Unfortunately, even parents who are not privy to medical subtleties are familiar with the opinion that a short frenulum of the tongue in a child is the cause of speech therapy problems.
Why "Unfortunately"? Because it is ignorance of the material that leads to a clear decision - the bridle needs to be trimmed! Do you remember in the film “Pokrovsky Gate” the characteristic female surgeon with her famous phrase “Cut!.. without waiting for peritonitis”? So the same thing often happens to the poor bridle. However, as experience shows, there is not always only one way out. Not every case of the so-called “short frenulum” requires radical measures.
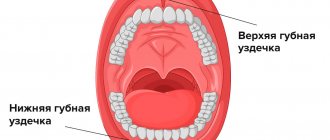
Frenules in the oral cavity
When parents talk about the frenulum in the child’s mouth, most often they mean the frenulum of the baby’s tongue, which is quite natural. Problems arise more often precisely because of this oral frenulum: from improper attachment to the breast in the first days of life to speech impairment in the future.
Even dentists give the leading role and importance to this particular frenulum, but this does not mean that the remaining frenulums are unimportant and cannot provoke any pathology.
There are three frenulums in the child's mouth. A frenulum in the oral cavity is nothing more than a small strand of mucous membrane. But, despite this, the frenulum in the oral cavity is of great importance in the life of a child; the child’s nutrition, correct pronunciation of sounds, the condition of the mucous membranes, not to mention the child’s bite and facial aesthetics depend on their condition.
Dentists distinguish between the frenulum of the upper and lower lips and the frenulum of the tongue. Each of them has its own location and performs a number of functions. The frenulum of the lower lip connects the body of the lower jaw and the lower lip; normally, the frenulum is woven into the gum of the lower jaw below the level of the central incisors.
The frenulum of the upper jaw is located according to the same principle as the frenulum on the lower lip. This mucous cord also raises many questions and complaints from parents, since it is primarily associated with the formation of an aesthetic defect in the oral cavity - a gap between the teeth. And the last frenulum in the baby’s mouth is the lingual frenulum, which is woven into the tongue and sublingual space.
In what cases is it necessary to trim the bridle?
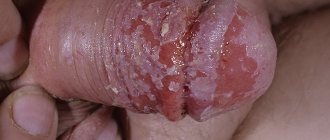
The operation of cutting the frenulum of the tongue is called frenulotomy . It is classified as simple and requires only local anesthesia.
Heavy bleeding during frenulotomy is very rare; after a couple of hours the child will be able to return to the usual rhythm of life.
If a short frenulum interferes with the newborn baby's ability to receive nutrition, it must be trimmed. The decision about surgery is made by a pediatric neonatologist.
For infants, as a rule, the operation is performed without anesthesia, since only the sublingual film of connective tissue is dissected, which has practically no blood vessels or nerve endings.
For children aged 3-5 years, surgery to cut the frenulum is performed under local anesthesia. The dentist decides whether surgery is necessary, and the speech therapist prescribes the referral.
Before the operation, the child needs to donate blood for a detailed analysis, which will display numerous indicators, including the number of platelets and the rate of blood clotting.
Surgical intervention is performed provided that the pathology is moderate or severe with limited tongue mobility. After surgery, speech therapy sessions are necessary.
There are a number of indications for frenulotomy, and limited tongue mobility is not the only one. The formation of malocclusion in a child, displacement and disturbances in the formation of the dentition, low effectiveness of speech therapy and articulation gymnastics, as well as the need to install dental implants or orthodontic structures for the child.
Pathology of the tongue frenulum does not always require surgical intervention. If the child does not experience any discomfort during breastfeeding, and his pronunciation of sounds is satisfactory, then it is likely that a speech therapist will help solve the problem. In this case, the child attends special classes, performs speech therapy exercises, articulation gymnastics, etc.
Why are short bridles dangerous?
