and even oncological processes in the body. It is very important to determine the cause of uvulitis as soon as possible. Delay stimulates the development of severe complications that pose a serious danger to human life.
Content:
- Liver
- Stomach
- Heart
- The immune system
- Nervous system
- Alcoholic delirium is a dangerous symptom complex after binge drinking
After taking a large dose of alcohol, the condition always worsens.
The next day the person feels exhausted, lethargic, suffers from severe headaches and muscle weakness. But in the absence of alcohol dependence (subject to one-time use of alcohol), negative symptoms usually go away quite quickly - within 24 hours. Symptoms after a long binge are always more painful. It's difficult to get rid of them. This is because severe ethanol intoxication develops. To eliminate it, it is necessary to conduct complex detoxification therapy in an inpatient drug treatment clinic.
When talking about the symptoms that plague addicts after binge drinking, narcologists always focus on changes in the functioning of internal organs. Particular attention is paid to malfunctions:
- liver;
- stomach;
- immune system;
- central nervous system.
Diagnosis of liver dysfunction due to coronavirus
The onset of most liver diseases is asymptomatic until serious damage to the organ tissue, which subsequently requires long-term treatment.
Diagnostics of all liver functions can detect organ diseases in the early stages, when the problem can be solved faster and more effectively. Therefore, as a rule, after recovery from coronavirus infection and in the absence of the symptoms described above, it will be enough to take a liver test.
A biochemical blood test for basic liver parameters, such as bilirubin (direct and total) and liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and alkaline phosphatase), will assess how well the liver copes with its functions . Thus, a significant increase in bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia) is often observed in patients with coronavirus infection.
Alanine aminotransferase is an enzyme of liver cells. When liver cells are damaged, the level of ALT in the blood rises. A significant increase in ALT levels (more than tenfold) is usually associated with acute toxic liver damage. A slight increase in ALT levels is characteristic of liver damage due to infectious diseases.
AST is one of the main indicators in identifying liver pathologies. Not only the content of these substances is important, but also the AST/ALT ratio, which is normally 1.33 ± 0.42. Thus, in patients with different forms of coronavirus infection, there was a significant increase in the activity of the liver enzymes ALT and AST. Typically, mild or asymptomatic coronavirus infection causes a short-term increase in ALT levels without significant impairment of liver function.
An increase in alkaline phosphatase most often signals a violation of the outflow of bile and difficulty in bile secretion.
GGT is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids. Most often, an elevated GGT level in the blood serum indicates a difficulty in the outflow of bile, as well as intoxication caused by drugs.
If there are one or more deviations in the above parameters, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the functional state of the liver.
, a prothrombin test can be prescribed to assess the condition of the blood coagulation system.
Additionally, it is necessary to evaluate the liver’s ability to synthesize cholinesterase and cholesterol, as well as conduct a study of protein fractions in the blood (proteinogram).
If necessary, a gastroenterologist or therapist will prescribe an ultrasound or tomography to more accurately assess the size and structure of the liver, bile ducts and gallbladder. If an oncological process or fatty degeneration of the liver is suspected, the doctor may additionally prescribe a biopsy.
Liver
Many symptoms after heavy drinking are associated specifically with liver damage. Alcohol has a toxic effect on the organ, as a result of which individual tissues begin to die. In advanced cases, cirrhosis and hepatitis develop.
that the liver is not in order :
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth (more often appears in the morning on an empty stomach);
- the appearance of a jaundiced skin tone;
- bloating;
- nausea (worsens after eating fatty foods).
If, along with the standard symptoms of a hangover after binge drinking, signs of liver pathology appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Delay is fraught with dangerous complications.
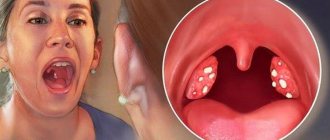
Swollen tongue in the throat: causes and treatment. How to relieve inflammation?
- This condition may be accompanied by increased pain in the larynx, if you move the tongue and breathing is disturbed, it becomes difficult and confused.
- In the list of diseases, this pathology is called uvulitis and means acute inflammation of the tongue.
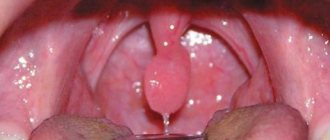
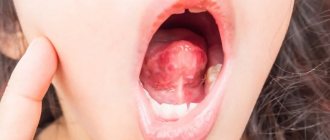
- In this case, the tongue changes color from soft pink to intense purple, covered with a thin whitish film-like coating, and becomes noticeably larger (may hang down to the root of the tongue).
