candidiasis in children is an infectious dental disease caused by fungal microflora (microorganisms belonging to the genus Candida). According to WHO statistics, manifestations of this pathology are observed in 5% of newborns and 10% of infants. Illness in pediatric dentistry can be chronic or acute. In this case, candidiasis can act as an independent dental pathology or be one of the signs of severe systemic diseases.
Sodium tetraborate: definition and composition
Sodium tetraborate is a derivative of boric acid. Simply put, it is borax (a salt that is formed as a result of the interaction of boric acid and sodium) enclosed in glycerin. The drug is sold in the form of a solution, bottled in tinted glass bottles with a capacity of 30 ml. The composition of the drug is 20% borax and 80% glycerin.
The main properties of sodium tetraborate are antiseptic and bacteriostatic. The use of the drug helps to destroy the Candida fungus. In addition, the product prevents the attachment of the fungus to the child’s oral mucosa and at the same time destroys the cell membrane of the pathogenic flora. At the same time, glycerin, which is part of the drug, is aimed at enhancing the effect of borax and at the same time softening the mucous membranes.
It is worth knowing that throughout the world the use of sodium tetraborate for newborns is not approved, since the drug is considered to be quite toxic. However, in practice, if the recommendations for safe use are followed, the use of borax is effective and does not cause problems.
Important: the use of sodium tetraborate should be prescribed exclusively by the treating pediatrician. Self-administration of any medications to an infant is strictly prohibited.
Thrush during pregnancy
The development of vaginal candidiasis during pregnancy is dangerous for the expectant mother and the fetus. There is an increasing threat of the development of inflammatory processes during pregnancy, postpartum complications, and infection of the fetus, which can lead to fungal infection of its organs and even death. It is possible that the baby may become infected during childbirth. Treatment of thrush in pregnant women is complicated by the ban on taking antifungal drugs orally. Local treatment with vaginal tablets and suppositories is acceptable (Pimafucin is considered the safest among them during pregnancy). All the more important is the observance of personal hygiene rules, as well as protection from stress, proper nutrition with sufficient vitamins, walks, healthy sleep, which help strengthen the natural immune defense. If signs of thrush appear in a pregnant woman, she should immediately contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to carry out timely, adequate treatment and avoid complications.
For diagnosis and successful treatment of vaginal candidiasis, come to the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. You can see
prices for services Make an appointment
Indications for use
Composition and instructions for use of Sebozol shampoo
The instructions for use of the drug state that it can be prescribed in the following cases:
- Oral candidiasis in infants (thrush/stomatitis);
- Vaginal candidiasis and colpitis;
- Fungal infections of the throat and sore throat;
- Diaper rash on the skin, bedsores, cracks in the skin.
Signs of the disease
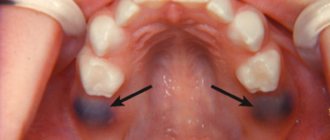
The key sign of the disease in childhood is the appearance of a whitish coating on the epithelial tissues, hiding eroded areas of tissue underneath. Lesions may appear on the tonsils, in the pharynx, on the tongue, in the corners of the mouth and on the edges of the lips.
In children with unformed speech, acute candidiasis can manifest itself in the form of refusal to eat, irritability, tearfulness, somnological disorders, and bleeding from the gums. Older children may complain of pain in the mouth when eating, itching and burning of epithelial tissue in the affected area.
The main signs of chronic candidiasis are:
- swelling of the epithelium;
- the appearance of light brown plaque on epithelial tissues;
- dryness, pain in the mouth;
- systematic bleeding from gum tissue.
Possible adverse reactions
It is worth understanding that when using borax in the treatment of thrush in newborns, the following adverse reactions may occur:
- Moderate redness in areas where the mucous membrane was treated with the drug;
- Burning and itching;
- Swelling in the form of an allergic reaction;
- Rash.
In case of an overdose of the drug, the baby may experience the following reactions:
- Abdominal pain;
- Vomiting, diarrhea;
- Weakness and cramps;
- Headache.
If the mother observes similar symptoms of overdose in the baby, it is necessary to take the newborn to the hospital as soon as possible for detoxification procedures. In this case, the baby will undergo gastric and intestinal lavage, as well as IV drips to restore water and electrolyte balance.
Instructions for the use of Taktivin injections and analogues
To prevent the risk of overdose, it is recommended to use the drug in newborns for no more than seven days and only in minimal doses. If, during treatment with sodium tetraborate, the baby’s thrush does not go away within a week, it is advisable to contact the pediatrician again to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a new treatment.
Important: it is strictly forbidden to use borax in combination with drugs based on clotrimazole and other antifungal components. It is also prohibited to use boric acid with corticosteroids and phenol.
Diagnosis and treatment of thrush at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of vaginal candidiasis begins with interviewing the patient.