Short frenulum in the mouth can cause many unpleasant consequences. The first of them: the baby cannot attach to the breast correctly, so during feeding it expends a lot of effort, but at the same time receives a smaller volume of milk, and it is simply not enough to satiate. This is sometimes the reason for poor weight gain, but quite often mothers and doctors mistakenly look for the cause in a mythical lack of milk, or some disease, although, first of all, it is necessary to look into the oral cavity and assess the condition of the frenulum.
It is very important for parents to know and remember about this problem, because according to statistics, every 14th child has short frenulum in the oral cavity. If you notice this feature in time, then in the future you can avoid many problems and unpleasant consequences - disturbances in nutrition, speech, bite and, accordingly, facial aesthetics.
For the first time, doctors may notice a short frenulum in the baby’s mouth during the first examination, immediately after birth, and if the fact is confirmed, correction is carried out on the spot. This rule applies to a short frenulum of the tongue, but if the frenulum does not interfere with full natural feeding, the frenulum will not be trimmed in the maternity hospital. Symptoms of a short frenulum may appear later - the child may have difficulty pronouncing some sounds, in which case “treatment” will be carried out later, and, as a rule, in tandem with a speech therapist.
Exercises for correcting the frenulum of the tongue and in the postoperative period
Postoperative frenulum stretching and correction exercises are aimed at developing new muscle movements of the tip of the tongue inside and outside the mouth. Regular practice will increase the range of movement of the tongue.
Articulation exercises by themselves will not improve speech and will not be able to correct the defect, so it is very important to carry them out in conjunction with individual speech therapy sessions.
The most common and universal exercises for stretching and correcting the frenulum of the tongue are given here in the article. Following them, you can study at home with your child on your own:
- Stretch your tongue forward, then stretch the tip up to your nose, then down to your chin. Relax, repeat the exercise several times (at first, up to five repetitions are enough, gradually the number of repetitions must be increased, bringing them to twenty).
- The exercise is performed by analogy with the previous one, moving the tongue left and right. The number of repetitions is also gradually increased to twenty.
- Open your mouth wide. Use the tip of your tongue to touch the upper incisors and try to press on the teeth with all your might, not allowing your mouth to close. During each execution, mentally count to ten. The number of repetitions is the same as the previous ones.
- The exercise is performed in front of a mirror. The mouth is wide open. When performing the exercise, it is important to monitor the movements of the tongue. Pronounce the syllables “dar-dar-dar”, “nar-nar-nar”, “tar-tar-tar”, etc.
- Sticking your tongue forward as much as possible, alternately “lick” your upper and lower lips.
- Closing your mouth, move your tongue from right to left and back, forcefully pressing the inside of your cheeks with the tip of your tongue.
To achieve good results, exercises should be performed daily, in several approaches, for 15-20 minutes . The articulation of specific sounds can be gradually corrected.
Important! You can begin to perform exercises for the frenulum of the tongue only after the wound has completely healed.
Speech therapy classes should include exercises to improve the functioning of the speech apparatus and oral kinesthesia, without which it is difficult to claim significant improvements in the development of a child’s speech. Many young patients, after cutting the frenulum, begin to speak more quietly and more quickly, trying to “drown out” speech problems.
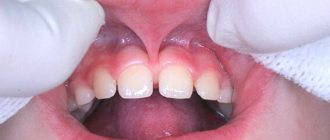
Upper lip frenulum
Even with a simple smile you can see the frenulum of the upper lip, but few people pay attention to it. During a routine examination, the doctor assesses its length; in order to assess the size of the frenulum at home, parents just need to move the baby’s upper lip, and it will become noticeable where exactly the frenulum is woven. In the event that the frenulum is woven between the two front incisors 5–8 mm higher, this is a normal option. If the frenulum is woven below this level, these are obvious symptoms of a shortened frenulum, but the final word always remains with the doctor.
A short frenulum on the upper lip can provoke a violation of the aesthetics of a smile when a gap is formed between the central incisors - a trema, a diastema. It is worth remembering that tremors can be physiological; this period is observed during the period of primary occlusion, when the child’s jaws are preparing for the change of primary teeth to permanent ones. In addition, trems can be pathological, which are formed as a result of some pathology. Treatment of this problem is most often carried out in tandem by a surgeon and an orthodontist.