Sometimes it becomes so deformed that it interrupts the pronunciation of certain sounds and causes vomiting. The causes of this pathology are different, and all of them must be eliminated immediately.
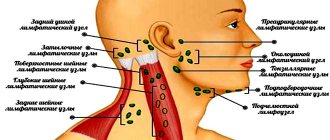
The palatal tongue is the removed tongue, which is located in the mouth, on the edge of the soft part of the palate, just above the tongue, is in good condition, small in size and color, and is identical to the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Performs important functions for the body:
- protects the nasopharynx from the penetration of food during swallowing;
- separates air flows and heats them;
- is a barrier against infections;
- prevents accidental regurgitation of food;
- causes spasm of the larynx, preventing a person from suffocating;
- participates in the production of some sounds;
- if necessary, induces vomiting.
Why the tongue in the throat swells: reasons
When the soft palate is clear and the tongue is inflamed, the red doctor diagnoses uvulitis. Basically, it is an acute disease characterized by suddenness - pain and swelling occur while eating or even at night while sleeping. The reasons for this are, among others:
- Inflammatory pathologies - ENT infections, angina pectoris, advanced dental diseases, abscesses, diphtheria, tuberculosis, sexually transmitted diseases, HIV;
- chemical or thermal damage to the mucous membrane as a result of exposure of tissue to aggressive compounds (caustic or acid burns) and consumption of hot food and alcohol;
- allergies - if allergic products are contained in food, inhalation of allergens (chemicals, natural irritants), taking medications;
- allergies and sore throat - polyps, cysts. In addition to the immediate causes, there are associated factors that influence the expansion of the tongue in the throat. These:
- a stuck bone in the throat, injuring the mucous membrane;
- consumption of low-temperature drinks and food;
- consequences of instrumental manipulations during respiratory and gastrointestinal examinations and dental operations;
swelling of the tongue can occur after vomiting, especially after prolonged and repeated bouts, after snoring and in people who smoke a lot.
Stomach
If you abuse alcohol, gastric pathologies will occur. They are characterized by:
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- rapid weight loss;
- frequent belching;
- constipation alternating with diarrhea;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- repeated vomiting.
Dangerous complications of prolonged binge drinking are pancreatitis, inflammation of the pancreas. Such problems have specific symptoms:
- pain under the ribs;
- inability to reduce discomfort by changing body position;
- vomiting immediately after eating food or taking medications.
The pancreas needs to be treated urgently. Otherwise, its necrosis may develop, which will lead to death.
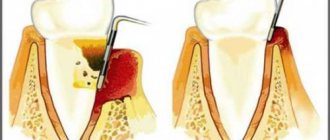
How is the operation performed at CELT?
In order for the removal of the uvula to have exclusively positive consequences, it must be carried out in a multidisciplinary CELT clinic. Before prescribing this operation, our specialists carry out a comprehensive diagnosis, which allows us to make a correct diagnosis. The operation itself can be performed using different techniques. The most effective and least traumatic for the patient are radiosurgery and laser techniques. These methods help avoid bleeding and reduce postoperative trauma.
Heart
Jumps in blood pressure, pain in the left chest, difficulty breathing - all these are symptoms after binge drinking, indicating disturbances in the functioning of the heart. Ethanol and its toxic metabolites destroy the myocardium, promote vascular stretching, and trigger reactions that provoke fibrosis.
In heavy drinkers, the veins become very fragile and easily damaged. The blood thickens, causing red blood cells to stick together. Then blood clots form. All this leads to:
- Arrhythmias, tachycardia. Heart beats too fast. An alcohol addict feels a pulsation in his temples and weakness. He may lose consciousness.
- Ischemic disease. When blood flow in the coronary arteries is disrupted and when they spasm, the death of individual zones of the myocardium occurs. Then the addict complains of pain behind the sternum, which radiates to the left shoulder blade or arm.
- Cardiomyopathies. An insidious condition that contributes to heart failure. Its appearance is indicated by swelling in the face, legs, and difficulty breathing.
- Arterial hypertension. Vascular spasms, blood clots, thickened blood - all these are prerequisites for arterial hypertension. Very often, after a binge, blood pressure rises sharply. It's hard to knock him down. It can reach a hypertensive crisis.