Some gynecological (bacterial vaginosis, inflammatory processes in the female reproductive system) and concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, candidiasis and intestinal dysbiosis, etc.) are important. It is not uncommon for thrush to develop after long-term use of antibiotics, hormones, or immunosuppressants. Upon examination, a characteristic clinical picture is revealed - a white coating on the inflamed mucous membrane of the genital organs, copious, curdled discharge. Examination of a vaginal smear reveals fungal flora. If necessary, a culture is carried out to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs (cultural analysis). Among additional studies, examination for sexually transmitted infections, diabetes mellitus and diagnosis of intestinal microflora may be recommended. Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Treatment
How to cure thrush?
General and local antimycotic therapy Gynecologists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital provide effective treatment for thrush in women. Today there are many medications to combat candidiasis: oral medications, creams, vaginal tablets, suppositories for thrush. Among the most popular drugs for vaginal candidiasis are flucostat, fluconazole (oral tablets), clotrimazole (vaginal tablets or cream), pimafucin (suppositories) and many other drugs. Your doctor should choose the optimal treatment regimen for you.
Reducing the role of predisposing factors To avoid relapses, it is necessary to identify and eliminate factors contributing to the disease. If possible, stop taking glucocorticosteroids and cytostatics. For diabetes mellitus, adjust blood glucose levels with medication. Restore normal microflora in the intestines. In addition, you need to take antibiotics with caution. Exacerbation/recurrence of thrush after or during a course of antibiotic therapy is common. Therefore, taking antibiotics must be combined with taking antifungals and probiotics. It is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, maintain immunity, and avoid stressful situations.
Sexual life with thrush Many people are interested in whether it is possible to be sexually active with thrush and its treatment? You can protect yourself with a condom. To achieve good results, it is often recommended to undergo treatment of vaginal candidiasis together with your sexual partner.
Instructions for the use of sodium tetraborate in infants
To overcome stomatitis and thrush in a newborn baby using sodium tetraborate, you must adhere to the following treatment regimen according to the instructions:
- Mom must wash her hands thoroughly and dry them well;
- Then a sterile bandage in two layers is wrapped around the index finger. It is not recommended to use cotton wool, cotton pads or cotton swabs to remove plaque, since their soft texture does not allow plaque to be removed effectively;
- Two or three drops of the medicine are dripped onto the bandage and treated with it. It is necessary to capture the palate, cheeks, tongue and gums. It is advisable to remove the white milky coating from the mucous membranes, avoiding injury to delicate tissues.
The course of such treatment is 5-7 days with treatment of the oral cavity 2-3 times a day.
Important: before going to bed, it is recommended to treat the pacifier with sodium tetraborate solution. It is recommended to pour boiling water over all bottle nipples.
Features of the treatment of candidiasis in children
The disease treatment program involves the use of antifungal agents and the adoption of measures aimed at comprehensively strengthening the body of the infected child. Until recently, nystatin was the drug of choice for this disease, but in modern dental practice more effective and harmless dental agents are used. Foods rich in carbohydrates (sweets, cookies, honey and others) must be excluded from the diet of a sick child.
There are a number of non-pharmacological methods to combat candidiasis in childhood. In particular, the following help to cope with the manifestations of this pathology:
- warm saline solution (used as a mouth rinse for children over three years old);
- lollipops with antiseptic components (prescribed for adolescents and children over 8 years old);
- solution of baking soda (used for systematic wetting of epithelial tissues of the mouth in infants and newborns).
When a disease is detected in breastfed babies, not only the babies, but also their mothers undergo treatment. This approach to therapy helps prevent re-infection of infants during feeding.
Drug analogues
In order to have a less toxic effect on the baby’s body, other drugs can be used to treat thrush. Especially if it occurs in a mild form in the baby. To do this, use simple baking soda or sodium carbonate. Prepare a soda solution from one teaspoon of soda and a glass of boiling water. The cooled solution is used to treat the baby’s oral mucosa according to the above scheme.
Tip: before each breastfeeding, it is recommended to treat the nipples of the nursing mother. If the baby is bottle-fed, then pacifiers and bottles are also treated with a soda solution before feeding.
And in order not to use toxic sodium tetraborate for thrush in children over one year of age, it is advisable to monitor the prevention of oral candidiasis in the baby. That is, keep the baby and his pacifiers/pacifiers/toys clean, trim his fingernails in a timely manner and be sure to wash the nipples before each feeding. After each feeding, it is advisable to give the baby one or two teaspoons of boiled water to wash away the remaining milk in the mouth and prevent it from fermenting.
It is worth remembering that it is always easier to prevent a disease than to fight it later. Moreover, the baby’s body is still so weak and cannot resist the influence of external aggressive factors.
Reasons for the development of candidiasis
Sources of infection for candidiasis are previously infected individuals. In this case, the main routes of transmission of infection to a child are:
- intrauterine;
- aerosol;
- infection during childbirth when moving through the birth canal of mothers suffering from urogenital candidiasis;
- contact.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
- violation of requirements regarding hygienic care of the child’s oral tissues and teeth;
- weakened immunity or the presence of severe disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- allergization of the body;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- anomalies in the structure of the tongue;
- oral acidosis;
- deficiency of vitamin C, B vitamins;
- long-term treatment using antibacterial agents;
- the presence of severe systemic diseases;
- morphological and functional immaturity of epithelial tissues in the mouth;
- undergoing a course of therapy using hormone-containing drugs.