A short frenulum in a child’s mouth can cause malocclusion, which is formed due to the constant tension of the mucous membrane on the upper jaw and bone tissue. As a result, the front incisors move forward. In addition, such pressure on the mucous membrane provokes inflammation of the mucous membrane - gingivitis. There is a loss of gums, as a result of which the necks of the teeth are exposed and the child develops hypersensitivity of the teeth, and all the conditions are created for the formation of cervical caries.
How does the correction happen?
Treatment of the problem is exclusively surgical, but with one big “BUT”. The frenulum on the upper lip can be corrected only after the eruption of the permanent central incisors, not earlier!!! In some cases, the doctor will recommend adjusting the oral frenulum at the time of the eruption of the permanent lateral incisors - in order to close the gaps between the teeth, such a correction can eliminate orthodontic treatment.
The reason for this ban is very simple. The fact is that during the growth of the jaws, the frenulum on the upper lip can self-correct. That is why there is no point in correcting the frenulum at an earlier age. The correction itself is carried out in a surgical room, under local anesthesia. There are no nerve endings in the mucous cord itself, and therefore the operation is painless; pain relief is necessary when suturing. The operation lasts no more than half an hour and ends with stitches. Thanks to the use of a laser, there is no need for stitches. But there is a certain condition that must be observed after excision of the frenulum: the little one must immediately be attached to the chest.
Classification of types of short frenulum of the tongue in children
In clinical practice, there are 5 types of short frenulums
that limit tongue mobility in a child:
- a thin, transparent shortened frenulum that limits the mobility of the tongue;
- a thin, translucent shortened frenulum, attached with its anterior edge close to the tip of the tongue, due to which, when it rises upward, the tip bifurcates in the shape of a “heart”;
- a short frenulum of the tongue in the form of a thick, powerful, opaque cord attached close to the tip of the tongue. The mobility of the tongue is limited; when extended, its tip is tucked in, the back rises in a slide;
- a short dense cord of the frenulum is fused with the muscles of the tongue. Occurs in children with congenital cleft lip and palate;
- the cord of the frenulum practically does not stand out; its fibers intertwine with the muscles of the tongue, sharply limiting the mobility of the latter.
of complete
and
partial short frenulum of the tongue
in a child. The level of discomfort of the child and the type of treatment chosen (surgical intervention or corrective exercises) depend on the type of pathology.
Frenum of the lower lip
Dentists say that not all babies have a frenulum on the lower lip; it may be completely absent or forked. To study the length of the frenulum, the same technique is used as for studying the frenulum of the upper lip. Normally, the frenulum should be thin and attached in the middle of the body of the jaw. An important condition is that the frenulum of the lower lip must coincide with the center line between the incisors. If these conditions are not met, the bridle is short.
A short oral frenulum interferes with breastfeeding, as the baby cannot properly latch onto the mother's nipple. Fortunately, this situation is quite rare; the most typical manifestation of a short frenulum in the oral cavity is the presence of inflammatory gum diseases in the area of the lower incisors and malocclusion according to the same principle as in the upper jaw.
There are no age restrictions when excision of the mandibular frenulum; usually the mandibular frenulum is diagnosed and corrected at approximately the same time. The principle of the operation is similar to correction on the upper jaw.
How to check if a child has a short frenulum
The presence of difficulties with the frenulum can be easily determined independently:
- Open your mouth slightly and place the tip of your tongue in the area behind your upper teeth. In this position, the place of attachment of the frenulum is clearly visible. If it is not “where it needs to be,” it is difficult to lift the tongue up.
- Pull your tongue forward. A short frenulum does not allow this to be done; in addition, the tip of the tongue visually looks forked
- Open your mouth and try to touch your upper lip with your tongue and lick it. Difficulties with the bridle make this movement difficult to perform.
Please note: sometimes a child cannot cope with these exercises not because there is something wrong with the frenulum. The cause may be weak muscles of the articulatory apparatus. Take a clean handkerchief and try to help your tongue. If resistance is felt when moving, then the problem is still in the hyoid frenulum.