Any heart problems should be treated under the supervision of a doctor. Carrying out self-therapy, an alcoholic risks dying.
Treatment of a swollen tongue in the throat
Inflammation of the tongue in the throat is a rather unpleasant symptom that can be a sign of various diseases. The tongue is located at the back of the soft palate. In its normal state it is small and its presence is usually not felt.
The inflammatory process associated with the expansion of the tongue and its swelling is called uvulitis. This is a rather unpleasant symptom, which is also life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Problems with swallowing food;
- Hoarseness,
- Language problems;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Increased salivation.
The problem usually occurs in the morning, right after sleep, so it can cause serious anxiety, which only worsens the patient's condition.
If you experience the symptoms described above, you should carefully examine your mouth and throat. If the tongue is grown, swollen, red or cyanotic, then it is very likely that uvulitis is present in the nasopharynx.
Causes
There are many reasons why a tongue can grow. The cause may be an unpleasant symptom:
- inflammatory processes caused by viral or bacterial infections;
- allergies;
- injuries;
- chemicals;
- thermal factors;
- tumors localized in the nasopharynx.
Viral or bacterial infections are rarely accompanied by inflammatory reactions, which can enlarge the tongue. This most often occurs when the inflammatory area is located close to the roof of the mouth and the swelling affects the adjacent soft tissue.
The high pathogenicity of bacteria that cause pathology and significantly reduce the body's protective functions can lead to the inflammatory process in the throat affecting the tongue. Possible increase in size and swelling of the tongue:
- Inflammatory gland infections;
- Inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, for example, rhinitis, pharyngitis, adenoiditis;
- Throat abscess;
- Purulent inflammatory processes in the mouth, gums and teeth, for example. dentistry, gingivitis, periodontal diseases;
- infectious diseases such as diphtheria and mononucleosis, which cause inflammation of the soft tissues of the neck, enlarged lymph nodes, and plaque on the tonsils;
- inflammatory processes of the salivary glands;
- various diseases such as syphilis and tuberculosis
Important! If swelling of the tongue is caused by the above reasons, then the unpleasant symptom is usually preceded by clinical manifestations characteristic of the underlying infection.
In this case, the patient complains of painful swallowing, tightness in the throat and difficulty breathing.
Often the cause of inflammation of the tongue in the throat is cancer. Cancer and other types of benign and malignant neoplasms can affect the surface of the mucous membranes of the throat and mouth.
Considering the statistics, tongue cancer pathologies account for about one and a half percent of the total number of nasopharyngeal cancers, while swelling of the soft palate can also occur in tumors of surrounding organs and tissues.
Exposure to high or too low temperatures can lead to burns of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and cause inflammation of the tongue. Inhalation of vapors from various chemicals can also cause damage to the nasopharyngeal organs.
Hot food and drinks, strong alcohol are irritants in this situation.
Damage to the mucous membrane occurs not only as a result of direct burns, but also as a result of excessive dryness in the oral cavity.
Important! Accidental use of acetic acid, various chemical essences and rinsing with a highly concentrated soda solution can lead to tongue burns.
In case of allergies, the tongue in the throat often becomes enlarged and swollen. Allergies can be caused not only by food, but also by household chemicals, pollen and wool.
The fact that swelling of the tongue is caused by allergies should be taken into account by people prone to allergic reactions. In this case, an enlargement of the palate may be accompanied by urticaria, allergic dermatitis, and swollen angioedema.
In such a situation, symptoms develop quickly, swelling occurs against a satisfactory background of health.
Inflammation of the tongue can also occur as a complication after taking medications. In this case, allergic inflammation of the tongue is often accompanied by itching, rashes, swelling of various parts of the body and difficulty breathing. The reaction usually occurs as a result of topical application of a particular drug or injection of a drug.
Swelling of the tongue can also occur as a reaction to chemotherapy during cancer treatment.
The palate consists of a large number of small blood vessels, so inflammation develops quickly and causes significant swelling.
- damage to soft tissues from hard food;
- constant vomiting, especially in situations where it is caused artificially;
- damage to the tongue during medical procedures such as throat scans, dental examinations;
- snoring, which can cause swelling due to air vibrations;
- excessive craving for cigarettes, hookah;
- hereditary diseases such as angioedema.
Diagnostic features
In the case of inflammation of the tongue, the diagnostic procedure is usually simple. A specialist can determine the cause of an unpleasant symptom by analyzing only the patient’s symptoms and conducting an examination. If the diagnosis requires clarification, additional procedures are used.
- General blood analysis. This procedure helps determine the nature of the disease, excluding or confirming the presence of infection. For example, an infectious disease increases the number of white blood cells, while the allergic nature of the symptom increases the number of eosinophils in the blood.
- Culture of bacteria to determine the microflora that caused inflammation of the tongue will help determine the type of pathogen and its susceptibility to basic antibiotics.
- If your doctor suspects an allergic reaction, an immunogram or allergy diagnostic test may be needed.
- To rule out cancer, the doctor may order a histological examination of the tongue tissue, x-rays or tomography.
Important! If the tongue is very enlarged and prevents full breathing, you should immediately seek medical help from specialists.
The immune system
Symptoms after binge drinking associated with decreased immune defense are:
- weakness, insomnia, inability to focus on anything;
- exacerbation of existing chronic diseases;
- development of acute pathologies;
- pale skin;
- hair loss;
- decreased appetite.
The immune system fails after heavy drinking, as the body cannot function normally under conditions of constant ethanol attack. The situation is aggravated by poor nutrition - during drinking sessions, alcoholics eat anything.
Conclusion
Based on the statistical analysis of the comparison of two groups of patients who underwent bilateral tonsillectomy, in patients who received, in addition to the anesthetic drug ketorolac, Arnica Montana C9 (BUARON) for resorption, 5 granules 3 times a day from the 2nd day, the recovery time was significantly reduced . This is indicated, in particular, by a faster time for normalization of body temperature, disappearance of pain and a decrease in the inflammatory reaction in the pharynx after tonsillectomy. This may have a positive effect on the quality of life in the early postoperative period of patients taking the drug Arnica Montana C9 (BOIRON).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Nervous system
The central nervous system is depleted under the influence of high doses of alcohol. Then an alcohol addict trying to break his binge is faced with:
- insomnia, too light sleep;
- mood swings;
- uncontrolled aggression;
- inability to adequately perceive what is happening around;
- apathy;
- depression;
- visual, auditory and tactile hallucinations;
- memory loss;
- epileptic seizures;
- delusional;
- panic attacks.
Often, binge alcoholics behave in ways that pose a threat to others. They see their relatives as monsters who need to be killed, and they make attempts to do so. It is important not to treat mental disorders at home - this is impossible. The first thing to do is call a drug treatment ambulance, which will take the patient to the hospital.
The essence of pathology
- The uvula is a part of the soft palate, a conical process that performs the following functions:
- – protects the mucous membranes of the pharynx from exposure to cold air;
- – prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria;
- – when the need arises, pressing on the palatal tongue provokes a gag reflex;
- – takes over and distributes air and food flows.
Under the influence of external irritating factors (allergens, bacteria, mechanical and thermal damage), the body reacts when this organ increases to such a size that a person’s life is threatened. The process when the uvula becomes inflamed is diagnosed as the development of the disease uvulitis.
Swelling of the uvula contributes to the development of severe complications associated with the functions of breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
Symptoms
- Signs that the tongue in the throat has enlarged are pronounced, manifested in the form of:
- – active secretion of saliva;
- – wheezing and hoarseness;
- – pain (increases during swallowing and talking).
- Swelling of the tongue in the throat, provoked by an allergic reaction, manifests itself in the form of:
- – debilitating cough or sneezing;
- – tearing;
- – sensations of constant tickling of the root of the tongue;
- – a rash may appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- When your throat hurts and your tongue is swollen due to an infection, the pathology manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- – feeling of weakness;
- – chills or fever;
- – discomfort and pain when swallowing and speaking;
- – sensations of dry mucous membranes of the throat;
- – possible purulent lesions of the oral mucosa.
Causes of pathology
- The causes of swelling of the uvula are varied.
Inflammation can be caused by: - – diseases of an inflammatory nature (the process is activated when the human immune system is unable to fight a large number of bacteria in the growth cavity);
- – chemical, mechanical and thermal damage to mucous membranes;
- – uvulitis as a reaction to contact with an allergen;
- - formations localized in the nasopharynx.
Allergic uvulitis
Prolonged contact with household, chemical, and food allergens is one of the causes of a swollen tongue in the throat. Most often, edema is diagnosed in severe allergic reactions: Quincke's edema or urticaria.
Important: when the first symptoms of an allergy appear, the patient must be immediately taken to a doctor.