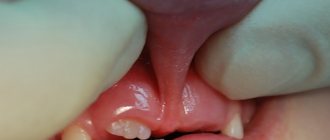
Tongue frenulum
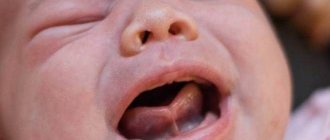
The most complex and insidious frenulum in a child's mouth. It is this frenulum that is able to regulate the movement of the tongue in the oral cavity. Normally, the frenulum is woven approximately in the middle of the tongue, and its length is approximately 8 mm. If the frenulum is attached almost to the tip of the tongue, this is a direct indication for correction.
After birth, the doctor must examine the baby’s oral cavity, which makes it possible to diagnose the pathology. If the frenulum is short, this can lead to difficulties in feeding, and correction is carried out in the maternity ward.
In some cases, the doctor may not notice a short frenulum, but when feeding, the child may experience symptoms that indirectly indicate pathology.
When feeding, the baby makes “smacking” sounds, often drops the breast and tries to rest - the feeding schedule changes, and the number of feedings increases. Babies may be capricious at the breast or even refuse, as a result the child does not gain weight well. Mothers often complain that babies bite their breasts because they cannot get their tongue between the gums and the mother’s nipple.
A short frenulum in the oral cavity can be diagnosed throughout life. In order to make sure once and for all that everything is in order in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to carry out a series of tests. Parents can also do this, although the doctor will most correctly conduct the tests.
The child should be asked to open his mouth and reach his tongue to the roof of his mouth. If the baby performs this operation without any difficulties, there is nothing to fear. But, if the child experiences unpleasant or painful sensations, or the baby is not able to reach the sky, this is an indication for a quick visit to the dentist. Parents should remember that such a test is informative only for children two to three years old.
Only a dentist or speech therapist can confirm shortening of the frenulum of the tongue in children of school and preschool age. Usually, an examination is prompted by a speech disorder in a child, when the child cannot pronounce a certain set of sounds - “r”, “sh”, “sch”, “zh”, “ch”, etc.
How does the correction happen?
There are features of correction depending on the age of the child. In the case of frenulum correction in newborns, which occurs in the maternity ward and with the obligatory presence of the mother, the frenulum is cut using special scissors or a laser, the latter is preferred. There are no nerve fibers in the frenulum itself, but there are many blood vessels. When using a laser, all blood capillaries are closed - there is no bleeding, and there is no need for stitches. A prerequisite is the presence of the mother during the procedure, since immediately after excision of the frenulum, the baby must be attached to the breast. It is at this time that the frenulum returns to normal and possible bleeding stops.
In the case of correction of the tongue frenulum in older children, both surgical and speech therapy treatment can be used. Everything will depend on its length and the age of the child, and on the consequences that this pathology provoked. Parents must clearly remember that the final verdict rests with the dentist, and not with the speech therapist, who can sometimes give false hopes for stretching the oral frenulum using various exercises.
It is the dentist who can assess the damage and clearly predict whether speech therapy treatment is suitable in each specific case. Quite often, dentists advise using complex treatment: surgical dissection of the oral frenulum and the use of speech therapy exercises - this combination gives excellent results.
Consultation with a speech therapist teacher “Hyoid frenulum: trim or stretch?”
Evgenia Kovalevskaya
Consultation with a speech therapist teacher “Hyoid frenulum: trim or stretch?”
“Hyoid frenulum: trim or stretch?”
The sublingual frenulum is a membrane that is located under the tongue and connects the tongue to the sublingual space.
How to determine whether the hyoid frenulum is long enough?
The hyoid ligament (frenulum) can be of different lengths in different people.