Allergies can also cause swelling of the uvula in the throat in asthmatics. Long-term use of medications may cause allergic swelling of the tongue in the throat. Swelling caused by an allergy to medications develops immediately after injections or use of the medicine.
The cause of uvulitis can be an allergy to certain foods: honey, chocolate, citrus fruits. Important: before taking any action to eliminate the swelling of the tongue in the throat, it is important to establish why it is swollen and what (what allergen) causes the disease.
Getting burned
One of the reasons why a small tongue in the throat may swell is a burn. A person swallows large pieces of hot food or suddenly drinks hot liquid, as a result of which blood actively rushes to the tongue and swelling develops. The patient feels very unpleasant pain.
A burn to the mucous membrane and swelling of the tongue in the throat can cause solutions of alkalis or acids to enter the oral cavity. For example, swelling can be caused by rinsing with a strong soda solution or accidentally swallowing vinegar.
Complication of sore throat
Inflammation of the small uvula in the throat as a complication of sore throat is a dangerous condition. Swelling causes the following symptoms:
- - cardiopalmus;
- – difficulty breathing, swallowing and speaking;
- – pain in the throat and ears;
- – wheezing, cough;
- – blue discoloration of the skin (a sign of lack of oxygen).
Ignoring these signs or delaying medical care can cause asphyxia. It is necessary to eliminate swelling in severe sore throat as quickly as possible.
Infectious lesion
Penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the nasopharynx area can provoke inflammation of the uvula in the throat.
The most common cause of swelling of the tongue in the throat is infection:
- Staphylococcus aureus. Provokes a severe inflammatory process of purulent uvulitis. It is difficult to treat with antiseptics and antibiotics.
- Streptococcus. Provokes the development of a mild, sluggish form of uvulitis.
- Herpes virus. Affects the entire body with pathogenic elements. Inflammation of the uvula in the throat is most often provoked by Epstein-Barr infections and cytomegalovirus.
- Chlamydia, gonococci and other pathogenic structures. It provokes uvulitis if there has been sexual intercourse in the recent past.
- Human papillomavirus. More than 500 strains of this virus are known, most of which provoke not just swelling of inflammation, but malignant formations.
Most often, swelling of the uvula is a consequence of damage to the body by infectious diseases, a signal of weakened immunity. As soon as the body's defenses weaken, infections affect the oral cavity, throat (palatal tongue), and provoke an inflammatory process.
Excessive alcohol consumption and frequent smoking
The palatine tongue is covered with multiple small blood vessels, which, irritated by tobacco smoke during active smoking and alcohol due to excessive consumption of alcohol, become inflamed.
Also, abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products reduces the body's resistance to pathogenic bacteria and can cause burns.
What is the danger?
The uvula protects the respiratory organs from food particles entering them, distributes warm air, activates processes provoked by the gag or cough reflex, and participates in spoken speech.
Acute processes of inflammation of the uvula affect the surrounding soft tissues of the oral cavity, which is not just accompanied by unpleasant sensations, but sharply worsens the general physical condition of the patient and provokes breath holding.
Ignoring the pronounced symptoms of the disease can cause asphyxia.
- Swelling of the throat and tongue can provoke a number of negative changes in the body:
- – difficulties in speaking;
- – clogging of the respiratory system with food particles (this case requires an immediate response and can lead to respiratory arrest);
- – damage by infections and bacteria to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- – constant unpleasant feeling of nausea, gag reflex;
- - inflammation of both tonsils.
- Important: swelling of the nasopharynx and palatal tongue is life-threatening and therefore requires prompt medical attention.
Diagnostics
- An ENT specialist conducts diagnostics and determines treatment options (and, if necessary, surgery).
- During the appointment, the ENT doctor:
- Examines the oral cavity for the presence of pathological structure and the presence of foreign objects.
- Collects the patient's medical history.
- Clarifies the location of the pain, the intensity and nature of the pain, the severity of the symptoms.
The doctor can confirm the suspected diagnosis based on the results of the following studies:
- Laboratory blood test.
- Bacterial blood test.
- Immunogram (helps determine the presence of allergies).
- Histological examination of the mucous membranes and tissues of the uvula (recommended if cancer is suspected).
Drug treatment
Only an ENT doctor can determine how to treat pathological processes in the throat. This is due to the high risk of side effects on the respiratory system when taking incorrectly selected medications.