Ask your child to lift his tongue up toward the hard palate. With a normal hyoid frenulum, the child freely raises the tongue to the hard palate. With a short hyoid frenulum, the child cannot stretch the tongue forward and lift the tongue upward towards the hard palate. When the child pulls his tongue up, you will see how the hyoid ligament, limiting the rise of the tongue, stretches, becomes more pronounced, protrudes more prominently under the tongue, and becomes thinner. Another reason that a child cannot lift his tongue up is that the child’s tongue muscles are not strong enough and are inactive. Then you will see how he cannot cope with the muscles, then the tongue trembles, deviates to the side, twitches, and goes down.
Normal: at 5 years of age, the frenulum in a stretched state should be at least 8 mm. The average length of the frenulum is 1.5 cm.
What does this mean?
Short hyoid frenulum:
- can cause difficulty in moving the tongue, as it does not allow it to rise high. In this case, the so-called “upper sounds” suffer, i.e. the pronunciation of sounds such as Ш, Ж, Х, Ш, Р, Рь is disrupted
- can lead to a displacement of the center of the tongue, its asymmetrical development and low mobility, which prevents the formation of the correct articulatory posture of some sounds.
- may also cause problems with sound pronunciation
– in some cases, it can provoke problems with the formation of the lower jaw, i.e. the teeth may deviate and the necks of the teeth may be exposed. There is a risk of developing periodontitis and gingivitis. Therefore, a consultation with an orthodontist is necessary.
What to do?
1. Surgery
2. Stretching the hyoid frenulum
Even if the frenulum is somewhat shortened (equal to 8 mm), it is better to stretch it than to operate, since this procedure is somewhat painful and unpleasant for the baby!
Strong indications for trimming the hyoid frenulum:
1. It is better to trim the short frenulum of the tongue at an early age, up to one year.
Indications for surgery if the child while feeding:
• the child sucks poorly at the breast due to the fact that the shortened frenulum prevents the mother from tightly clasping the nipple.
• throws back his head.
• smacks and cries when sucking.
2. At an older age, the indication is when, due to a shortened frenulum, the child’s dentition shifts and an abnormal bite is formed.
3. Difficulties in pronouncing sounds; only in some cases does it require surgical intervention. In 90% of cases, when 1-4 sounds are violated, the short frenulum of the tongue is easily stretched with the help of special articulatory gymnastics exercises.
Methods and techniques for stretching the hyoid ligament (frenulum).
MECHANISM OF EXERCISES for stretching the frenulum: since this is a fold (like a muscular, mucous fold, that is, the ability to carefully and slightly correct the initial state of the frenulum, the exercises give the tongue the opportunity to rise up, thereby gradually stretching the muscle (it is quite elastic, these exercises cannot be performed jerkily, very smoothly and slowly.
Sounds that require a noticeable upward movement of the tip of the tongue ([р], [ш], [ж]) are placed after the child’s hyoid ligament is fully stretched.
Sounds ([l], [h], [sch], [t'], [d']) can be started when the frenulum has not yet fully stretched, but there is already some upward movement of the tip of the tongue.
A short frenulum does not interfere with the normal pronunciation of other sounds of the Russian language.
It is recommended to start stretching the frenulum at an early age. All children are recommended to do gymnastics for the tongue - this will help avoid a lot of problems at 5-7 years old (talking about pronunciation).
Attention! Parents!
Before you start doing exercises to stretch the hyoid frenulum, you need to visit a speech therapist so that he can show you how to do them correctly! Your inept movements can lead to a rupture of the frenulum - and this is terribly unpleasant once, and then a knot twice.
Articulation exercises for stretching the frenulum of the tongue:
1) “Lick the saucer.”
Invite your child, like a kitten, to lick a saucer smeared with jam or something else.
You can reach for the spoon with your tongue.
2) "Swing"
Open your mouth, reach with the tip of your tongue first to your nose, and then to your chin, then again to your nose, and then again to your chin.
5) "Horse"
Smile, open your mouth. Click the tip of your tongue like a horse clicking. The mouth is open, the tongue should be wide. Make sure that the tip of the tongue does not turn inward and that the lower jaw remains motionless.
6) "Painter"
Smile, open your mouth. Using the wide tip of your tongue, stroke the palate from the teeth to the throat. The lower jaw should not move.