Antihistamines
Treatment of uvulitis caused by an allergic reaction involves eliminating contact with the allergen and taking certain medicinal antihistamines. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications: Claritin, Diazolin, Fexofenadine, Suprastin.
- The tongue in the throat can swell under the influence of various allergens, therefore only after the type of allergen has been determined can one decide what to do next.
- Important: in case of severe allergic reactions (for example, angioedema), the doctor may decide to perform a tracheotomy procedure.
Diuretics
Taking diuretics (water medications) helps relieve swelling of the small tongue in the throat. The patient is prescribed: Veroshpiron, Chlorthalidone, Furosemide.
Glucocorticosteroid drugs
Taking glucocorticosteroid drugs: Betamethasone, Hydrocortisone will help prevent the development of breathing and swallowing complications with an enlarged tongue in the throat. These medications contain an anti-inflammatory component, which reduces capillary permeability and stops the development of edema.
Taking antibiotics
The situation when the tongue in the throat has enlarged due to bacterial infection requires taking antibacterial agents: Azithromycin, Timentin, Vilprafen.
Important: antibacterial drugs are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor. Only a specialist can determine exactly the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process and prescribe an antibiotic that is sensitive to this bacterium.
Therapy using traditional recipes
The use of traditional medicine in combination with traditional medications helps speed up the healing process if the tongue in the throat is swollen.
Important: traditional medicine must be taken strictly in combination with the dosage calculated by the doctor.
Herbal decoctions
To quickly relieve inflammation of the tongue in the throat at home, gargling with medicinal herbs will help reduce pain:
- Raspberry decoction. For a liter of water you need two tablespoons of dry raspberry leaves. The raw materials are steamed and left to simmer on the stove for twenty minutes. The prepared broth is cooled, filtered and used as directed at least three times a day.
- Chamomile and sage decoction. To prepare a decoction, you need to take one tablespoon of dry herbs per liter of water. The broth is brewed and left to brew for at least fifteen minutes. After the broth has cooled, filter it and gargle at least three times a day.
- Viburnum decoction. A spoonful of dry berries is poured with boiling water (one liter) and simmered over low heat for half an hour. Afterwards, gargle with a lukewarm decoction. This remedy is good for removing ulcers on the tongue.
Important: before using medicinal plants, you should consult your doctor about possible allergic reactions.
Inhalations
- Carrying out the inhalation procedure will speed up the treatment of laryngeal edema, swollen tongue in the throat, and inflamed tonsils.
- Recipe for decoction for medicinal inhalations:
Mix two tablespoons of pine buds with water. Boil the mixture for half an hour. Separately, boil the dry thyme leaves. Mix the resulting decoctions in a bowl and add a few drops of eucalyptus oil.
Medicinal tinctures
Medicinal tinctures will help to quickly cleanse the mucous membranes of the mouth from pathogenic microorganisms and relieve swelling of the tongue in the throat. Also, taking tinctures is indicated for the purpose of quickly removing toxins from the body and improving the general condition of the patient.
Recipes for the most effective medicinal tinctures:
- Rosehip tincture. Place a few tablespoons of dried rose hips in a thermos and pour half a liter of boiling water. The thermos is tightly closed and left to infuse for at least twelve hours. The tincture is drunk in small sips throughout the day.
- Anise tincture. In a bowl, combine half a glass of crushed anise and water. The mixture is heated and boiled for several minutes. Then add two tablespoons of honey and the same amount of cognac. Infuse the resulting product for twenty-four hours. Afterwards, the tincture is taken one tablespoon, several times a day, before meals.
In combination with traditional drug therapy, taking herbal tinctures can speed up the process of treating an inflamed tongue in the throat.
Preventive recommendations
- The following preventive measures will help prevent inflammation of the tongue in the throat:
- – timely diagnosis and high-quality treatment of ENT pathologies and infections of the mucous membranes of the growth cavity;
- – careful and regular oral hygiene;
- – health control and prevention of injury to the mucous membranes of the growth cavity;
- – giving up bad habits: alcohol and smoking.
Important: if symptoms of uvulitis appear, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. Errors in treatment actions taken can aggravate the course of the pathological process and provoke complications.
Alcoholic delirium is a dangerous symptom complex after binge drinking
Drinking alcohol for a long time and never experiencing delirium tremens is impossible. Sooner or later, any addict experiences all the horrors of this condition. You can recognize it by its symptoms:
- increasing level of anxiety;
- increased sweating;
- severe weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- blood pressure surges;
- tachycardia;
- involuntary trembling of the limbs.
A little later, hallucinations begin. A person cannot calm down or fall asleep. Due to strong excitement and uncontrollable actions, it becomes dangerous for those nearby.
Narcologists know of many cases where addicts, being in a state of “delirium tremens,” killed, robbed, attacked random passers-by, and attempted suicide. Delirium after binge drinking requires competent drug treatment and psychiatric treatment.
Binge drinking is a very big burden on the body. Even young and healthy people who abuse alcohol quickly turn into mentally ill and disabled people. Don't bring yourself to this state. If the craving for drinking has become irresistible, go through coding. Save your life!
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Uvulotomy
I would like to express my deep gratitude to otolaryngologist G.G. Zharova.
(doctor of the highest category) This is a Man and a Doctor with a capital letter. She is very attentive to people, gives the necessary recommendations, and prescribes treatment. Competent specialist. Galina Gennadievna not only confines herself to her area, she knows... Read full review Inga Vladimirovna M
17.12.2021
In July I had surgery to correct the nasal septum with Dr. Vasily Gennadievich Gogolev. The surgery went well and the recovery was quick and painless. Many thanks to Vasily Gennadievich for his golden hands!!! Read full review
Anastasia
30.10.2021
Literature:
- Alcoholism / Donald W. Goodwin; [Transl. from English B. Pinsker]. - M.: Olimp-business, 2002. - XII, 224 p.;
- Endogenous intoxication syndrome (manual) / S. G. Musselius. — Ed. 2nd, revised and additional - Moscow: Author's book, 2019. - 356 p.
- Chronic alcohol intoxication / A. Ya. Grinenko et al. - St. Petersburg: R. Aslanov Publishing House: Legal Center Press, 2007. - 537 p.
- Mental illnesses: clinic, treatment, prevention: [Ref. a manual for neurologists, psychotherapists and doctors of other specialties] / Tyuvina N. A. - M.: Publishing house. house "KRON-press", 1997. - 250 p.
How does Covid affect the liver?
Scientists have found that coronavirus directly affects the human liver , as pathological studies in patients with COVID-19 confirmed the presence of the virus in liver tissue.
According to scientists' research, the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters the host cell through the interaction of its S protein and the human membrane protein ACE2 . The ACE2 receptor is widely distributed in the cells of the heart, pancreas, intestinal epithelium, kidneys, endothelium of blood vessels, etc., so infection with coronavirus leads to systemic damage to the human body.
Studies have shown that the epithelial cells lining the bile ducts (cholangiocytes) contain the membrane protein ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to ACE2 on cholangiocytes, leading to their dysfunction. As a result, liver cells are destroyed. Under the influence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the barrier and transport function of bile acids of cholangiocytes deteriorates. Which leads to inflammation of the liver and the appearance of blood clots in the vessels of the organ.
In addition to direct damage to the liver by the coronavirus, damage to the organ occurs due to a violent immune reaction of the body , resulting in a powerful release of cytokines (proteins that are produced by immune cells in response to infection entering the body).
When cytokine levels are high, systemic inflammation develops : the more cells there are, the more cytokines are released, which means more new immune cells arrive. , reactive hepatitis may develop .
Liver damage due to coronavirus also occurs due to hypoxia (oxygen starvation), which develops against the background of pulmonary failure . Hypoxia that occurs during pneumonia is the cause of ischemic liver damage in patients with coronavirus infection. A decrease in oxygen content under hypoxic conditions can lead to the death of liver cells.
Also, complications on the liver after coronavirus are caused by medications : antibiotics, antiviral, antipyretic, hormonal, anti-inflammatory and drugs of other groups used in the treatment of COVID‑19. Many of the medications that are recommended for the treatment of coronavirus have a toxic effect on the liver, thereby causing liver damage.
The course of coronavirus infection is closely related to the degree of liver damage. In mild or asymptomatic cases of COVID-19, liver dysfunction is considered mild and recoverable. In this case, changes in liver enzymes are temporary and reversible. In patients with severe disease, significant impairment of liver function is more often detected.
Scientists also note that chronic liver diseases (chronic viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver, etc.) worsen the prognosis of COVID‑19. For example, patients with chronic hepatitis B who are infected with coronavirus may need more time to clear the virus from the body. Patients with a history of liver disease have a significantly increased risk of liver damage after coronavirus.