7) "Mushroom"
Smile, open your mouth. Suck your wide tongue to the roof of your mouth. This is the cap of the mushroom, and the hyoid ligament is the stalk. The tip of the tongue should not turn up, the lips should be in a smile. If the child is unable to suck his tongue, then he can click his tongue, as in the “Horse” exercise. Clicking trains the desired movement of the tongue.
 "Harmonic"
"Harmonic"
Position the tongue as in the “Mushroom” exercise, lips in a smile. Without lifting your tongue, open and close your mouth.
9) "Drum"
Smile, open your mouth. Repeatedly and clearly pronounce the sound D-D-D. When pronouncing this sound, the tongue rests on the upper teeth, do not close the mouth. Very often, when performing this exercise, the child closes his mouth. To prevent this from happening, you can hold a stick about 1 cm wide or the handle of a rectangular children's toothbrush between your teeth (the handle should not be thick, it should be straight, like a ruler).
10) "Football"
Close your mouth, press the tip of your tongue against one cheek, then the other, so that balls are inflated under the cheek.
11) Exercise “Mole”
Use your index fingers and thumbs to pull your tongue down by the tip.
- There is a slide in the yard, -
Use your index fingers and thumbs to pull your tongue upward by the tip.
— There is a mink under the hill. –
With your index finger, forcefully stroke the hyoid frenulum from bottom to top, stretching it.
- In this hole
— The mole is guarding the mink.
Reasons for the development of tongue frenulum pathology in a child
Pathology of the frenulum of the tongue can be congenital
and
hereditary
. It should be understood that these concepts are completely different. If a congenital pathology is already present at birth, then a hereditary pathology is most often already present in one of the family members.
The defect is more common in boys than in girls. In a child 5 years old, the length of the frenulum in an extended state should be at least 0.8 cm. For comparison, in an adult the length of the frenulum is no more than 3 cm.
The formation of an anomaly associated with a short sublingual membrane begins before the birth of the child. This is preceded by negative factors, which include:
- genetic predisposition;
- harmful, bad habits of the expectant mother;
- viral and infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters;
- mechanical injuries to the expectant mother’s abdomen;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- taking certain medications, stress, occupational hazards (working with paints, varnishes, chemicals, etc.)
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- the influence of other factors of unknown etiology (somatic diseases of the expectant mother.
How to recognize pathology in a child. Symptoms of a short frenulum of the tongue
A neonatologist can recognize a pathological frenulum of the tongue in a newborn.
,
pediatrician
or
mother herself
. If during the first and subsequent breastfeedings the baby experiences difficulties and cannot grasp the nipple correctly, then you should consult a doctor.
At the age of 3-4 years, children begin to speak in phrases, and, of course, you may notice speech defects and incorrect pronunciation of sounds. In this case, your child needs to be examined by a speech therapist.
.
A surgeon and an orthodontist can also identify a short frenulum of the tongue during preventive examinations.
The most common symptoms of a tongue tie
the child has the following:
- problems with feeding in newborns, difficulties in sucking the breast, with its normal grasp. The consequence of insufficient nutrition is poor weight gain, and in some cases, malnutrition (chronic malnutrition accompanied by insufficient weight gain of the child in relation to his height and age);
- the child is not able to reach the front teeth of the upper jaw or palate with the tip of his tongue;
- the child may have difficulty moving the tip of the tongue from one side to the other;
- the front teeth of the lower jaw may have a gap between each other;
- when the tongue is pulled forward, its tip remains flat, square, and when raised upward, the tongue forms a bifurcation in shape, resembling a heart, takes on a humpback shape, or is curled into a groove;
- incorrect sound pronunciation, in which the child’s speech becomes illegible and incomprehensible to others. A short frenulum of the tongue in a child prevents the correct articulation of sonors ([p], ([p´], [l], [l´]), plucking ([w], [z], [h], [sch]) and others sounds of upper articulation ([t], [t'], [d], [d']).
It is important to understand that if the problem of the tongue frenulum exists, then sooner or later it will have to be solved. The sooner measures are taken, the easier and more painlessly the child will endure them.